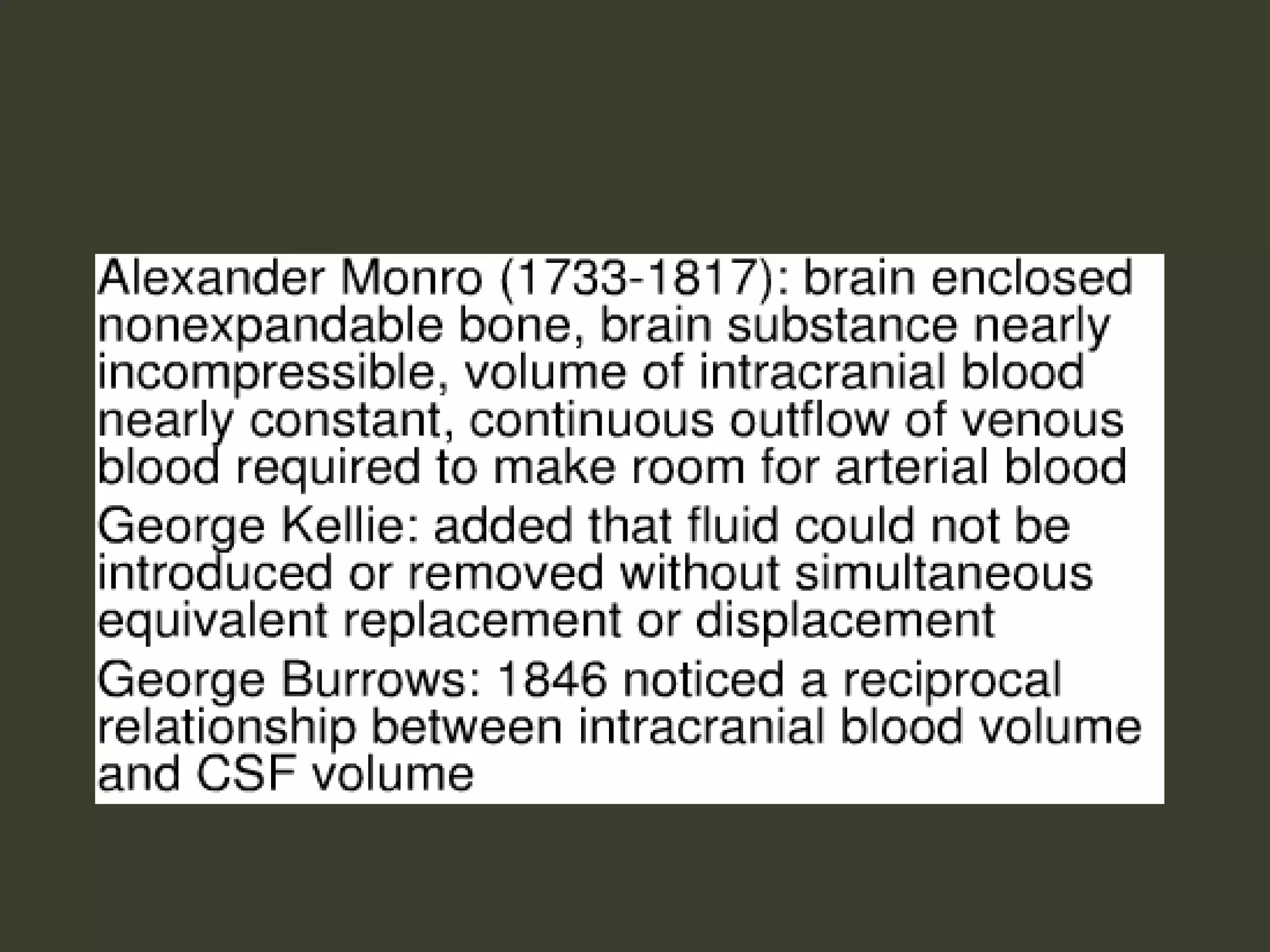
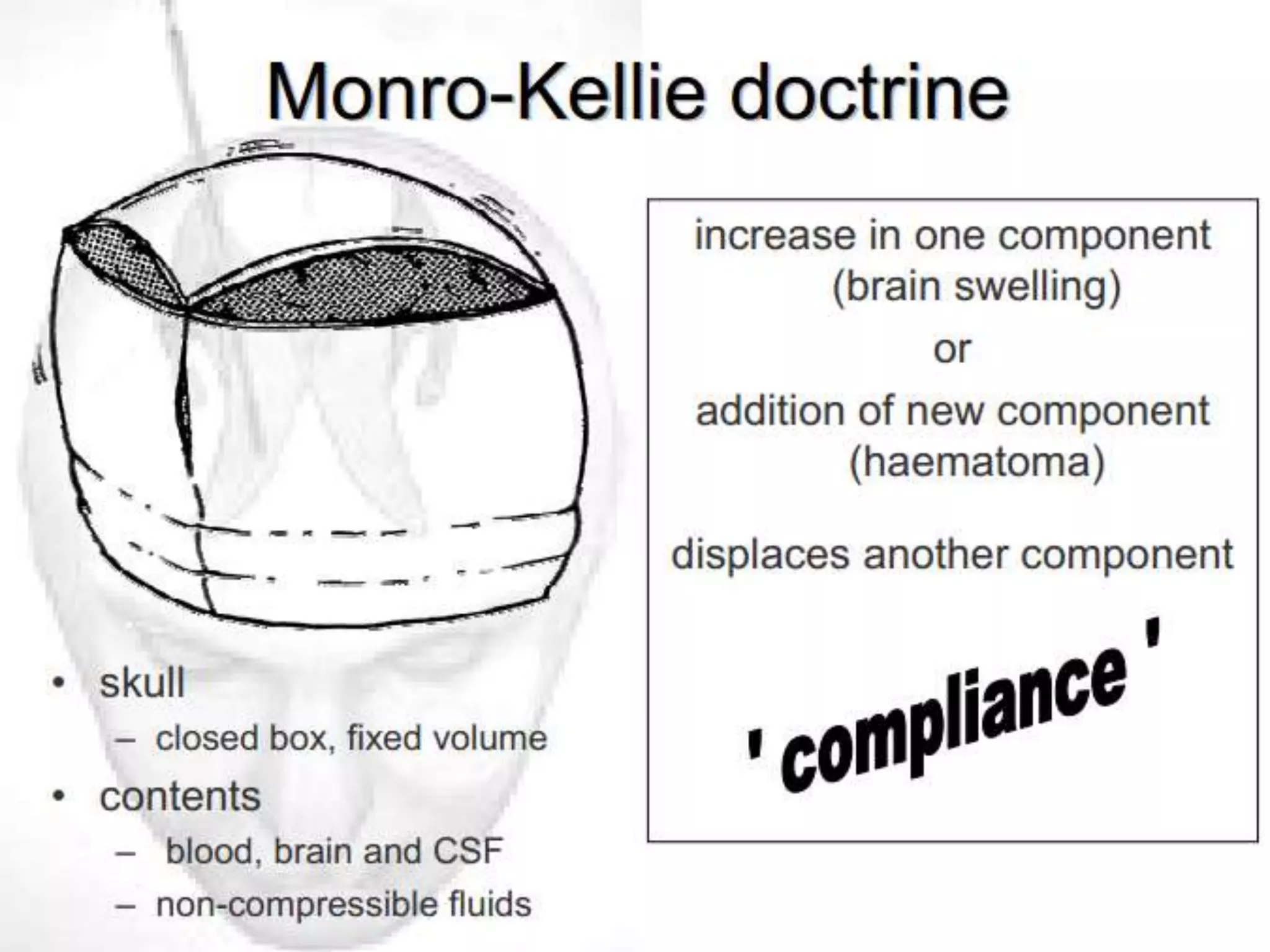
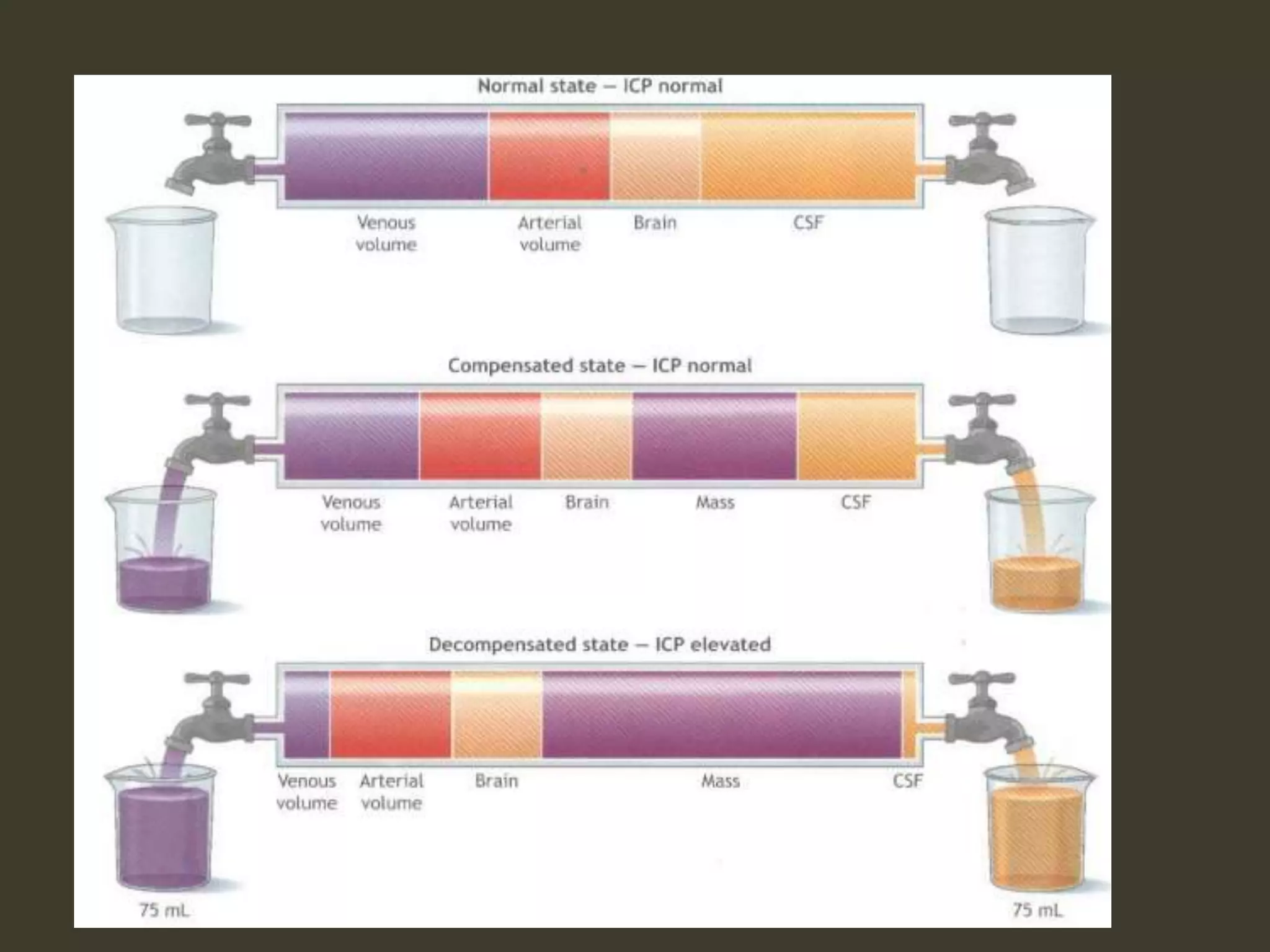
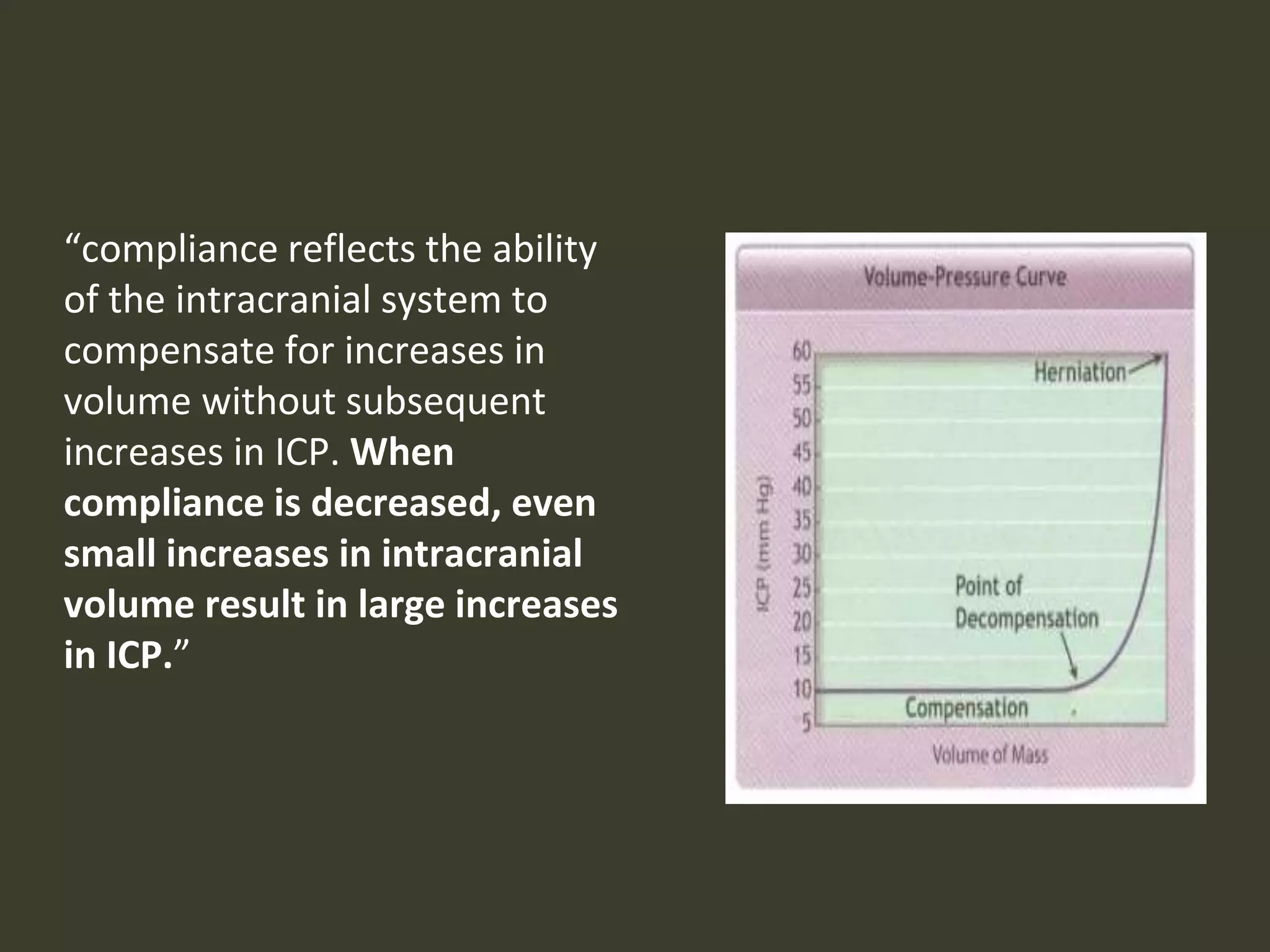
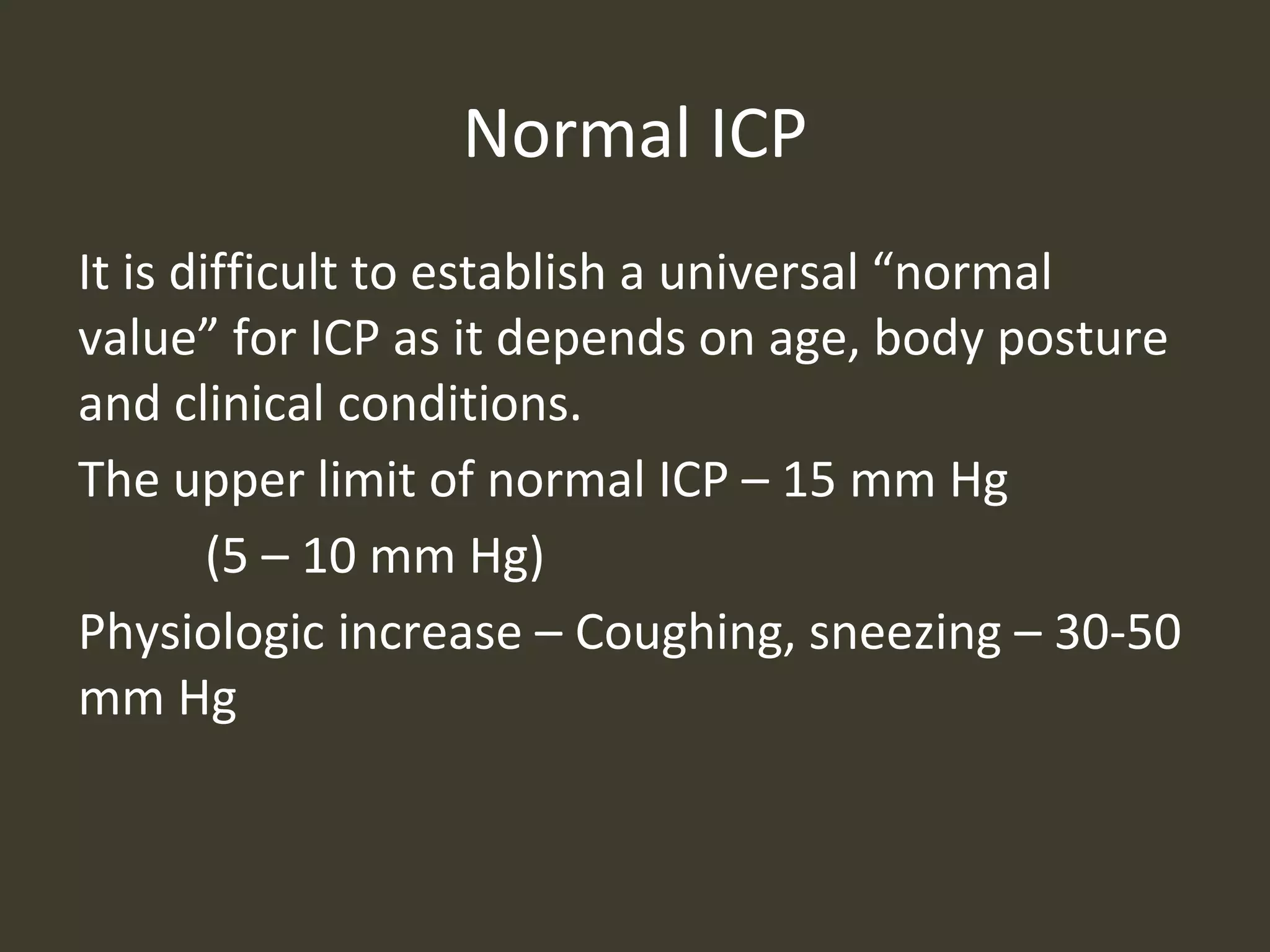
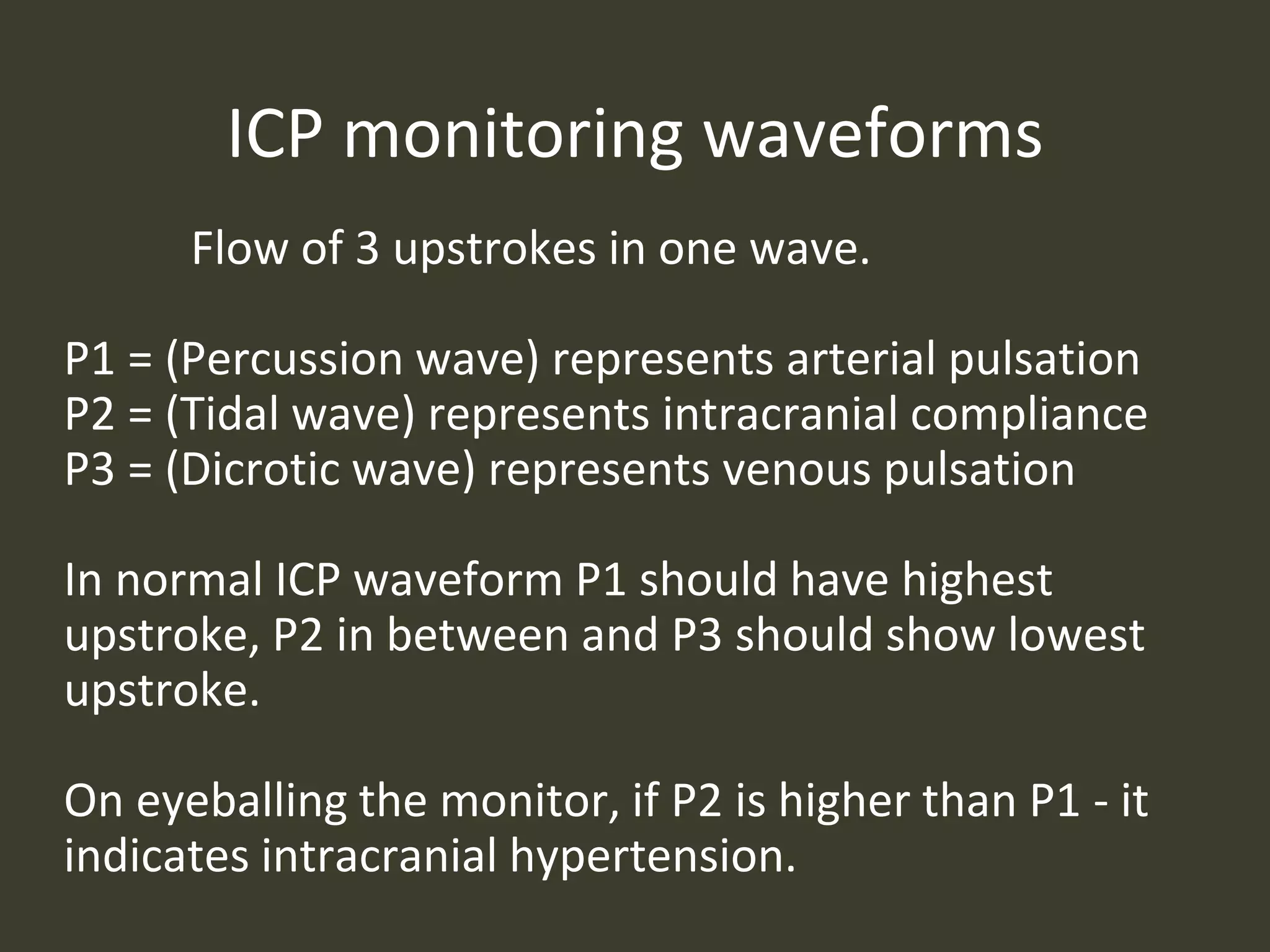
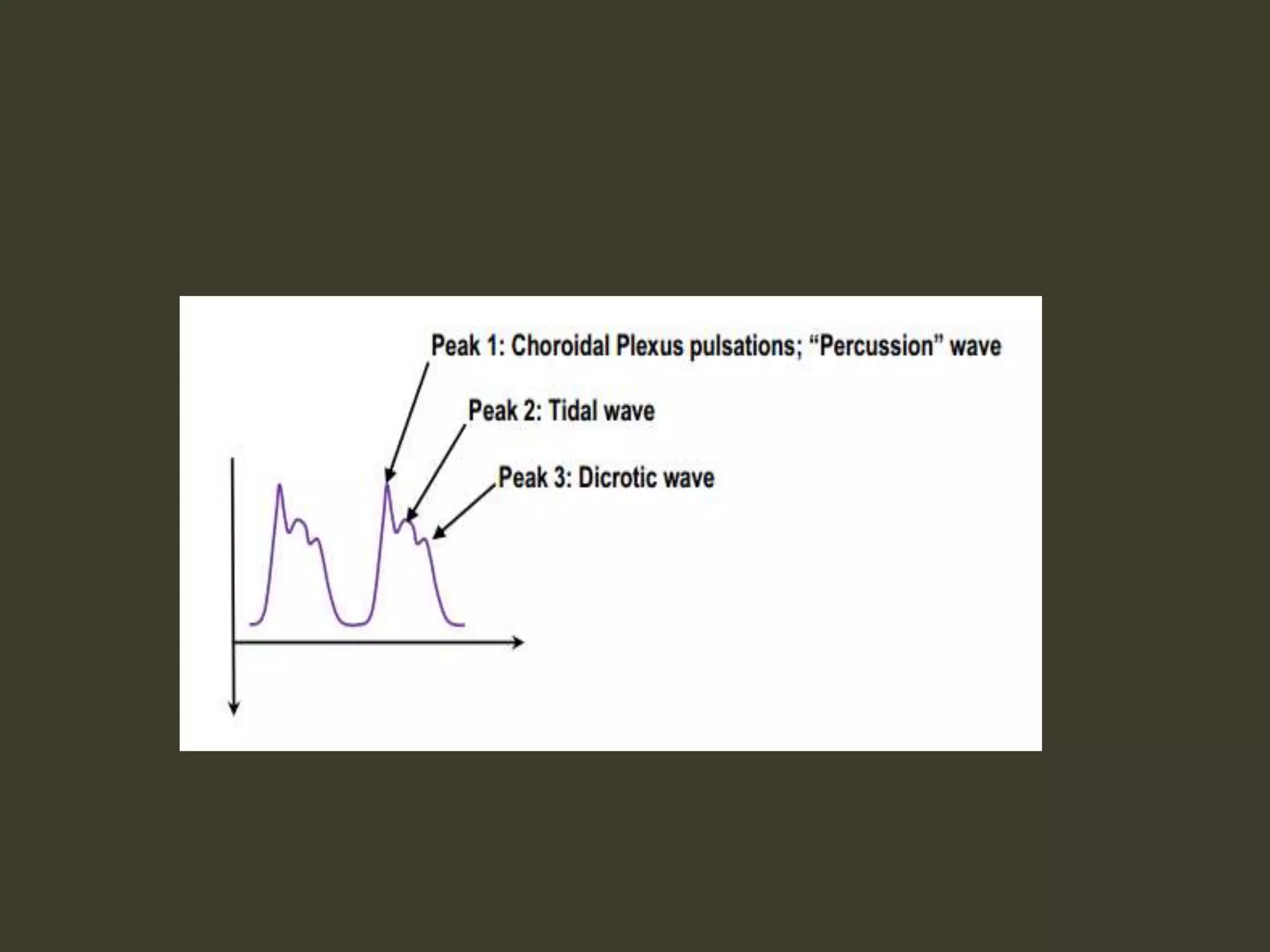
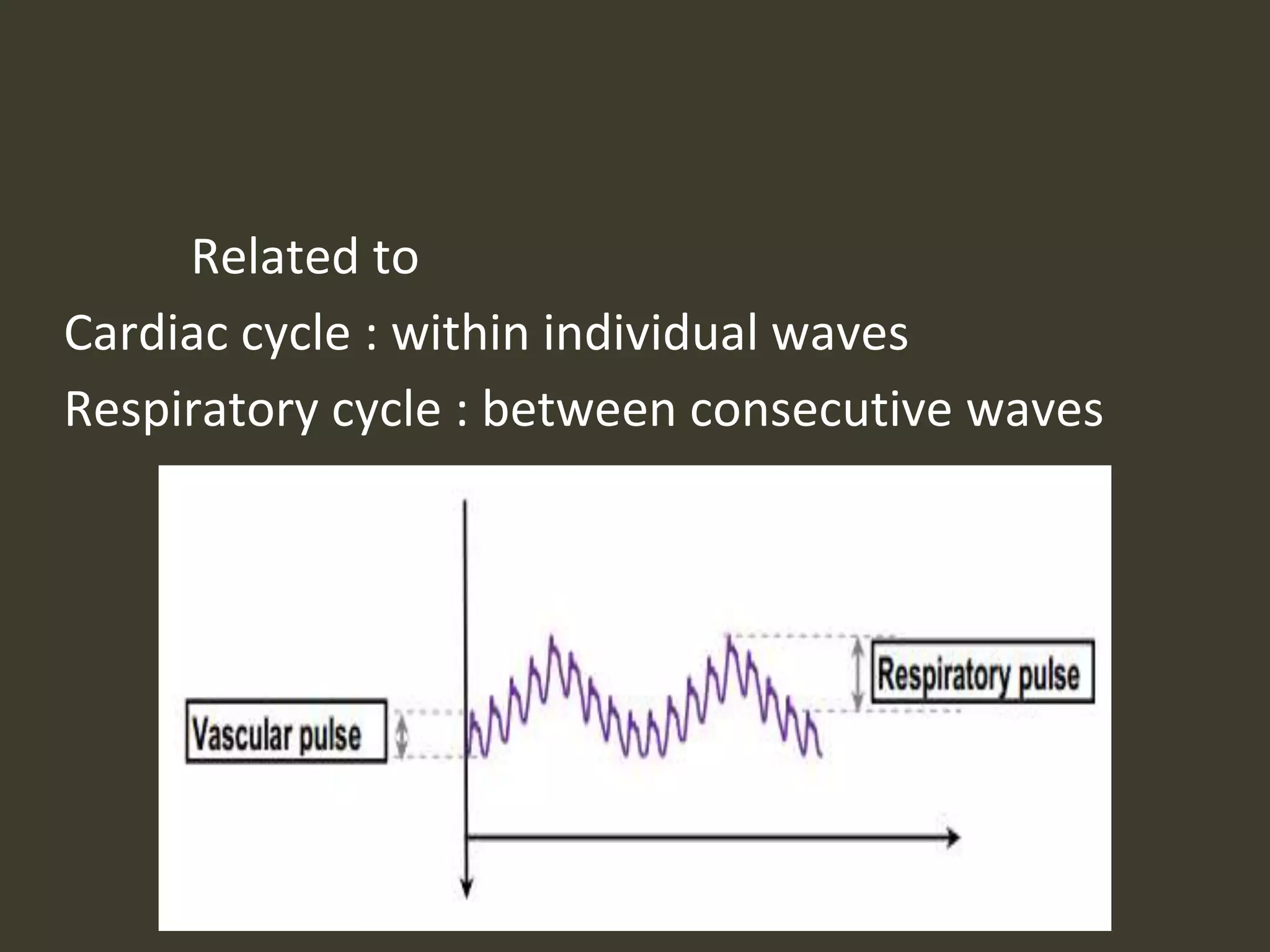
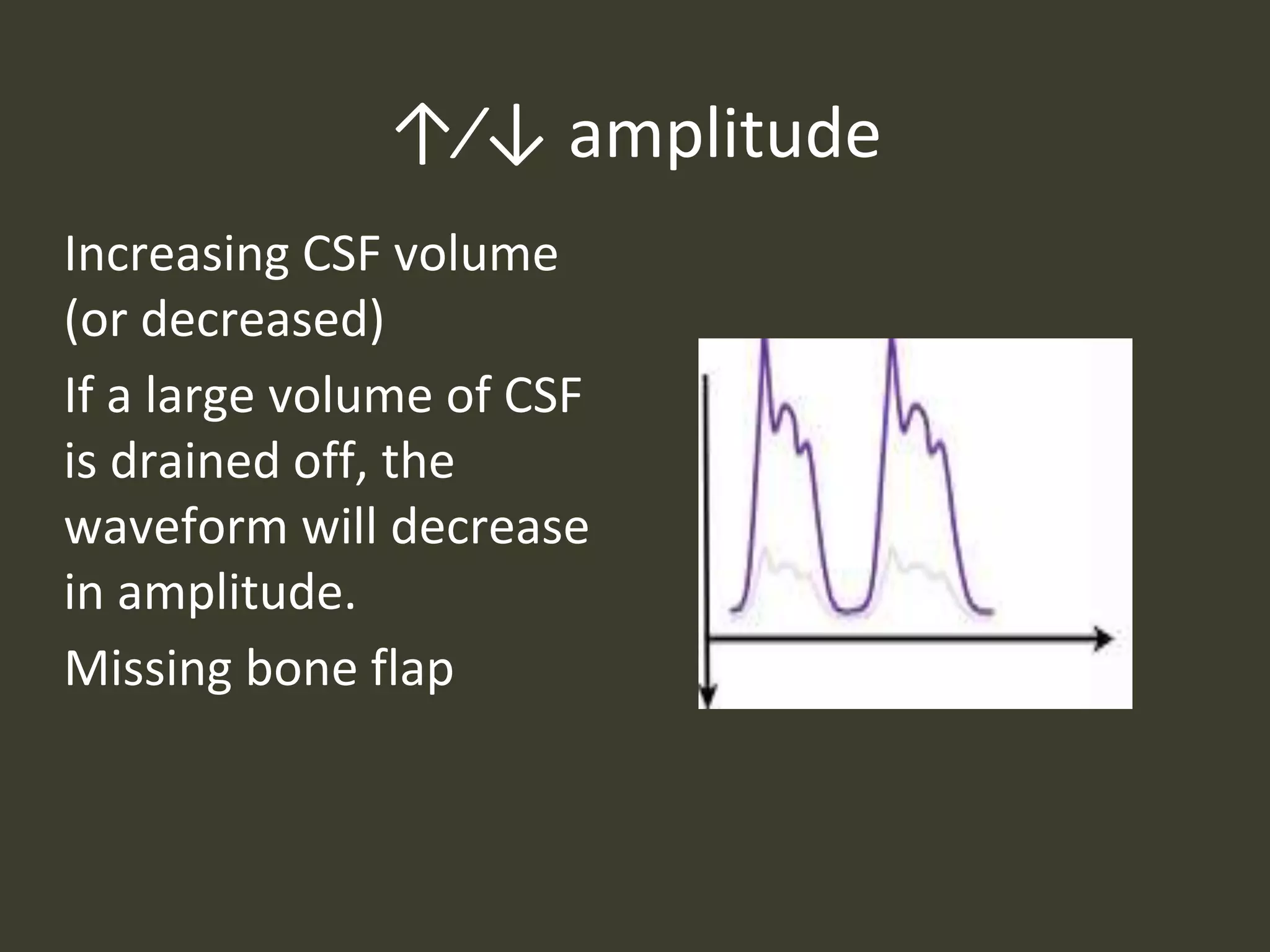
