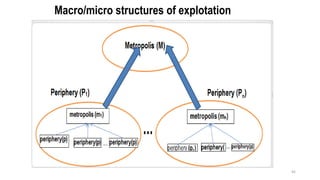
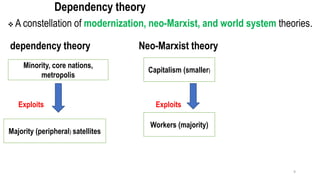
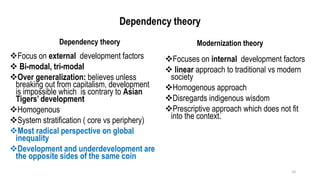
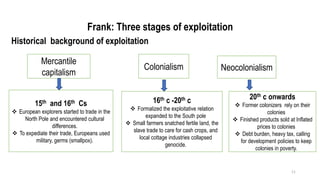
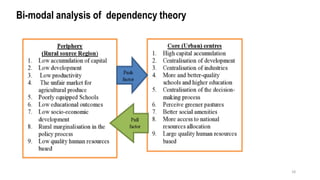
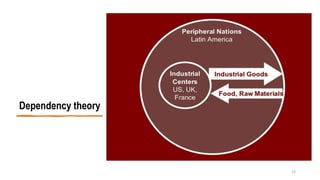
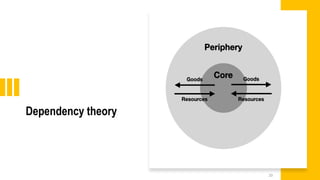
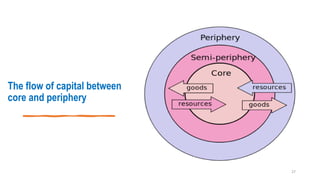
This document provides an overview of dependency theory, which emerged in Latin America in the 1960s. It defines key concepts like core and periphery countries, and describes how dependency theory views the global economic system as exploiting developing nations. The document outlines the background and influence of economists like Prebisch, Frank, and Wallerstein. It explains the central tenets of dependency theory, including that underdevelopment is caused by core nations extracting surplus from the periphery. The critique section notes that dependency theory ignores variations among developing countries and possible benefits of globalization.































![Paul Baran’s Analysis of Economic Backwardness and
Economic Growth
❖Paul Baran: father of modern Dependency Theory (1957): “The Political Economy of Growth”.
❖Argues that underdevelopment is a result of the world process of capital accumulation.
❖Rejects popular assumptions [modernization] in relation to the obstacles in poor countries for economic
development.
Obstacles of development according to Paul Baran
❑Lack of entrepreneurial talent
❑ Lack of capital
❑Population problem: overpopulation must be considered only with reference to the means of production and employment.
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencytheory-231108184400-93970600/85/Dependency-Theory-pdf-40-320.jpg)