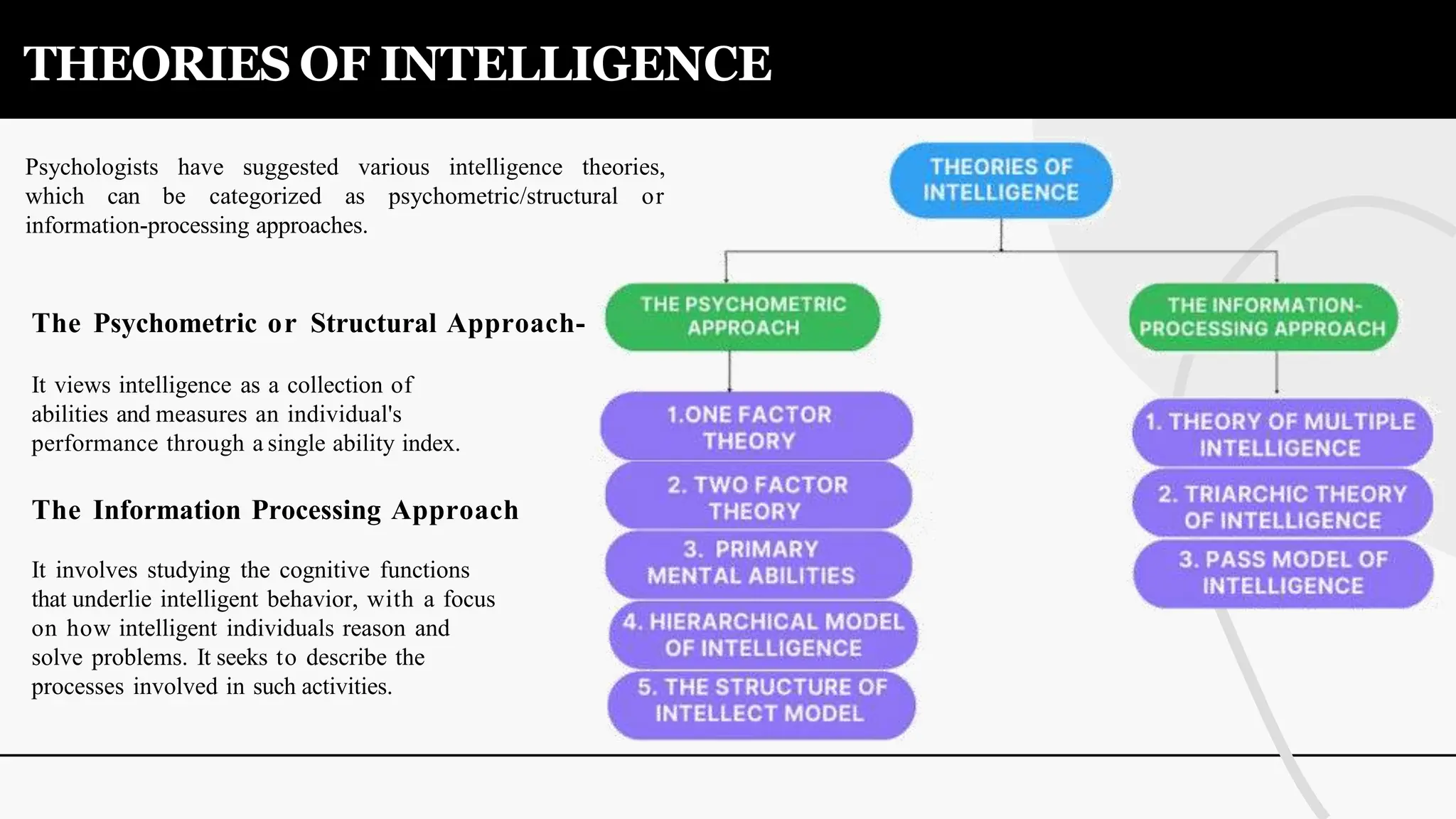
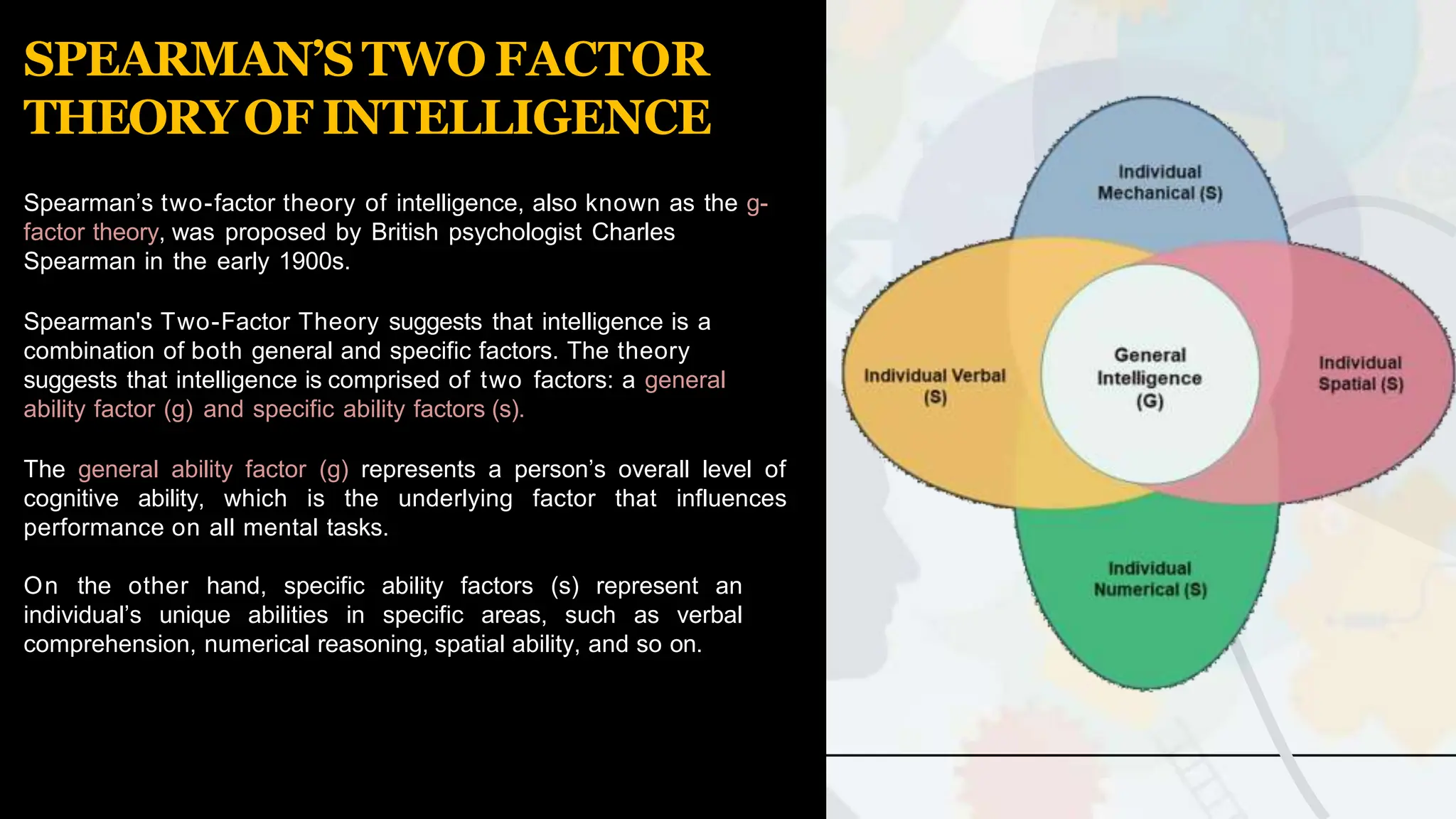
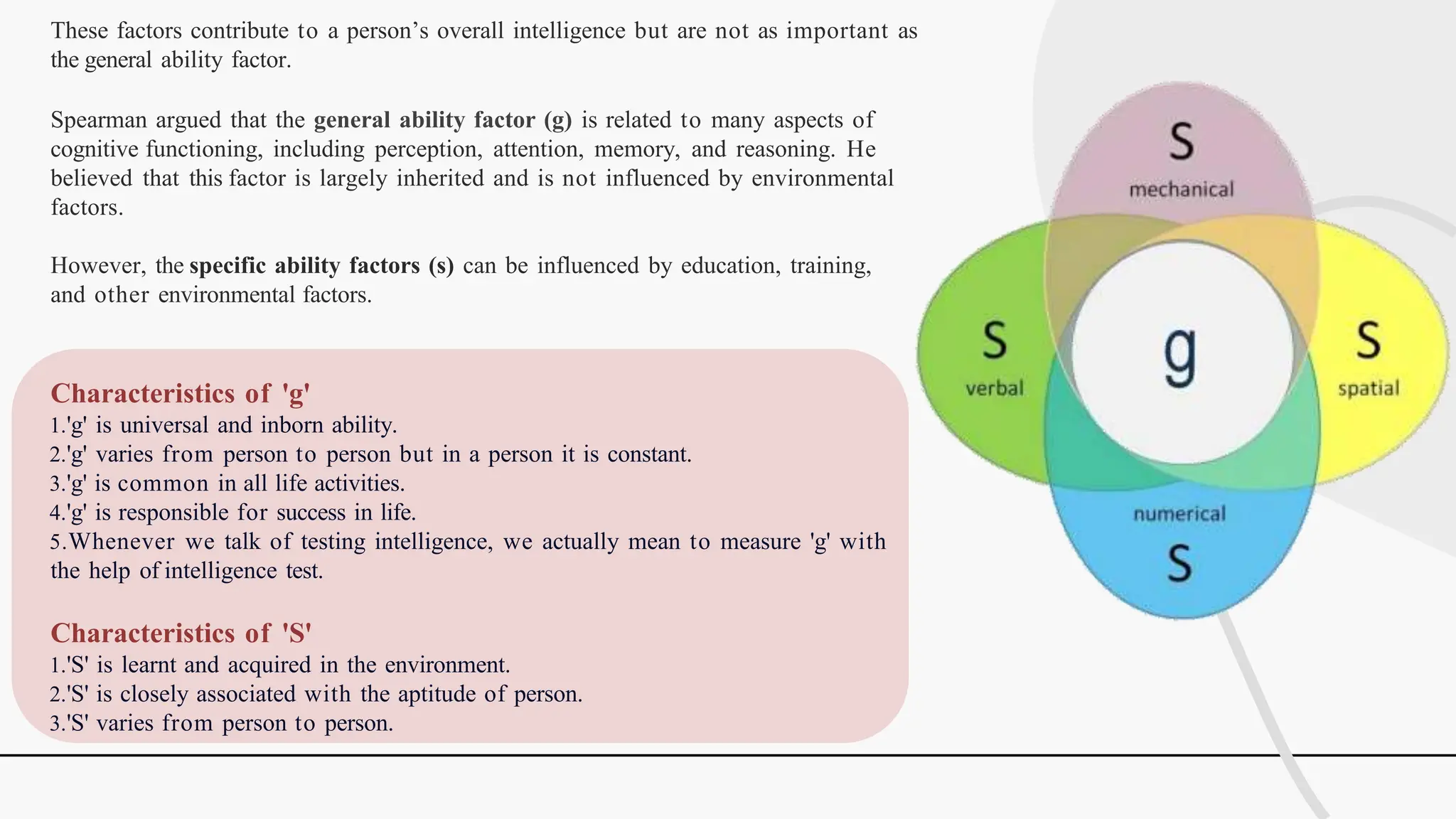
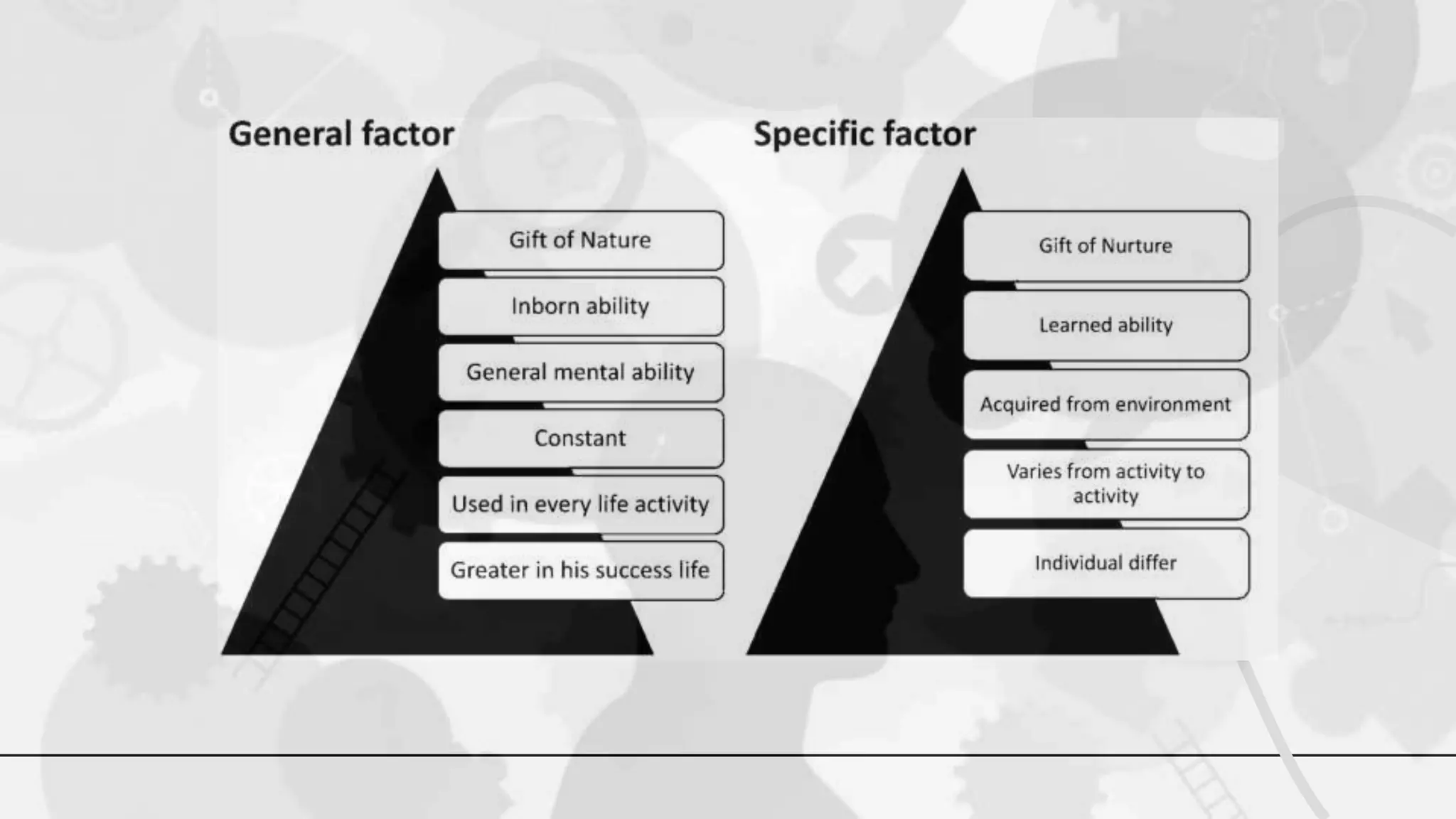