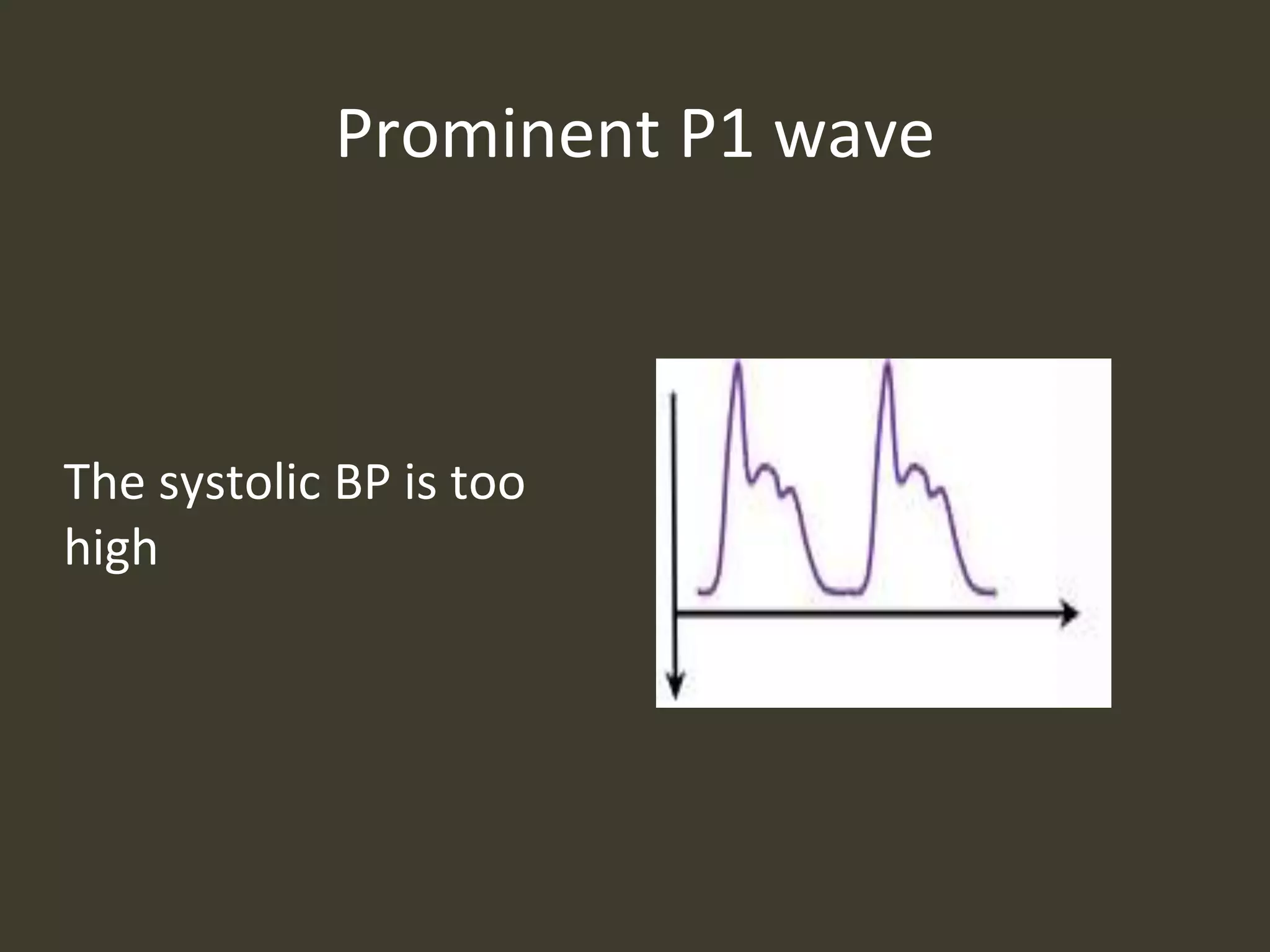
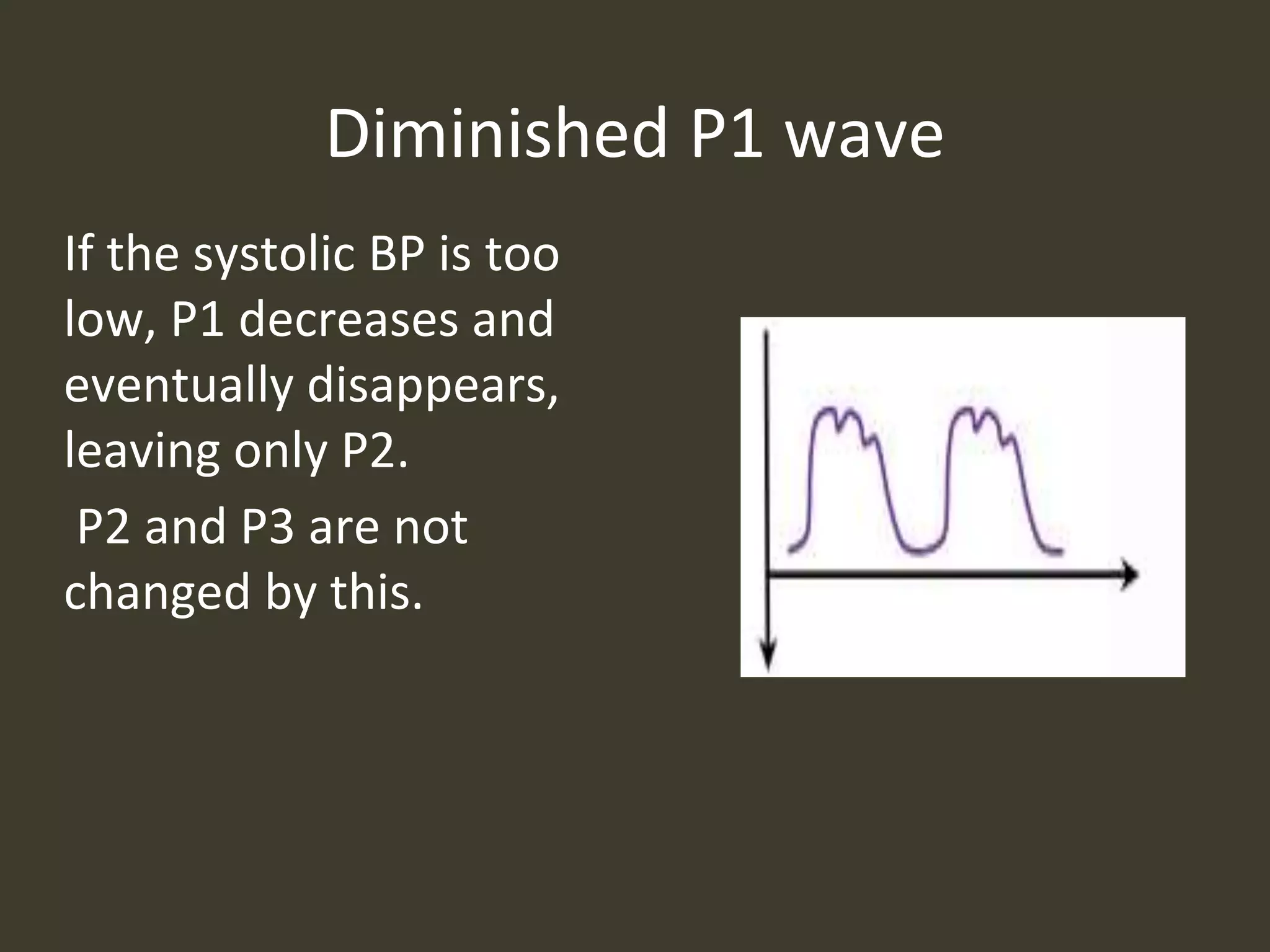
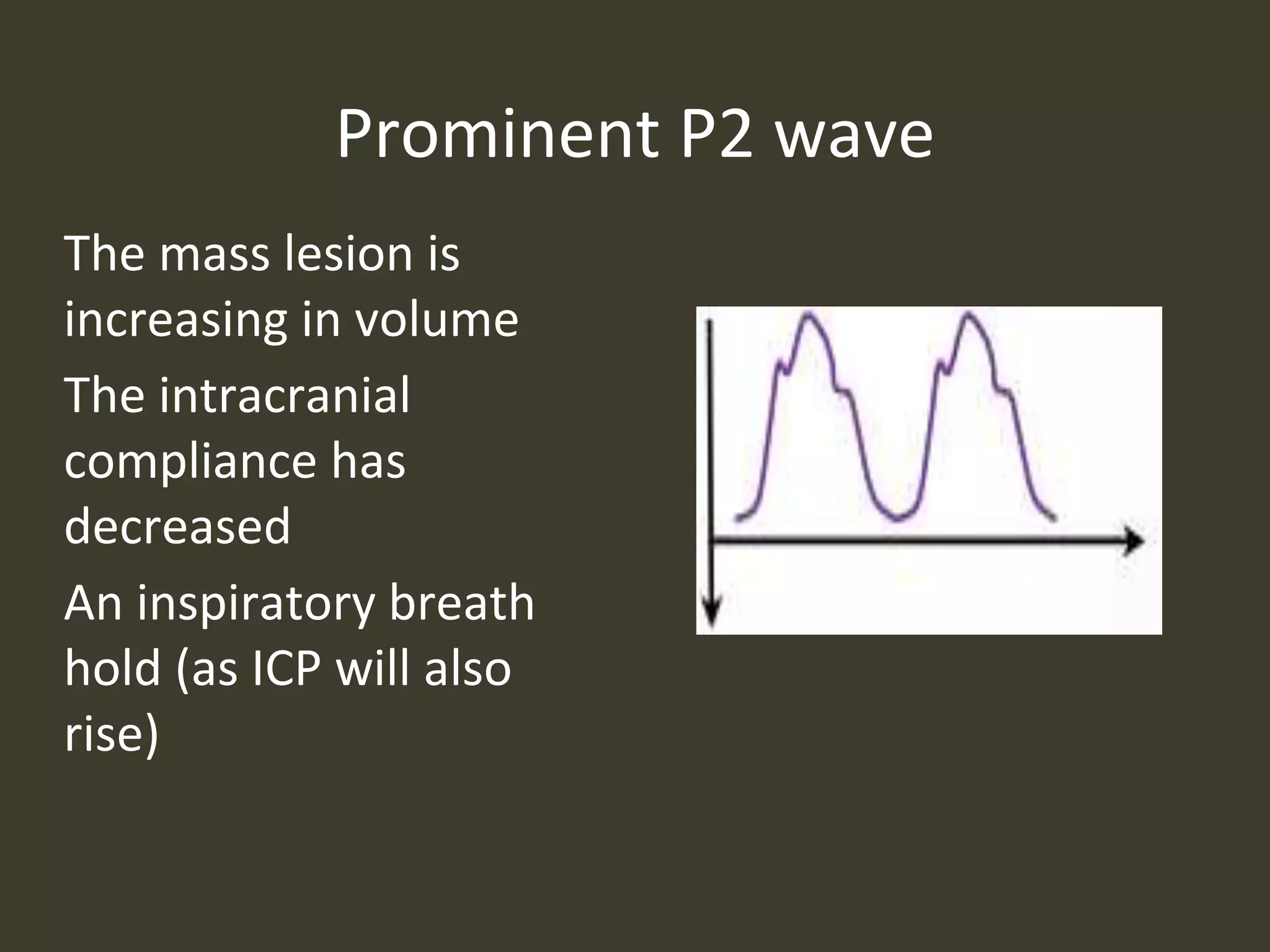
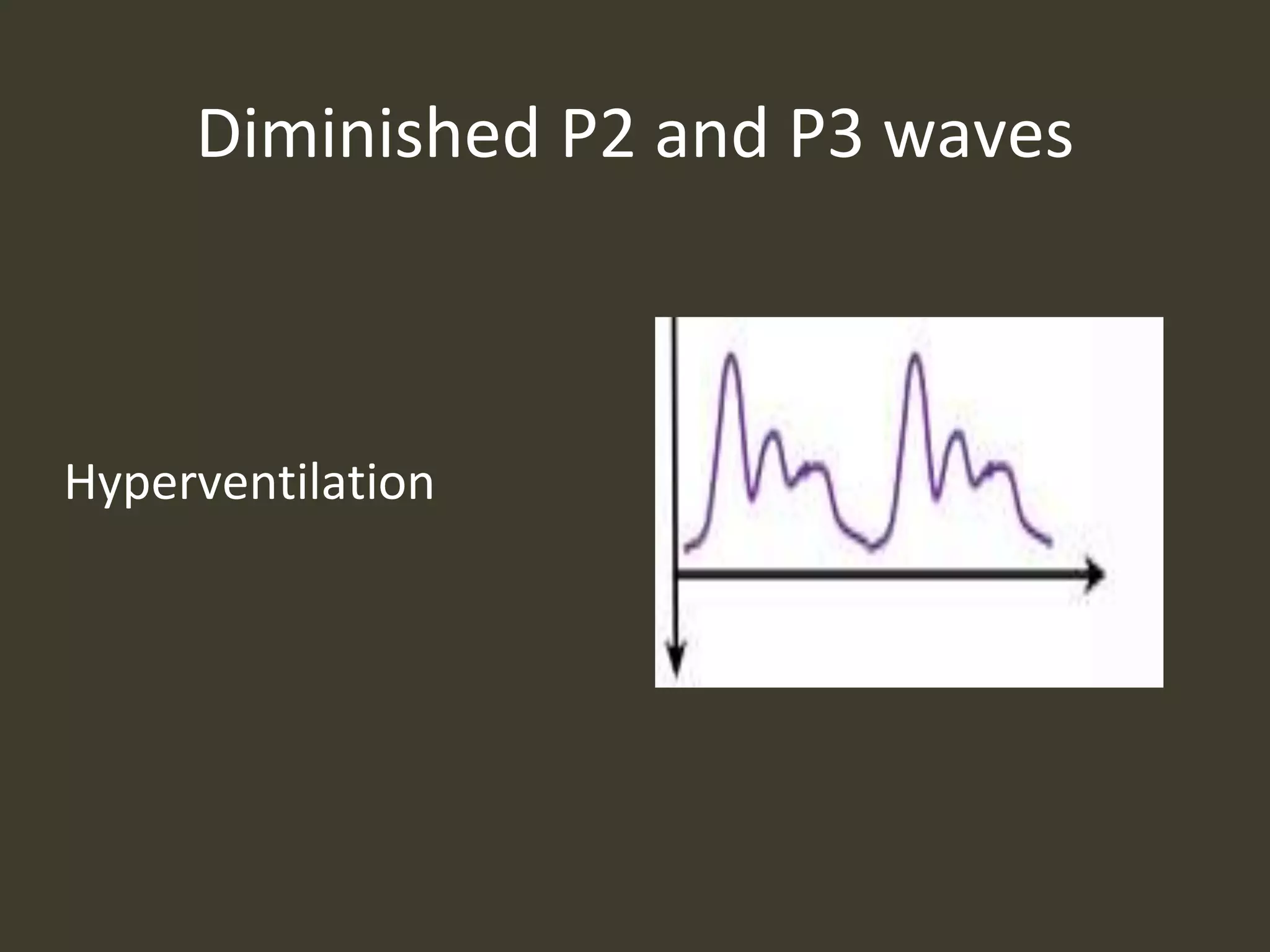
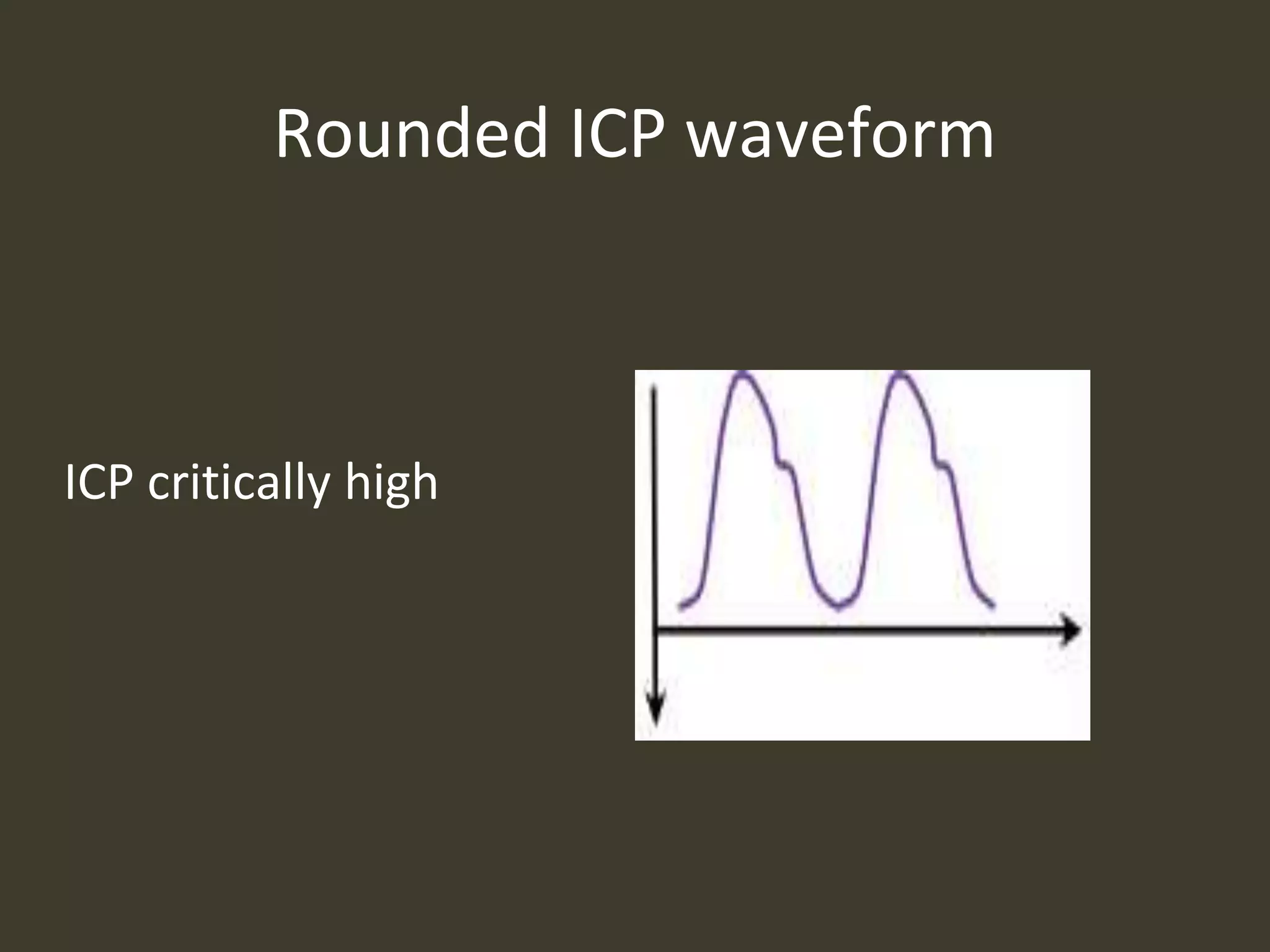
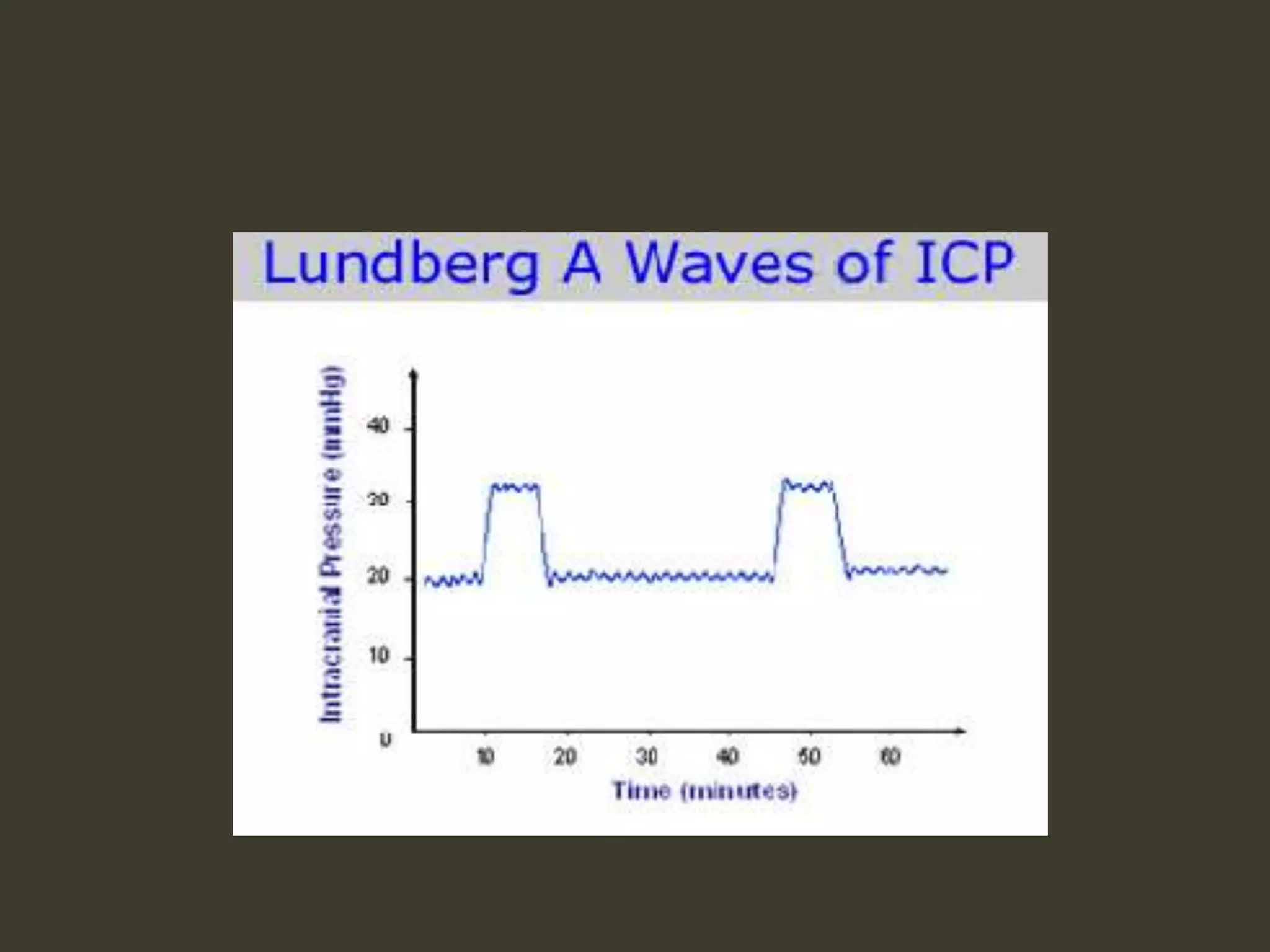
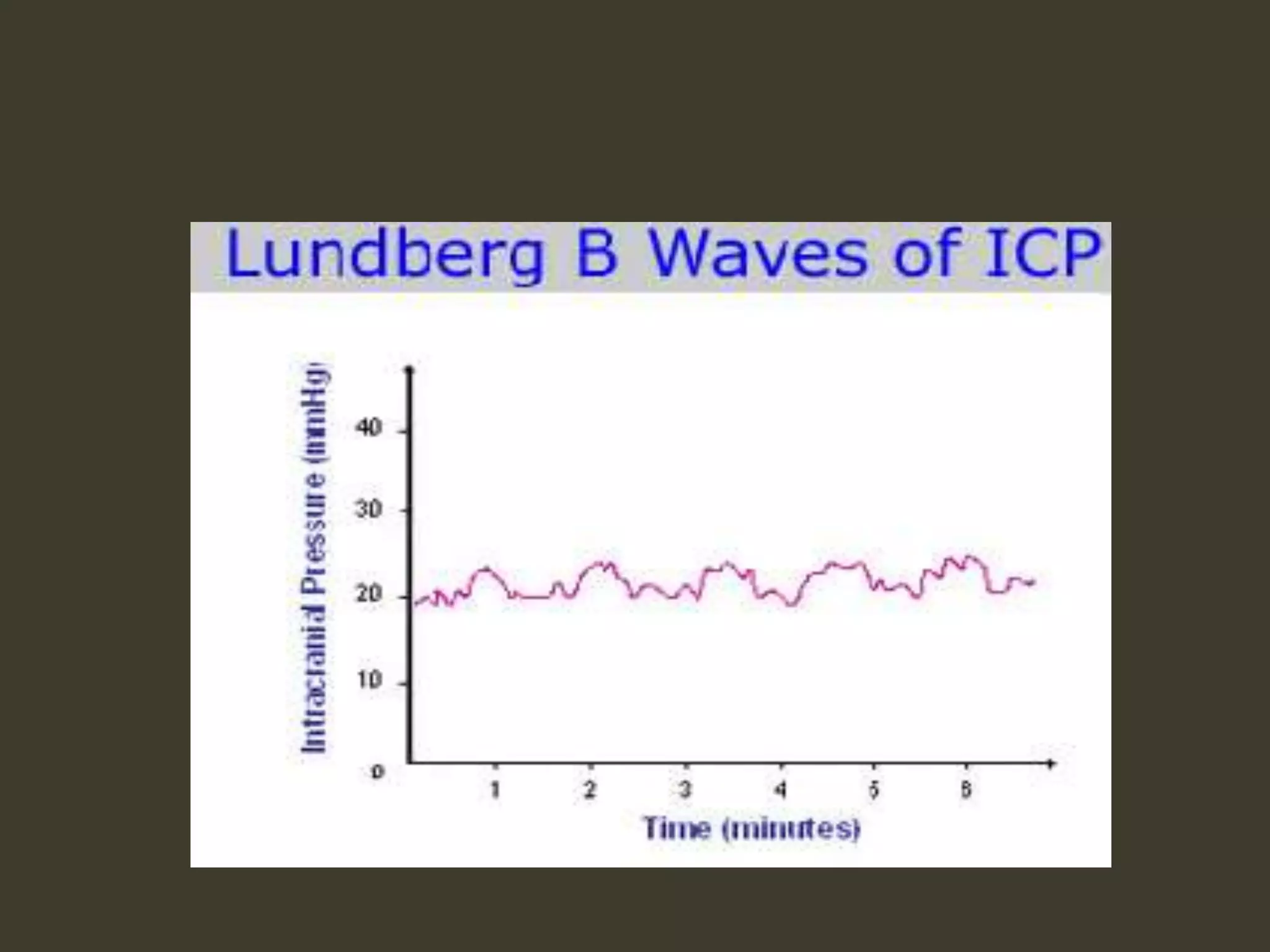
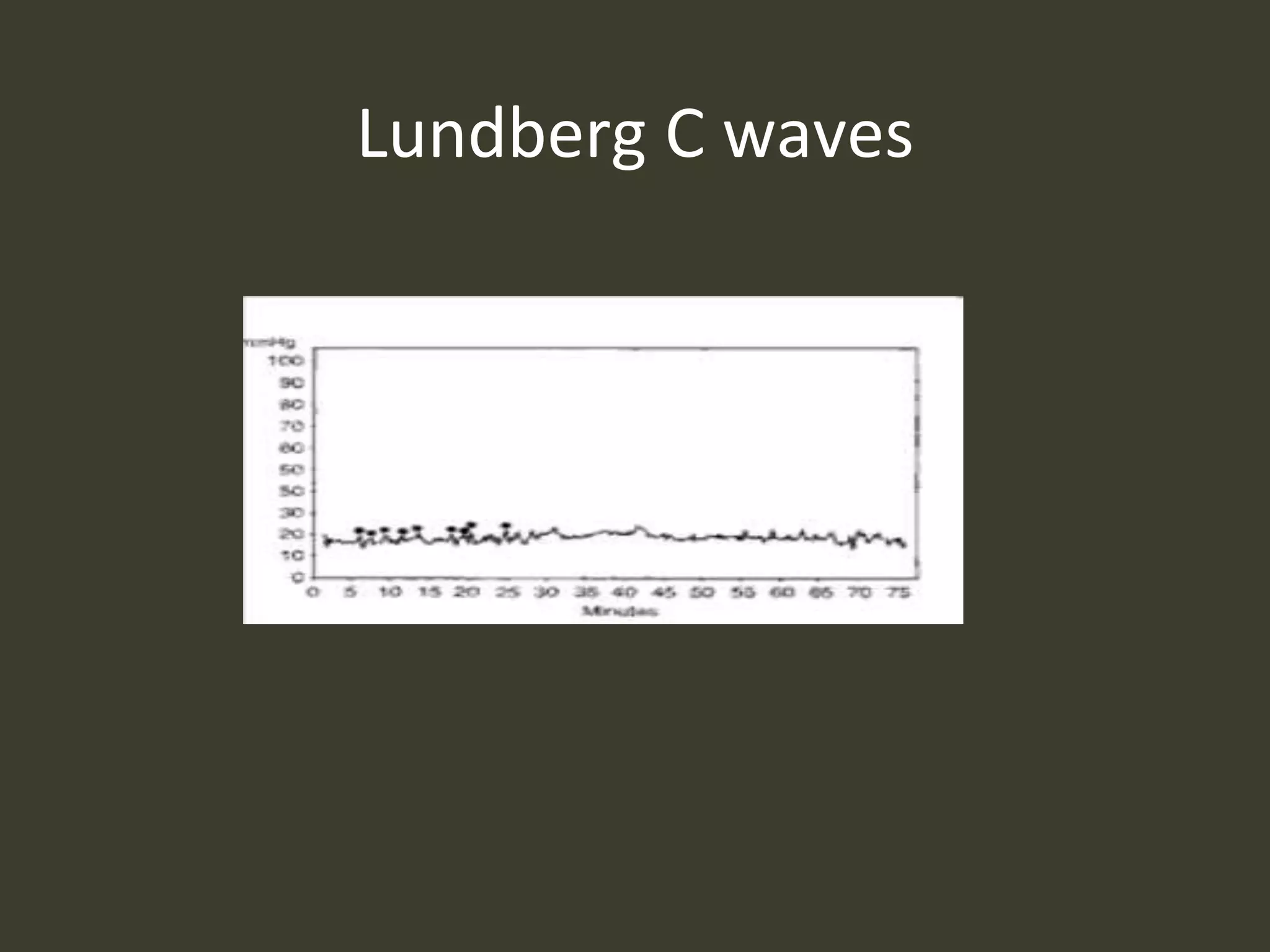
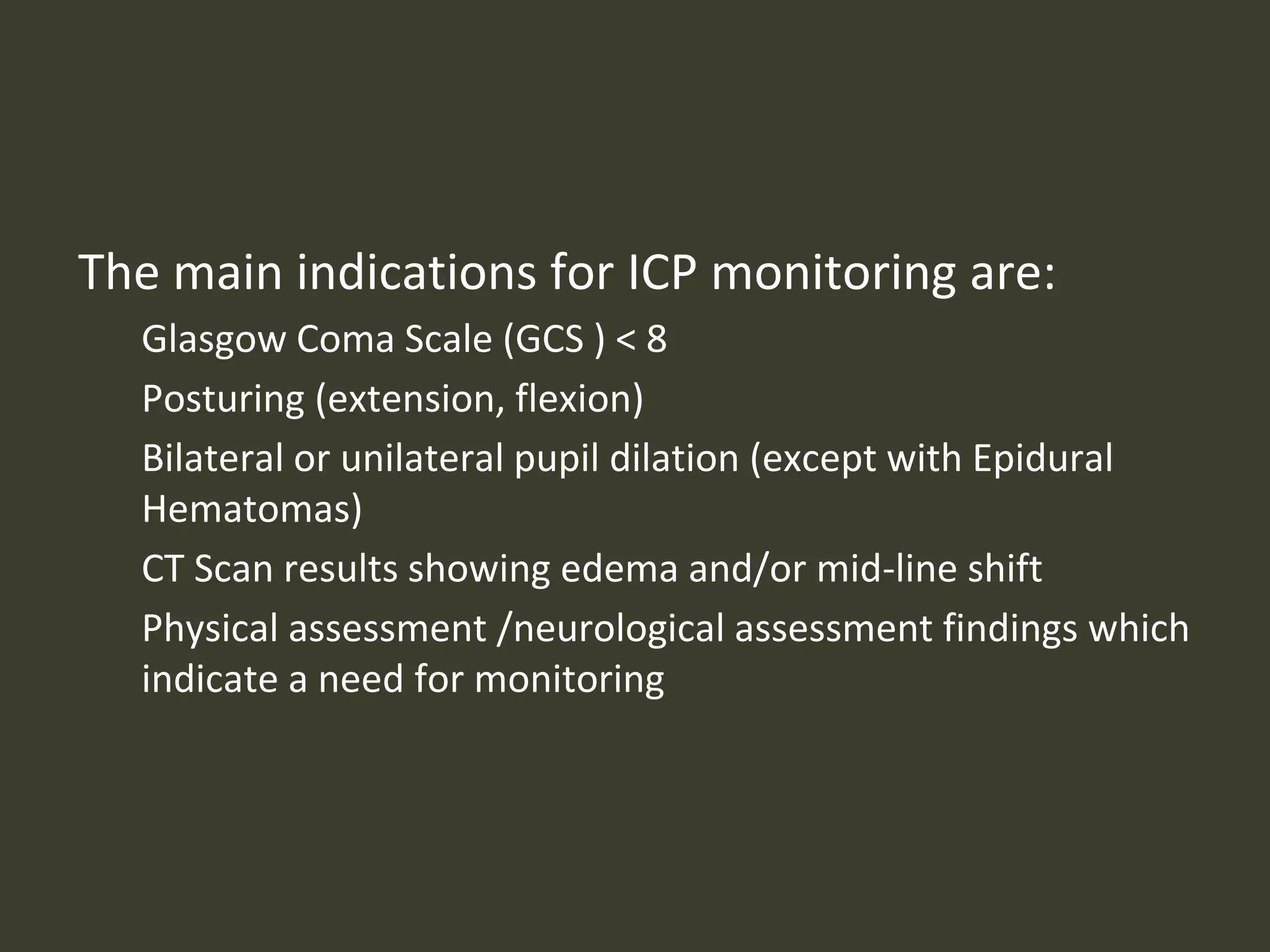
