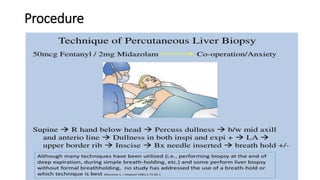
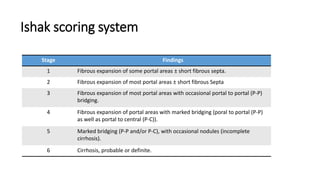
A liver biopsy is a procedure to remove and examine a small piece of liver tissue to confirm diagnoses, assess disease severity, and evaluate treatment response. It can be performed using various methods, including percutaneous and laparoscopic techniques, while careful preparation is needed to avoid complications. Indications for the procedure include chronic hepatitis, unexplained liver enzyme elevation, and suspected tumors, with follow-up required to monitor for complications.