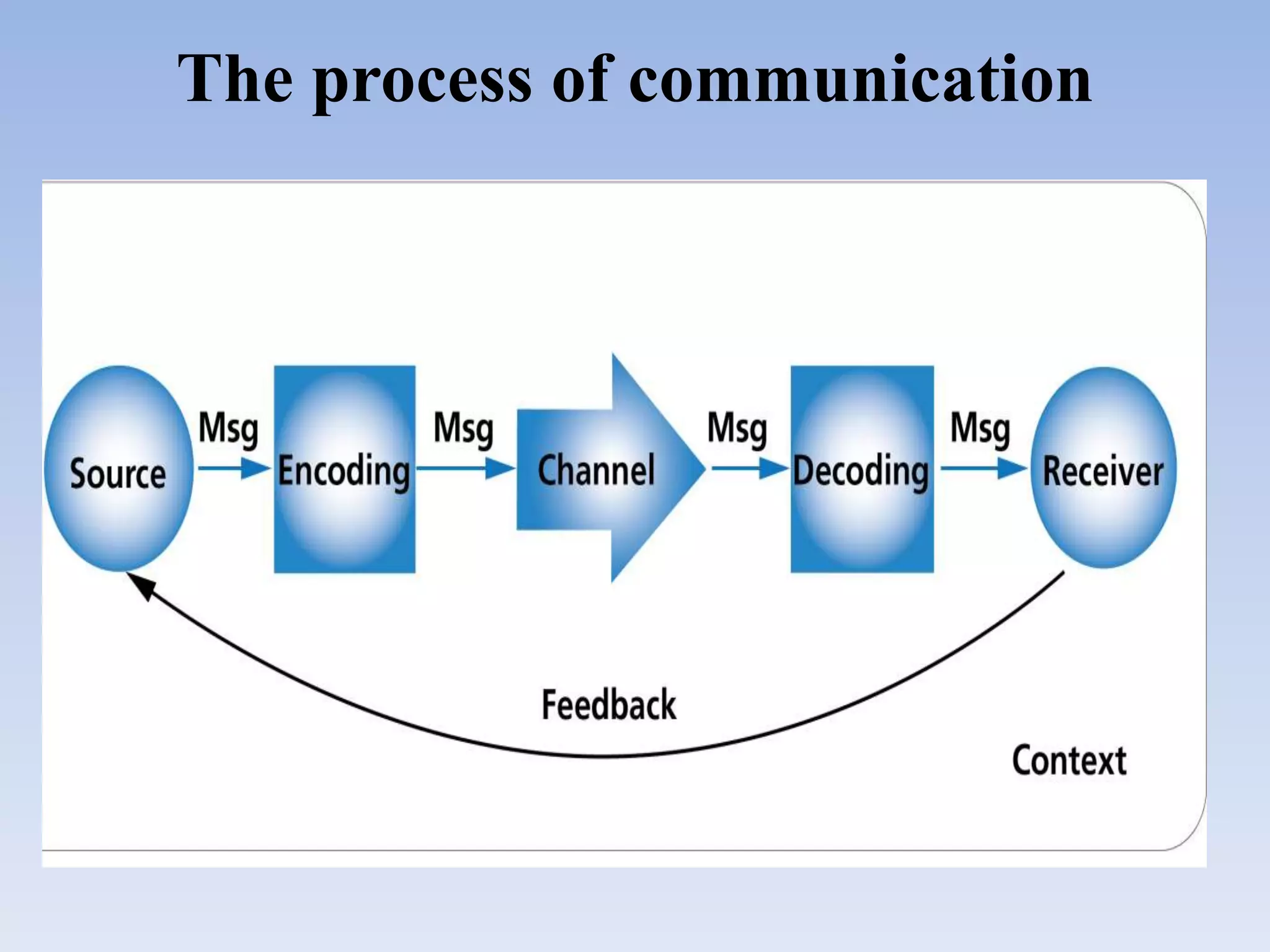
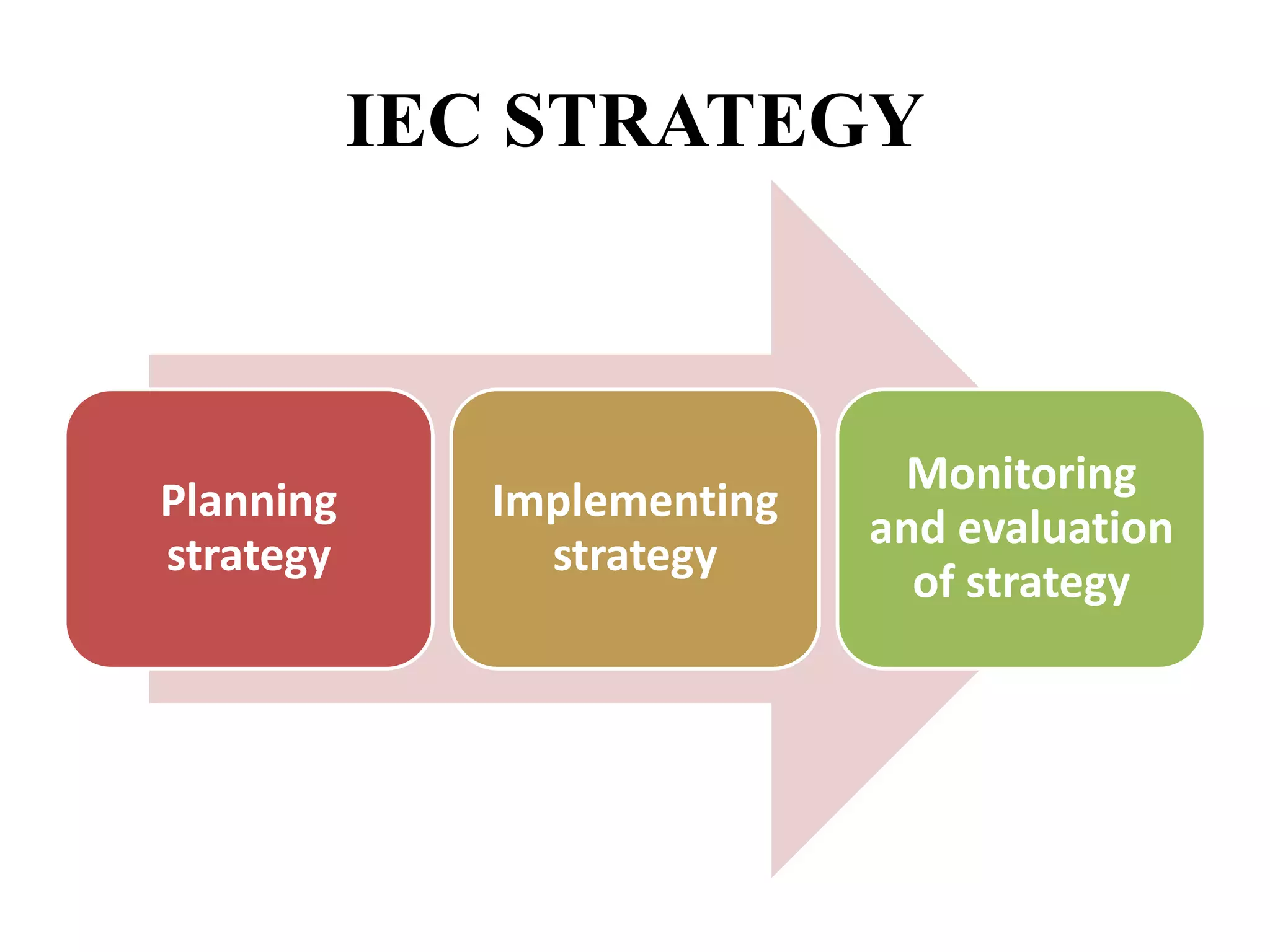
1. The document defines IEC (Information Education Communication) as an approach to change or reinforce behaviors in a target audience regarding a specific health problem over a predefined period of time.
2. IEC aims to change individual, family, and community health behaviors, educate audiences about public health, and facilitate support for health activities.
3. Nurses play an important role in IEC by gaining people's confidence, motivating behavior change, preparing people to utilize health services, and developing a sense of community responsibility for health.