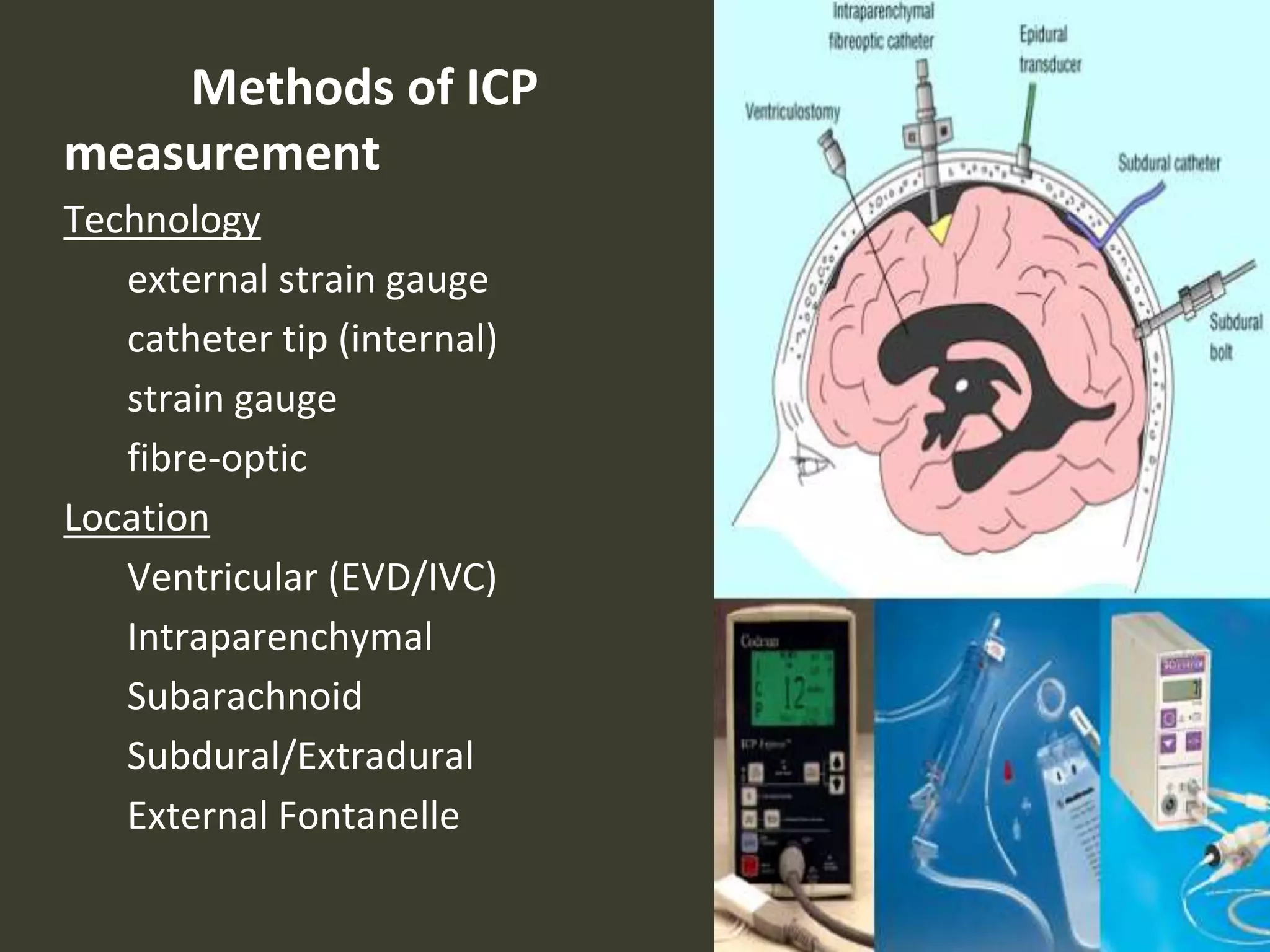
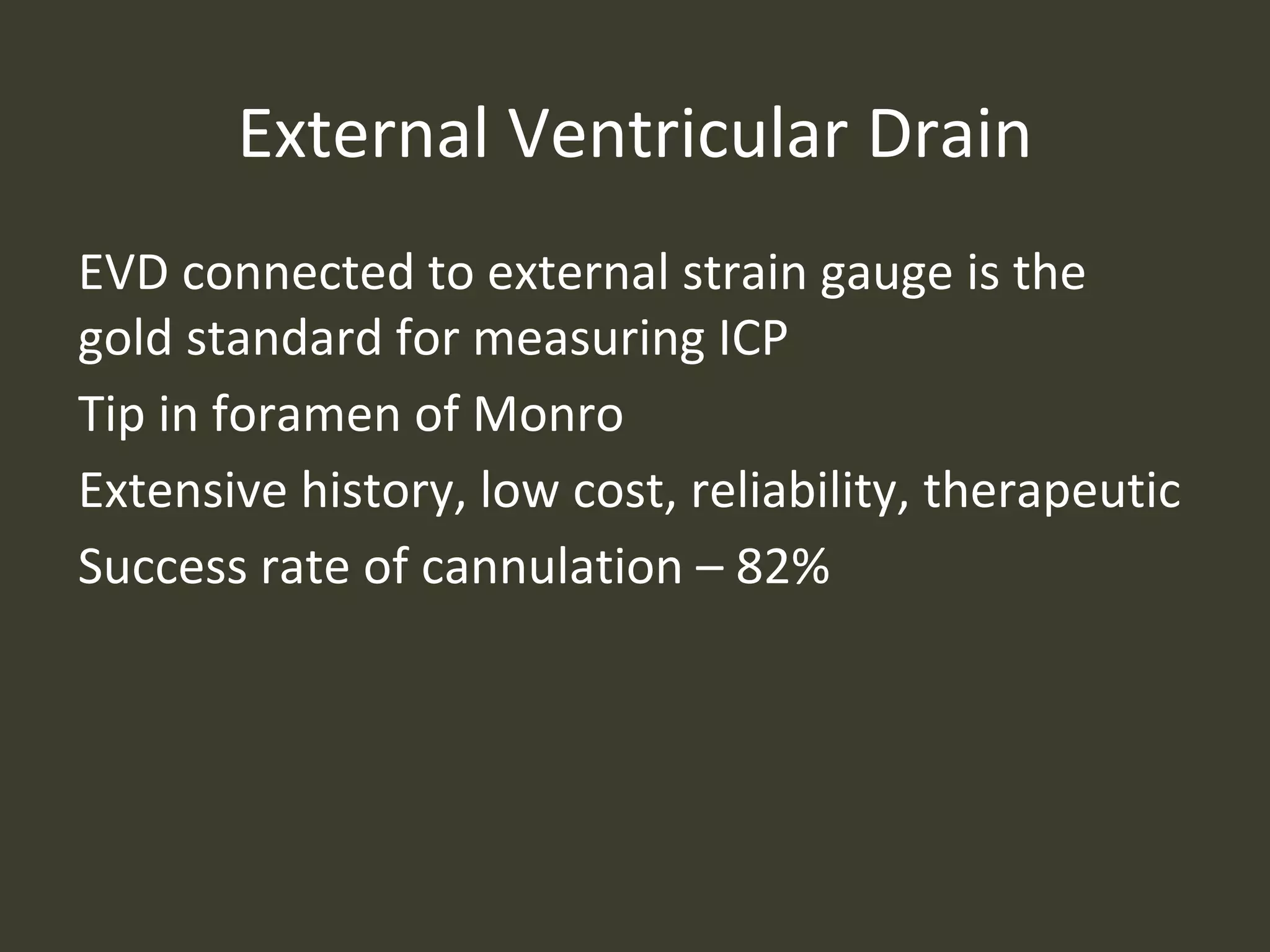
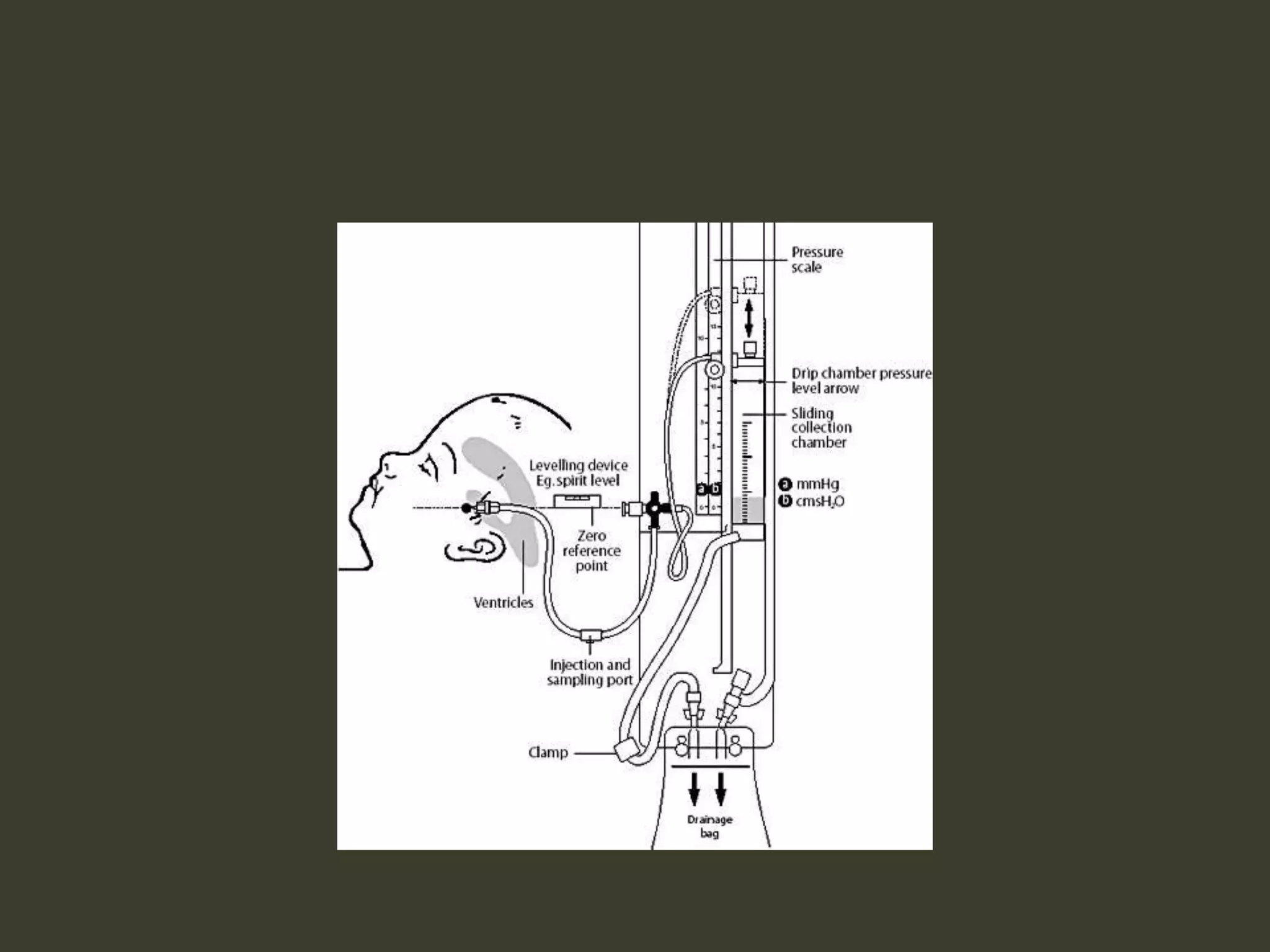
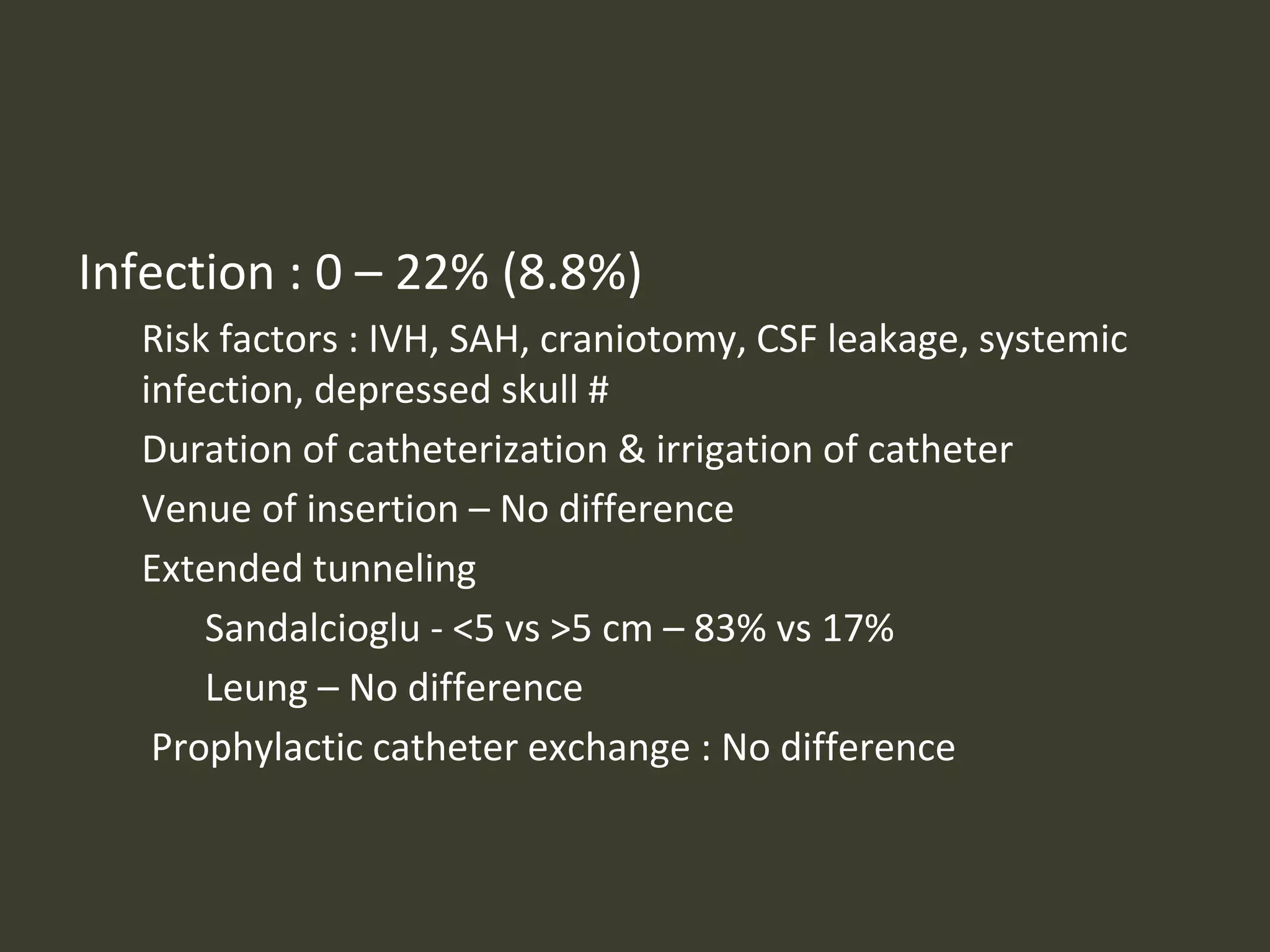
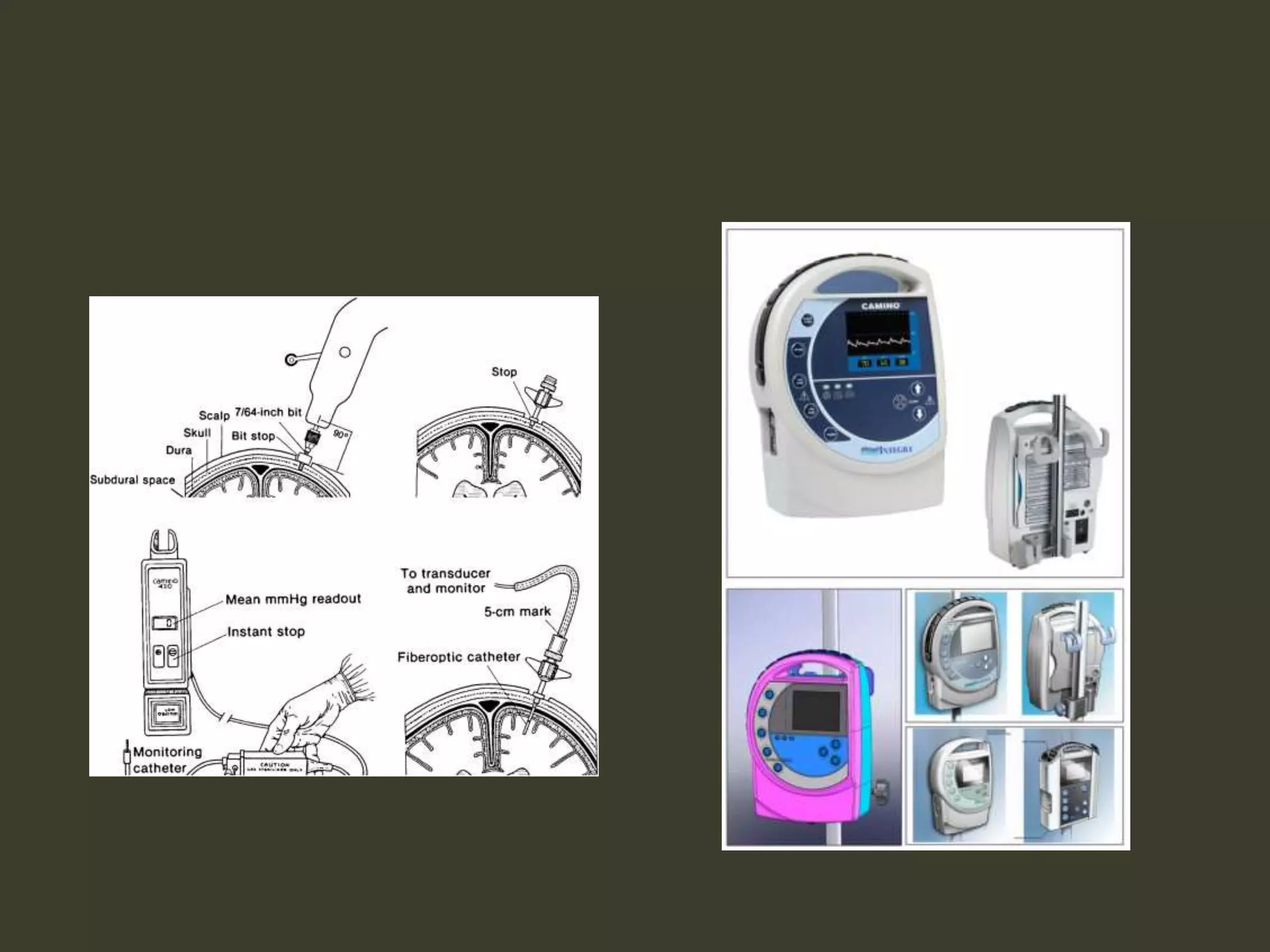
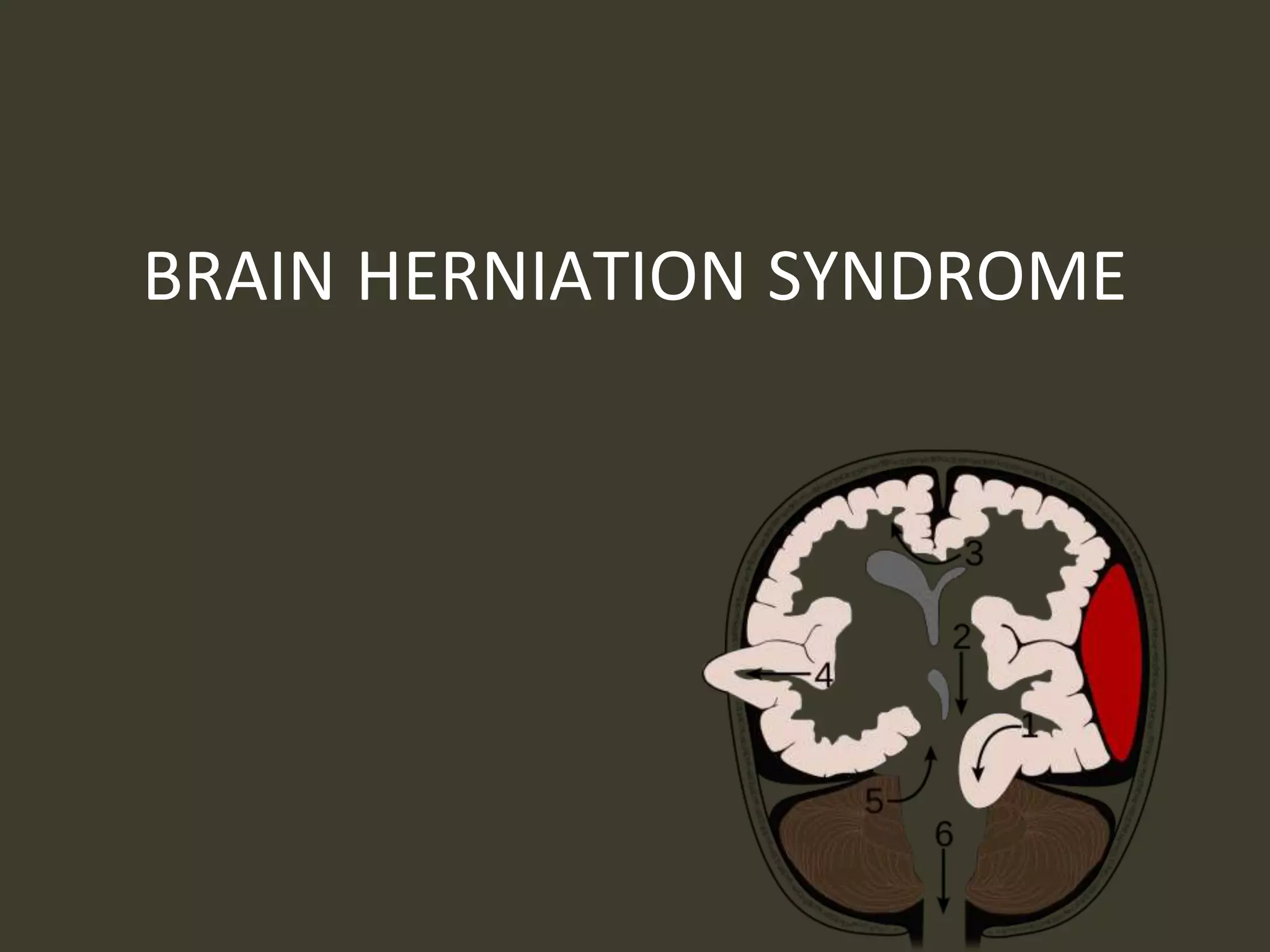
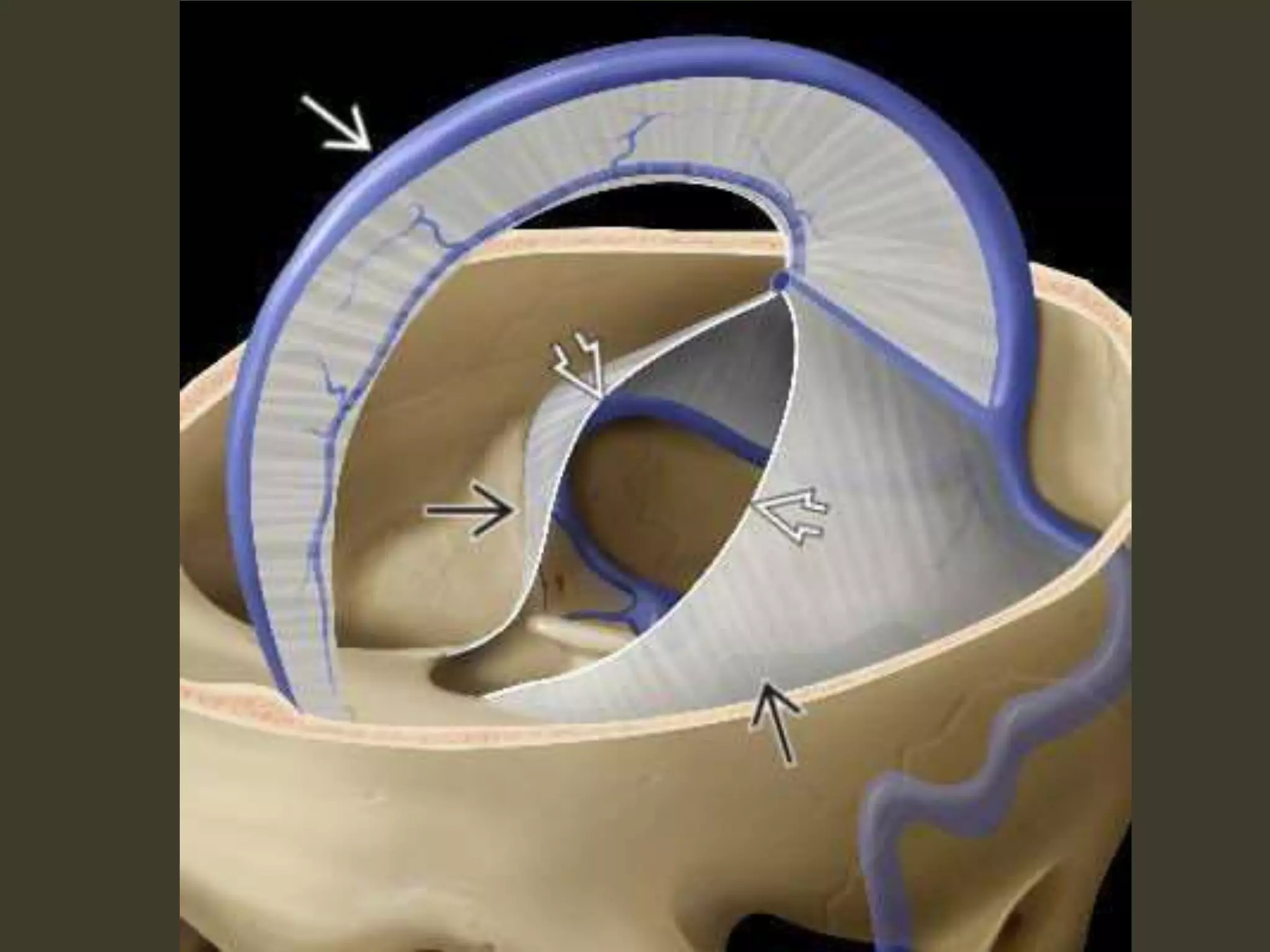
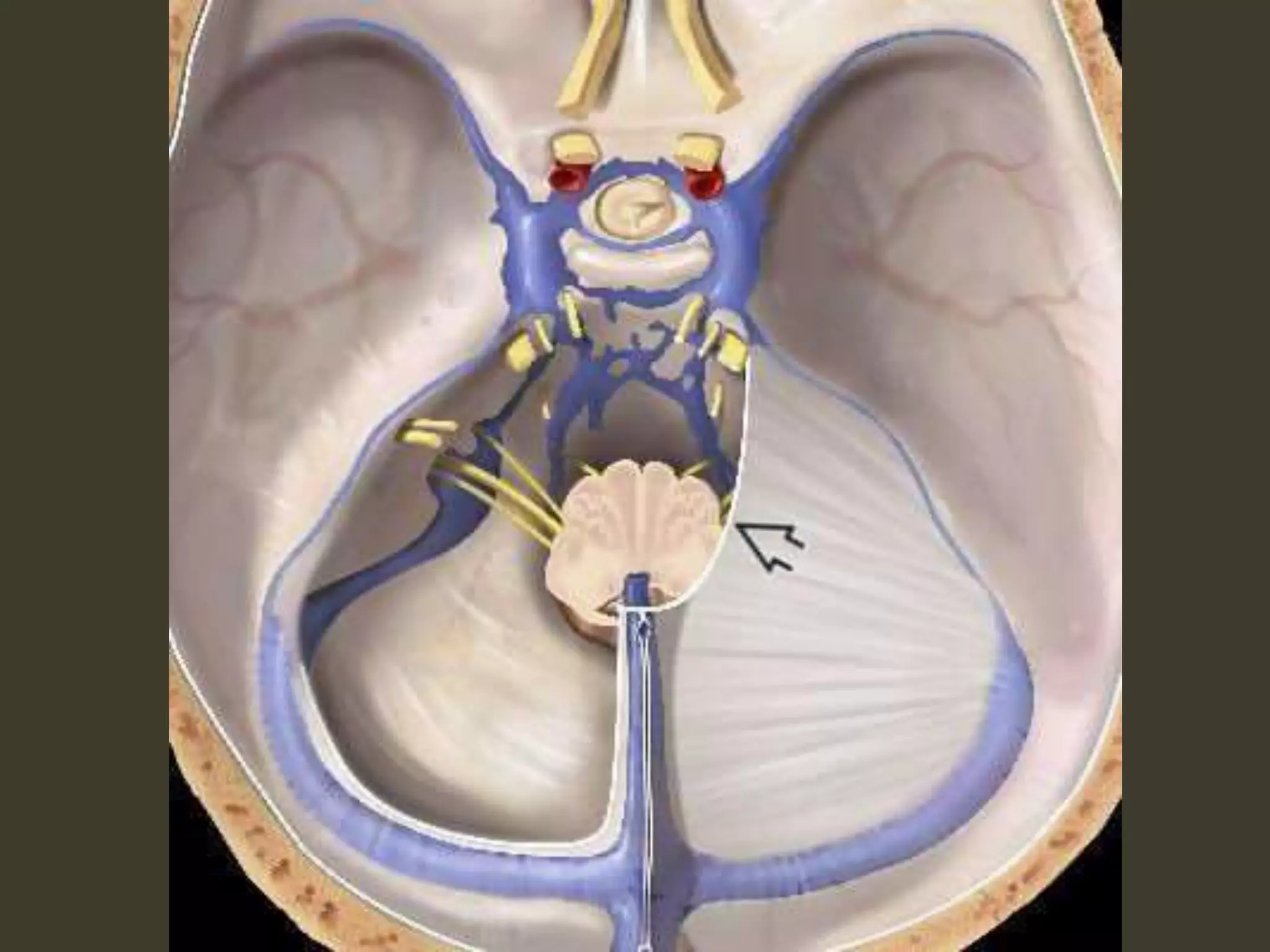