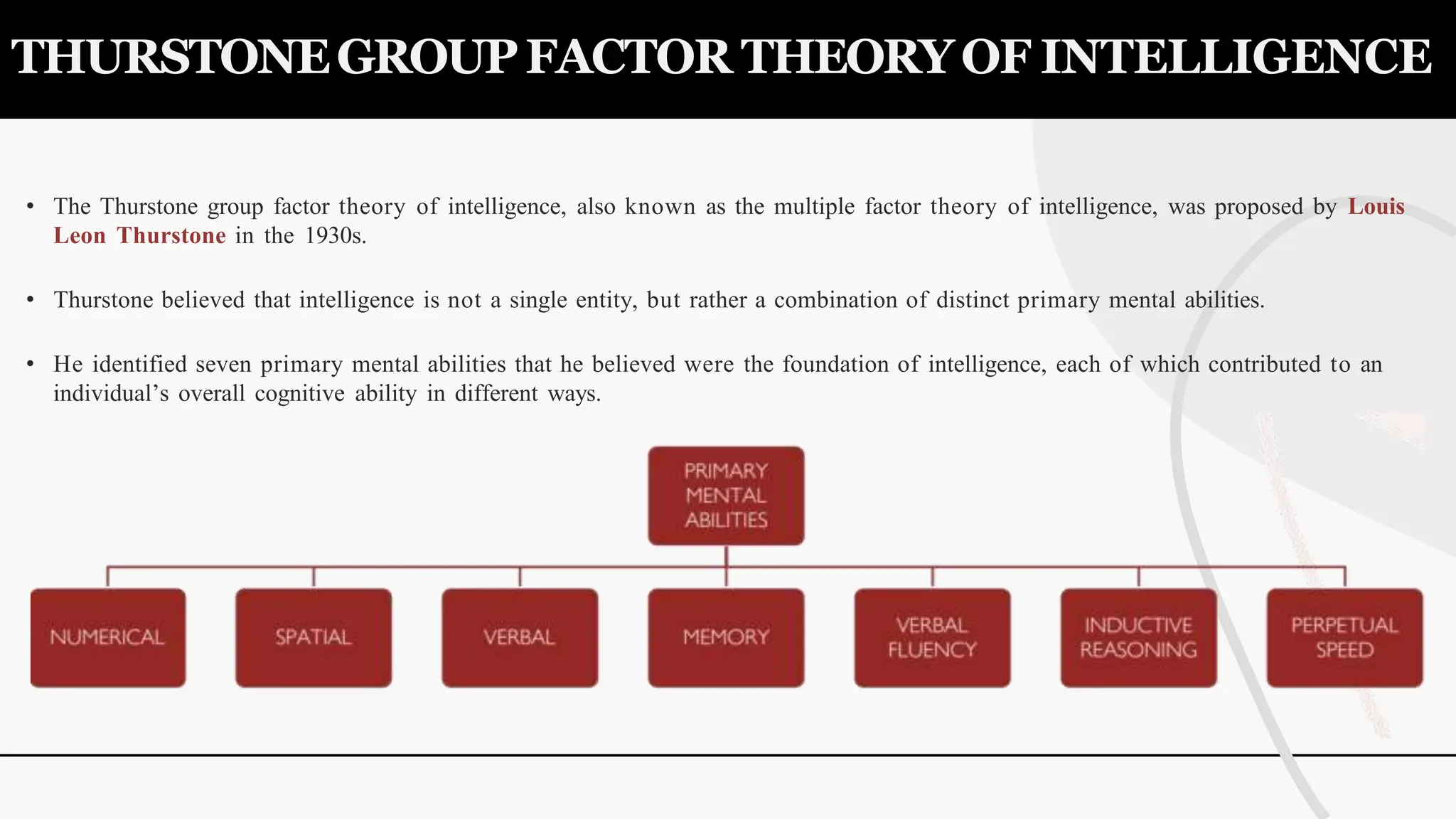
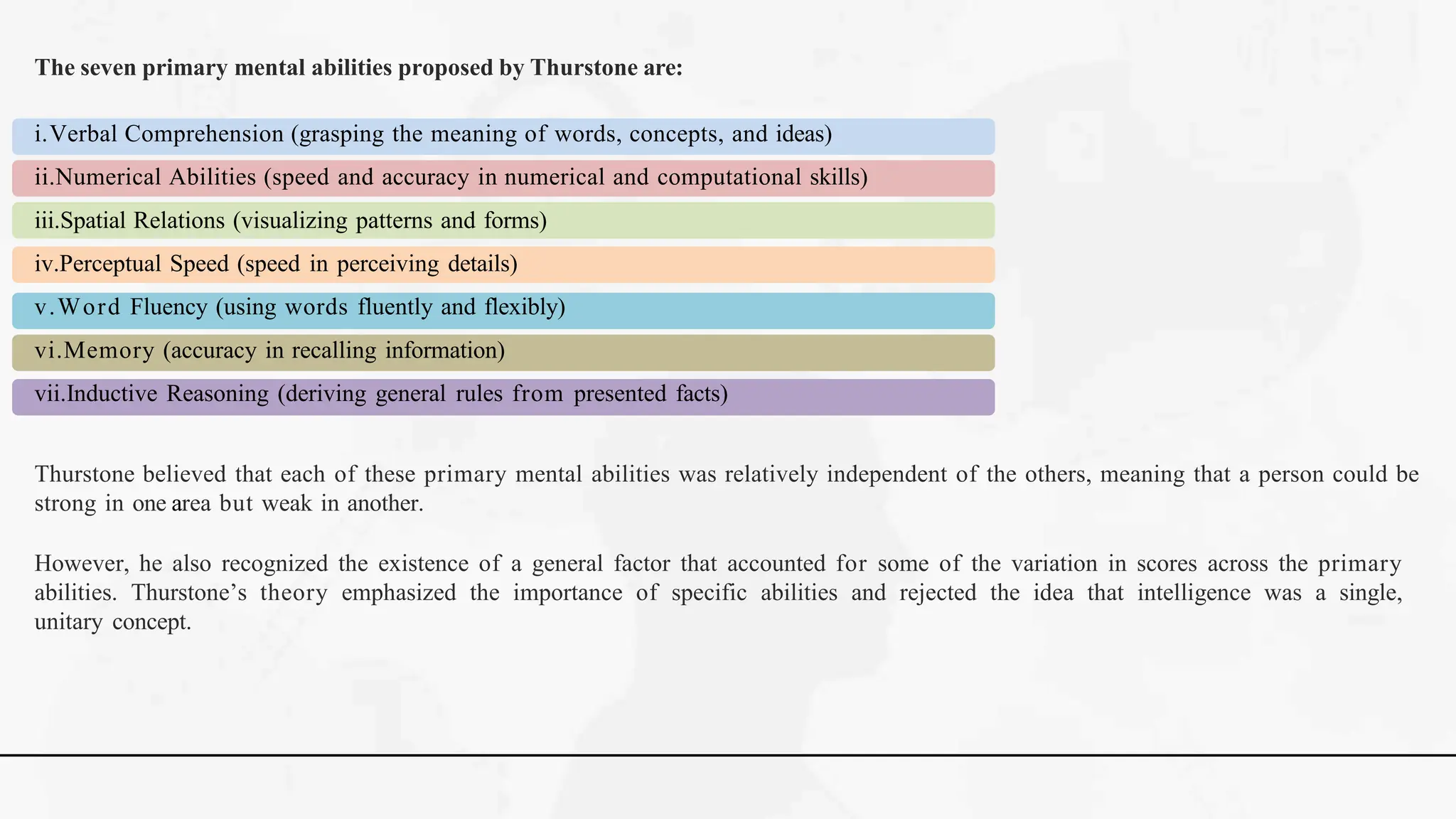
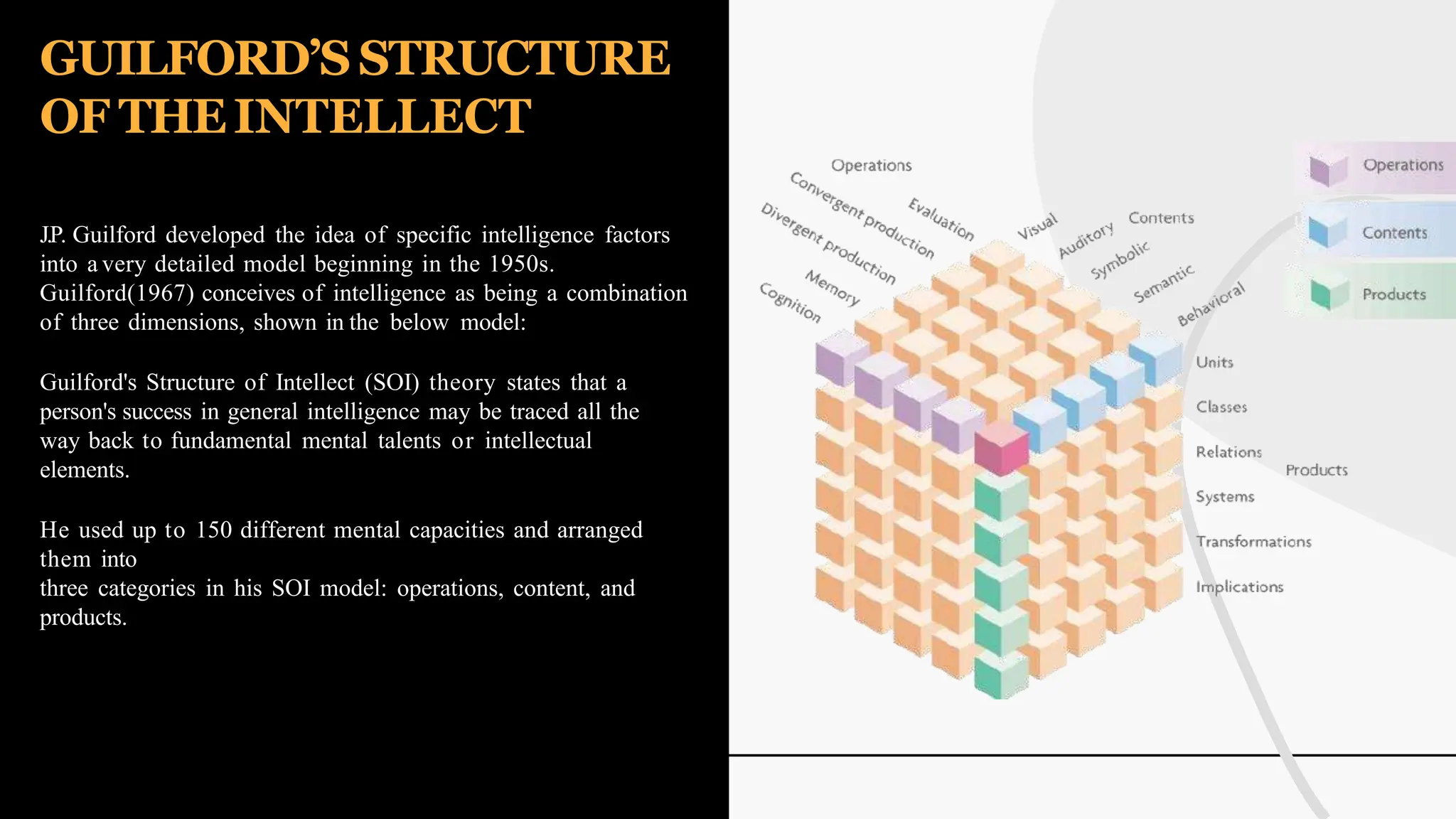
