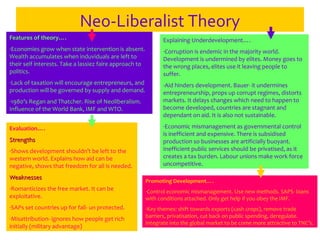
The document discusses various development theories, including modernisation theory and neo-liberalism, highlighting their stages, barriers, and catalysts for development. It evaluates these theories in terms of strengths and weaknesses, particularly focusing on economic and cultural factors that hinder or promote development in different contexts. Additionally, it touches on feminist theories related to development, emphasizing the roles of women and their relationship with the environment.