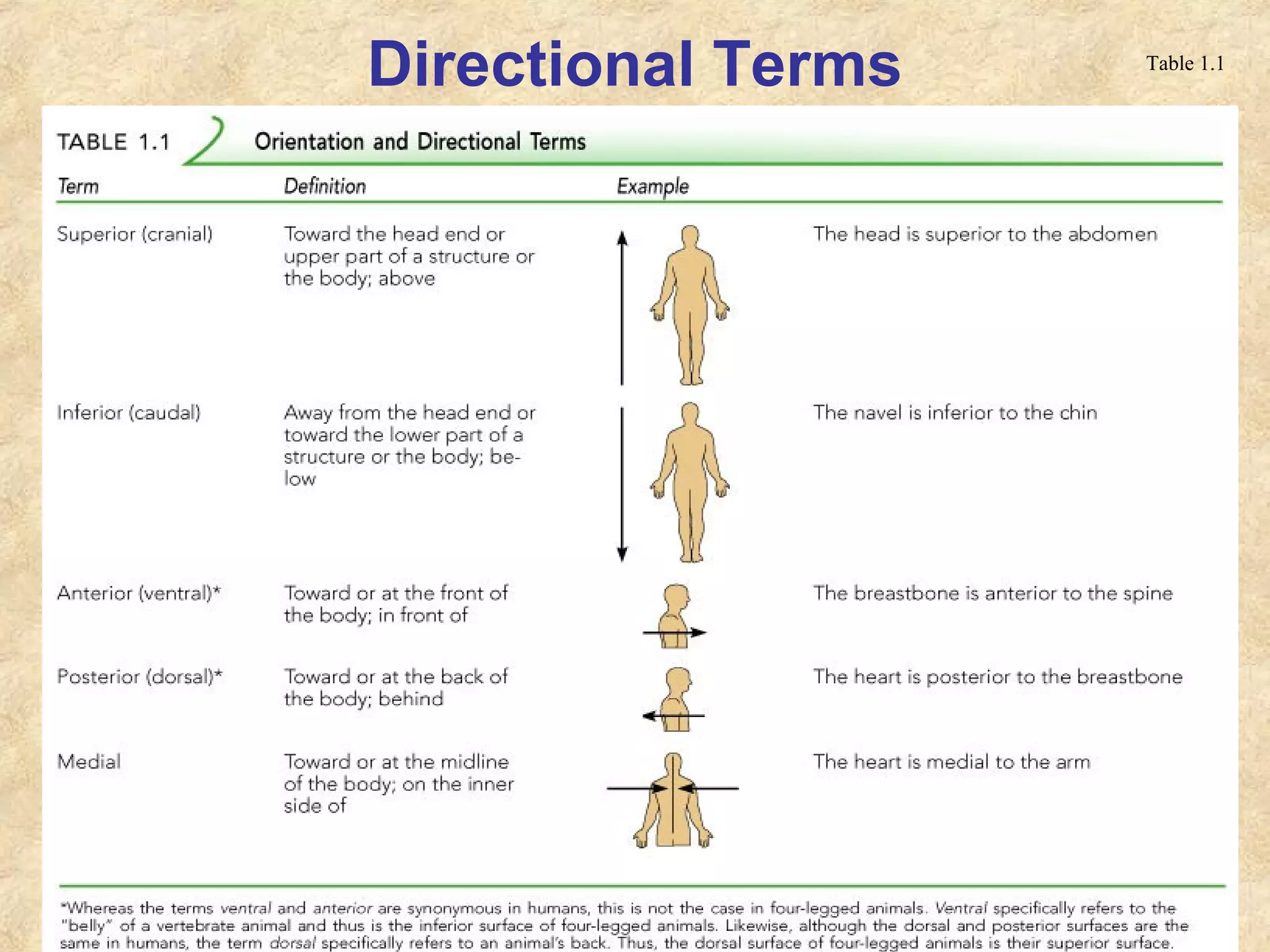
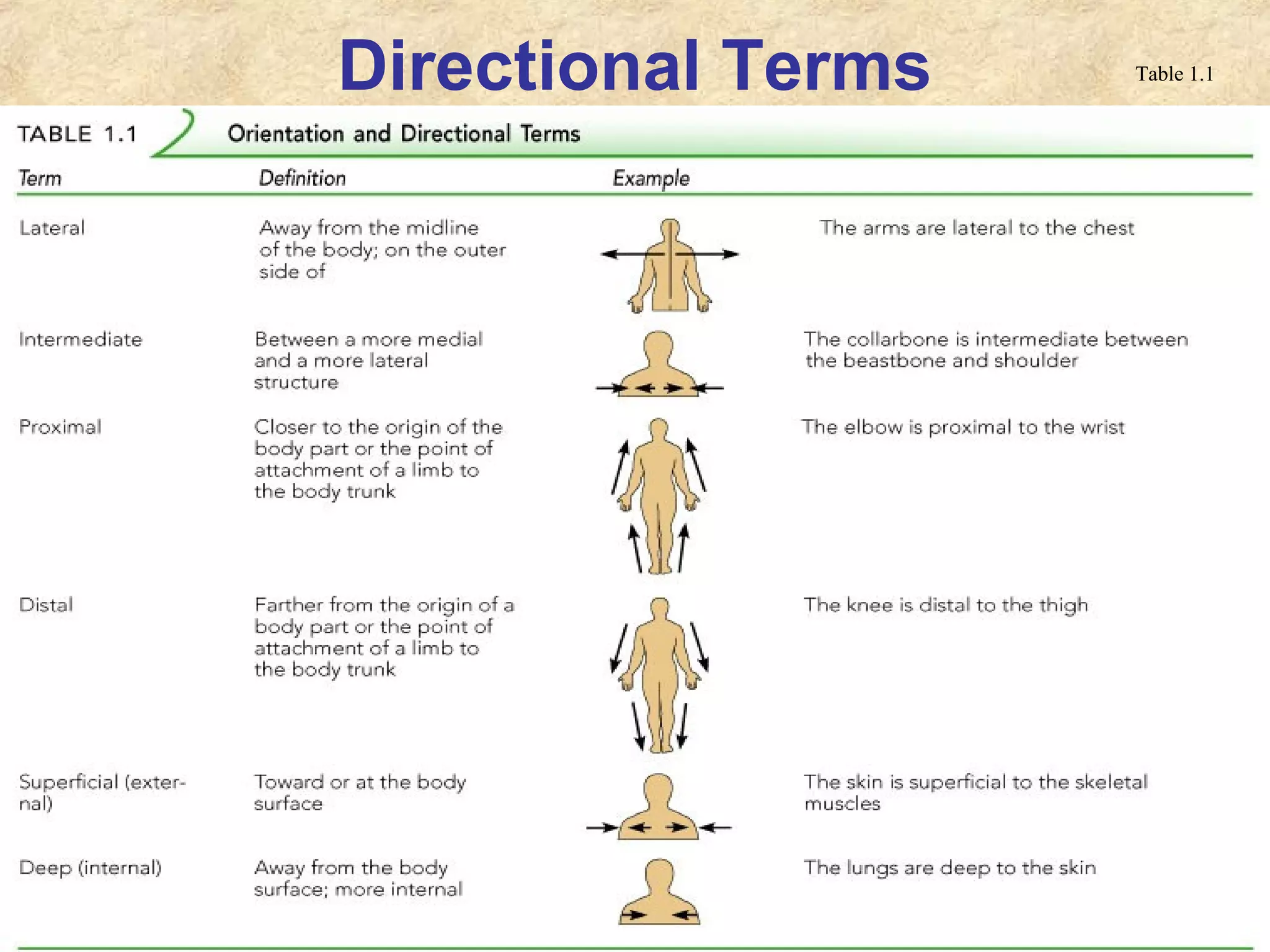
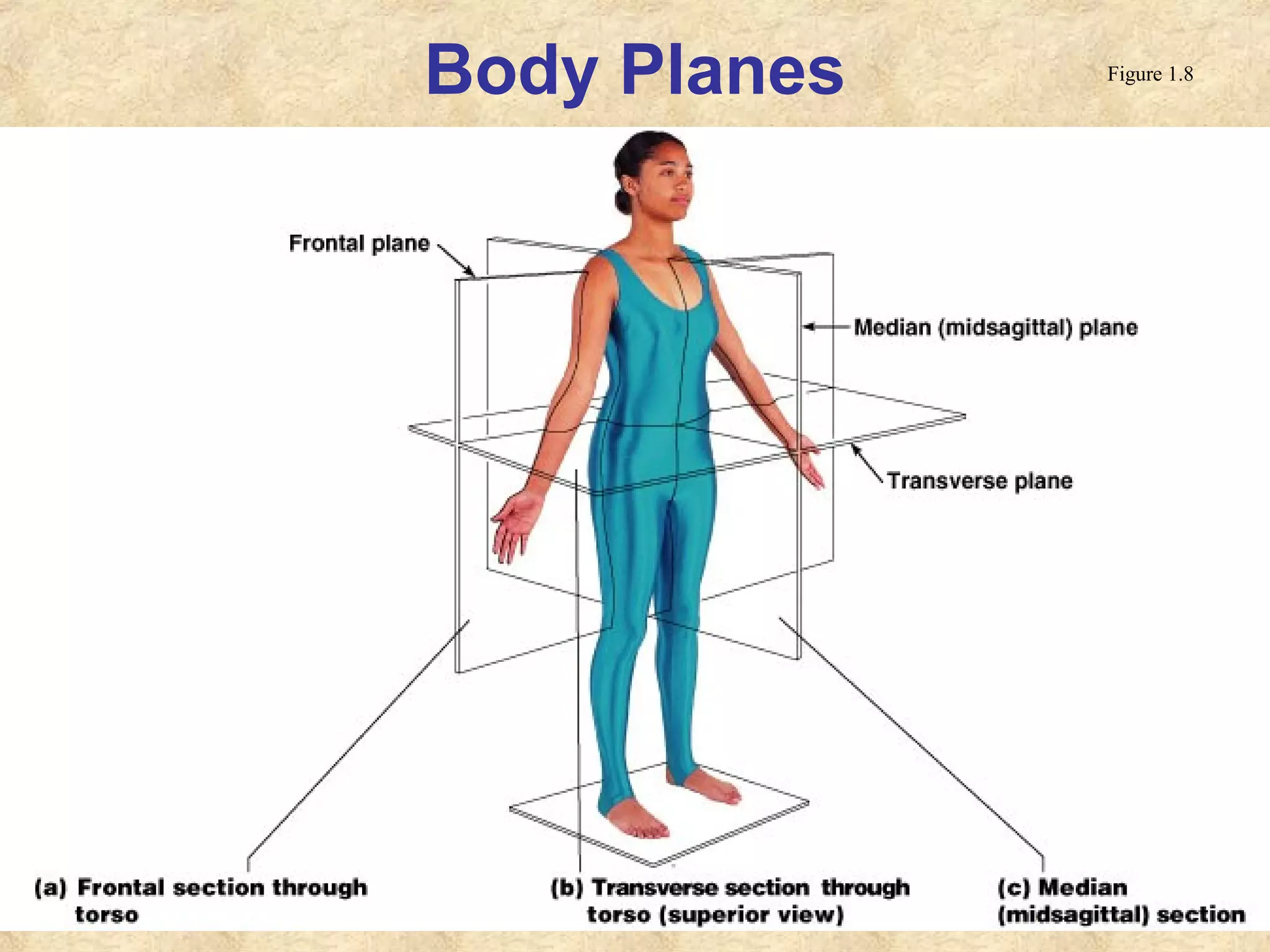
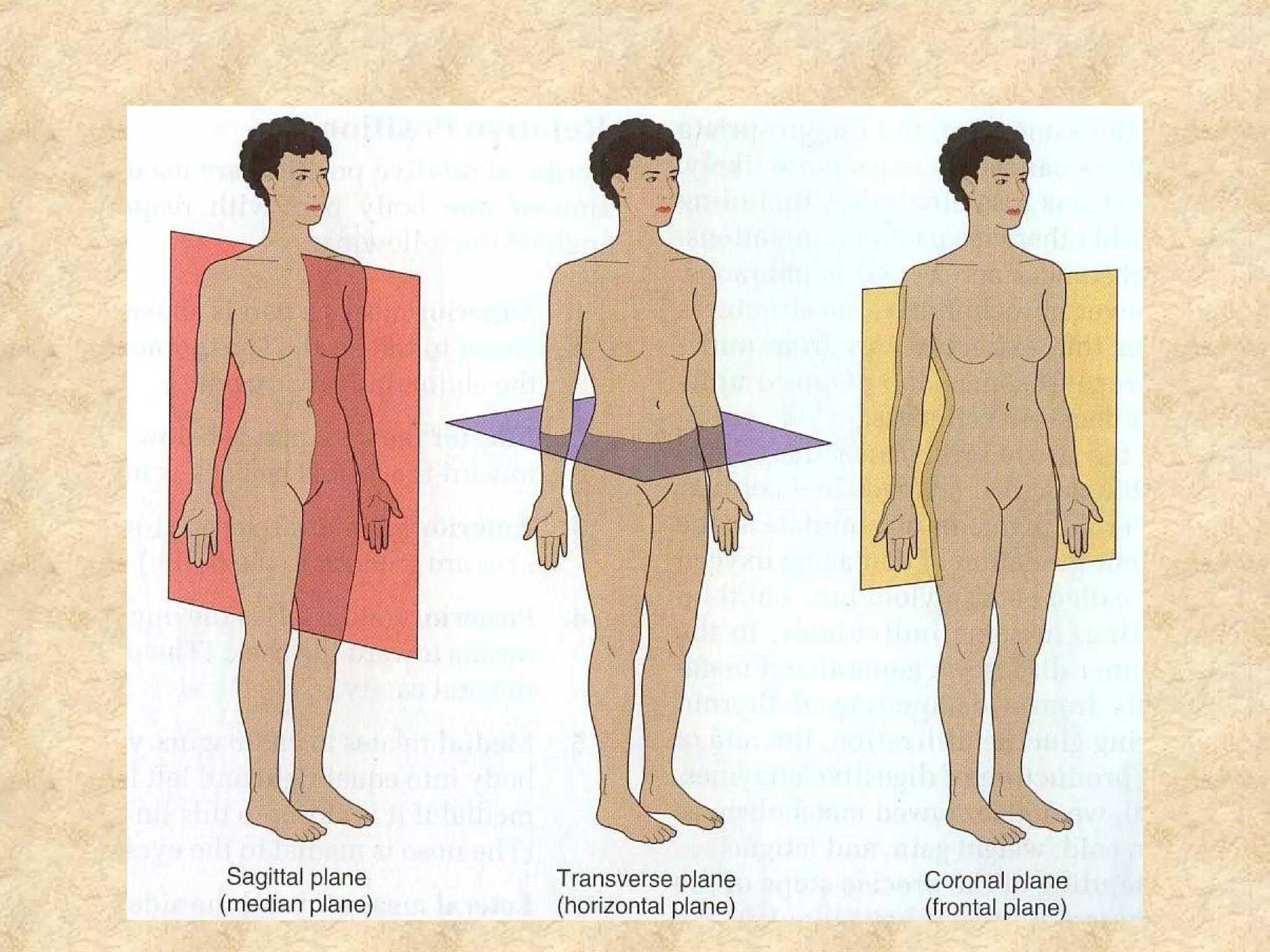
