Free radicals are unstable molecules that contain unpaired electrons. This instability causes free radicals to be highly reactive and seek to pair their unpaired electrons by interacting with other molecules. This reactivity can damage cells and lead to diseases. Specifically:
- Free radicals become more stable by taking electrons from other atoms, which can cause cellular damage and diseases or signs of aging over time.
- Common diseases associated with free radicals include atherosclerosis, heart disease, arthritis, stroke, respiratory diseases, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease.
- Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species/reactive nitrogen species like free radicals and a body's antioxidant defenses. This stress can damage biom










![©Lekhan
12
2 GSH + R2O2 → GSSG + 2 ROH (R = H, alkyl)
and with free radicals:
GSH + R•
→ 1⁄2 GSSG + RH
Regulation: Aside from deactivating radicals and reactive oxidants, glutathione
participates in thiol protection and redox regulation of cellular thiol proteins under
oxidative stress by protein S-glutathionylation, a redox-regulated post-translational
thiol modification. The general reaction involves formation of an unsymmetrical
disulfide from the protectable protein (RSH) and GSH
RSH + GSH + [O] → GSSR + H2O
Glutathione is also employed for the detoxification of methylglyoxal and
formaldehyde, toxic metabolites produced under oxidative stress. This detoxification
reaction is carried out by the glyoxalase system. Glyoxalase I (EC 4.4.1.5) catalyzes
the conversion of methylglyoxal and reduced glutathione to S-D-lactoylglutathione.
Glyoxalase II (EC 3.1.2.6) catalyzes the hydrolysis of S-D-lactoylglutathione to
glutathione and D-lactic acid.
OR
Mechanism of action
Glutathione (GSH) participates in leukotriene synthesis and is a cofactor for the enzyme
glutathione peroxidase. It also plays a role in the hepatic biotransformation and
detoxification process; it acts as a hydrophilic molecule that is added to other lipophilic
toxins or wastes prior to entering biliary excretion. It participates in the detoxification
of methylglyoxal, a toxic by-product of metabolism, mediated by glyoxalase enzymes.
Glyoxalase I catalyzes the conversion of methylglyoxal and reduced glutathione to S-
D-Lactoyl-glutathione. Glyoxalase II catalyzes the conversion of S-D-Lactoyl
Glutathione to Reduced Glutathione and D-lactate. Glyoxalase I catalyzes the
conversion of methylglyoxal and reduced glutathione to S-D-Lactoyl-glutathione.
Glyoxalase II catalyzes the conversion of S-D-Lactoyl Glutathione to Reduced
Glutathione and D-lactate. GSH is a cofactor of conjugation and reduction reactions
that are catalyzed by glutathione S-transferase enzymes expressed in the cytosol,
microsomes, and mitochondria. However, it is capable of participating in non-
enzymatic conjugation with some chemicals, as it is hypothesized to do to a significant
extent with n-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI), the reactive cytochrome P450
reactive metabolite formed by toxic overdose of acetaminophen. Glutathione in this
capacity binds to NAPQI as a suicide substrate and in the process detoxifies it, taking
the place of cellular protein sulfhydryl groups which would otherwise be toxically
adducted. The preferred medical treatment to an overdose of this nature, whose efficacy
has been consistently supported in literature, is the administration (usually in atomized
form) of N-acetylcysteine, which is used by cells to replace spent GSSG and allow a
usable GSH pool.
Q.9 what is the difference between GSH and GSSG
Glutathione (GSH) is a tri-peptide (g-glutamylcysteinylglycine) that acts as an
endogenous antioxidant, a xenobiotic detoxifier, and is involved in metabolic
regulation. GSH is the most abundant antioxidant in aerobic cells, present in
micromolar (mM) concentrations in bodily fluids and in millimolar (mM)
concentrations in tissue. The central nervous system (CNS) has GSH concentrations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freeradical-230315120806-460f5e39/85/Free-radicals-12-320.jpg)

![©Lekhan
14
2 GSH + R-S-S-R → GSSG + 2 RSH
The GSH:GSSG ratio is therefore an important bioindicator of cellular health, with a
higher ratio signifying less oxidative stress in the organism. A lower ratio may even be
indicative of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson's disease (PD) and
Alzheimer's disease.
GSSG, along with glutathione and S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO), have been found to
bind to the glutamate recognition site of the NMDA and AMPA receptors (via their γ-
glutamyl moieties), and may be endogenous neuromodulators. At millimolar
concentrations, they may also modulate the redox state of the NMDA receptor complex.
Q. 10 Discuss the mechanism of action of superoxide dismutase
Superoxide dismutases (SODs) are universal enzymes of organisms that live in the
presence of oxygen. They catalyze the conversion of superoxide into oxygen and
hydrogen peroxide.
SOD catalyzes the conversion of the superoxide anion free radical (•
O2−
) to hydrogen
peroxide (H2O2) and molecular oxygen O2 (Figure 1 A,B). Subsequently, H2O2 is
reduced to water by the catalase (CAT) enzyme, glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and/or
thioredoxin (Trx)-dependent peroxiredoxin (Prx) enzymes (Figure 1B). H2O2 may also
generate another reactive oxygen species (ROS), the hydroxide ion (•
HO) via the
Fenton reaction in the presence of Fe2+
(Figure 1B).
