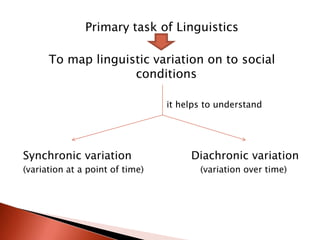
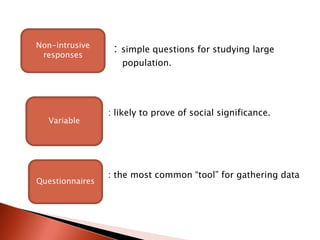
Sociolinguistics studies the relationship between language and society. It helps map linguistic variation onto social conditions and understand language change over time and variation at a single point in time. Sociolinguists study how language systems are used in living speech communities as opposed to the autonomous structure of language. The field can be divided into the micro-level which explores how society influences an individual's language, and the macro-level which focuses more on the role of language in society as a whole. Sociolinguists look for evidence of socially accepted rules that account for speech variation and aim to overcome the observer's paradox by eliciting examples of speech through interviews rather than clandestine recording.