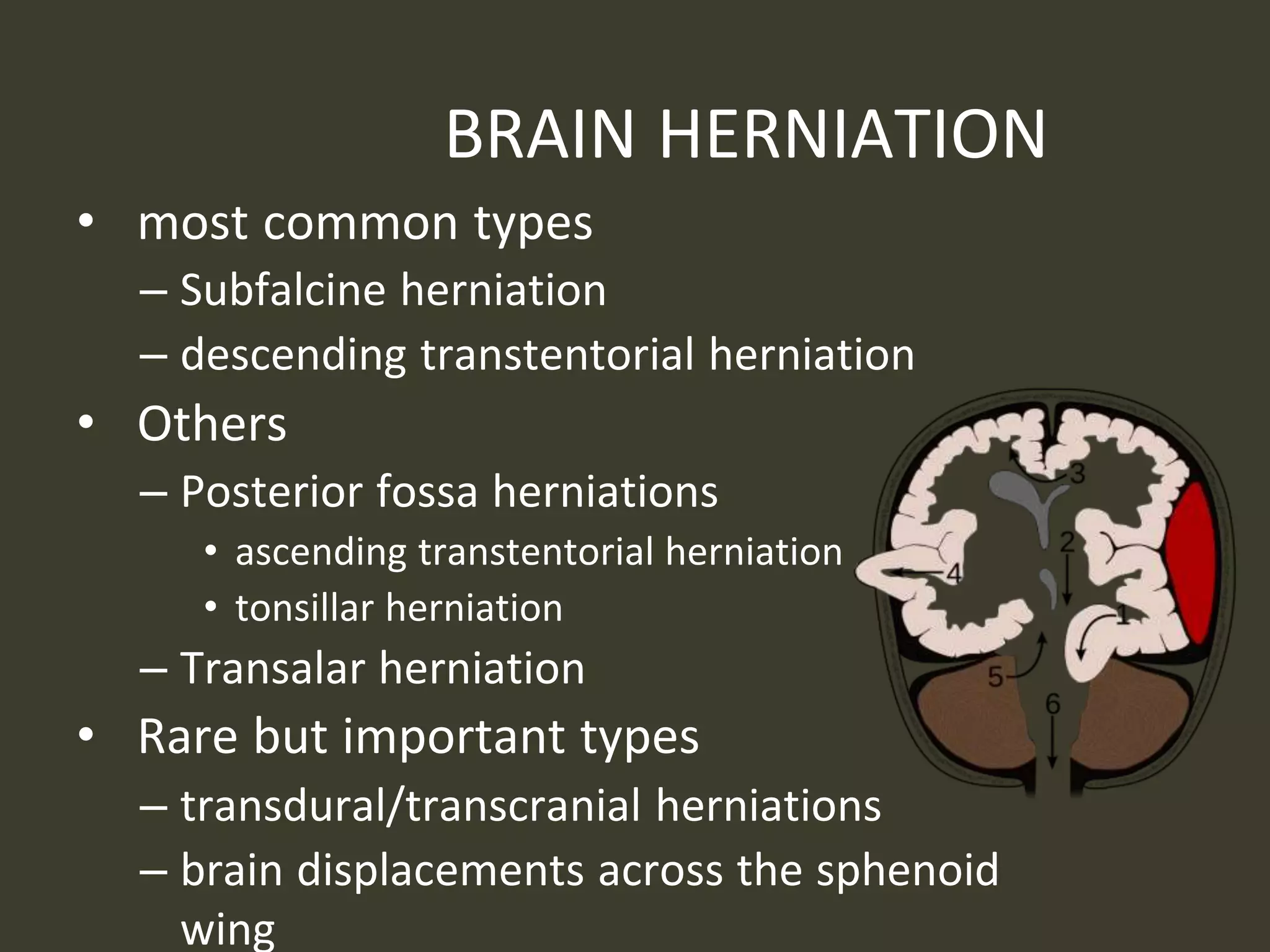
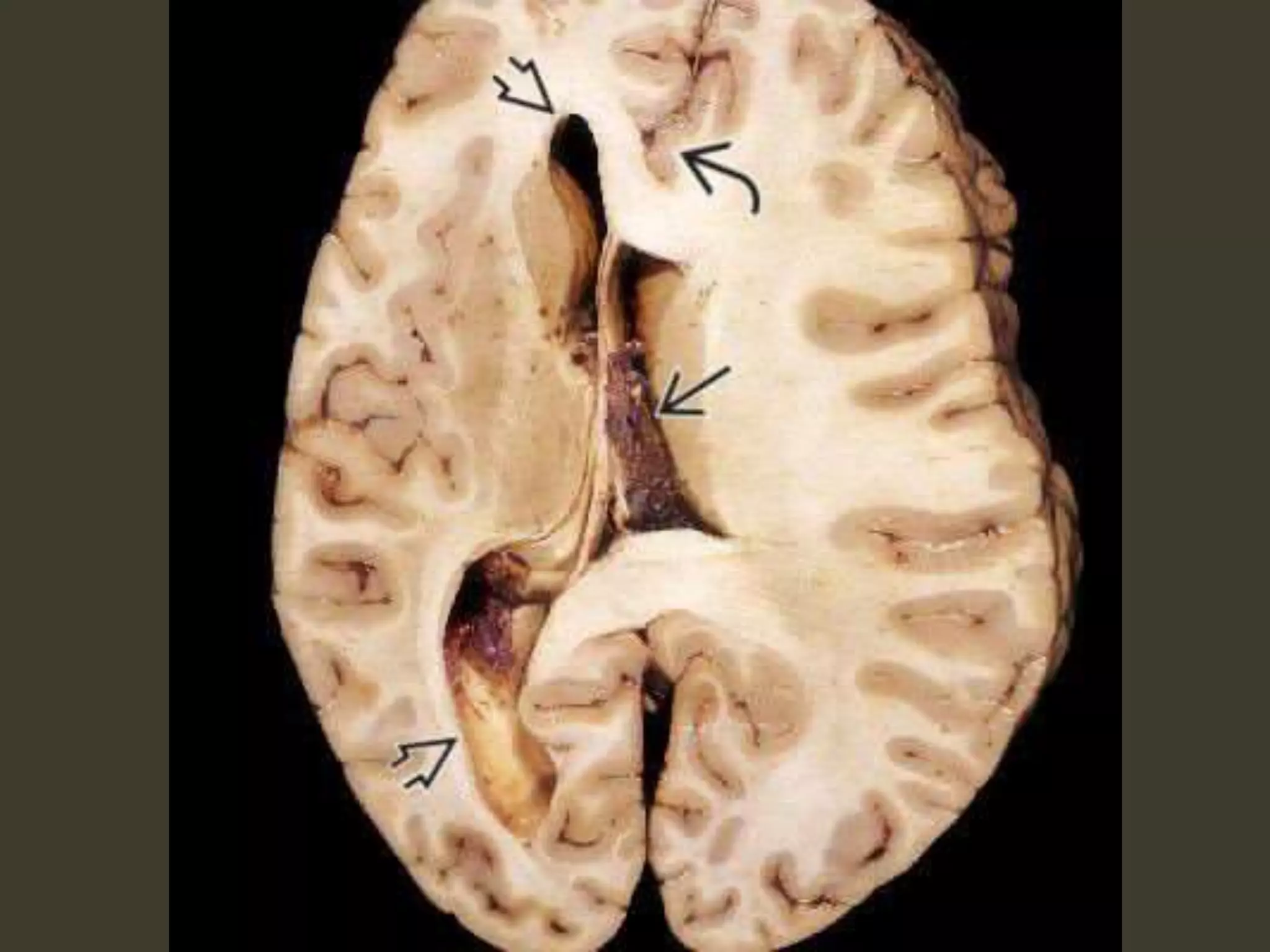
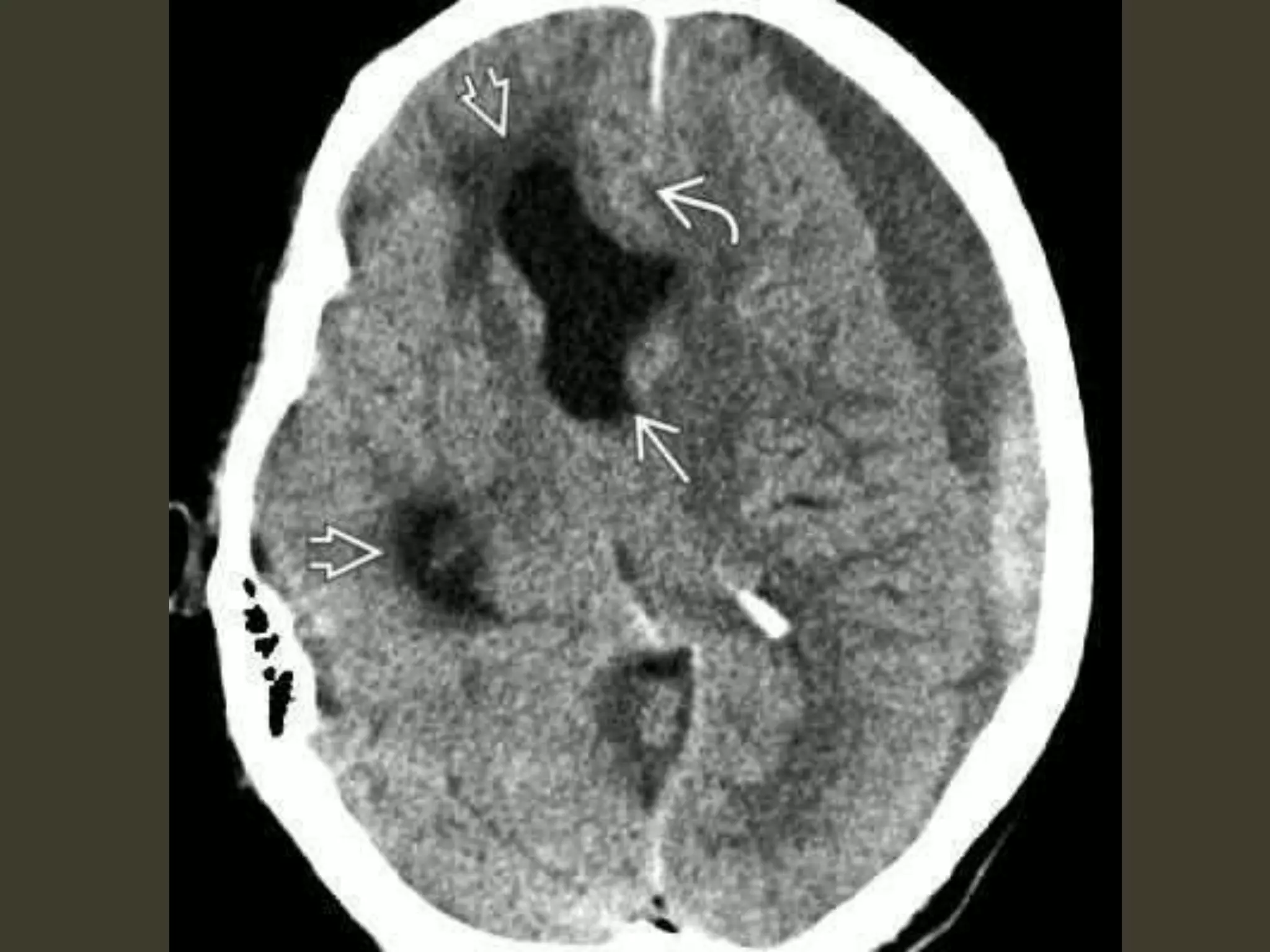
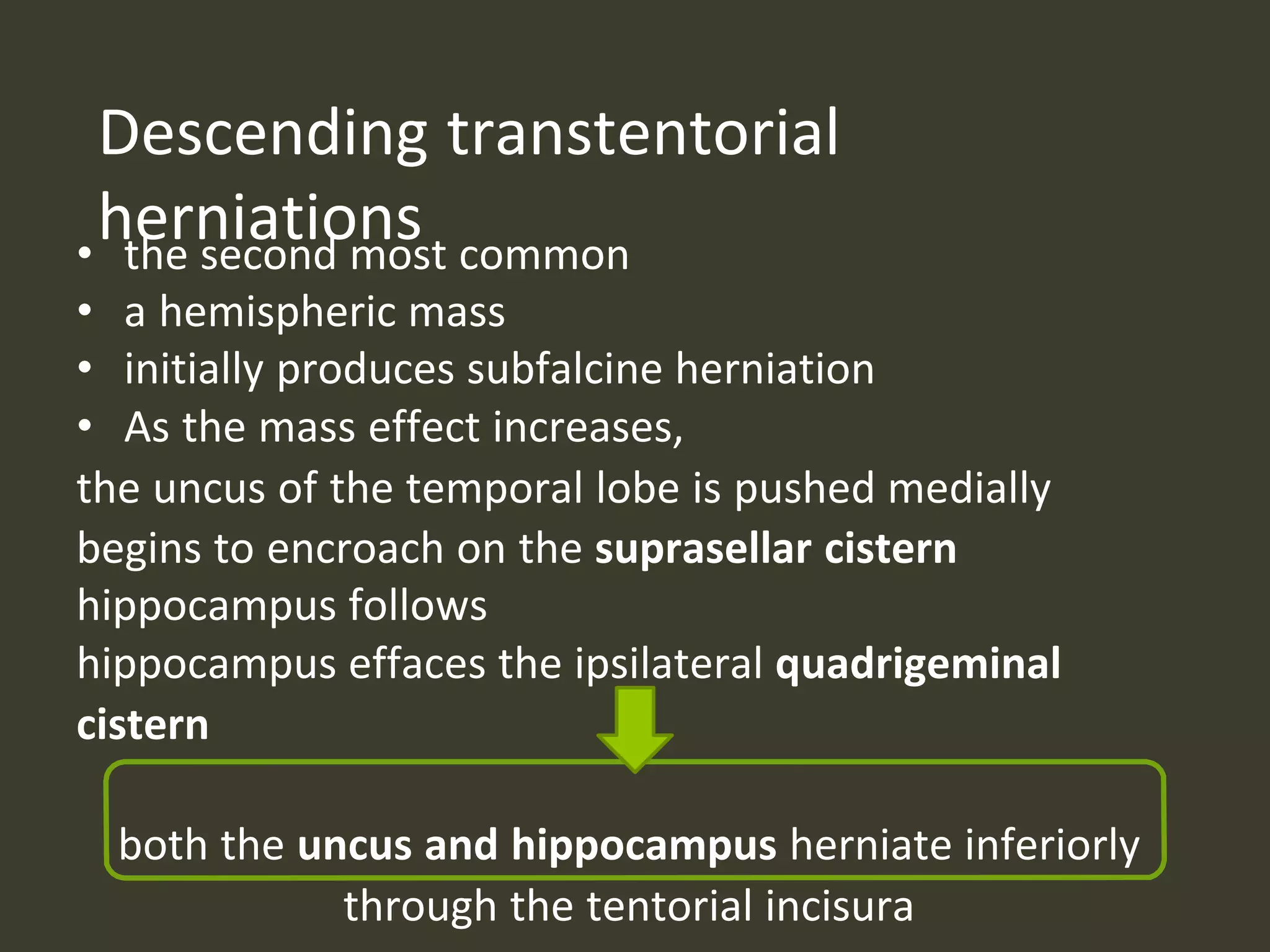
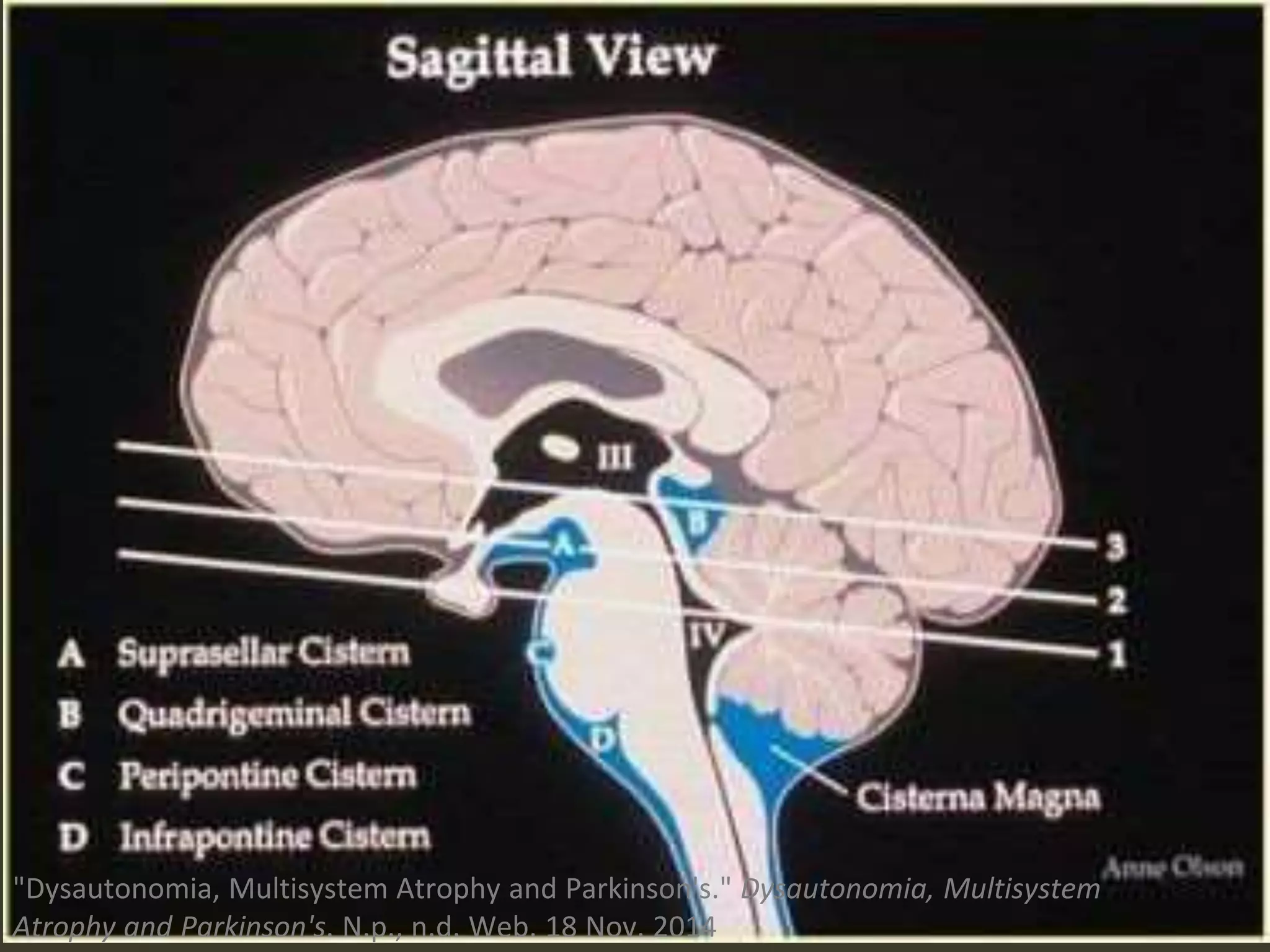
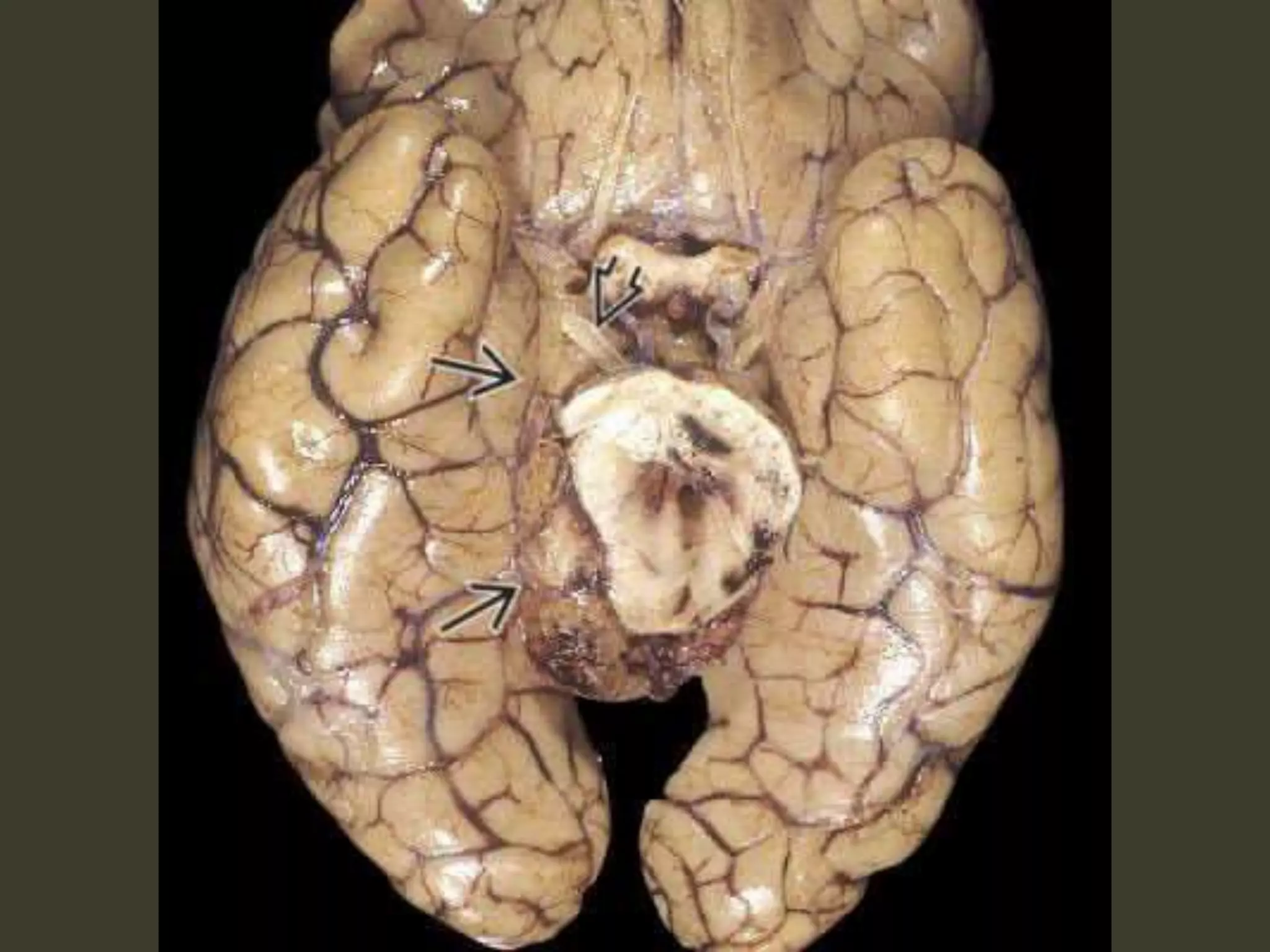
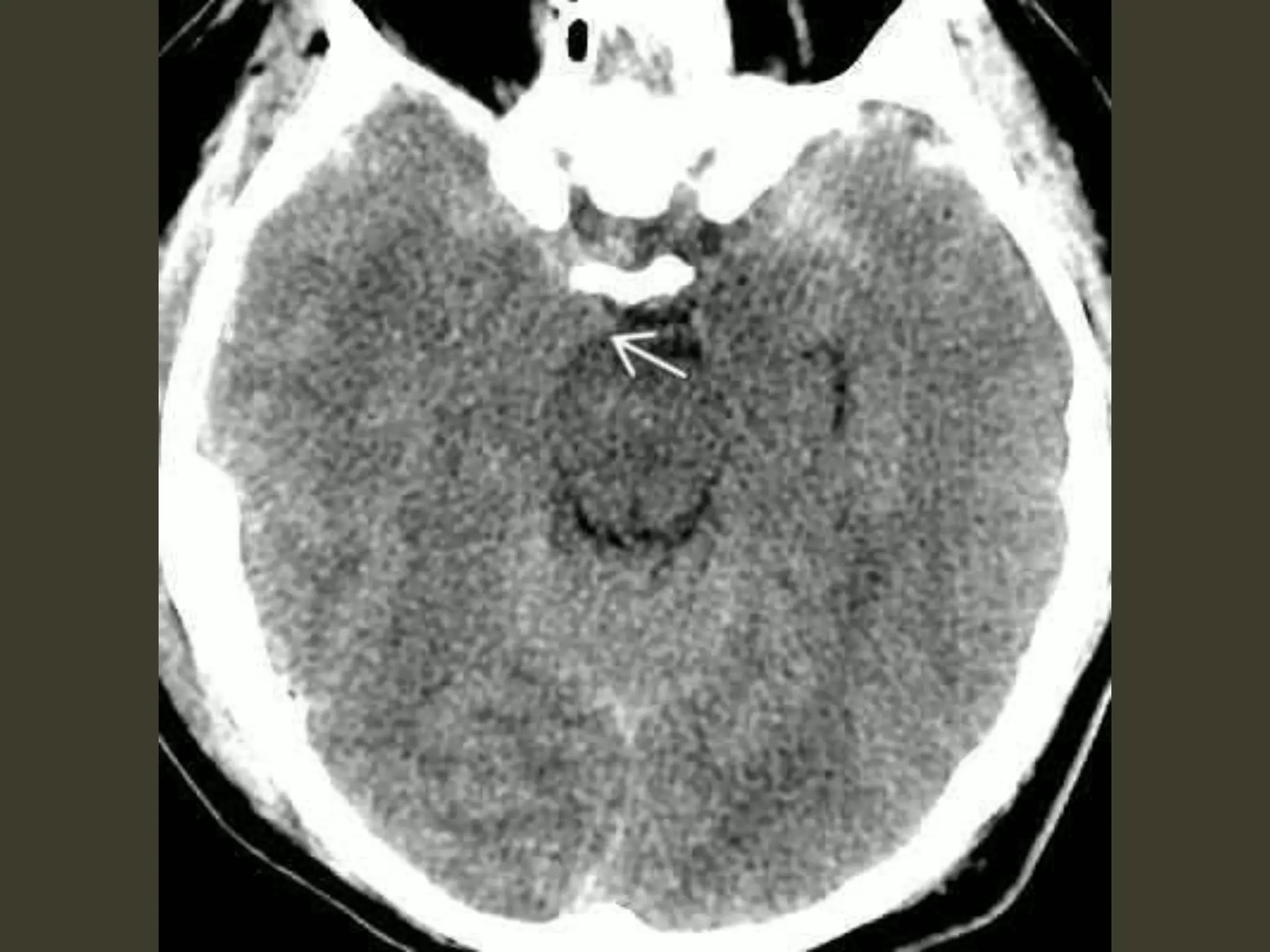
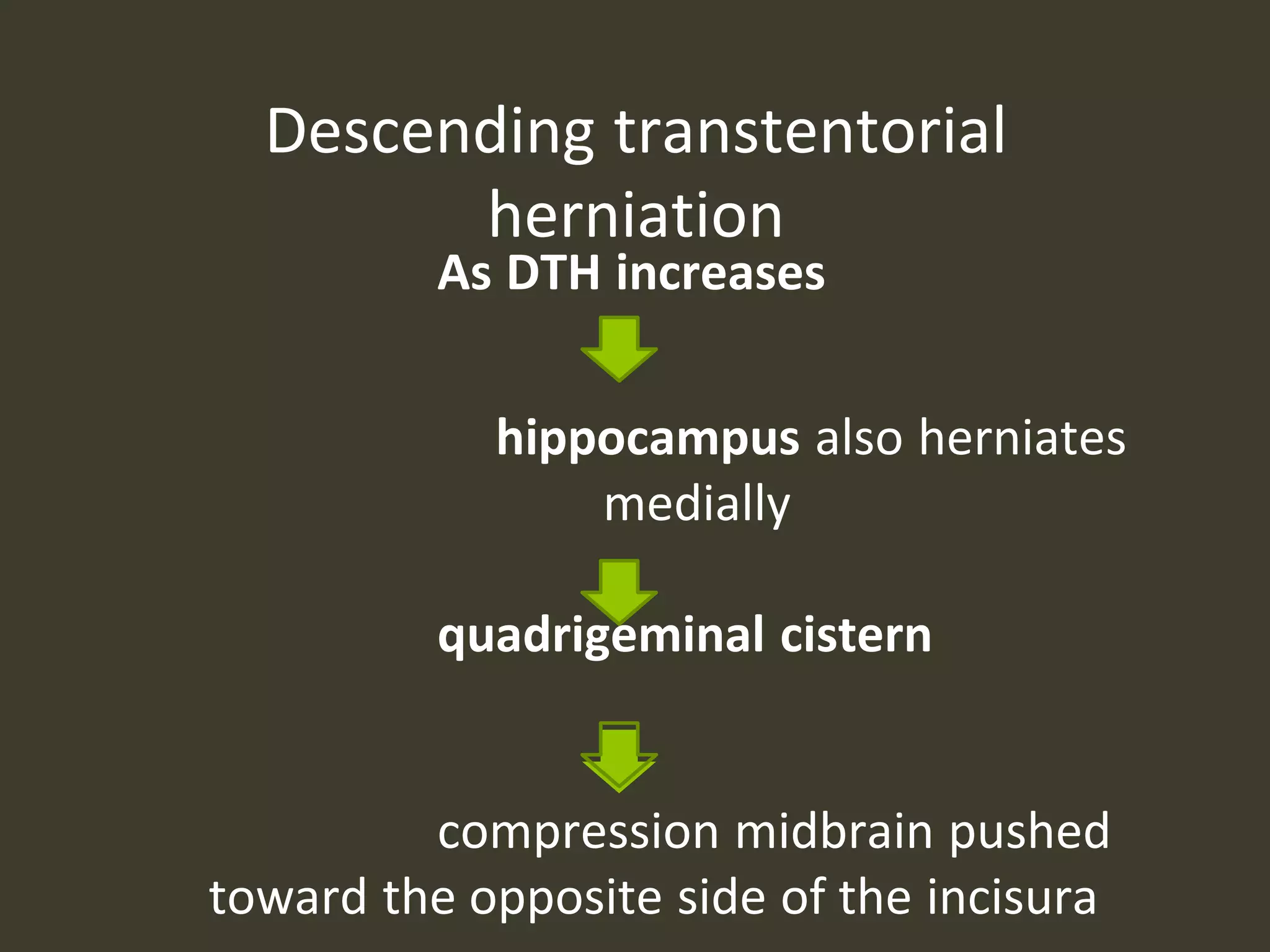
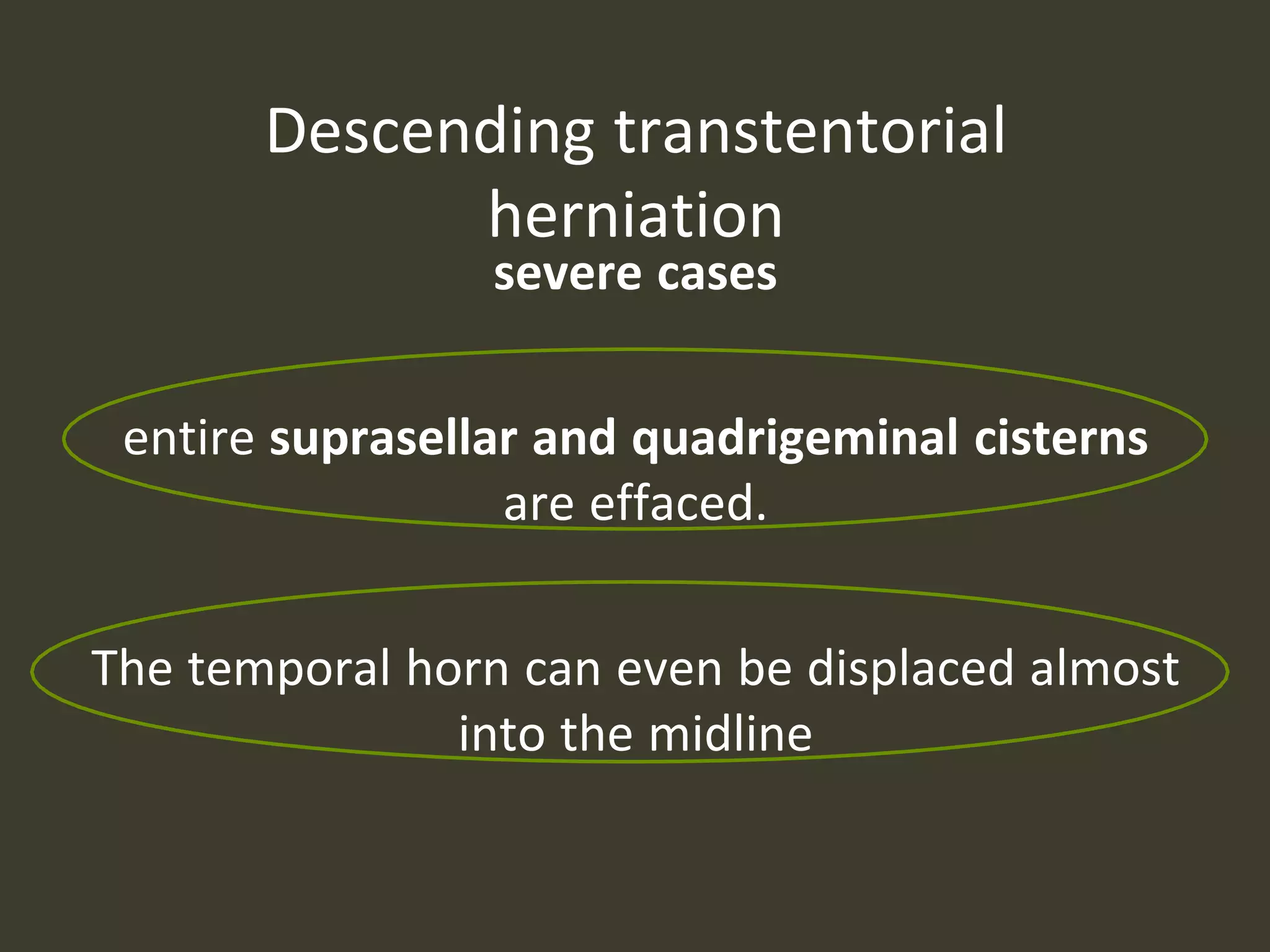