The major cellular defense against O2•−
and peroxynitrite is a group of oxidoreductases
known as SODs, which catalyze the dismutation of O2•−
into oxygen and H2O2. In
mammals, there are three isoforms of SOD (SOD1 [CuZnSOD]; SOD2 [MnSOD];
SOD3 [ecSOD]), and each is a product of distinct genes and distinct subcellular
localization, but catalyzes the same reaction. This distinct subcellular location of these
SOD isoforms is particularly important for compartmentalized redox signaling. The
mechanism of dismutation of O2•−
to H2
O2
by SOD involves alternate reduction and
reoxidation of a redox active transition metal, such as copper (Cu) and manganese (Mn)
at the active site of the enzyme as shown in Figure. This indicates that SOD activity
requires a catalytic metal.
FIGURE Common
mechanism of scavenging O2
•−
by
SODs. Enzymatic activity of SOD
involves alternate reduction and
reoxidation of catalytic metal (i.e.,
Cu or Mn) at the active site of the
enzyme. Thus, Cu or Mn will be a
key modulator of SOD activity of
SOD1/SOD3 or SOD2, respectively.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freeradical-230315120806-460f5e39/85/Free-radicals-14-320.jpg)
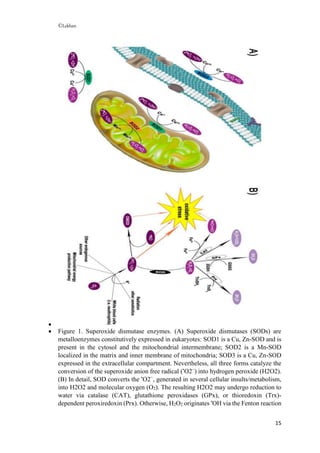
![©Lekhan
16
in the presence of Fe2+
. •
O2−
may also react with •
NO originating the oxidant and
nitrating agent peroxynitrite (ONOO−
), which further contributes to oxidative-stress
damage. GSH = glutathione; GSSG = glutathione disulfide; TrxSH2 = reduced
thioredoxin; TrxS2 = oxidized thioredoxin
Q. 11 Describe the Process of Oxidative stress in aging
Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) are produced by several endogenous and
exogenous processes, and their negative effects are neutralized by antioxidant defenses.
Oxidative stress occurs from the imbalance between RONS production and these
antioxidant defenses.
Aging is a process characterized by the progressive loss of tissue and organ function.
The oxidative stress theory of aging is based on the hypothesis that age-associated
functional losses are due to the accumulation of RONS-induced damages. At the same
time, oxidative stress is involved in several age-related conditions (ie, cardiovascular
diseases [CVDs], chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease,
neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer), including sarcopenia and frailty.
Pathophysiology of oxidative stress
Free radicals are highly reactive atoms or molecules with one or more unpaired
electron(s) in their external shell and can be formed when oxygen interacts with certain
molecules. These radicals can be produced in cells by losing or accepting a single
electron, therefore, behaving as oxidants or reductants.
The terms reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) refer to
reactive radical and non-radical derivatives of oxygen and nitrogen, respectively.
Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) are produced by all aerobic cells and
play an important role in aging as well as in age-related diseases.4 RONS generation is
not only limited to determine deleterious effects but also involved in the extraction of
energy from organic molecules, in immune defense, and in the signaling process.
There are endogenous and exogenous sources of RONS:
Endogenous sources of RONS include nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
(NADPH) oxidase, myeloperoxidase (MPO), lipoxygenase, and angiotensin II.
NADPH oxidase is the prevalent source of the radical superoxide anion (O2
•
) which is
formed by the one-electron reduction of molecular oxygen, with electrons supplied by
NADPH, during cellular respiration. Most of the O2
•
is dismutated into the hydrogen
peroxide (H2O2) by superoxide dismutase (SOD). H2O2 is not a free radical because it
has no unpaired electrons, but it is able to form the highly reactive ROS hydroxyl ion
(OH•
) through the Fenton or Haber–Weiss reaction. Hydroxyl radicals are extremely
reactive and react especially with phospholipids in cell membranes and proteins. In
neutrophils, H2O2 in the presence of chloride and MPO can be converted to
hypochlorous acid, an ROS particularly damaging cellular proteins. Nitric oxide (NO)
is produced from l-arginine by three main isoforms of nitric oxide synthase (NOS):
epithelial NOS, related to vasodilation and vascular regulation, neuronal NOS, linked
to intracellular signaling, and inducible NOS, activated in response to various
endotoxin or cytokine signals. Finally, O2 may react with NO to form another relatively
reactive molecule, peroxynitrite (ONOO−
).
Exogenous sources of RONS are air and water pollution, tobacco, alcohol, heavy or
transition metals, drugs (eg, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, gentamycin, and bleomycin),](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freeradical-230315120806-460f5e39/85/Free-radicals-16-320.jpg)

