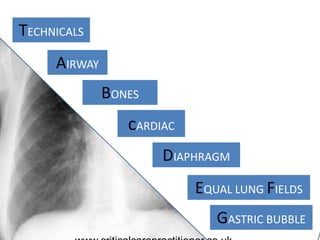
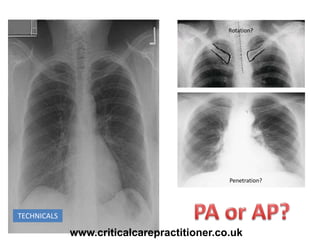
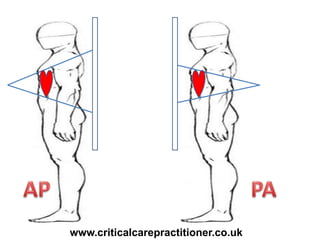
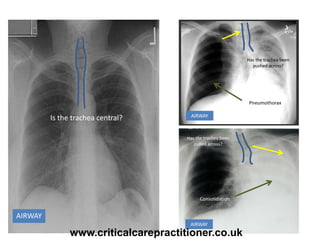
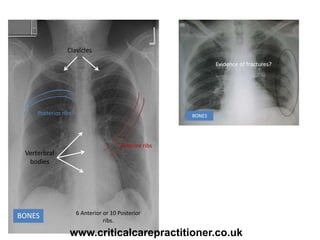
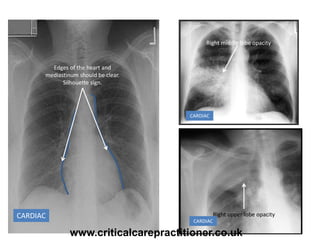
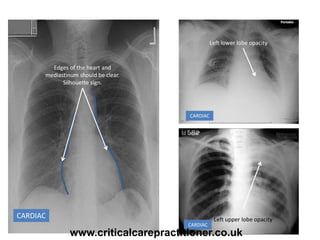
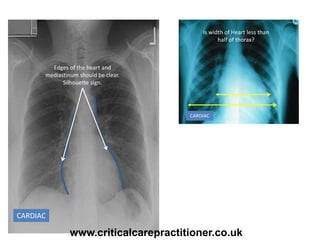
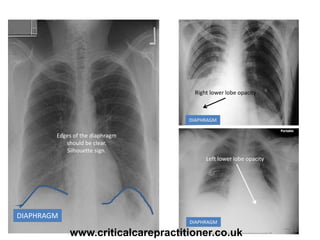
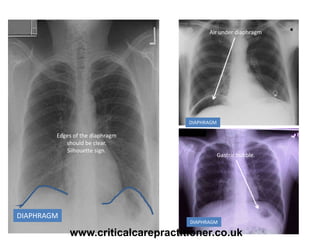
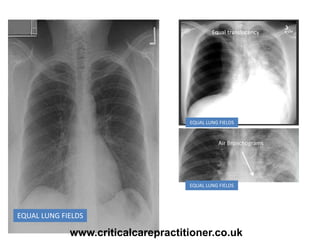
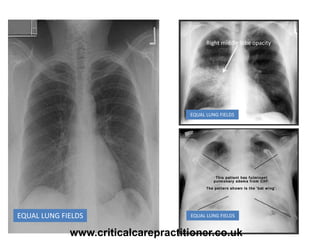
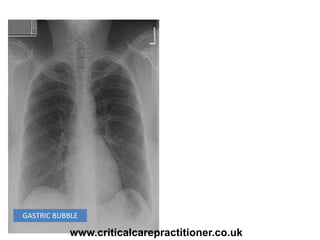
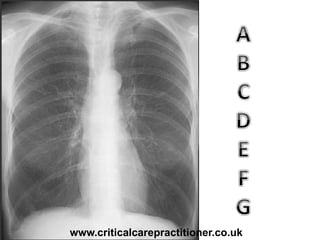
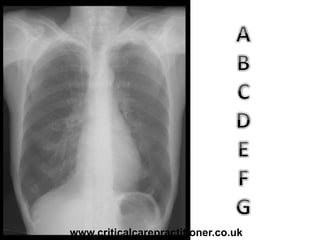
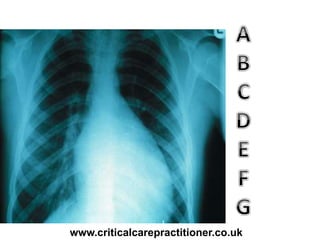
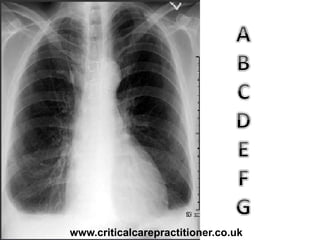
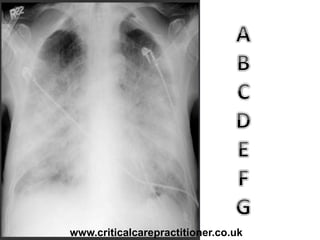
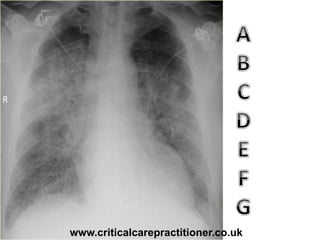
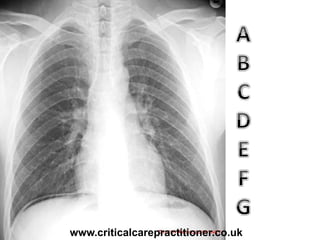
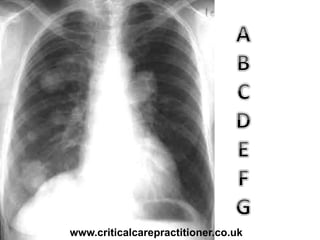
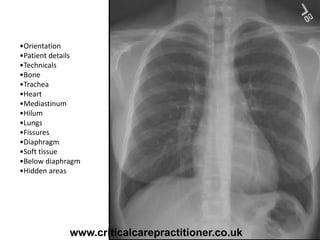
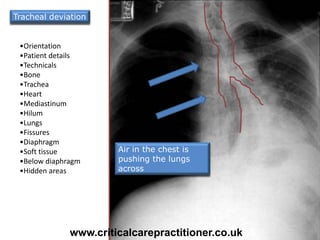
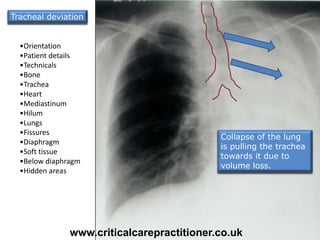
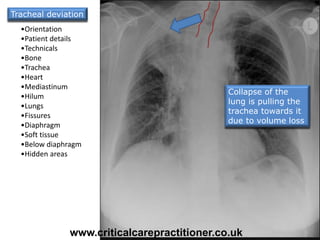