This document provides an overview of anatomical terms and the structural organization of the human body. It discusses the following key points in 3 sentences:
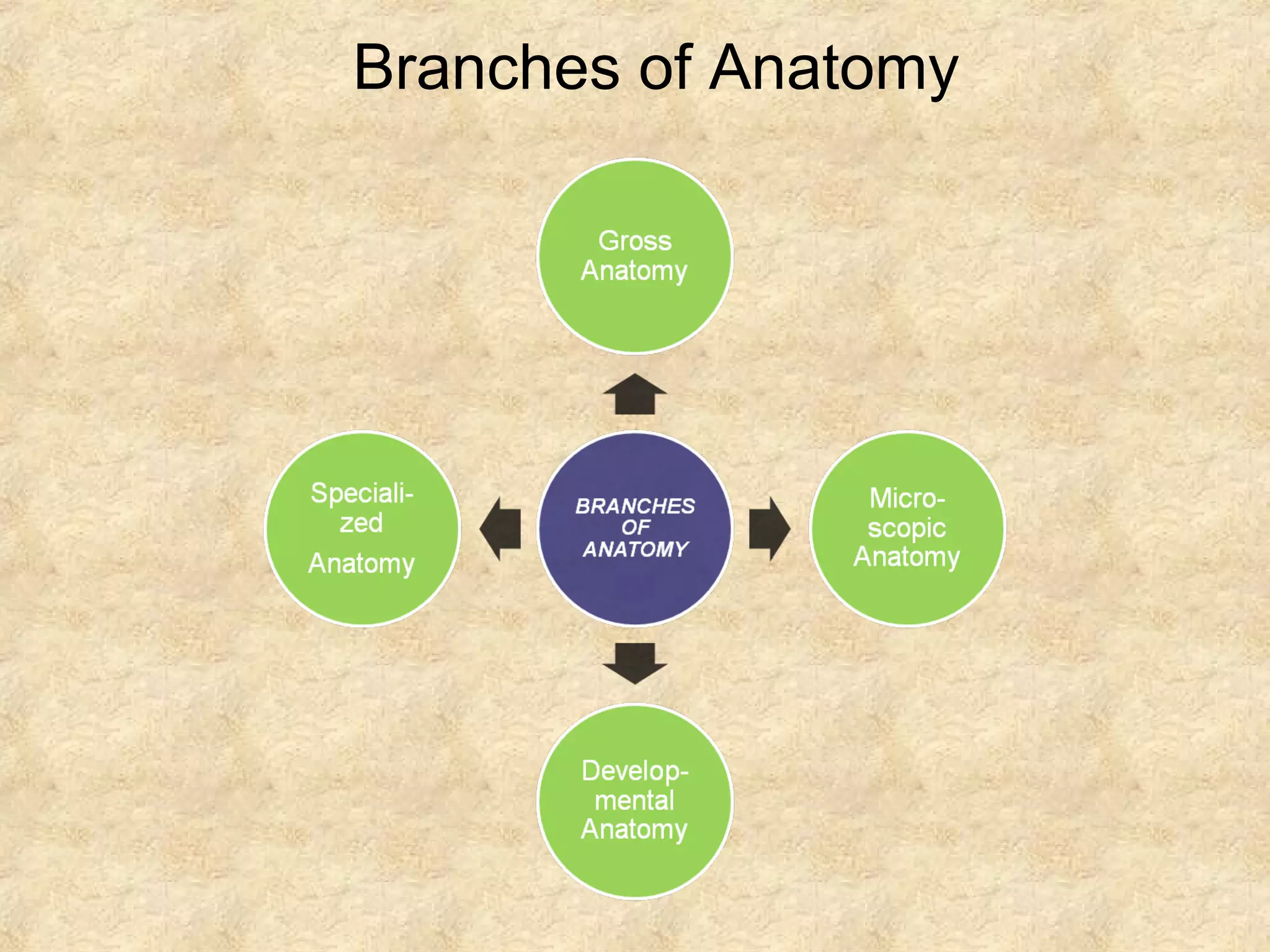
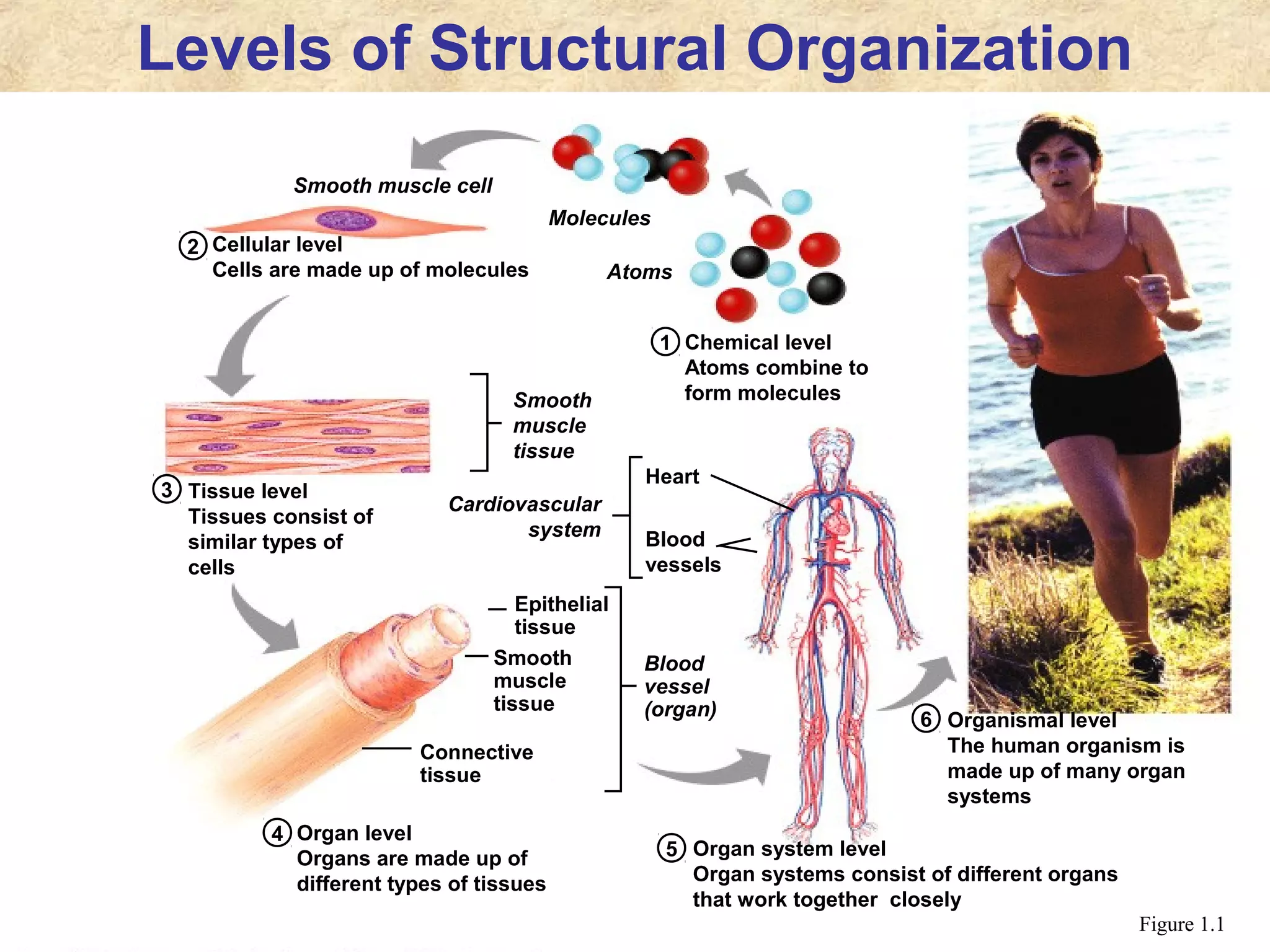
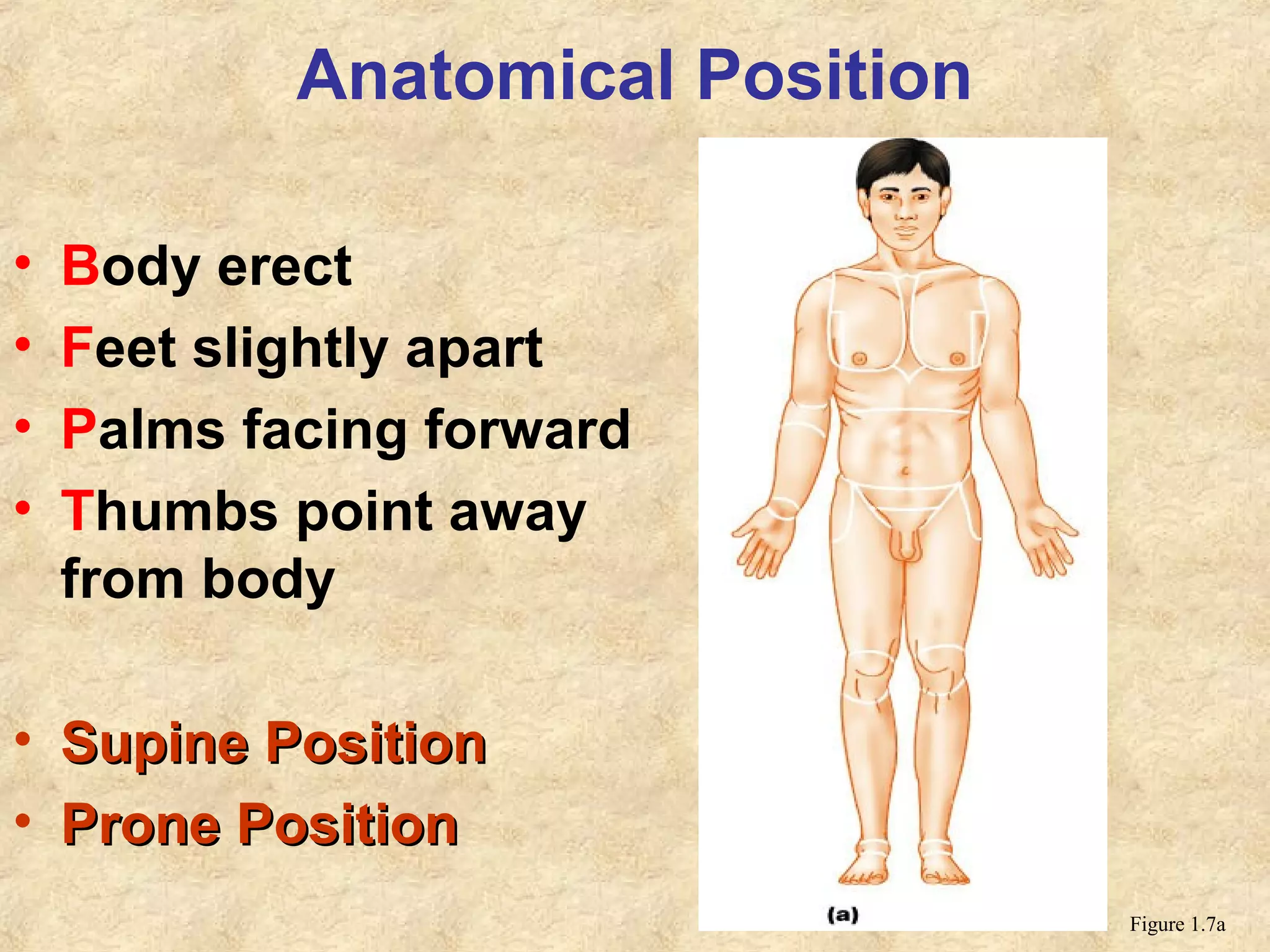
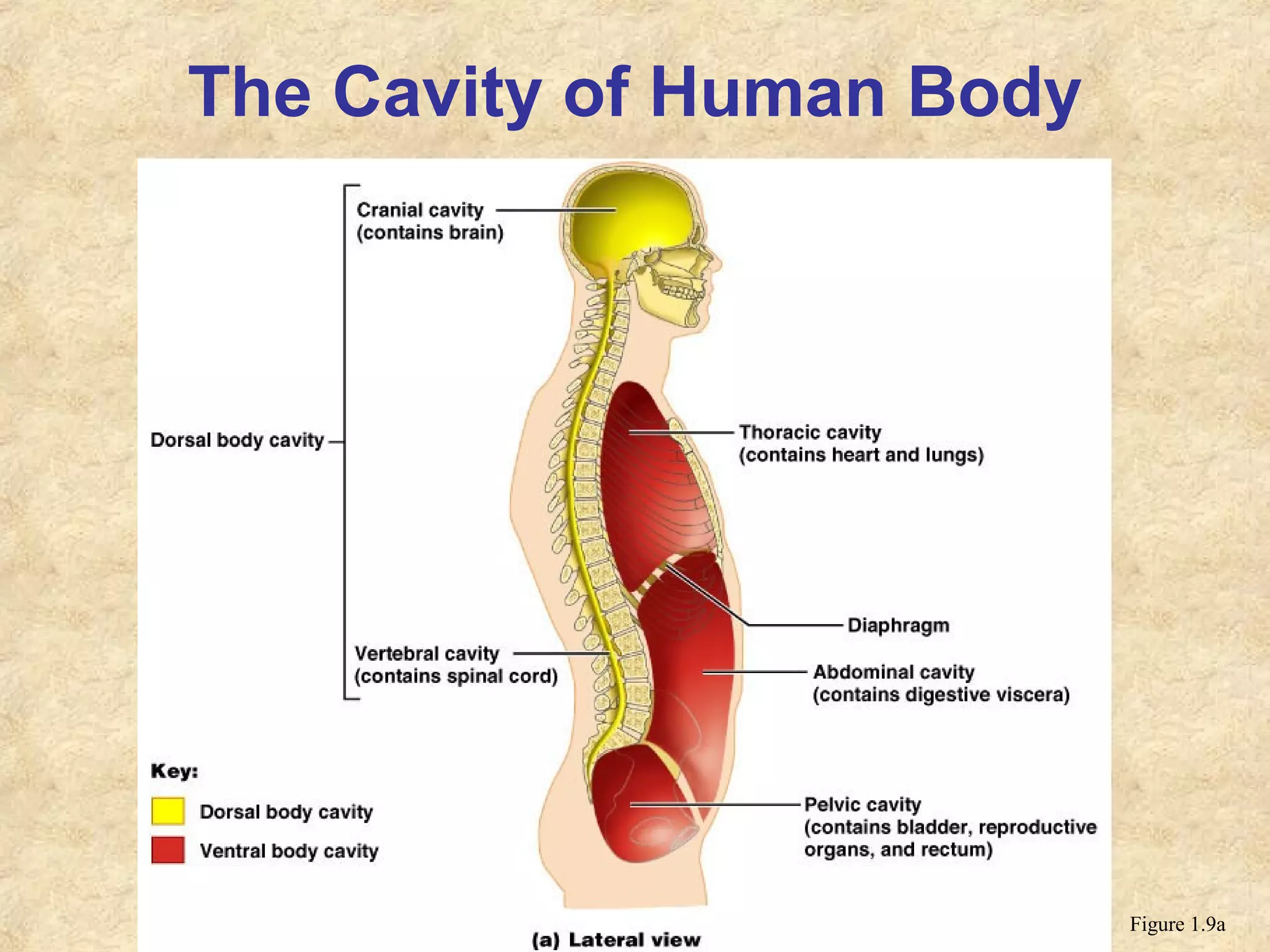