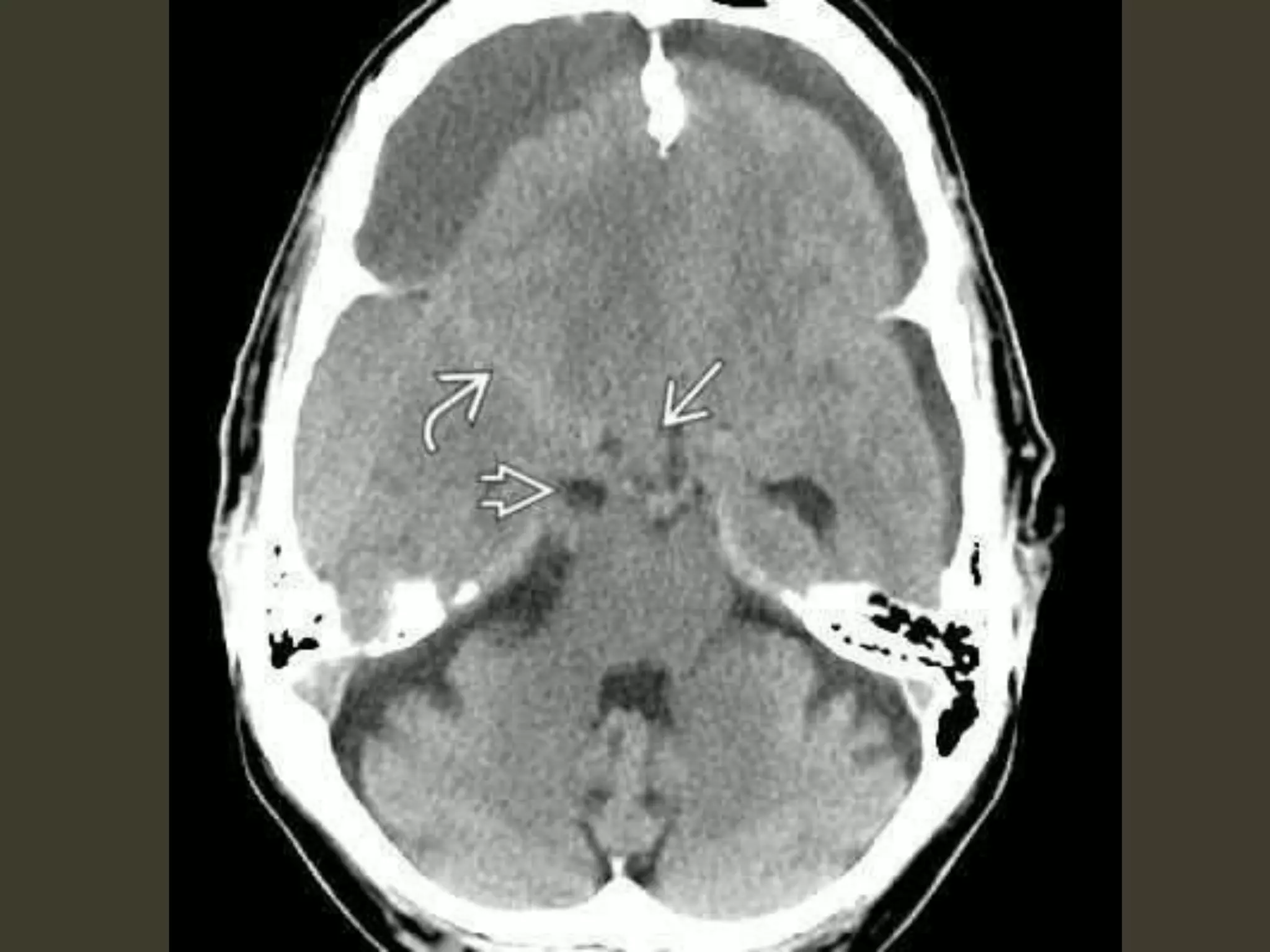
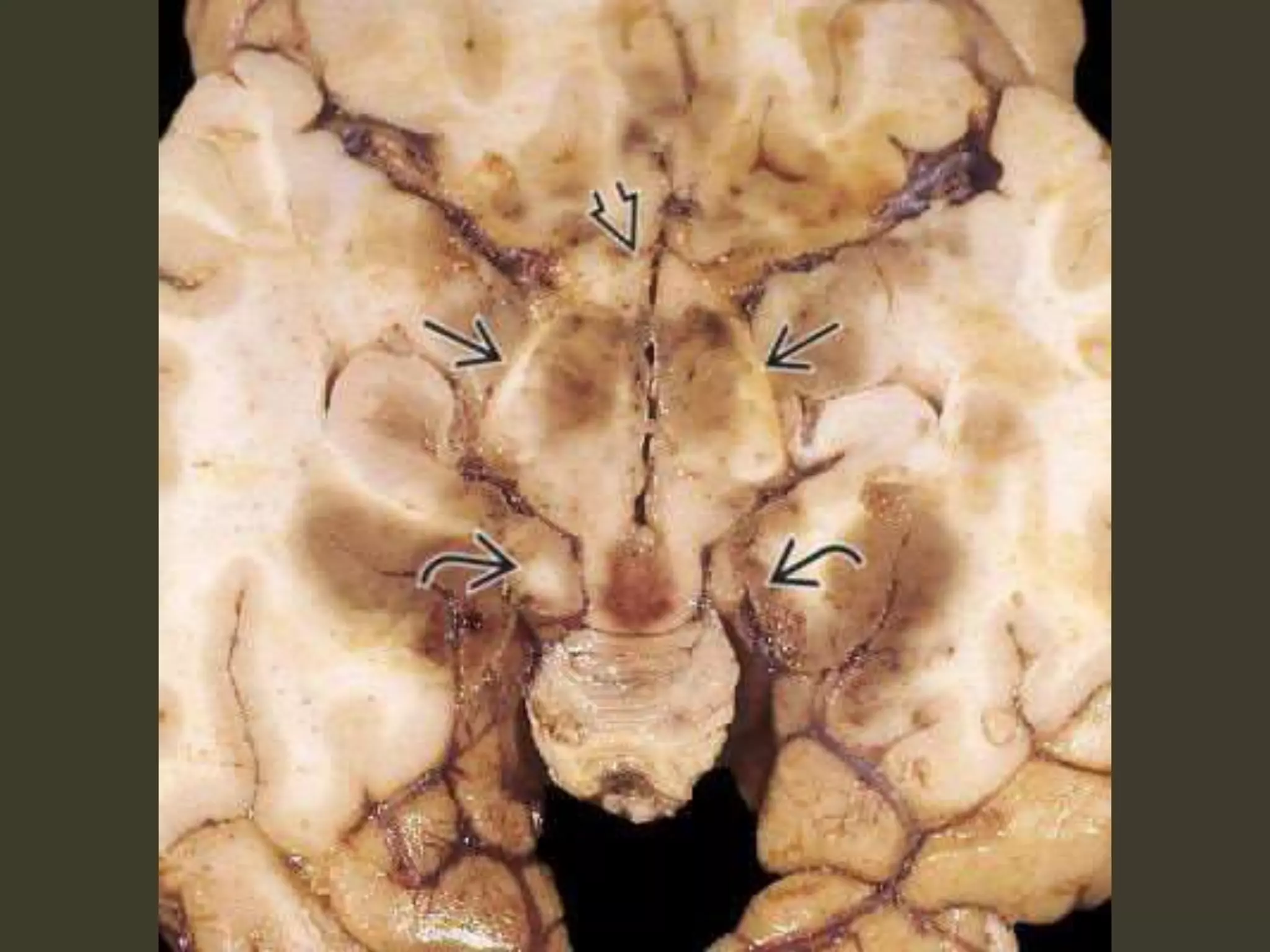
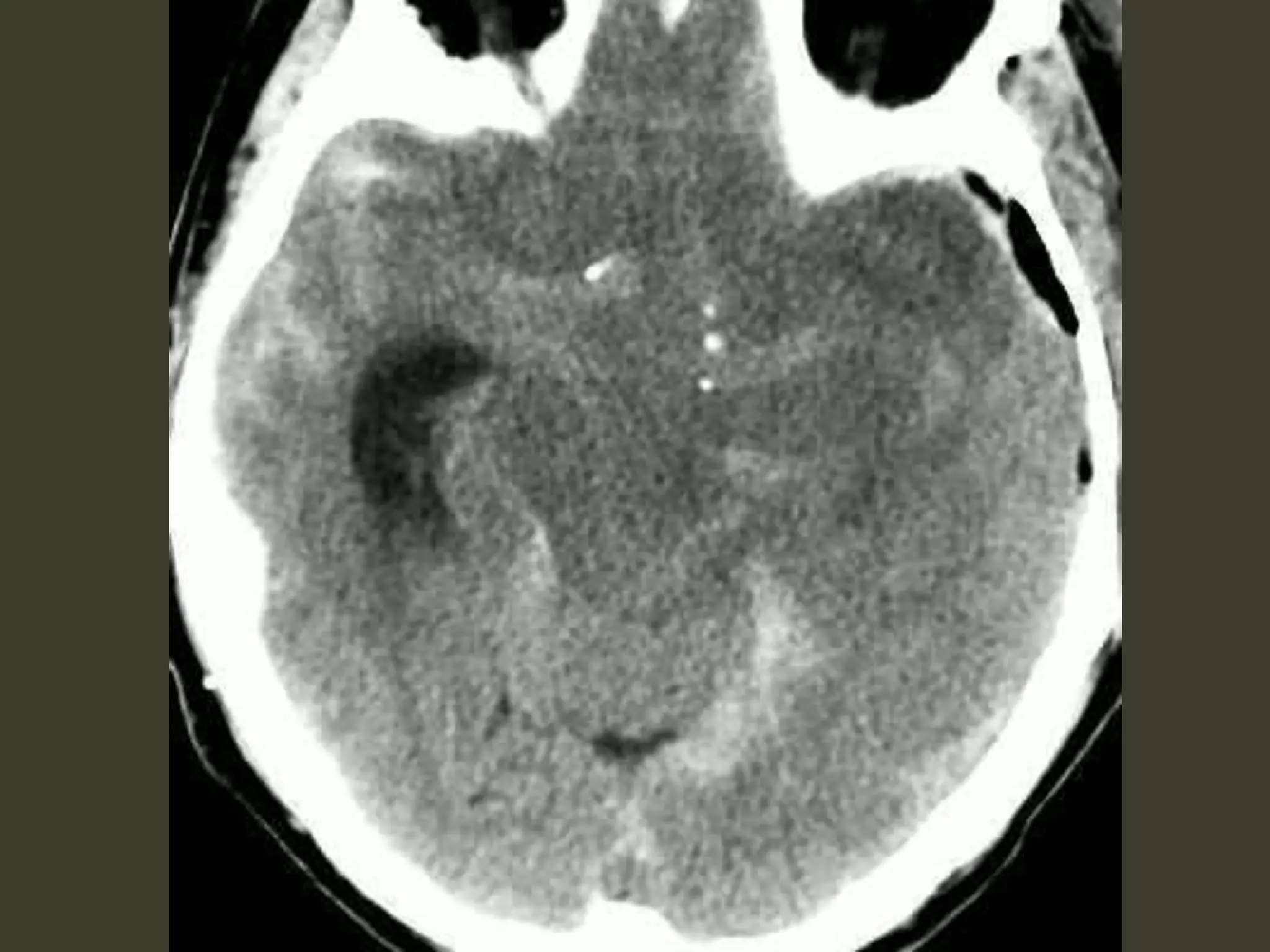
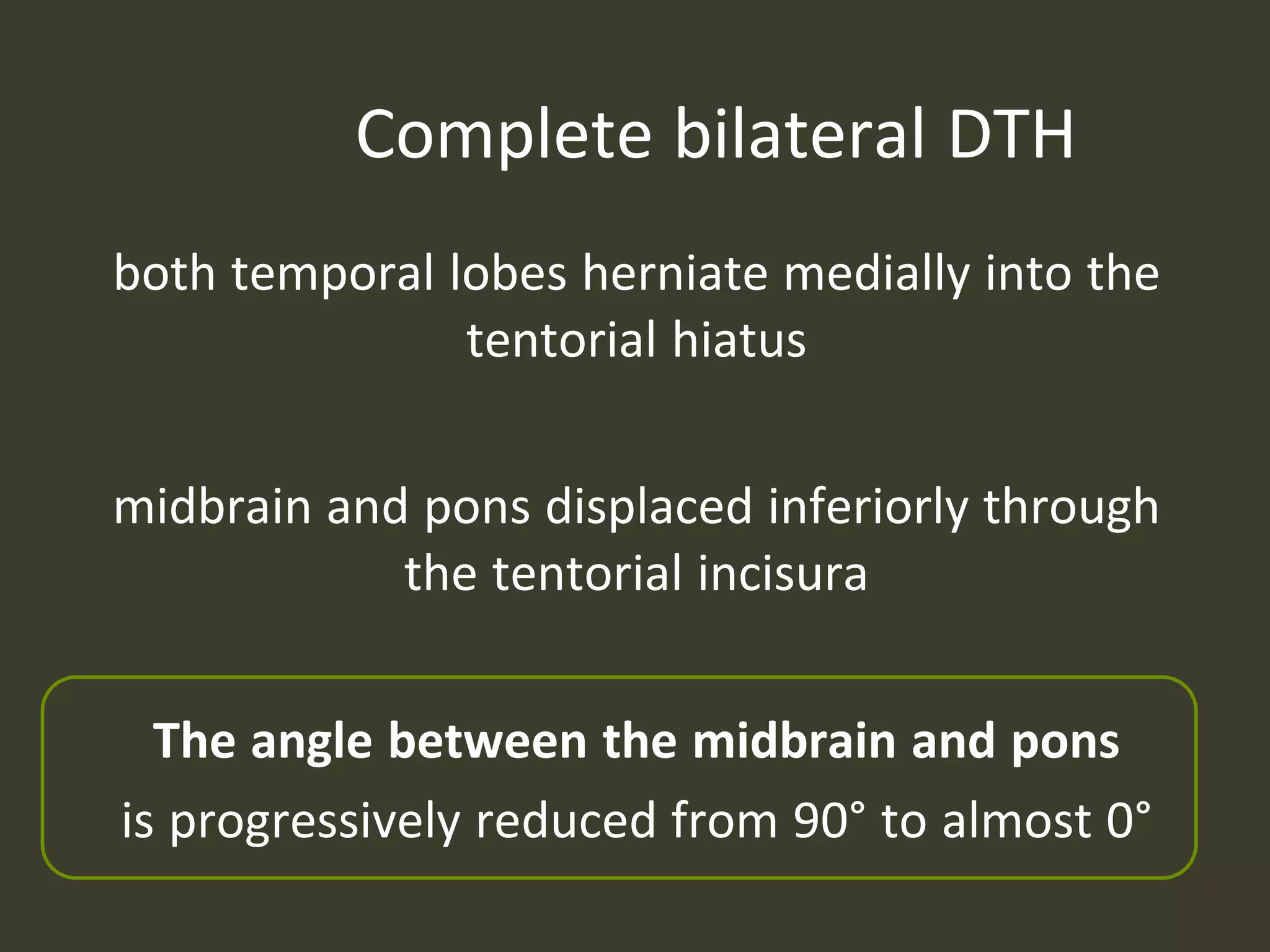
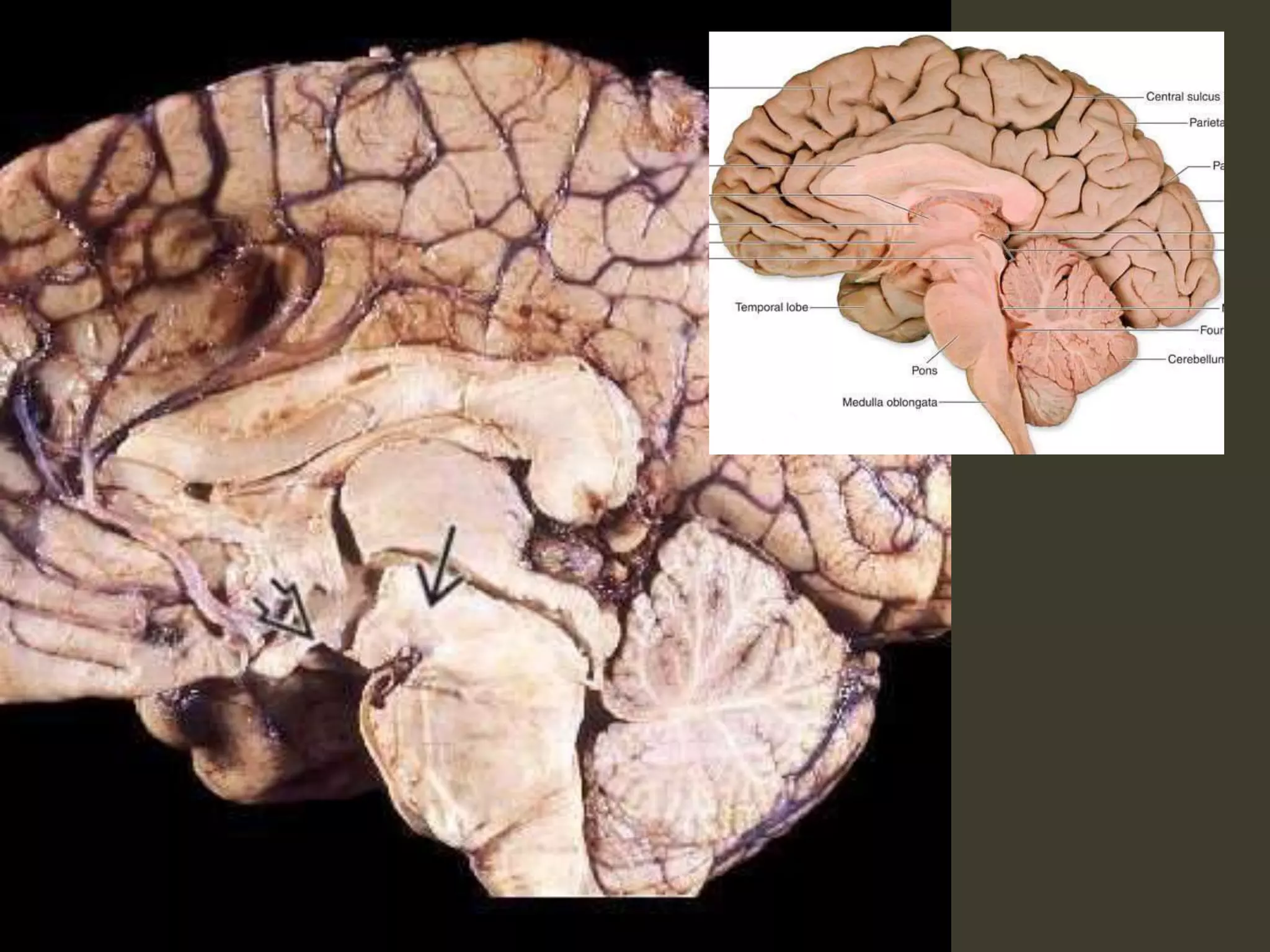
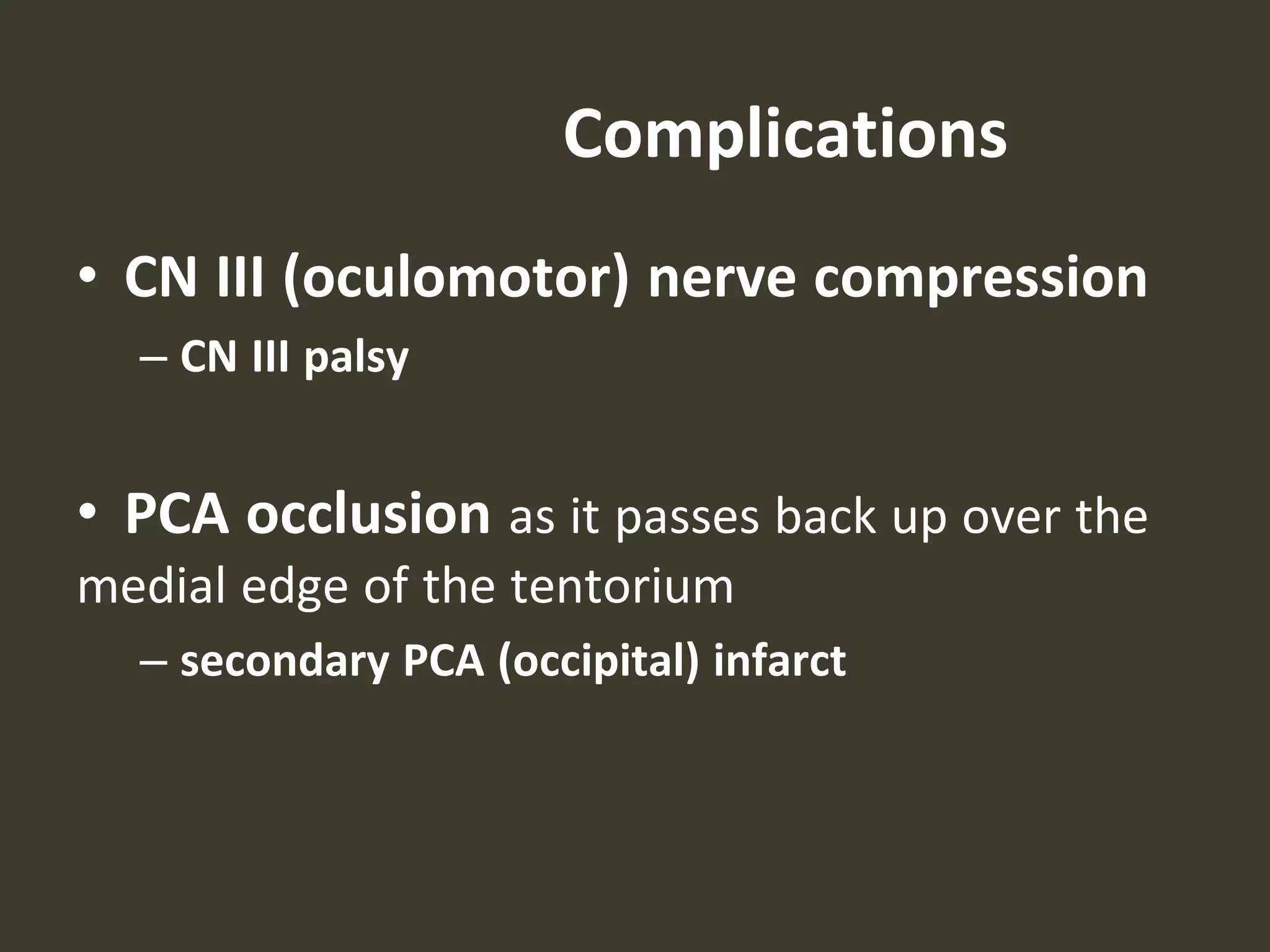
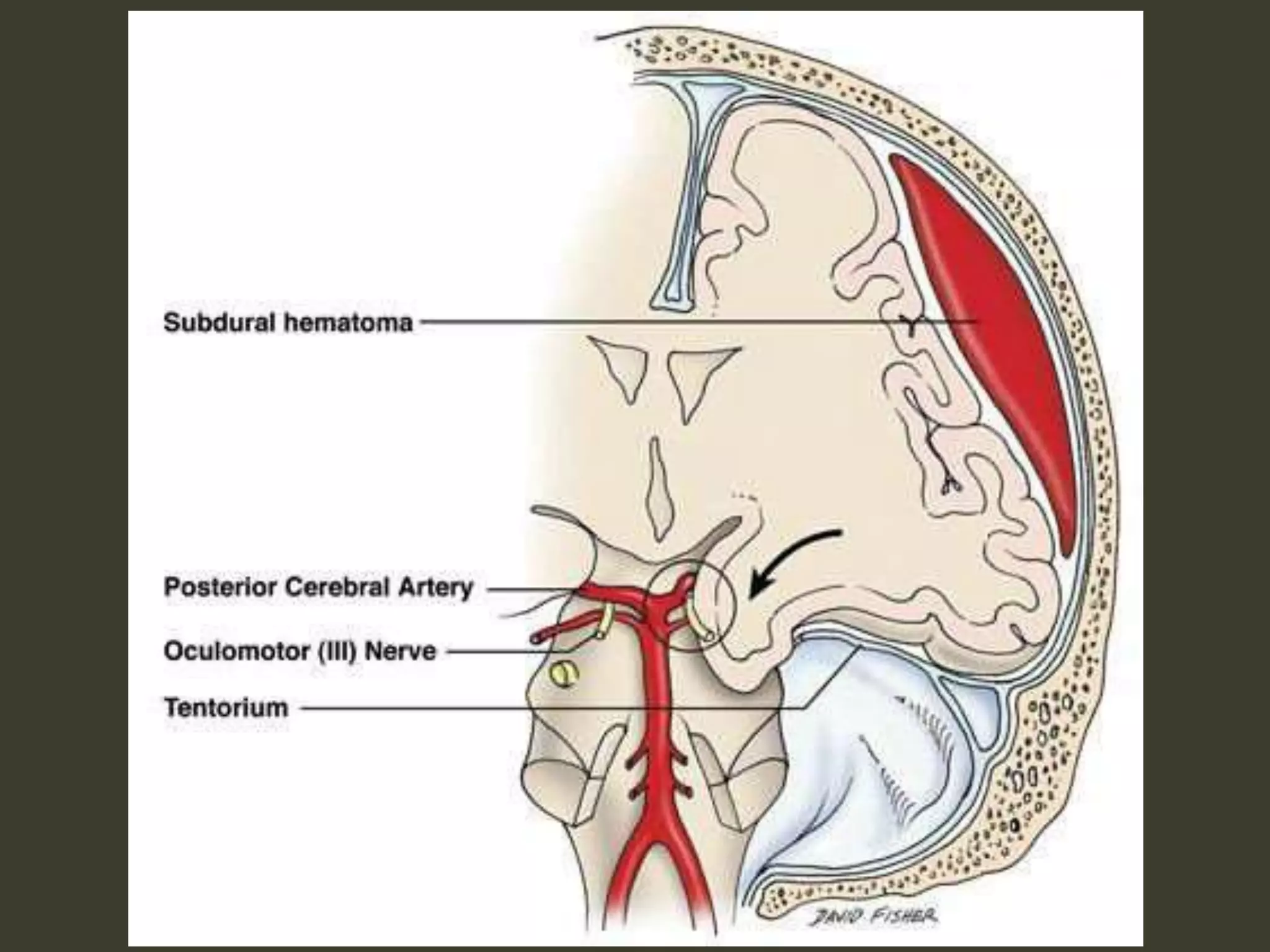
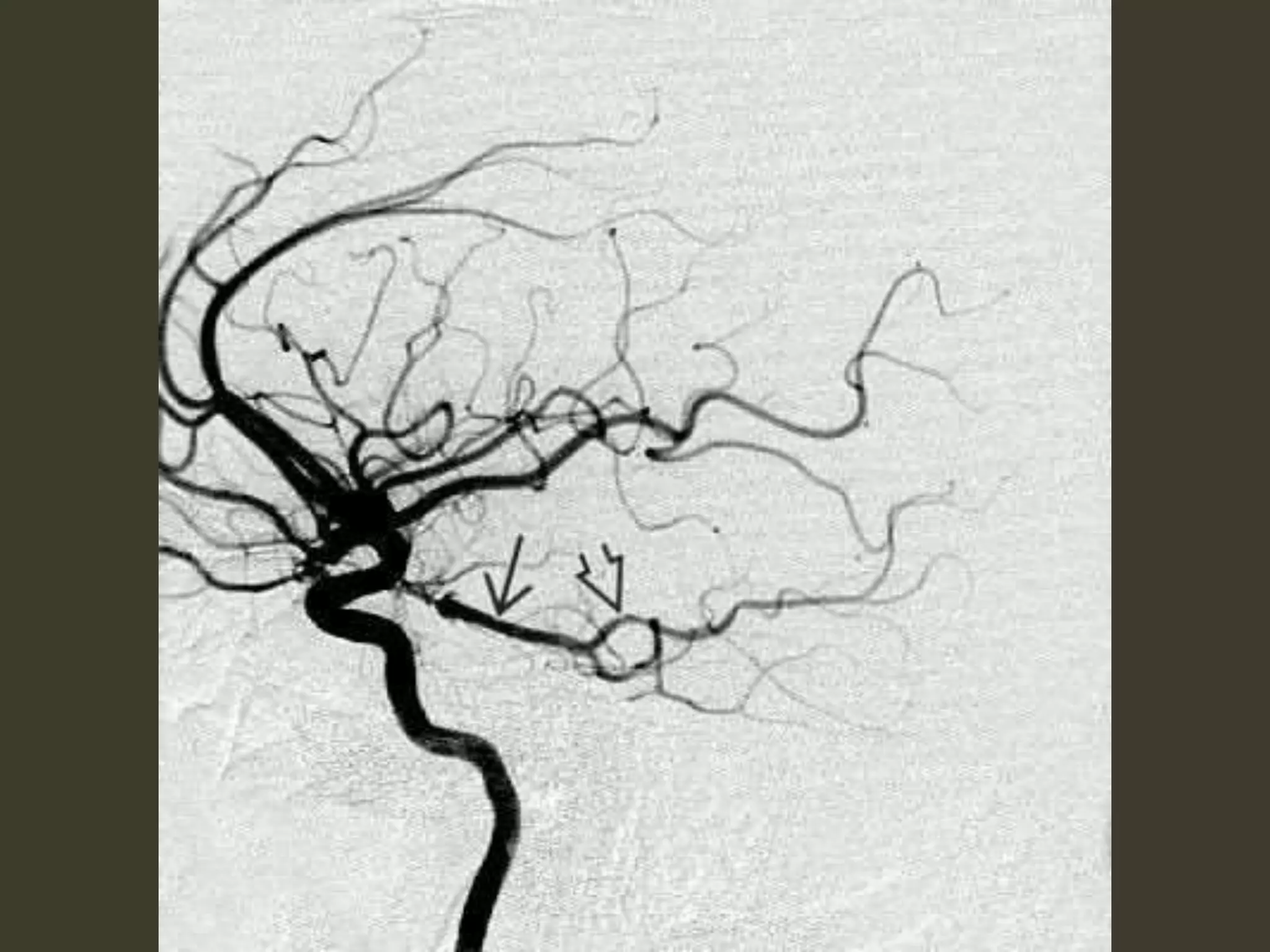
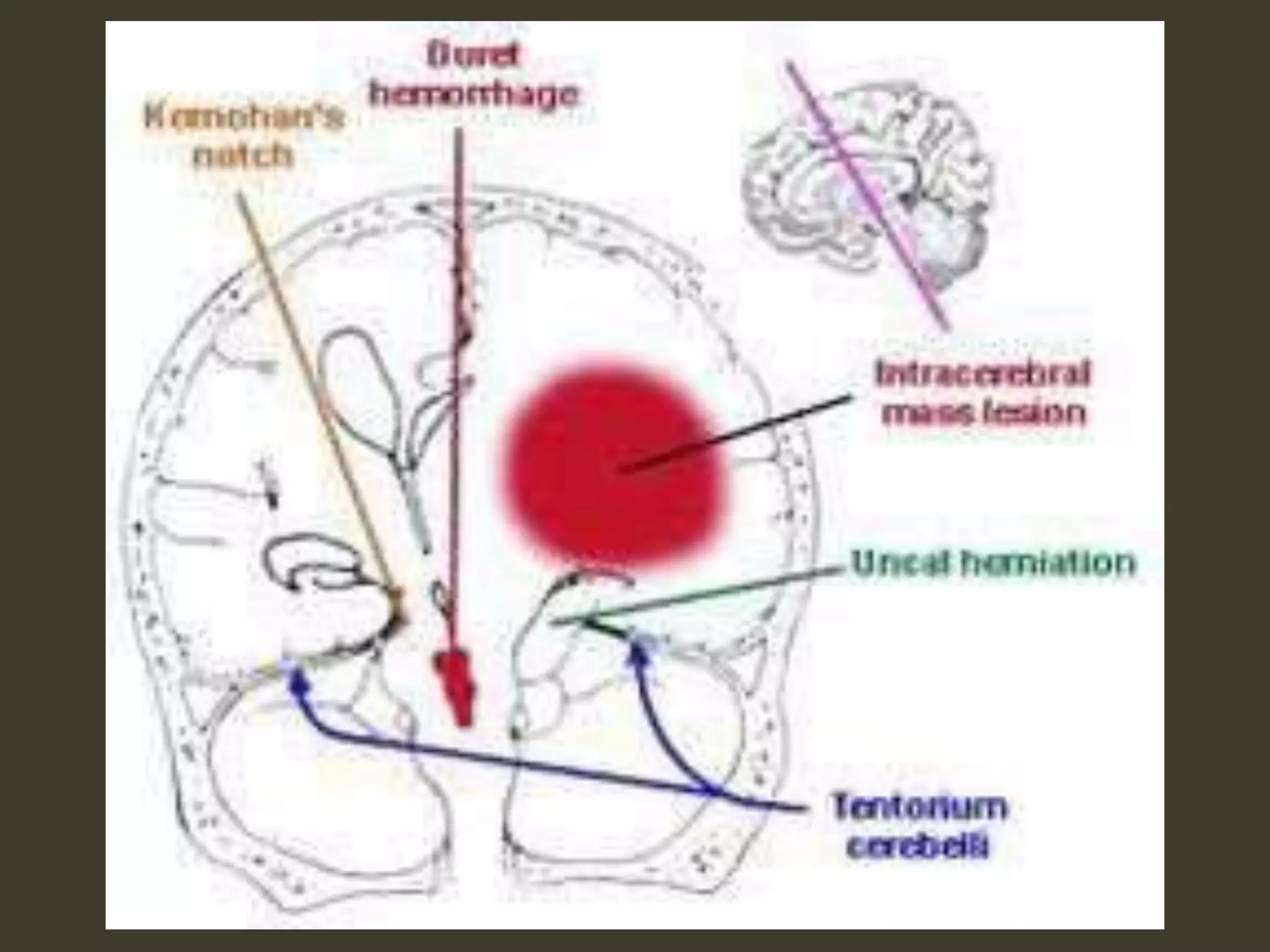
