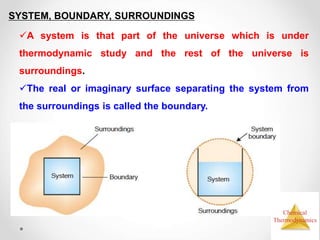
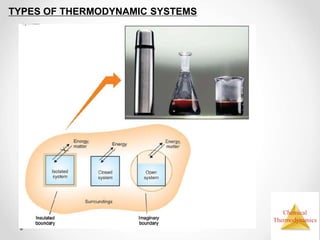
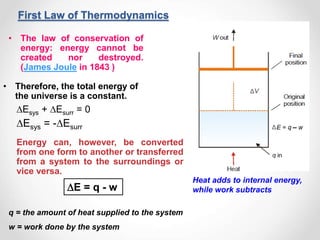
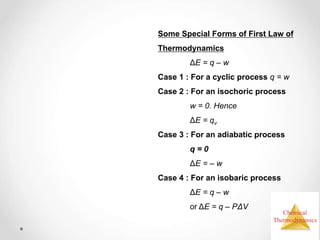
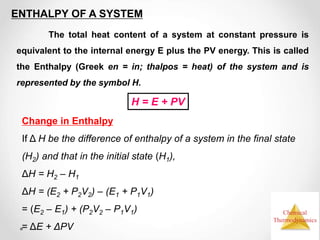
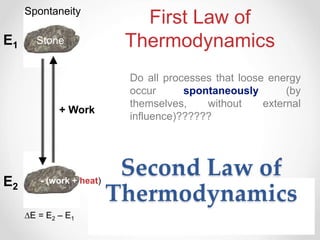
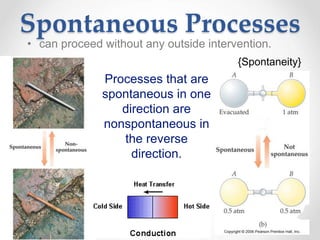
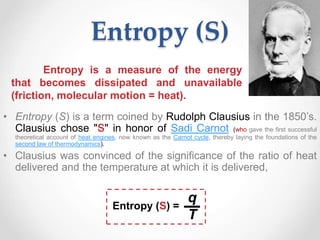
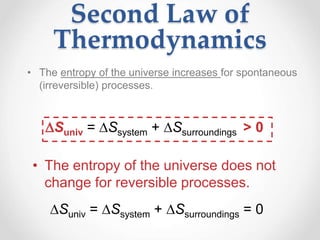
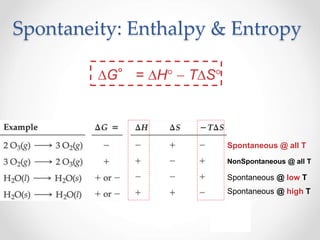
Thermodynamics is the study of heat and energy transfer during physical and chemical changes. The laws of thermodynamics state that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or changed in form. The second law states that the entropy of the universe increases for spontaneous processes, meaning some energy becomes unavailable. Entropy is a measure of disorder and randomness in a system. The spontaneity of a process can be predicted using the change in Gibbs free energy, with negative ΔG indicating spontaneity.