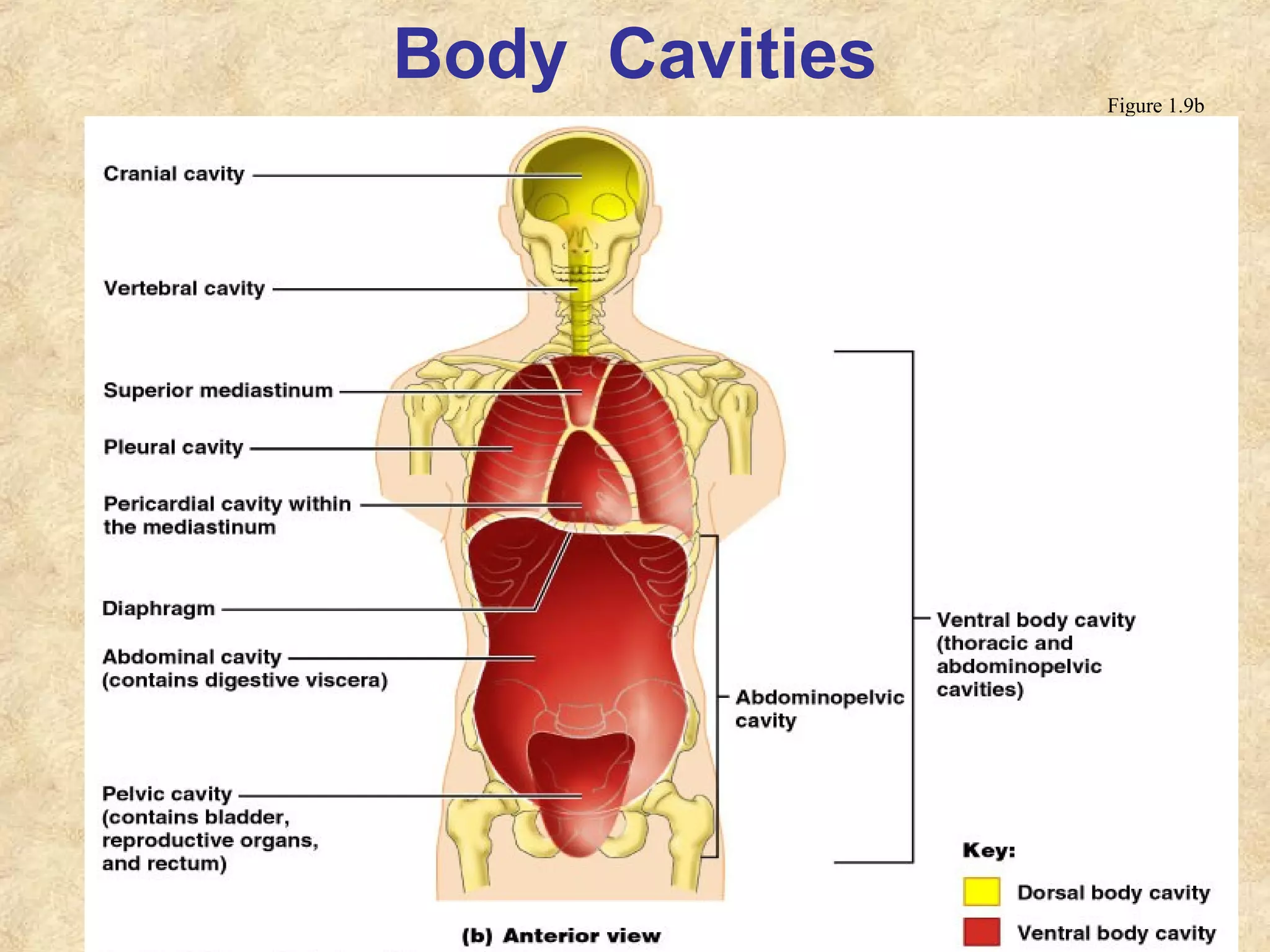
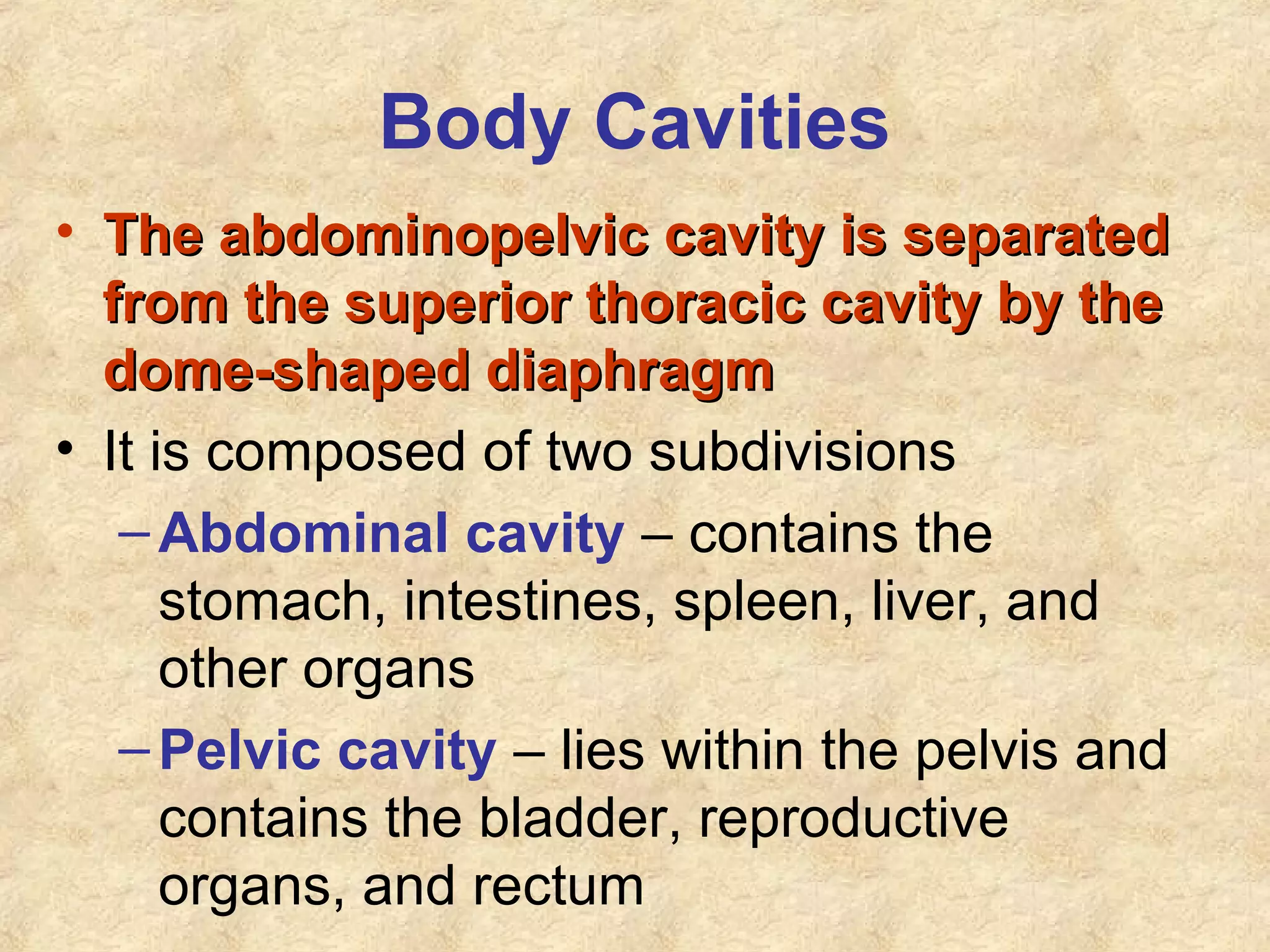
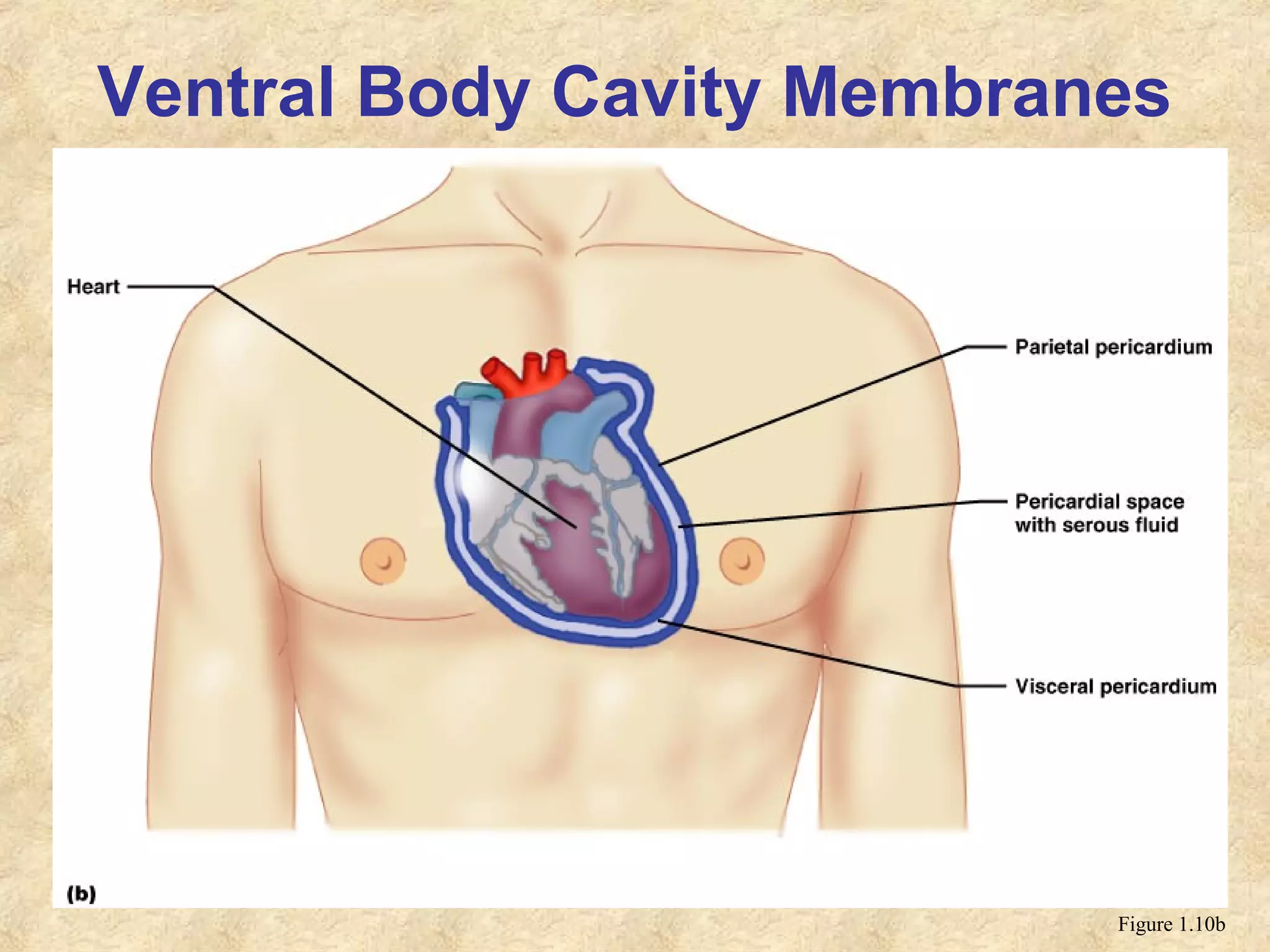
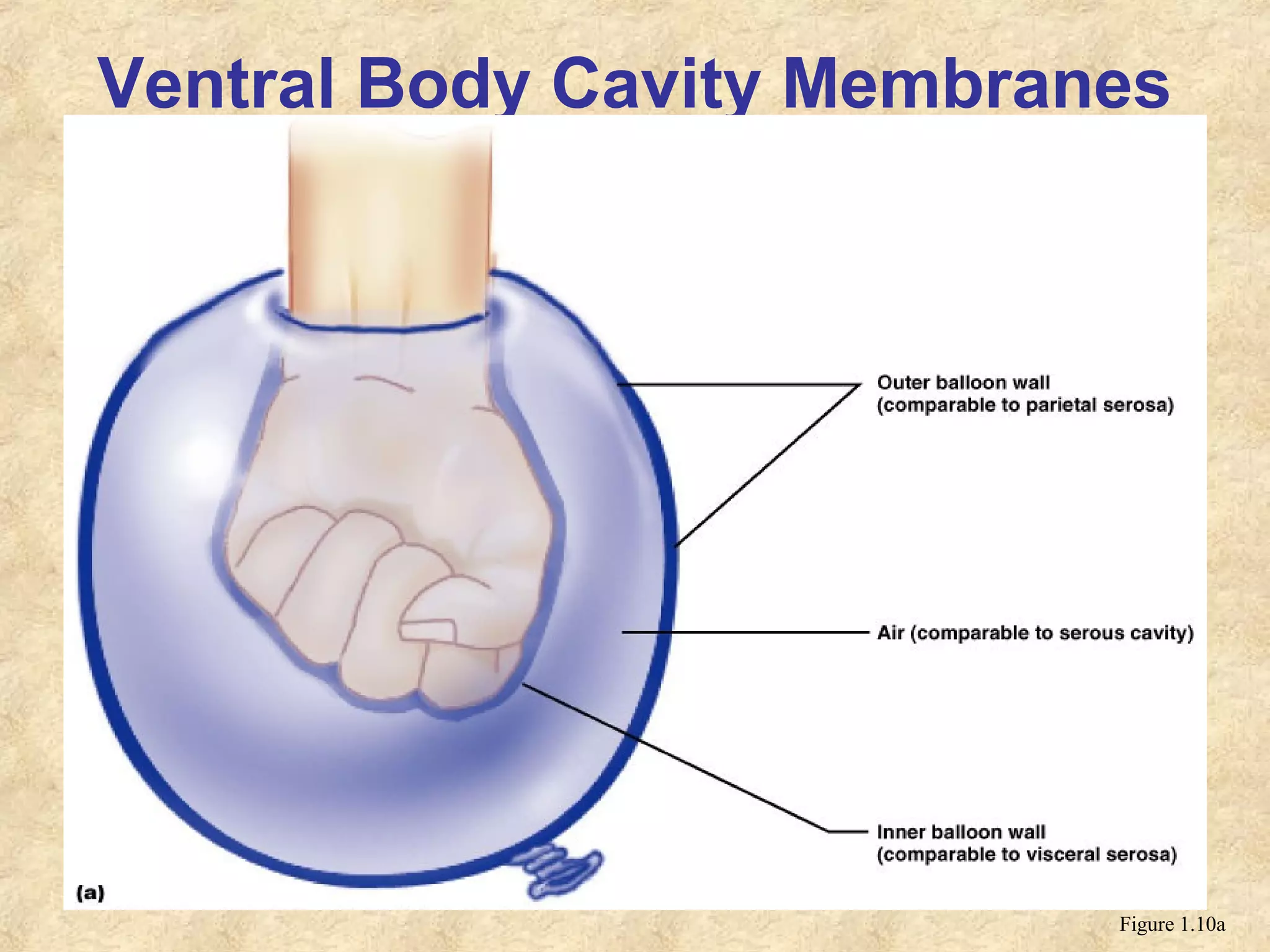