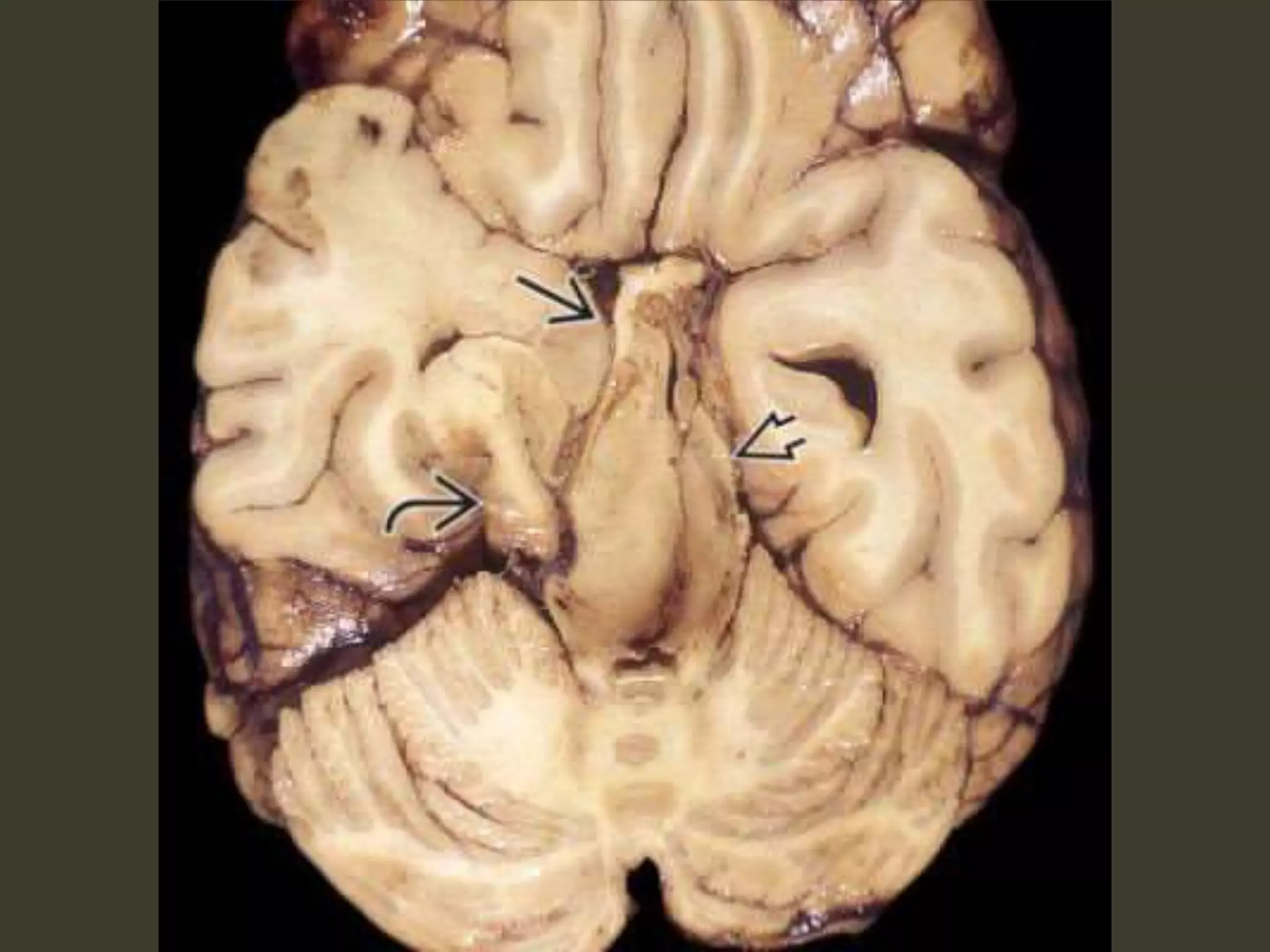
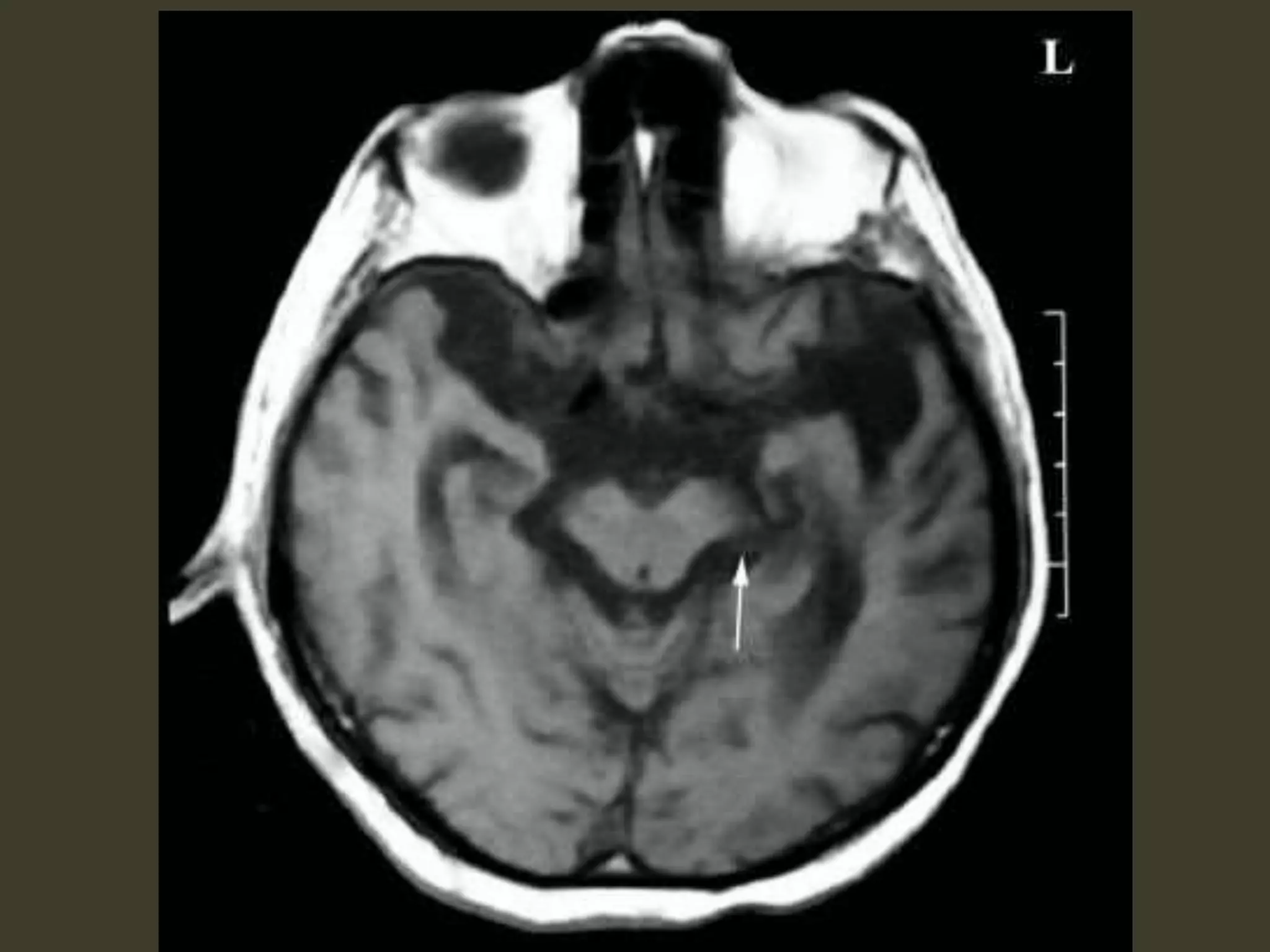
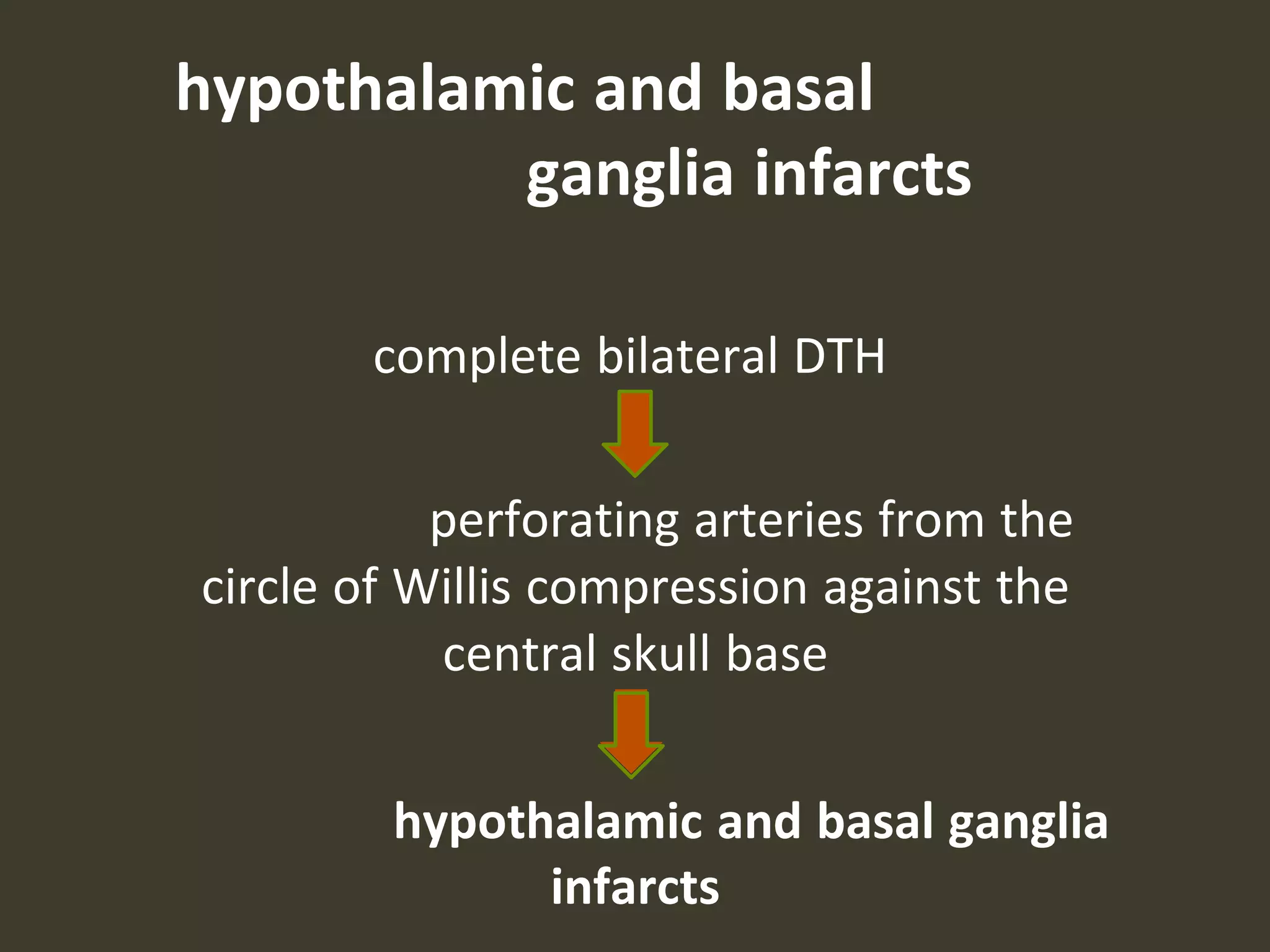
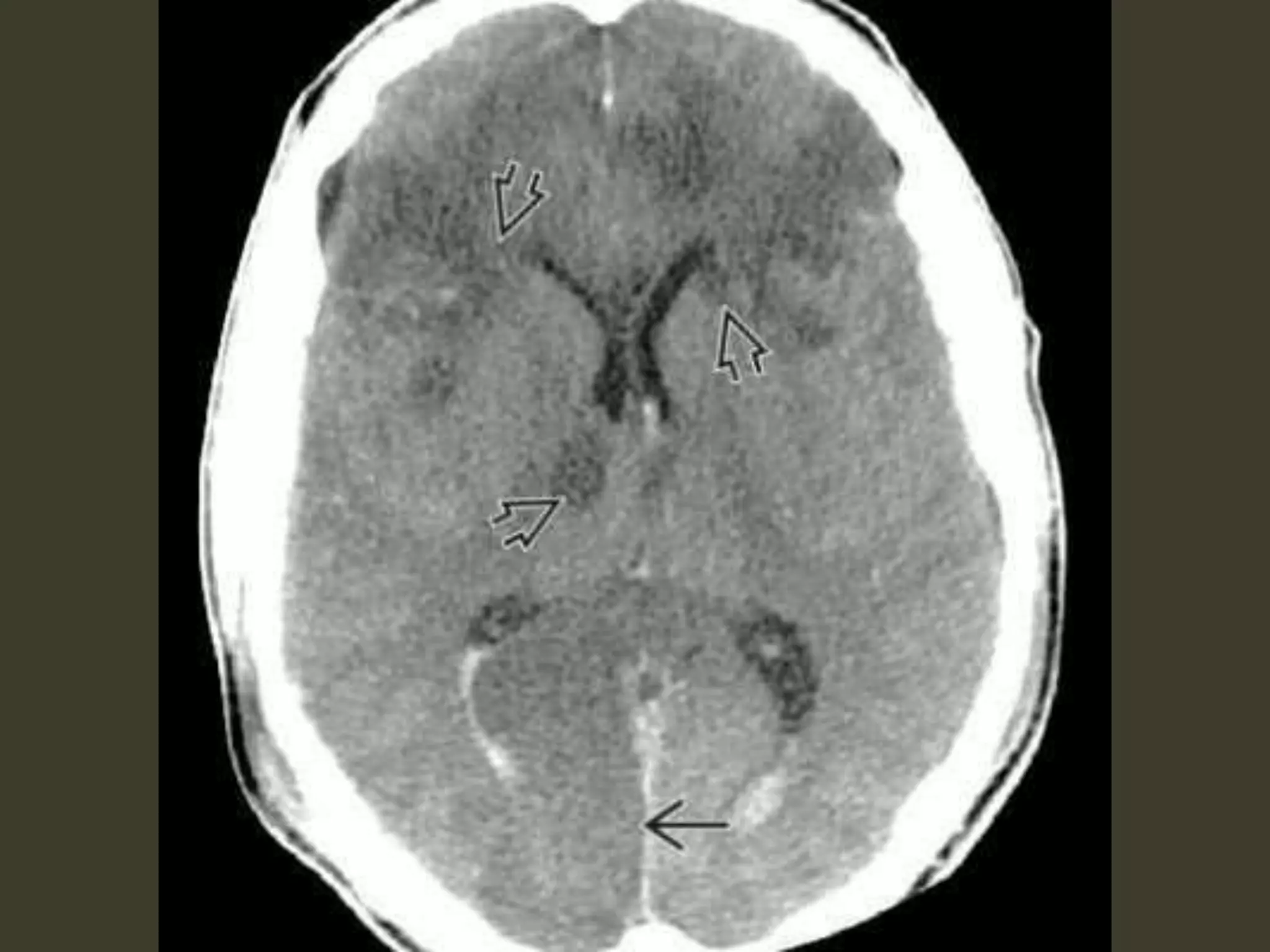
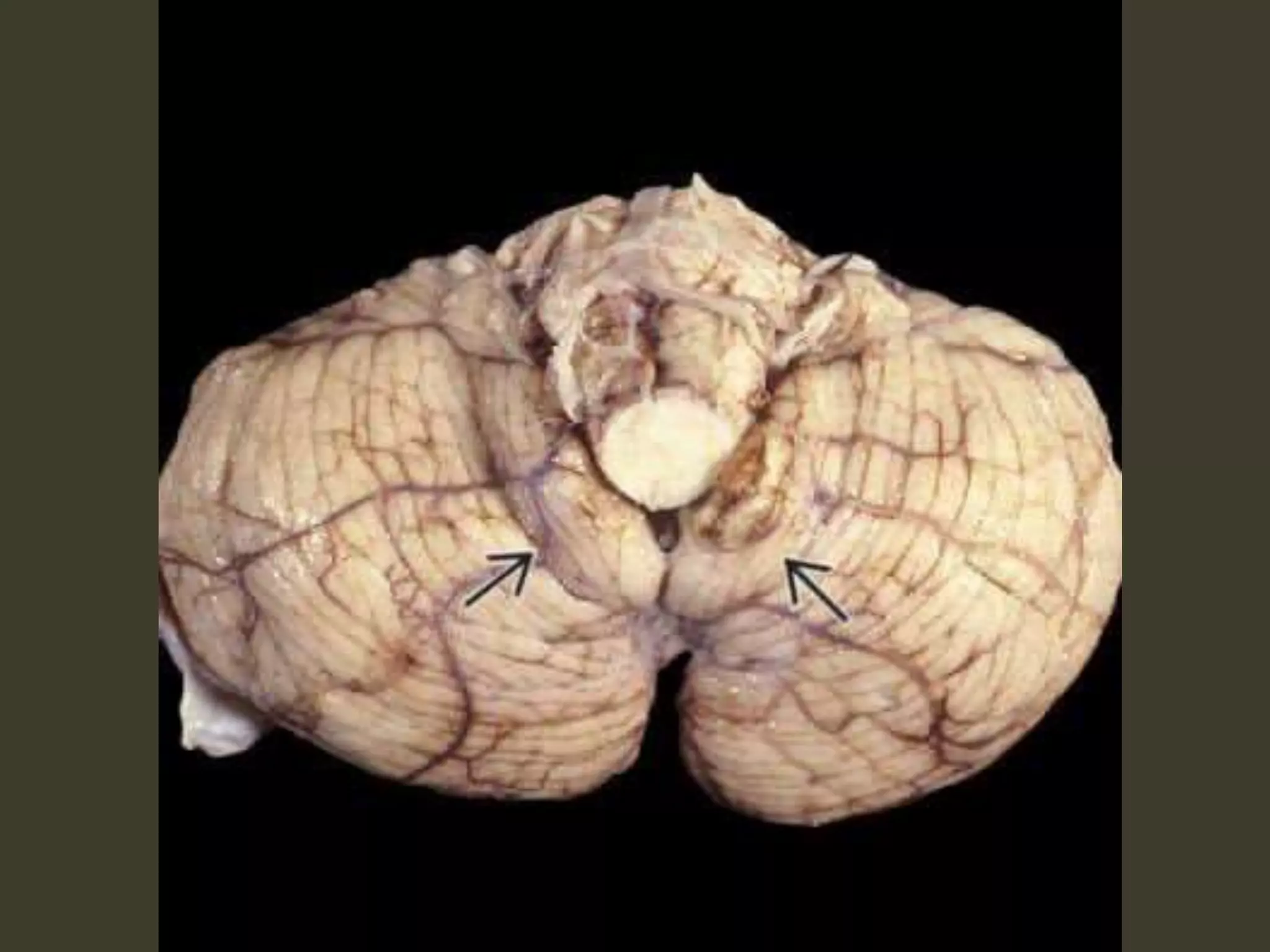
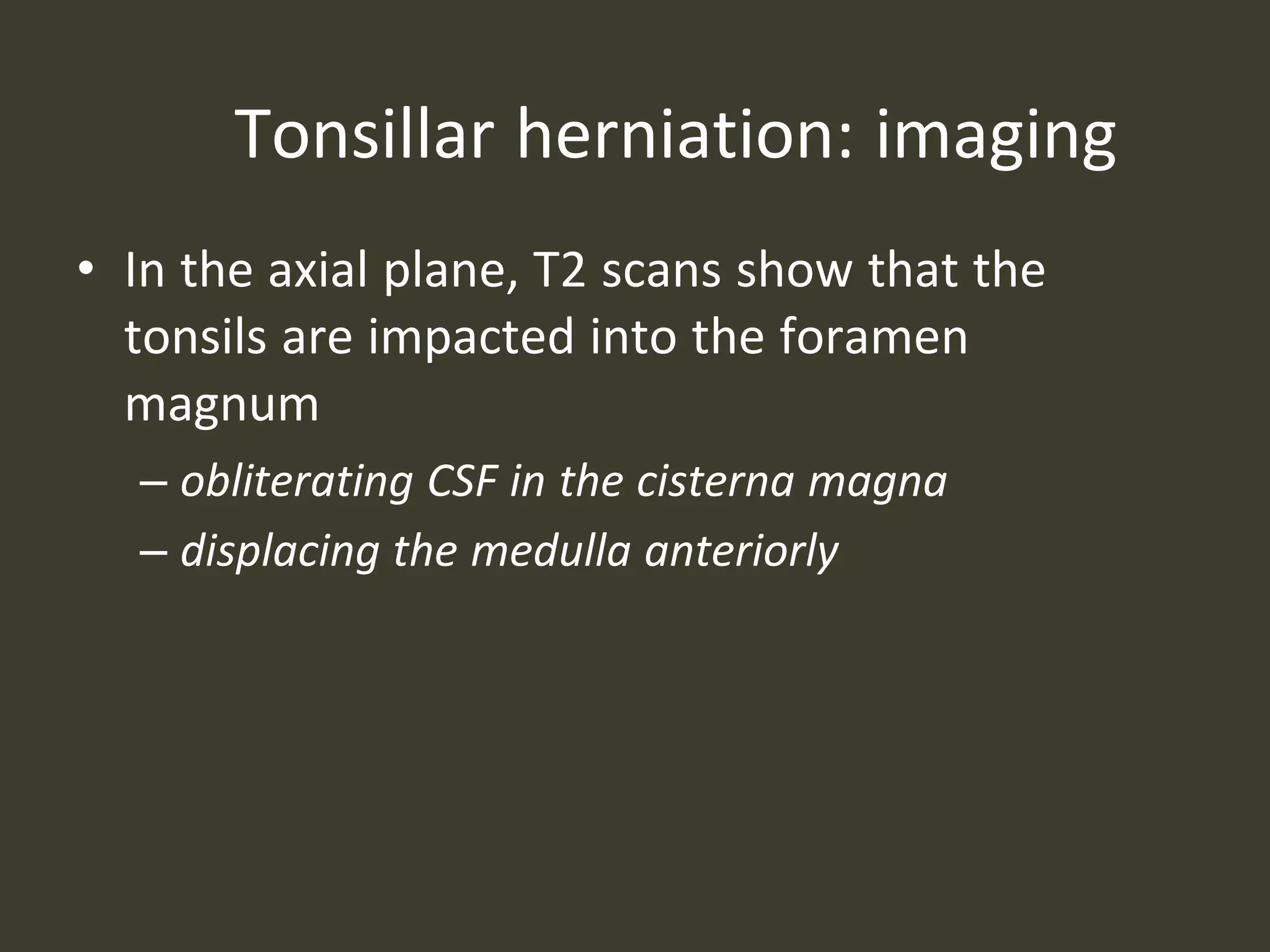
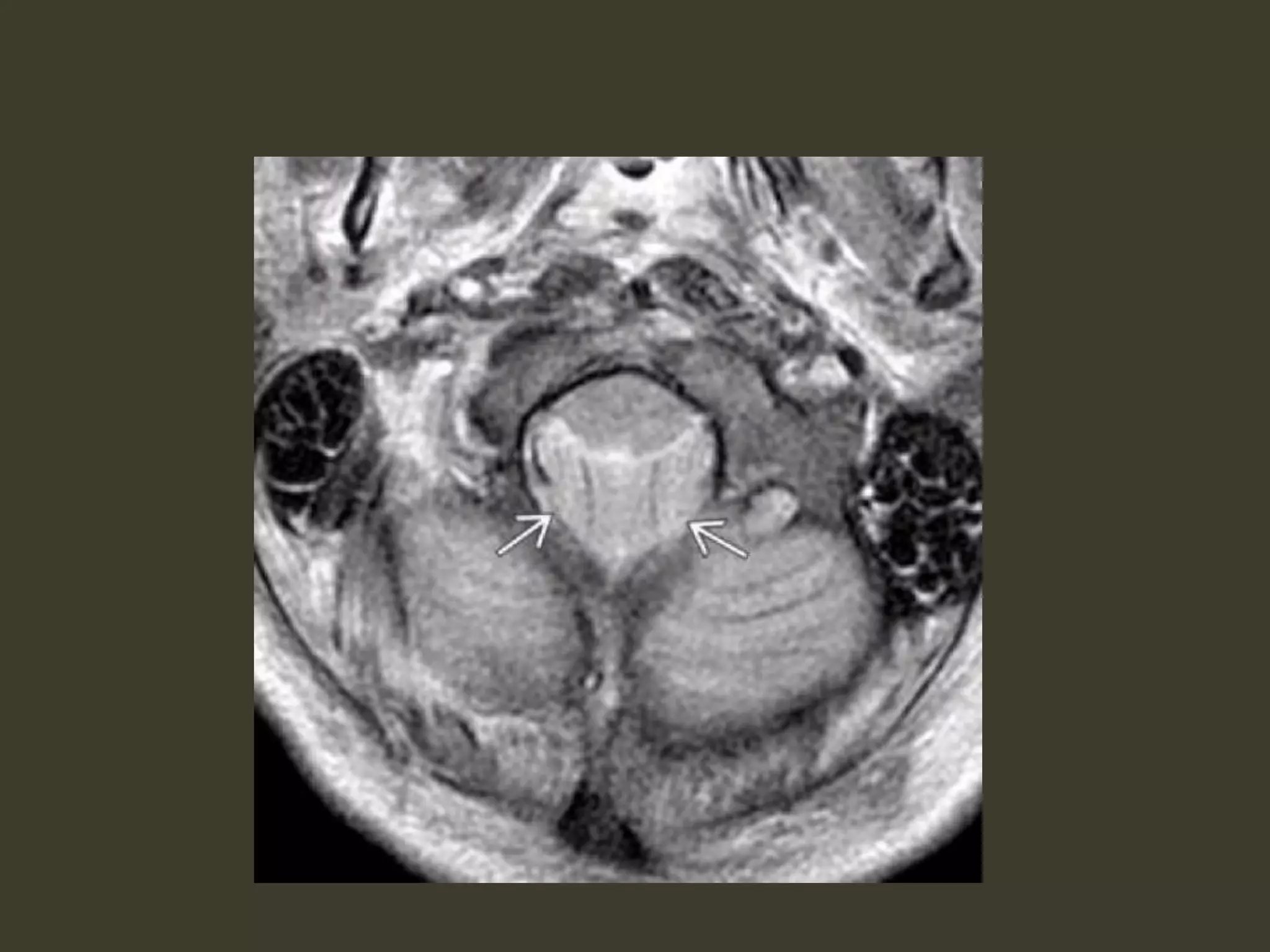
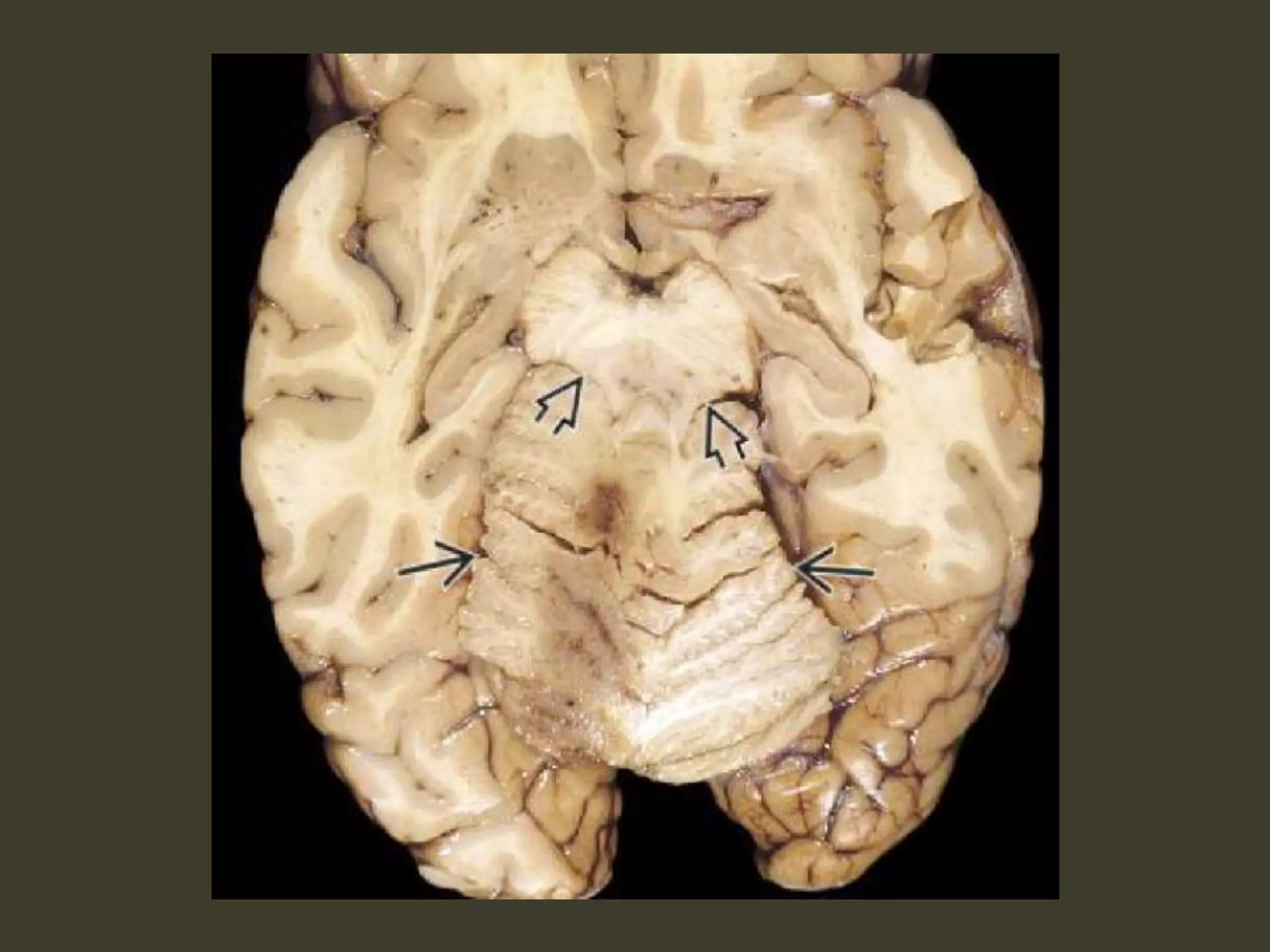
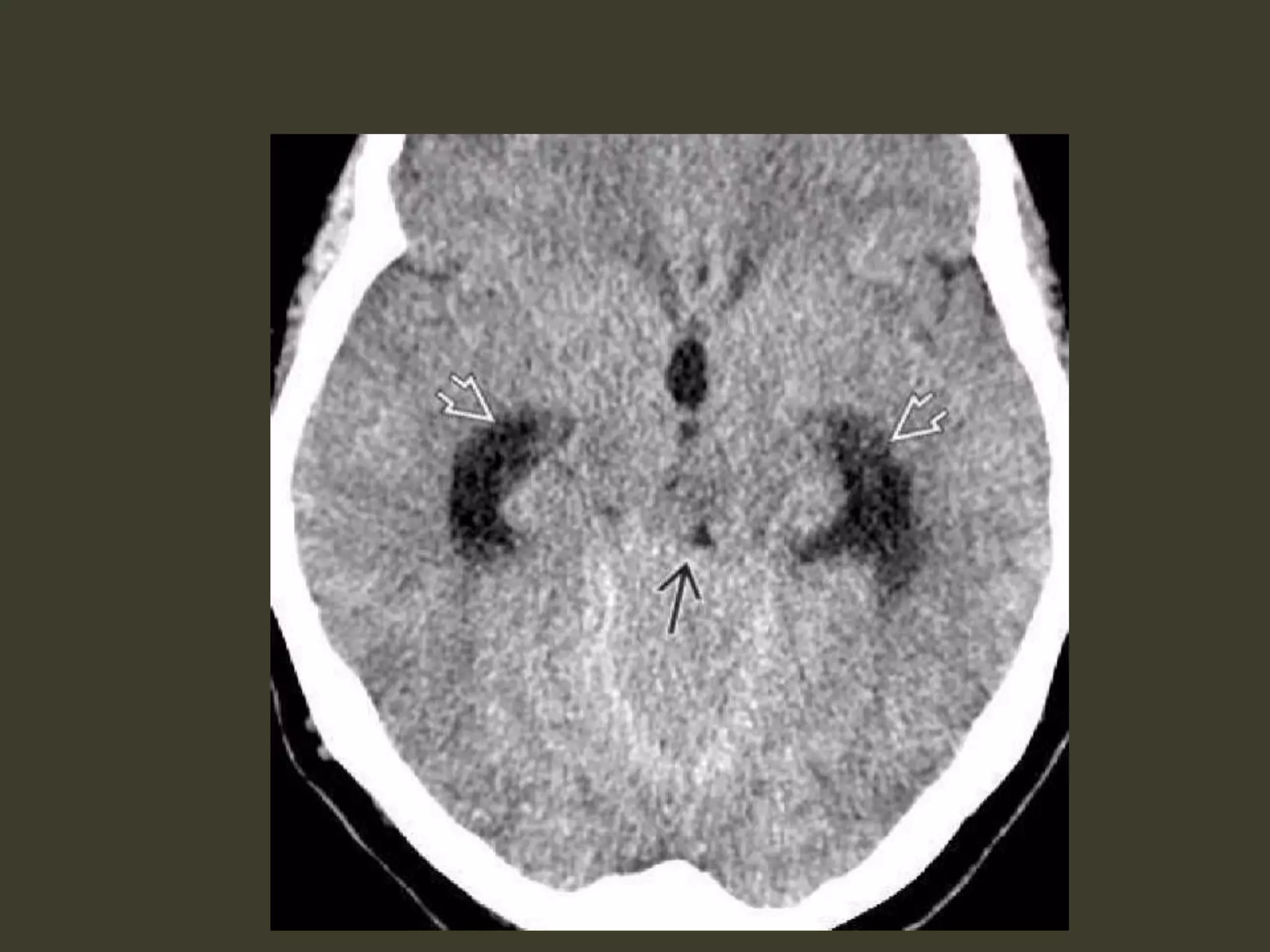