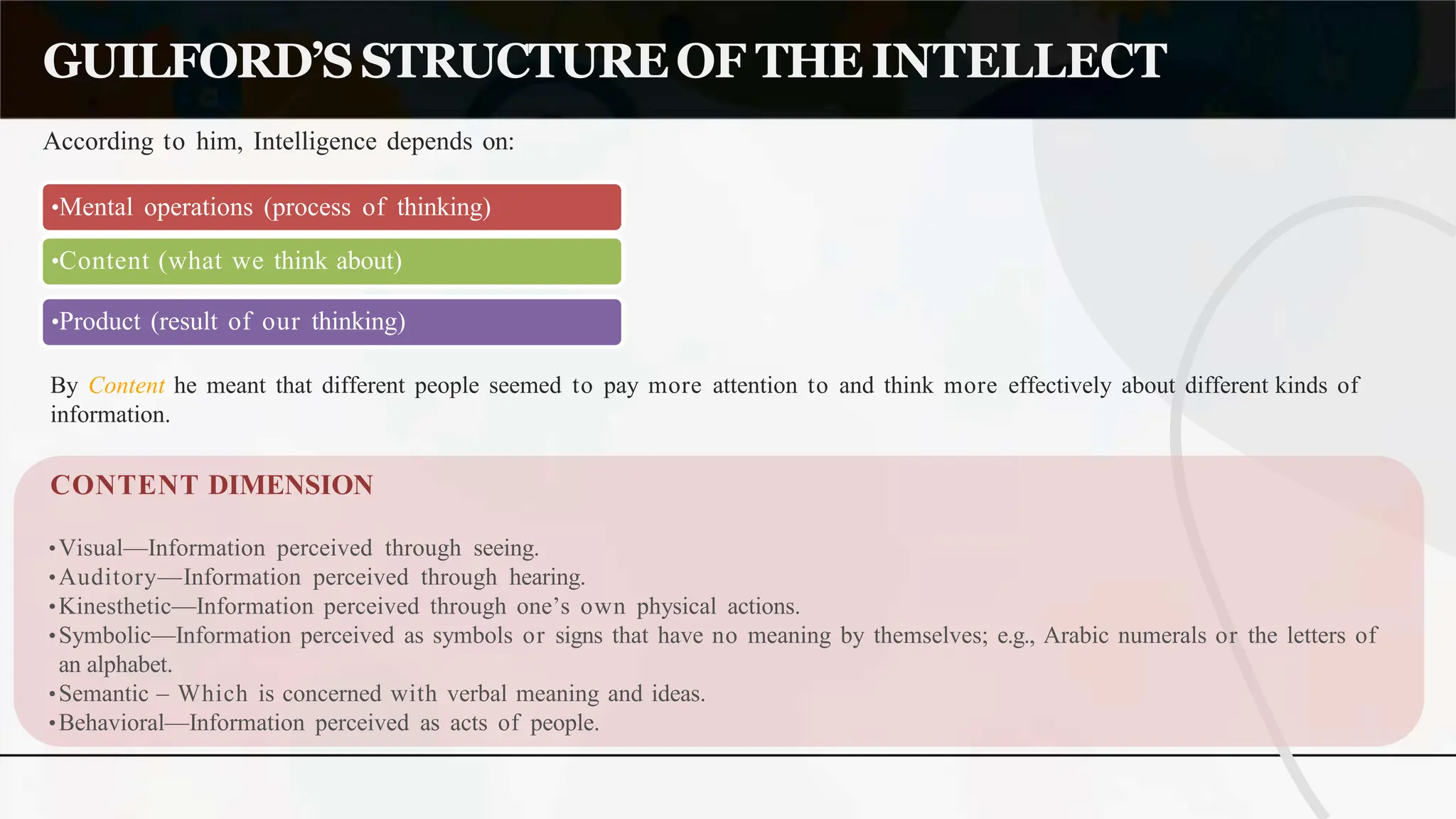
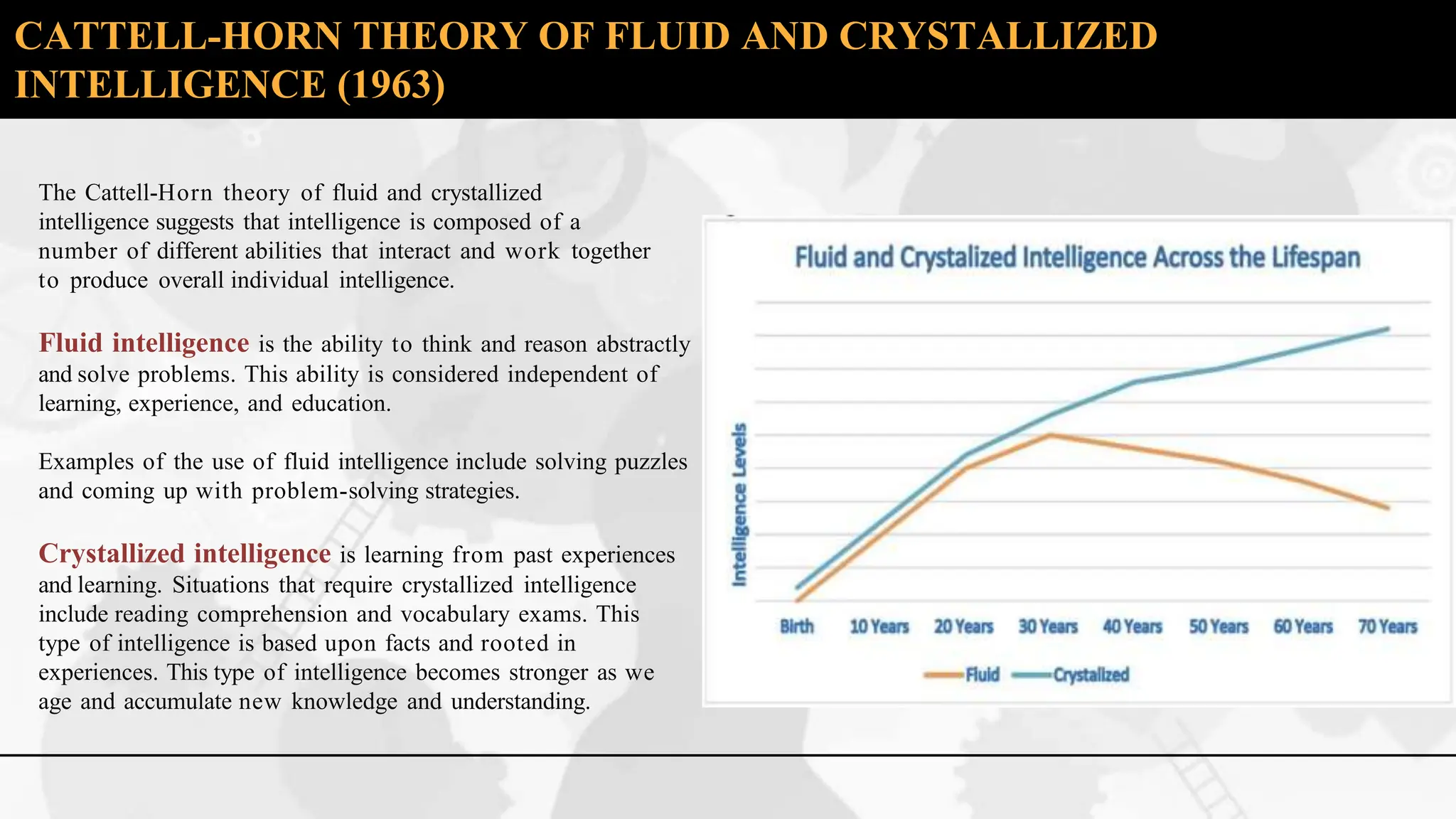
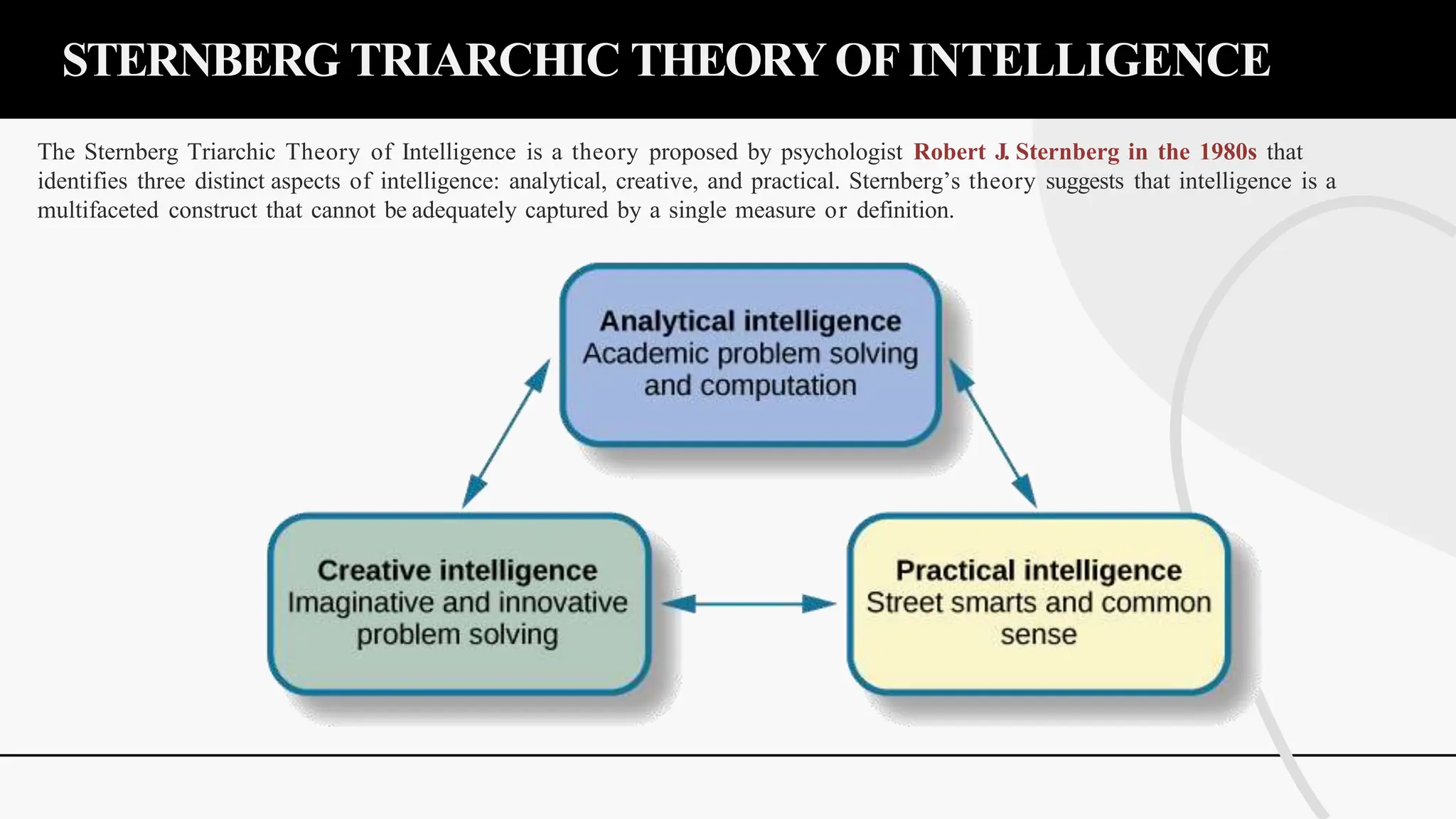
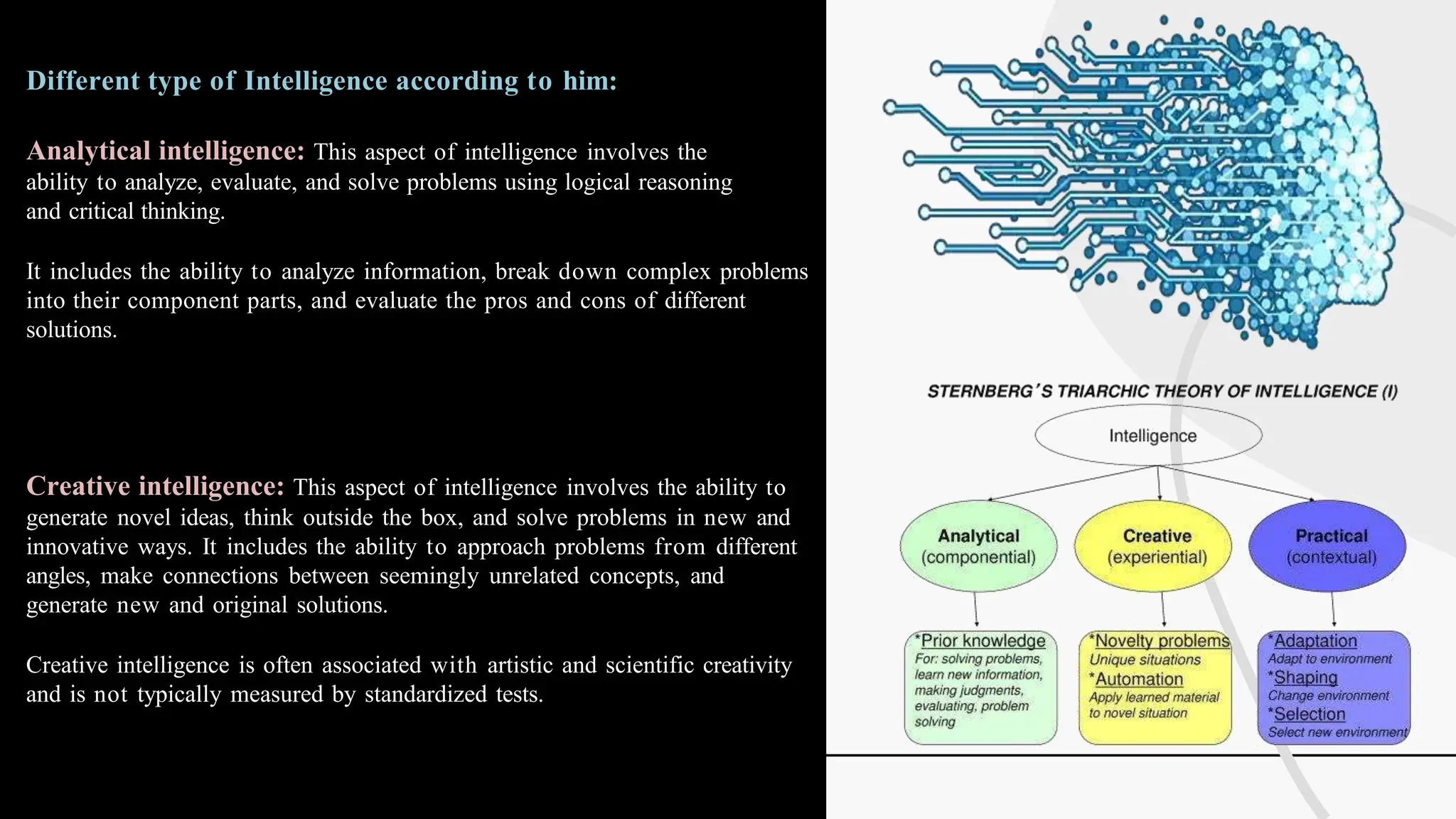
