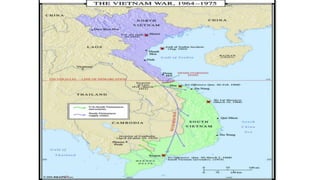
The document provides background information on the Vietnam War. It discusses:
- The war lasted from 1955 to 1975 between North Vietnam and the US-backed South Vietnamese government.
- Over 58,000 US troops and millions of Vietnamese civilians and soldiers were killed. The war cost the US $168-200 billion.
- The war escalated under presidents Kennedy and Johnson as the US increased support to South Vietnam against the North Vietnamese-backed Viet Cong. Heavy US bombing began in 1965 and US troop levels rose to over 500,000.
- Despite massive US military involvement, North Vietnam was able to withstand the attacks and launch the devastating Tet Offensive in 1968, weakening US public support for the war. Peace talks