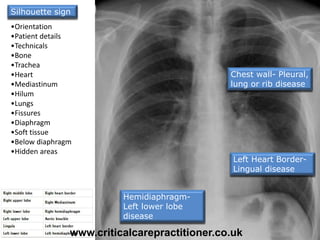
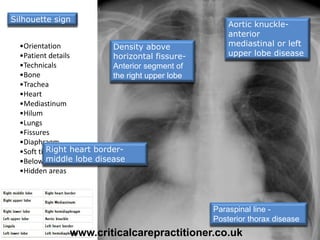
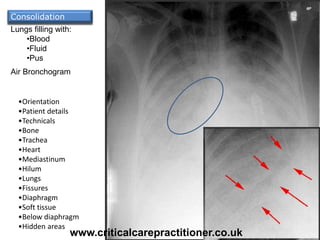
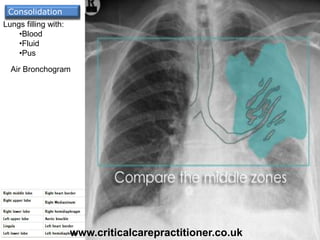
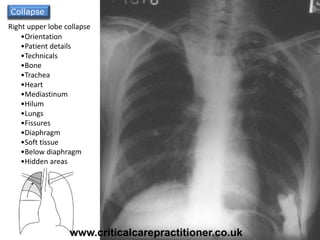
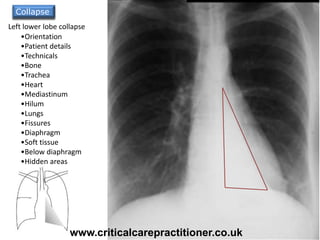
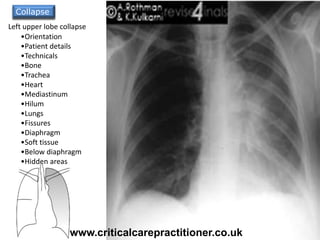
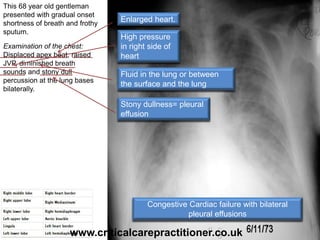
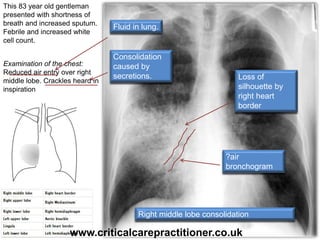
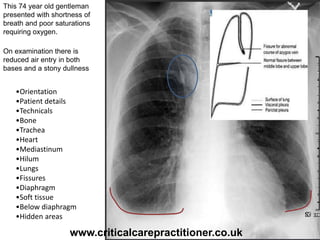
The document appears to be notes on assessing chest x-rays, listing various anatomical structures and abnormalities to check for, including the airway, bones, cardiac silhouette, diaphragm, lung fields, and other areas. It provides prompts for evaluating features such as tracheal deviation, the cardiac silhouette sign, consolidation, collapse, and pleural effusions. Examples are given of chest x-ray findings in patients with conditions like congestive cardiac failure, pneumonia, and pleural effusions. The document emphasizes a systematic approach to chest x-ray interpretation.