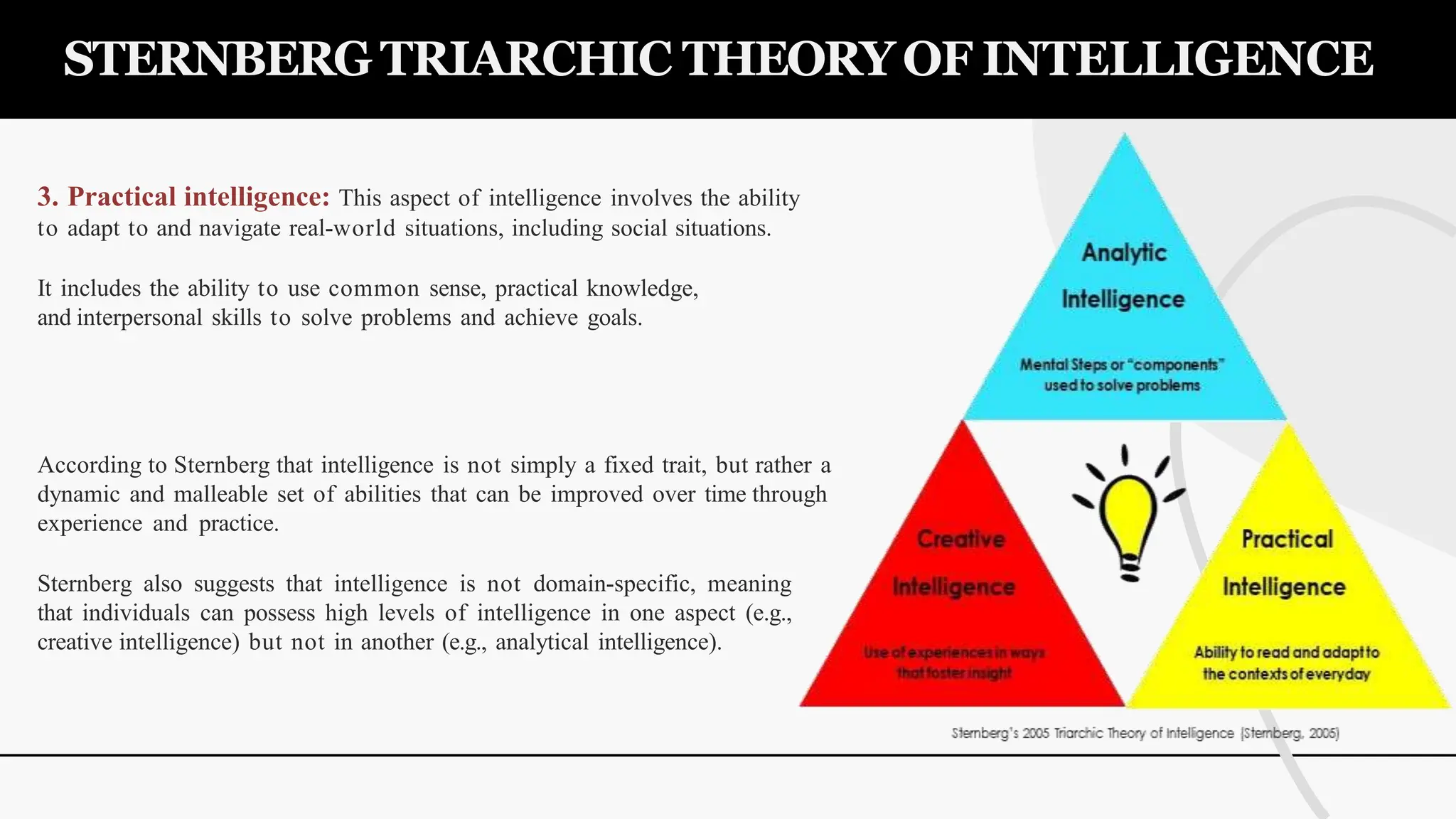
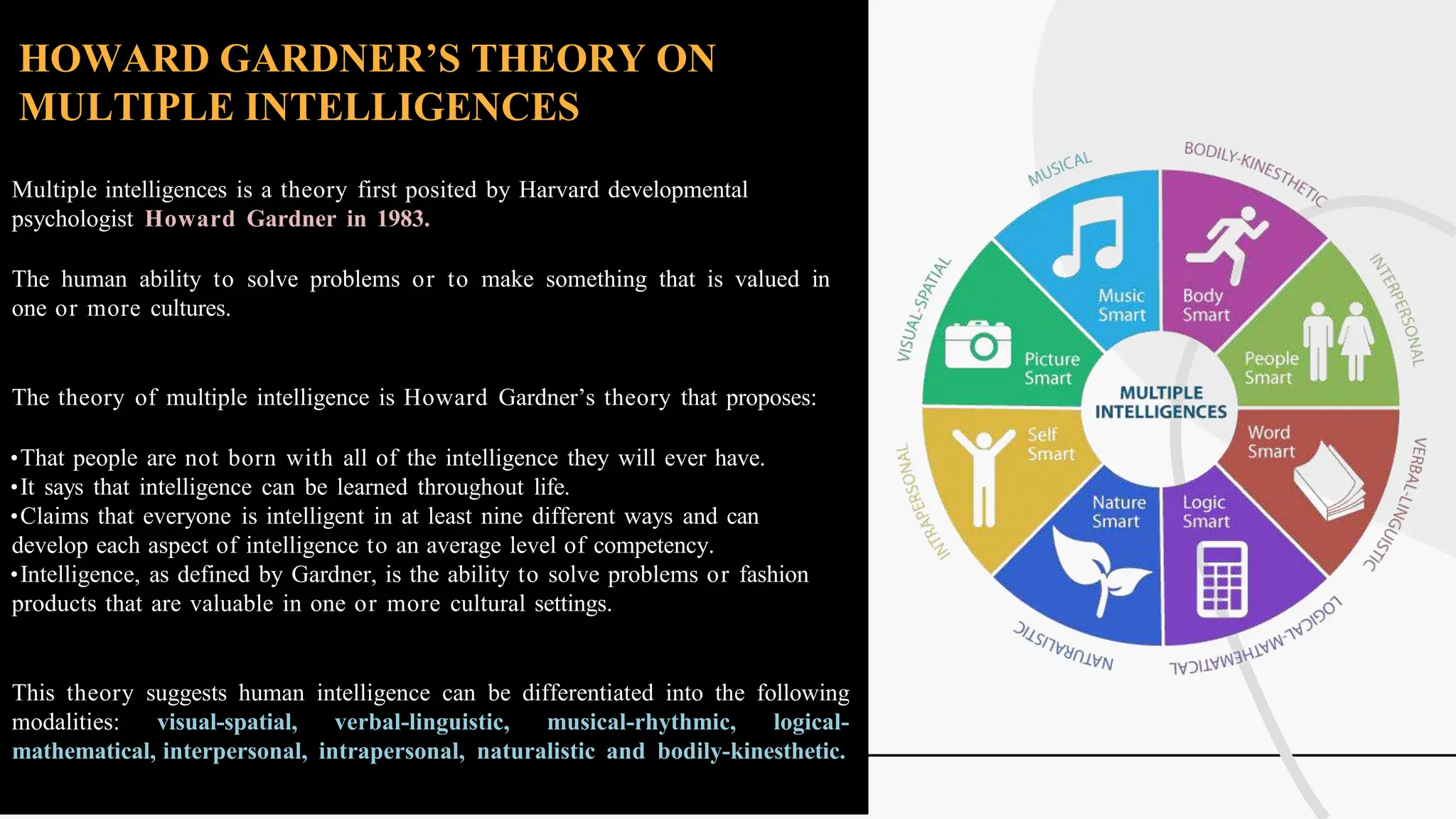
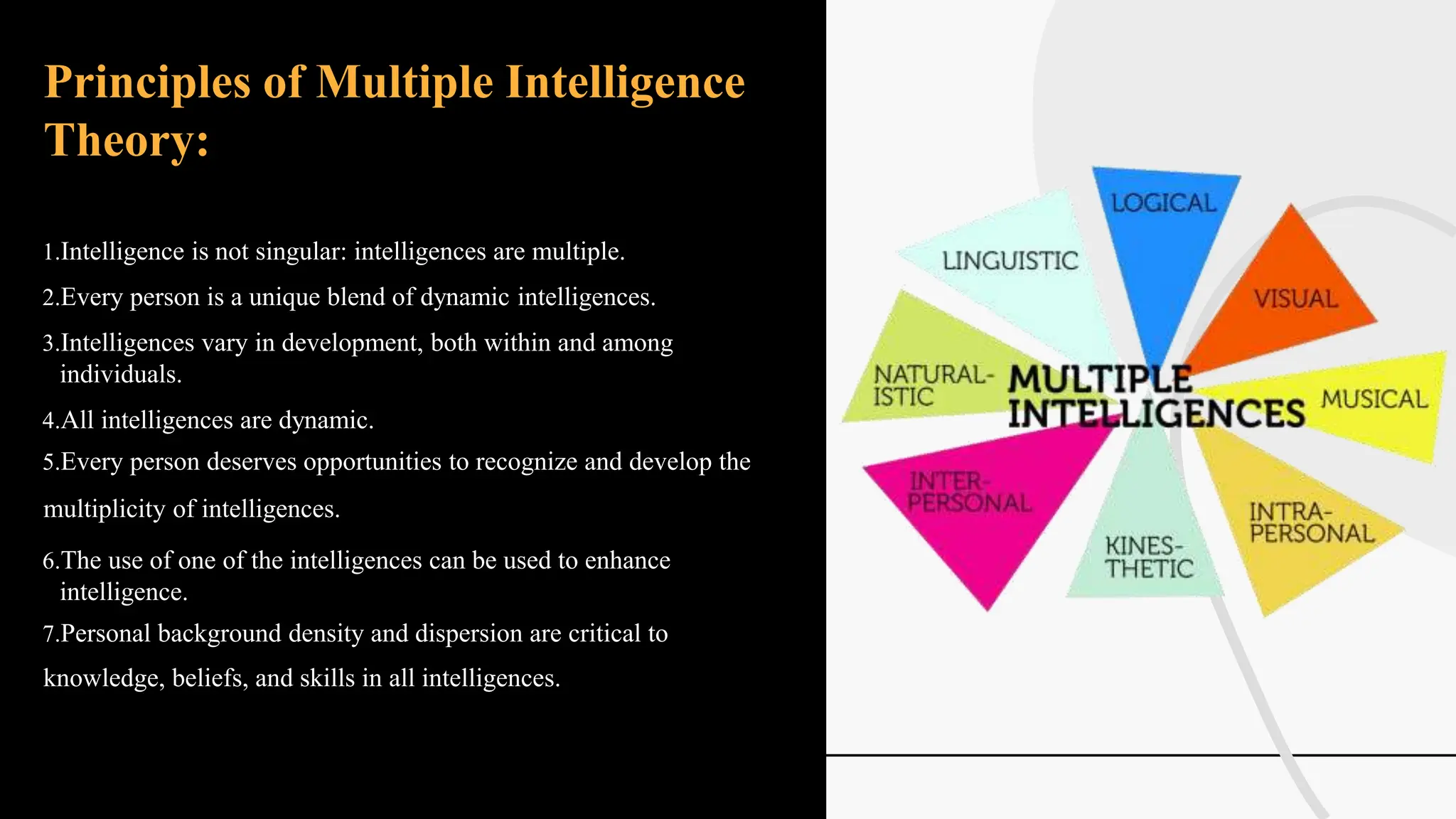
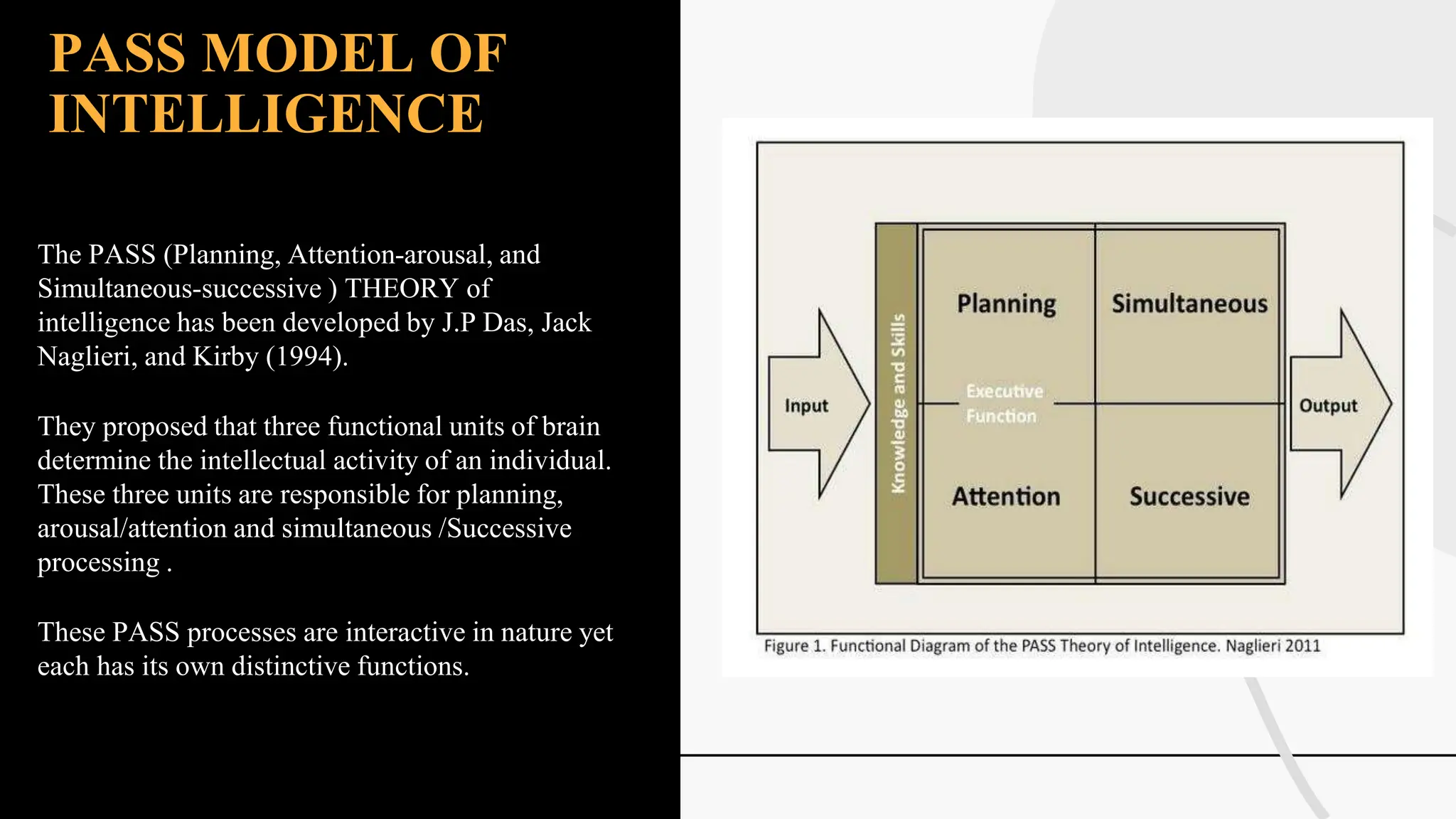
