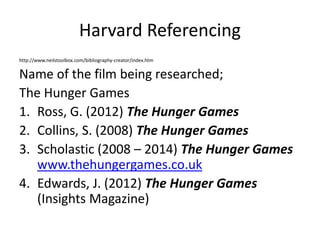This document defines key terminology used in research and summarizes different types of research. It discusses primary and secondary research, quantitative and qualitative research, audience research, market research, and production research. For each type of research, it provides the definition, advantages, disadvantages, and examples. It also defines objective and subjective research and valid and reliable research. Finally, it demonstrates how to reference a film source in the Harvard referencing style.