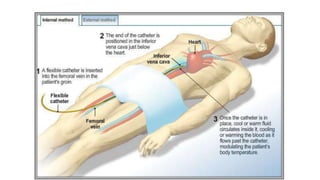
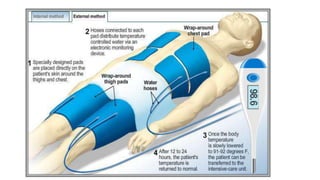
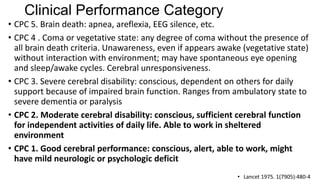
Therapeutic hypothermia, or targeted temperature management, has been shown to improve outcomes for patients who remain unconscious after resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Two key studies from 2002 demonstrated improved mortality and neurological function when patients' temperatures were cooled to 32-34°C for 12-24 hours after cardiac arrest. Subsequent meta-analyses and clinical guidelines have supported induced hypothermia for unconscious cardiac arrest survivors. However, the optimal target temperature range was still unclear. A 2013 randomized controlled trial compared outcomes between unconscious cardiac arrest survivors treated with targeted temperature management at 33°C versus 36°C and found no significant difference in mortality or neurological function between the two temperature targets.