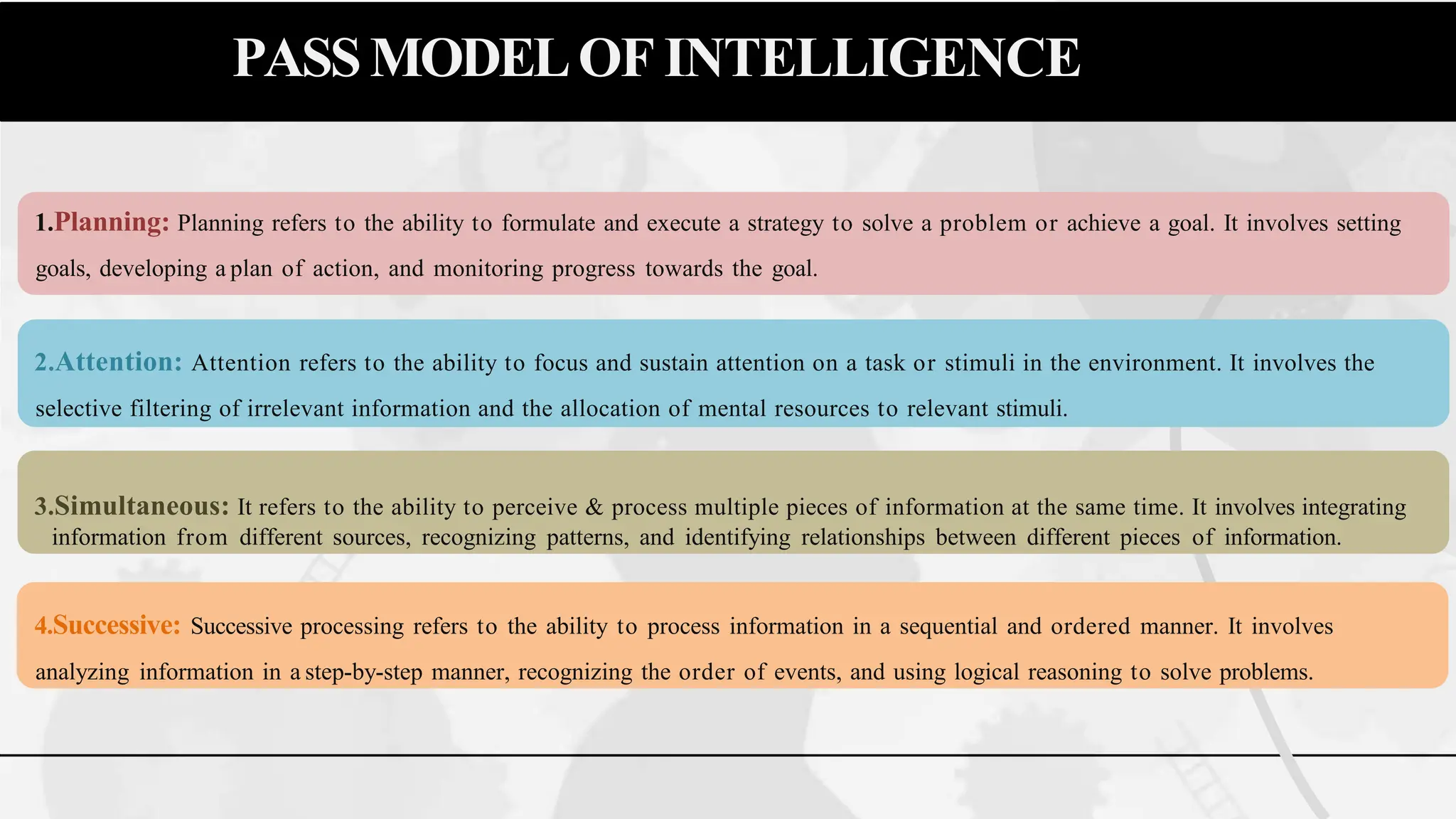
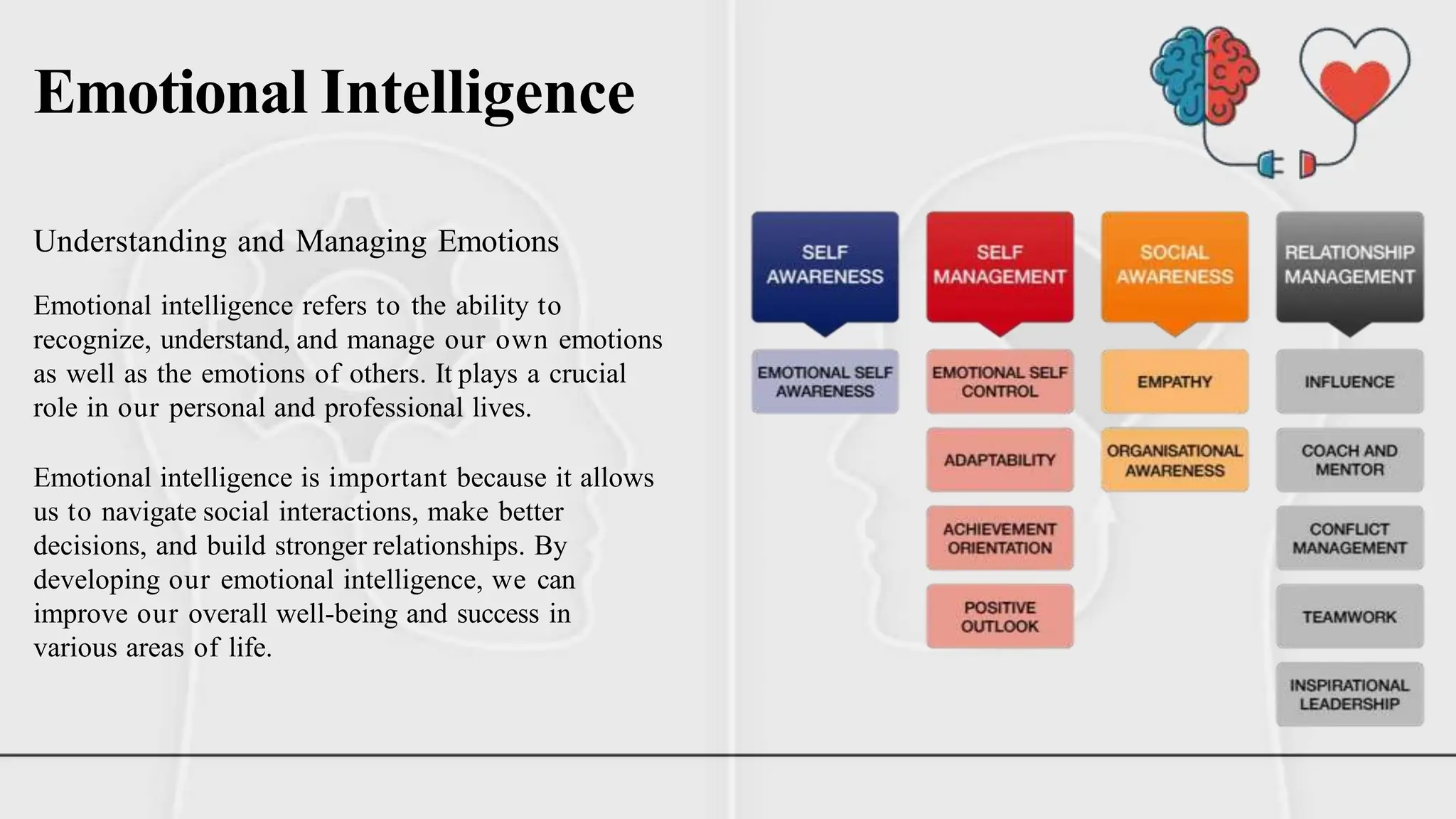
The document discusses various theories and concepts of intelligence, highlighting definitions by key psychologists such as Alfred Binet, Charles Spearman, and Howard Gardner. It categorizes intelligence into different approaches including psychometric, information processing, and multiple intelligences, while also addressing the significance of intelligence in personal and professional development. Additionally, it touches on variations of intelligence, including intellectual disabilities and giftedness.