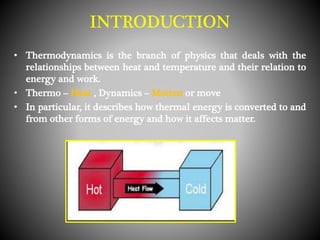
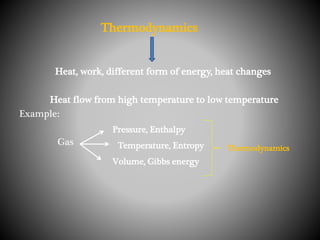
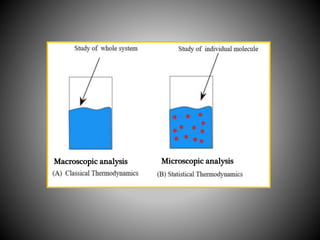
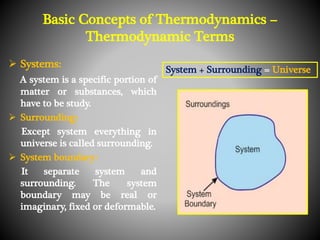
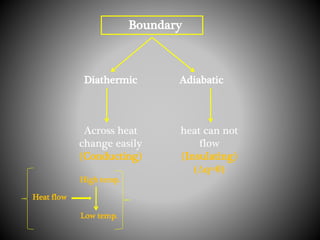
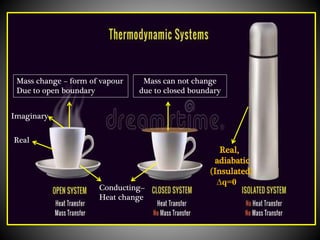
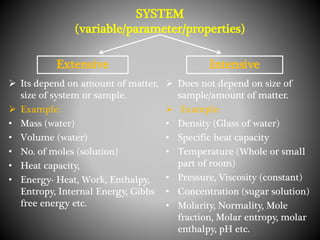
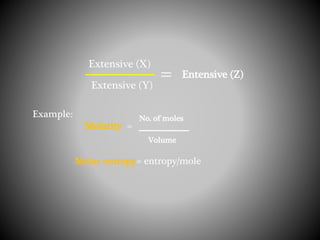
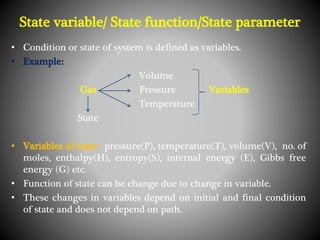
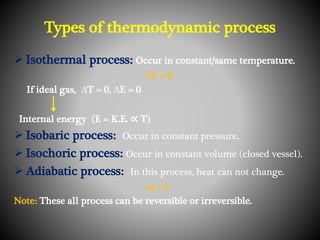
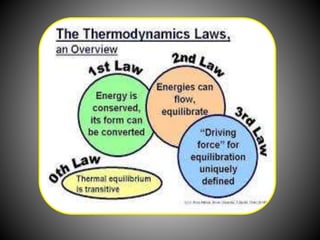
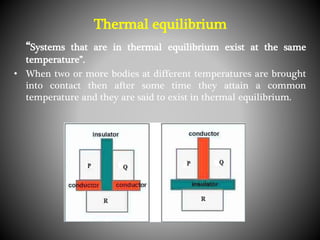
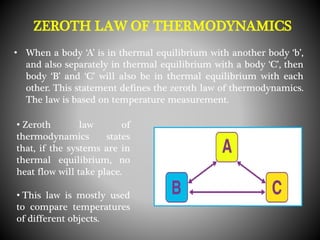
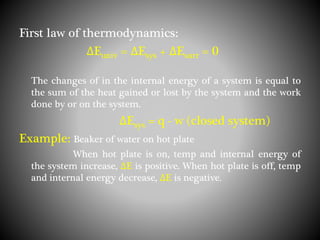
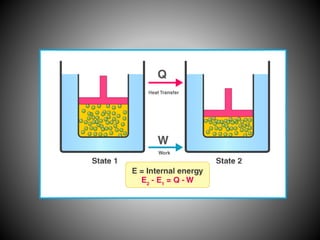
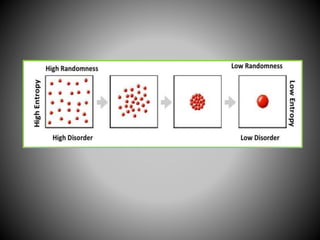
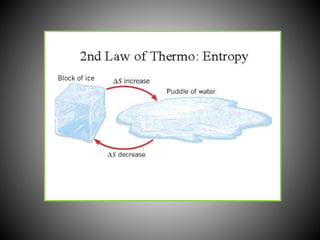
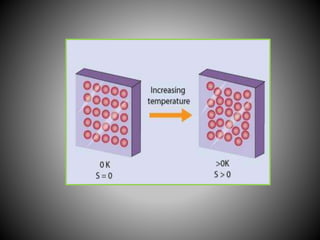
Thermodynamics deals with heat, temperature, and their relation to energy and work. It has four main branches: classical thermodynamics studies whole systems, statistical thermodynamics analyzes properties at a molecular level, equilibrium thermodynamics considers approaching equilibrium, and chemical thermodynamics relates heat and work to chemical reactions. The four laws of thermodynamics establish foundational concepts. The first law concerns conservation of energy, the second law involves increasing entropy, and the third law states that entropy approaches zero as temperature approaches absolute zero. Thermodynamic properties like internal energy, enthalpy, and entropy are defined in terms of heat and temperature.