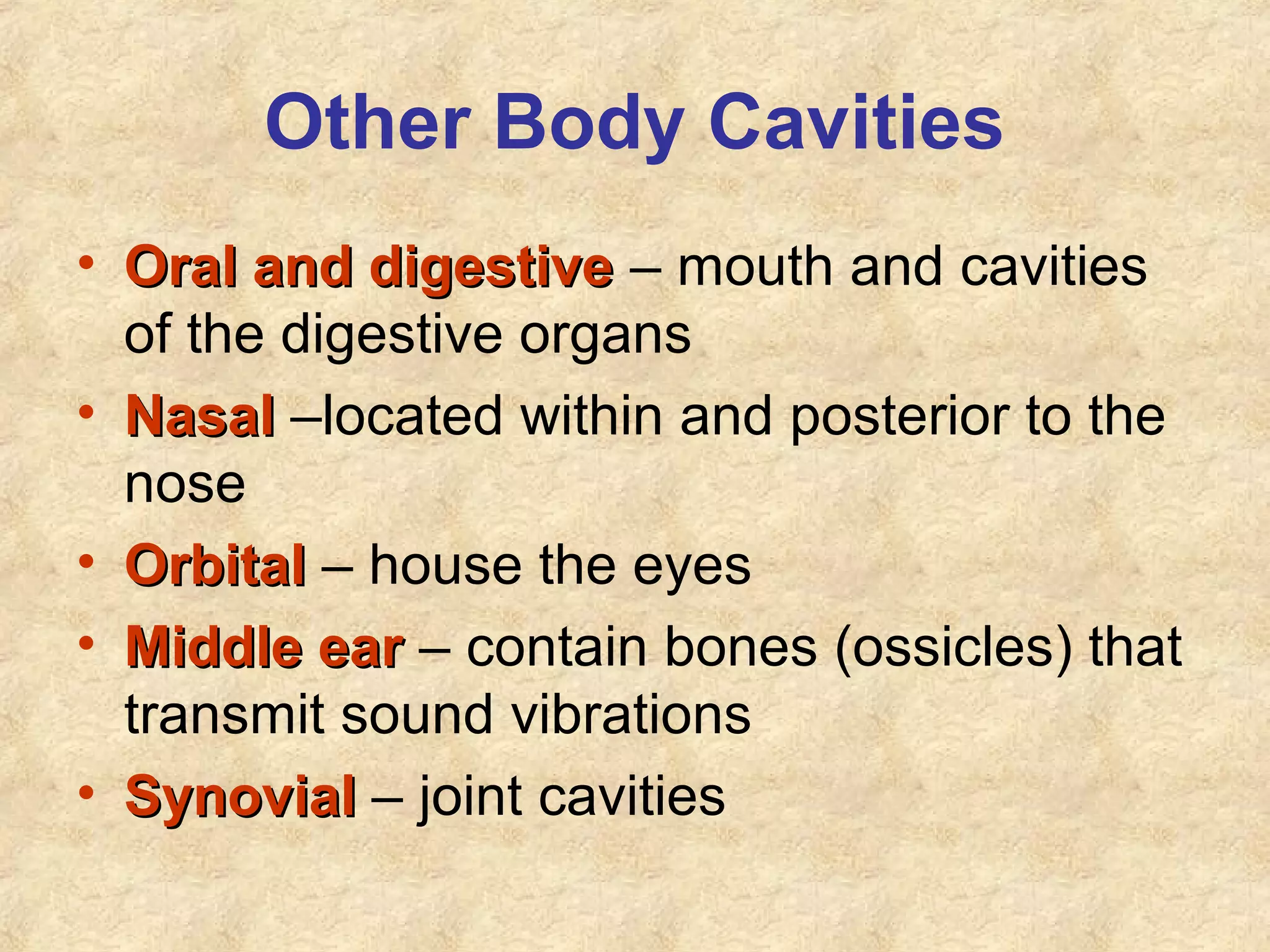
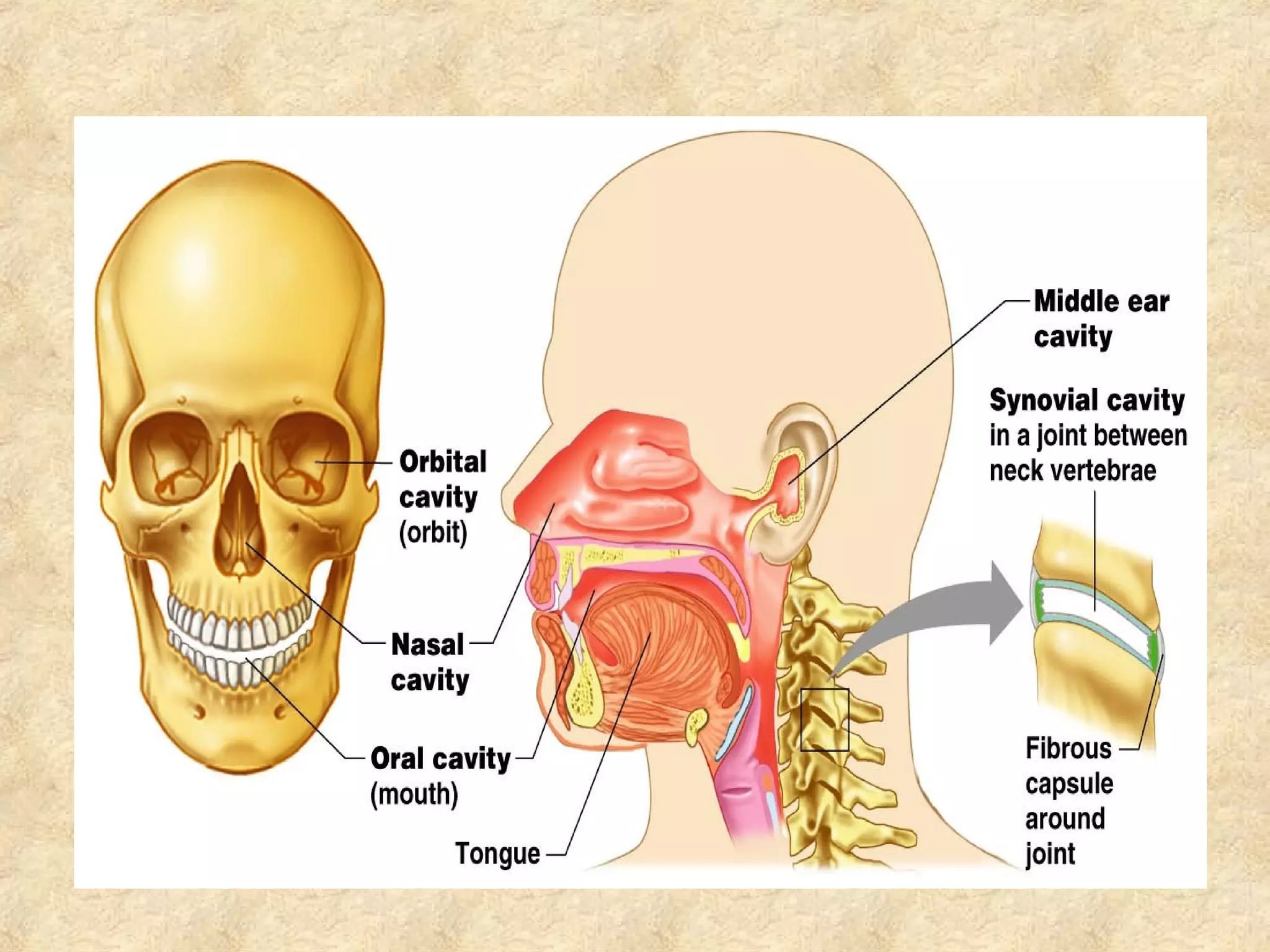
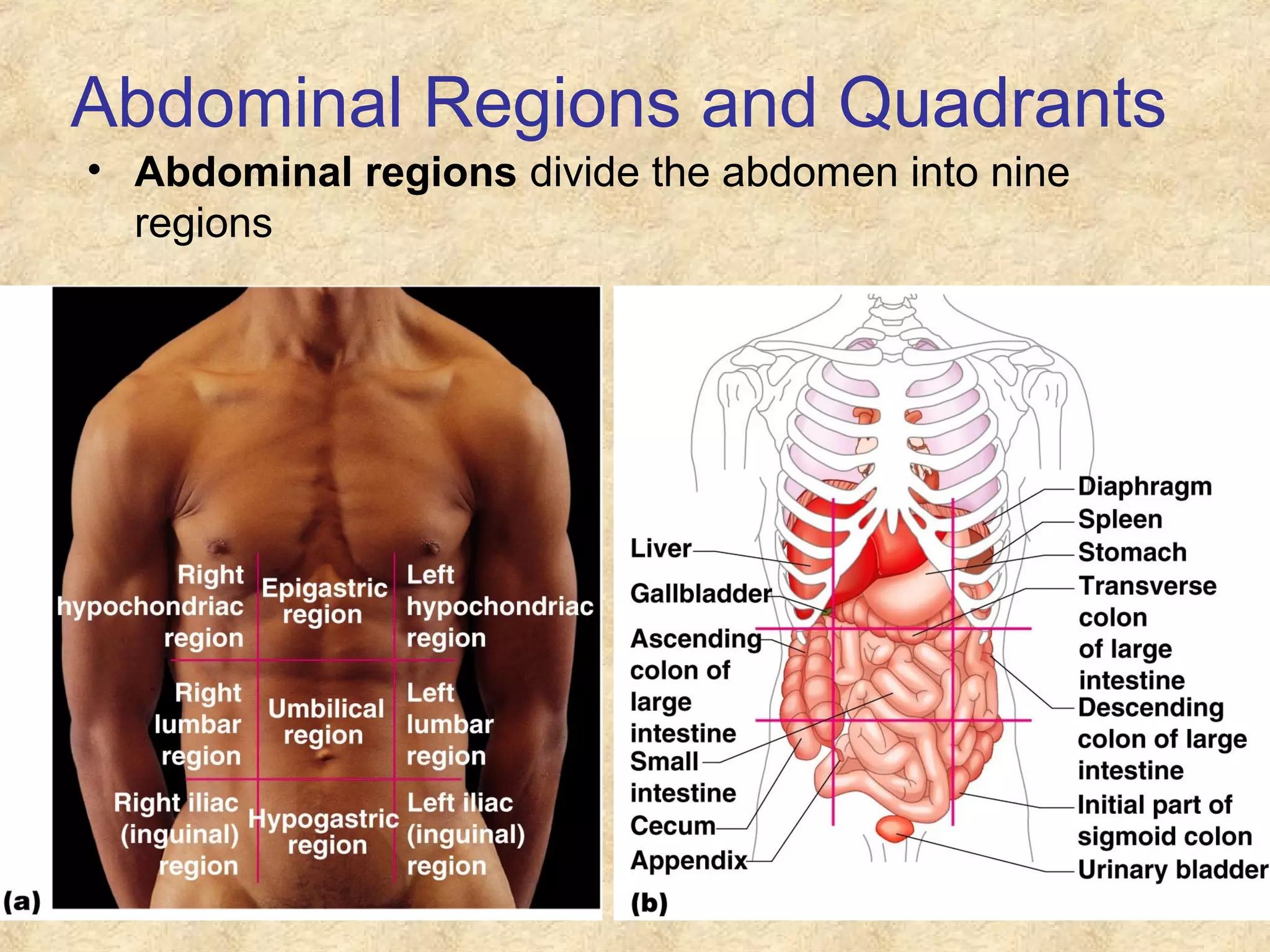
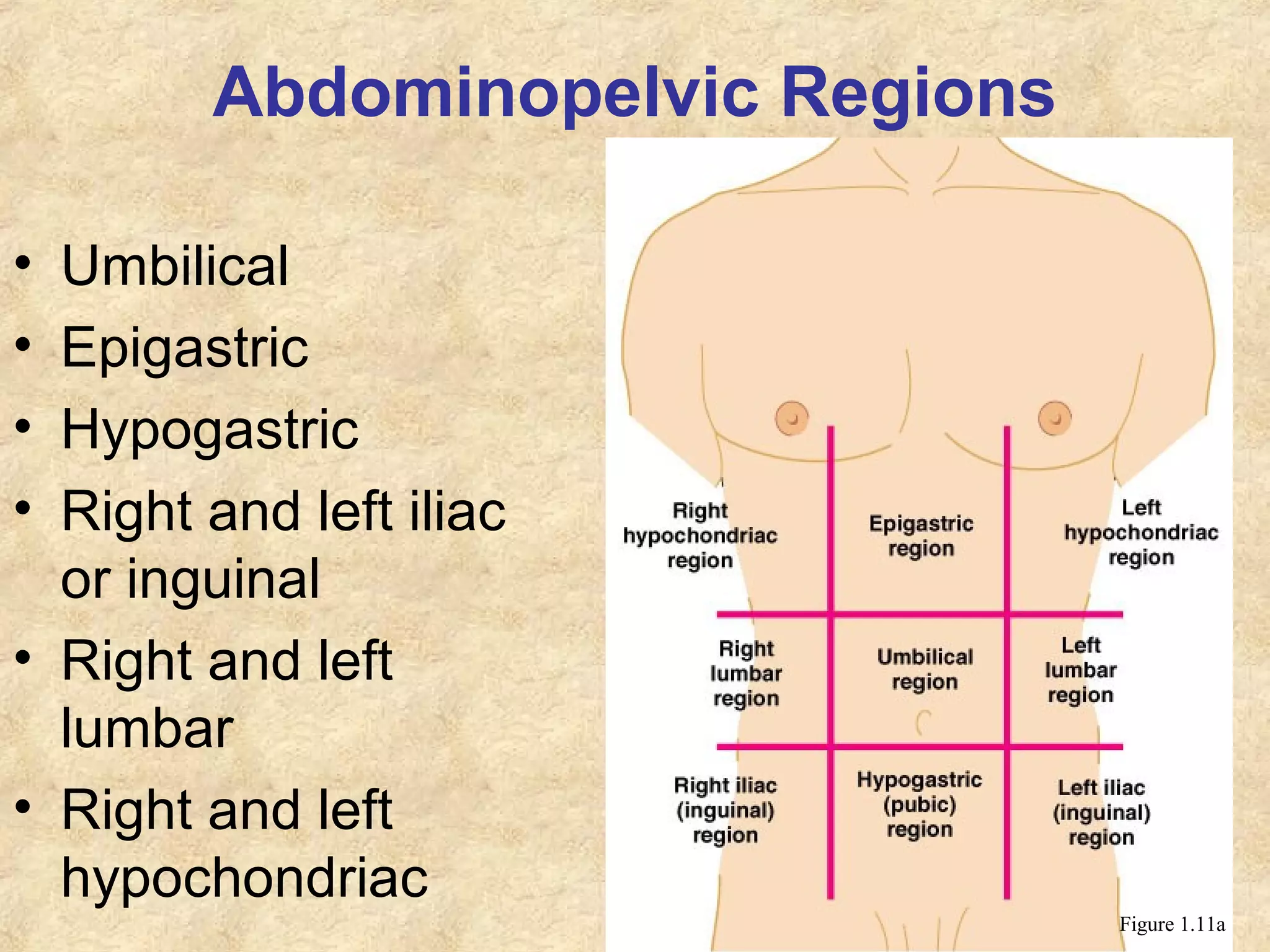