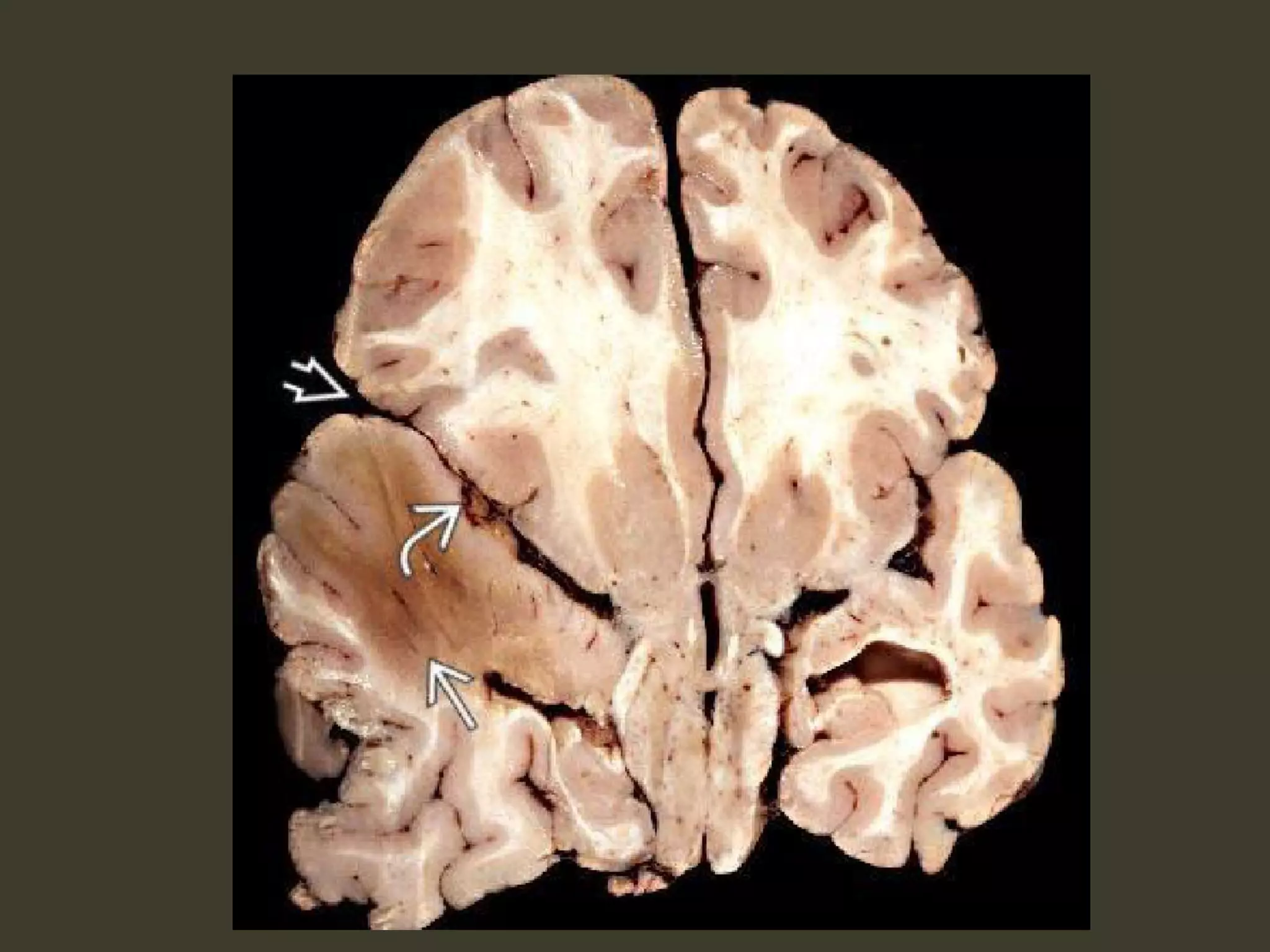
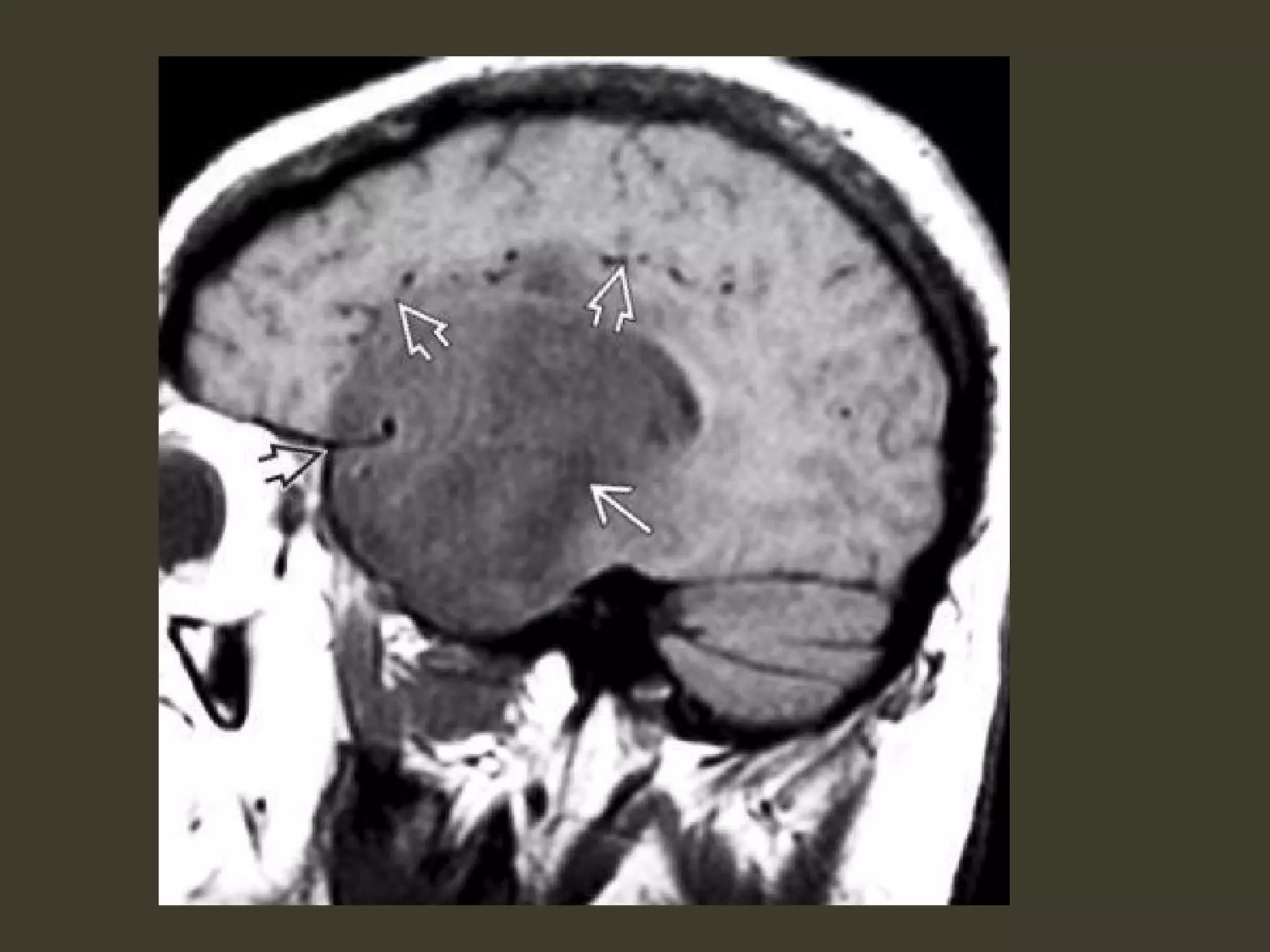
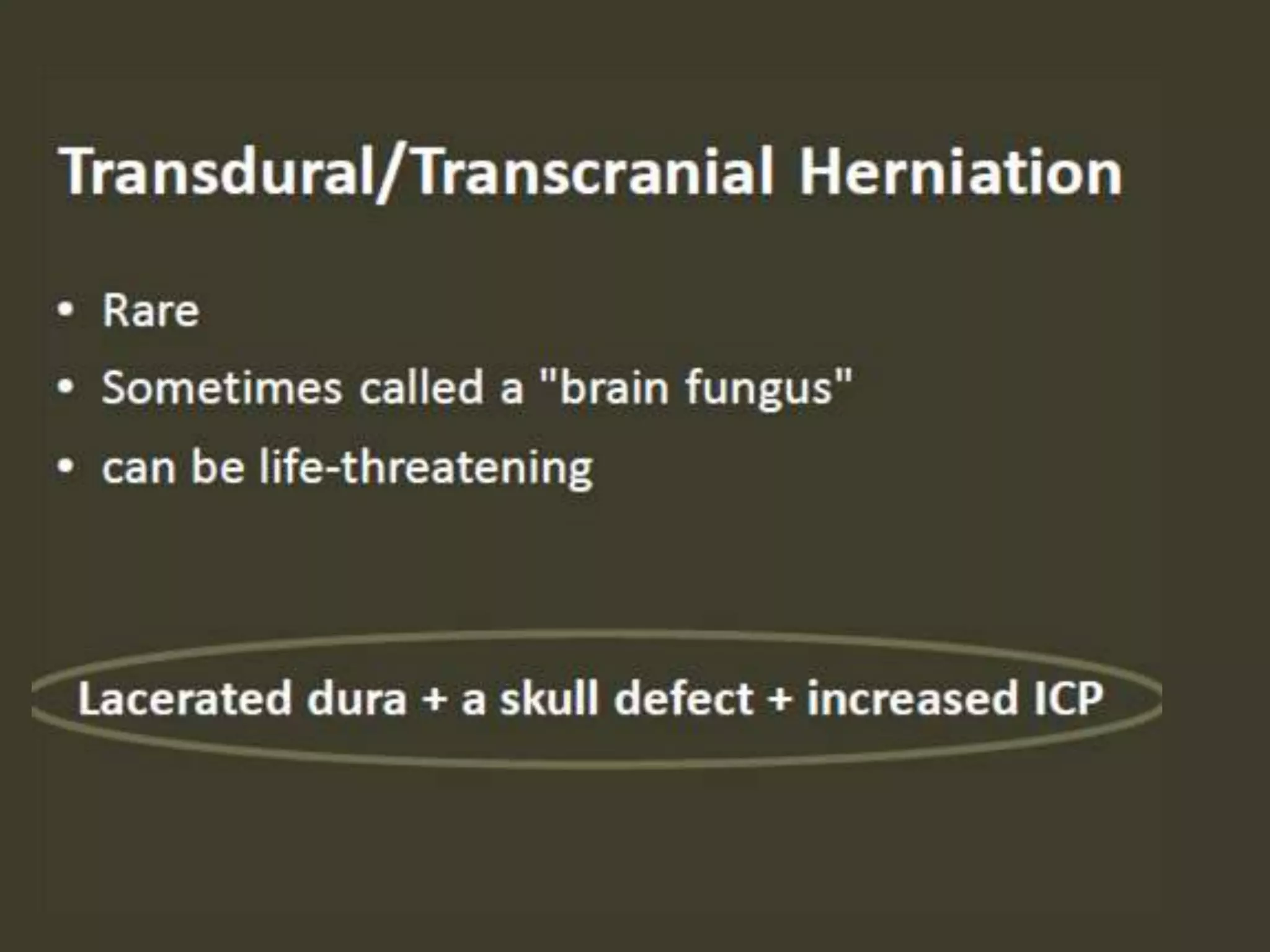
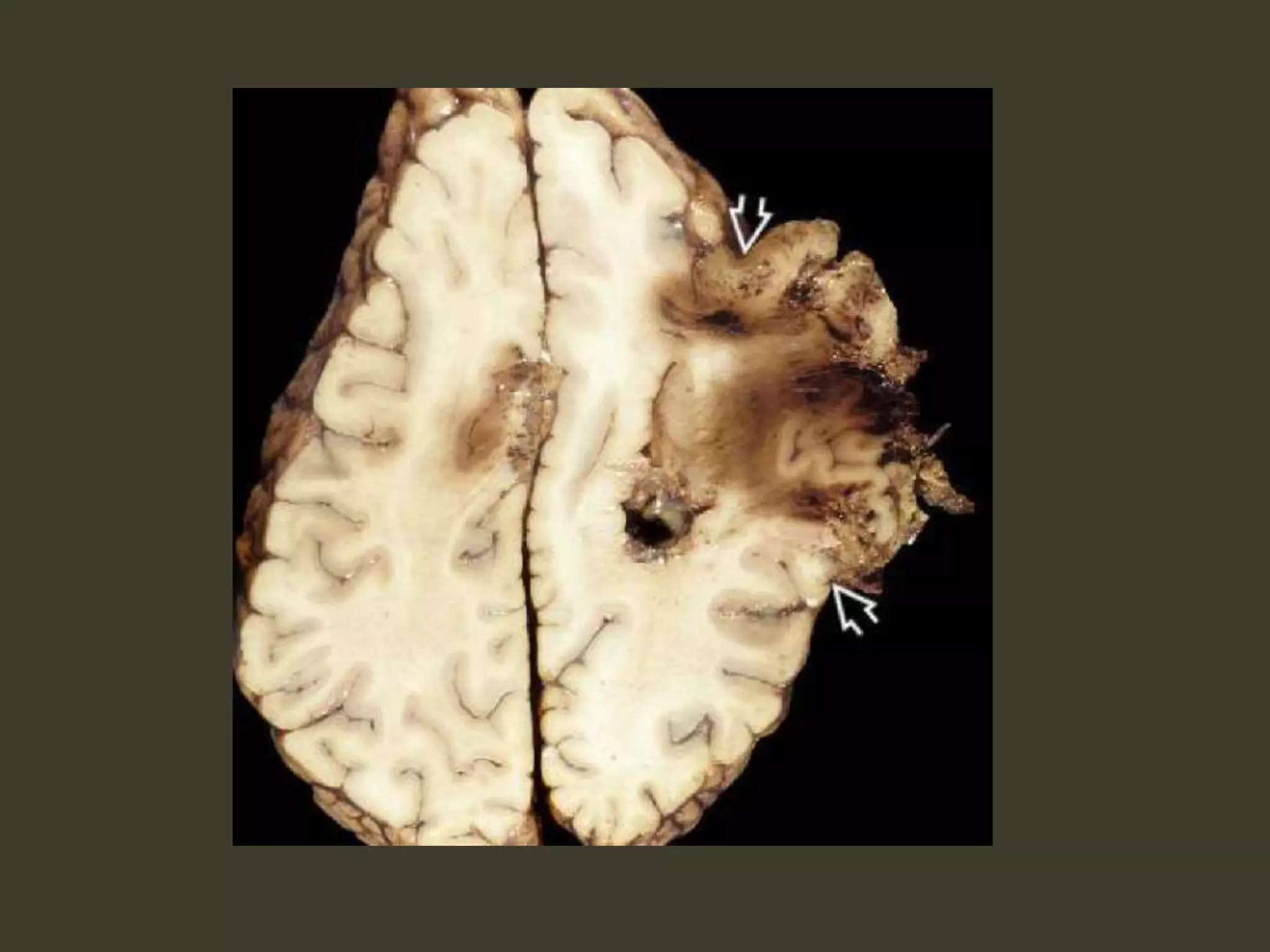
ICP waveforms provide information about intracranial dynamics and compliance. The normal ICP waveform has three peaks - P1, P2, and P3. An elevated P2 compared to P1 indicates increased intracranial pressure. Lundberg waves reflect fluctuations in ICP and cerebral blood flow. Invasive ICP monitoring is usually done via an external ventricular drain, while noninvasive methods include optic nerve sheath diameter. Brain herniation, such as subfalcine or descending transtentorial herniation, can occur due to increased intracranial mass or pressure.