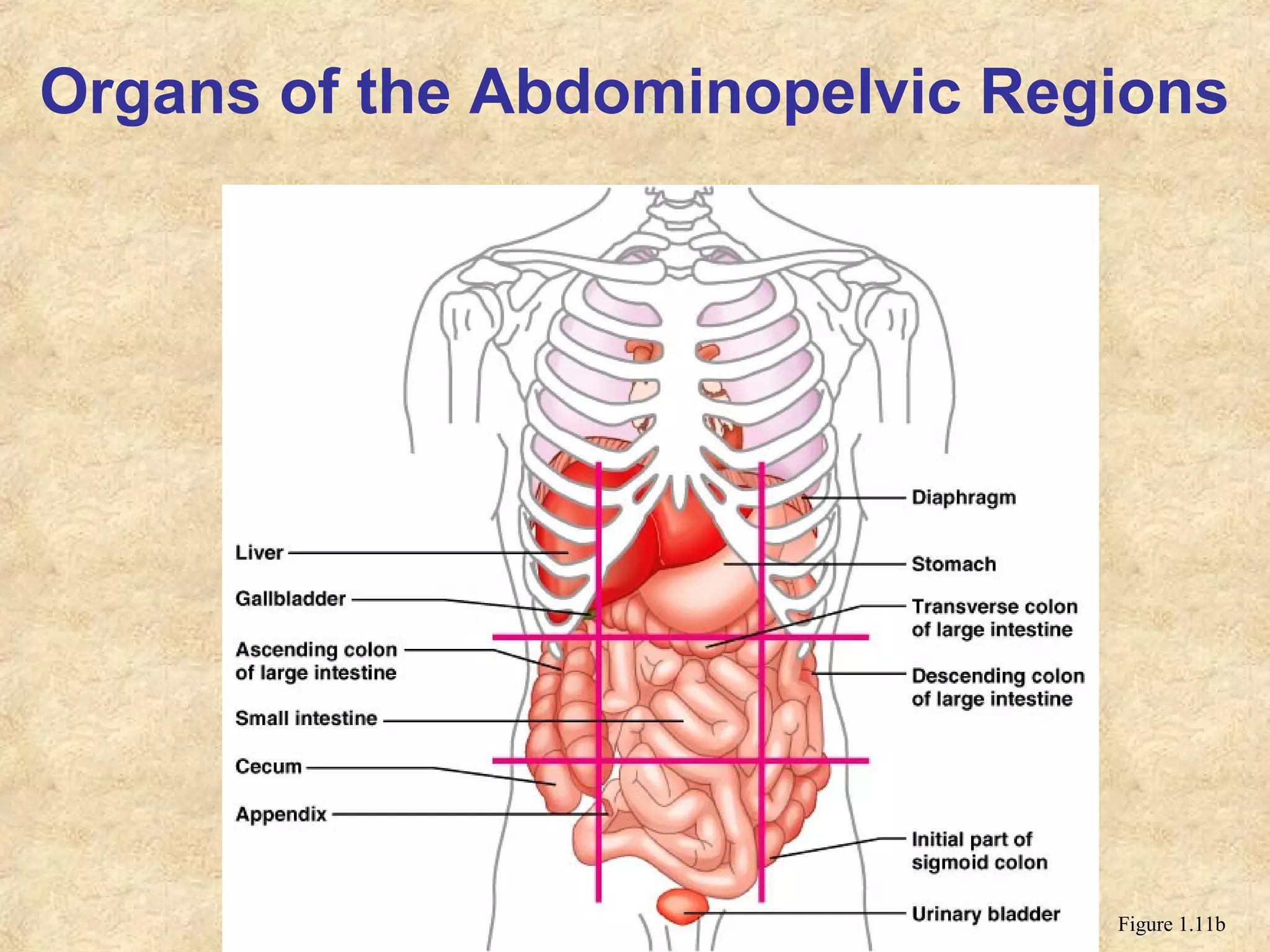
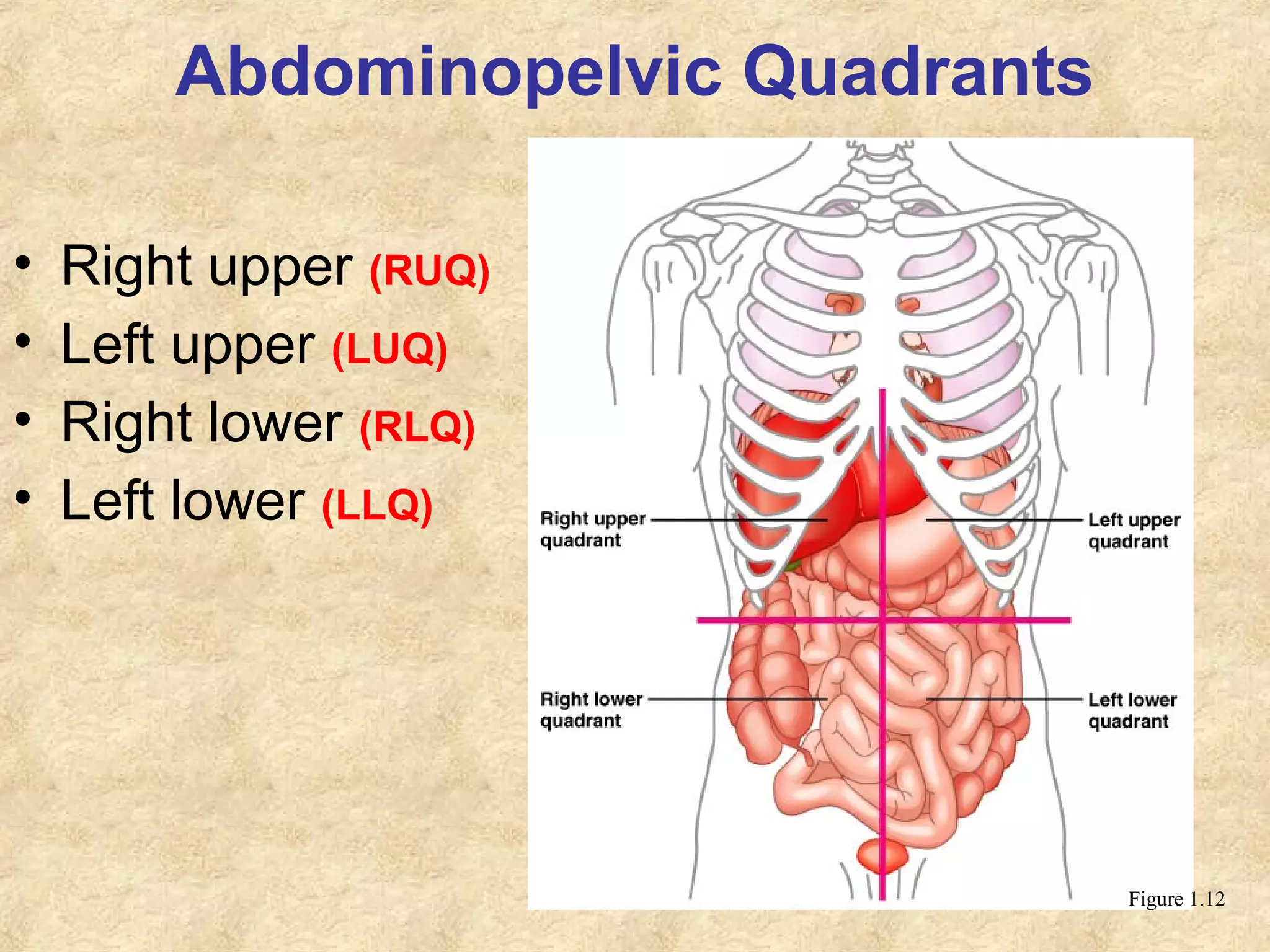
Anatomy is the study of the body's structure, while physiology is the study of its functions. The human body is composed of chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and organism levels of organization. The main body cavities are the dorsal cavity containing the brain and spinal cord, and the ventral cavity housing the internal organs and divided into the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic cavities.