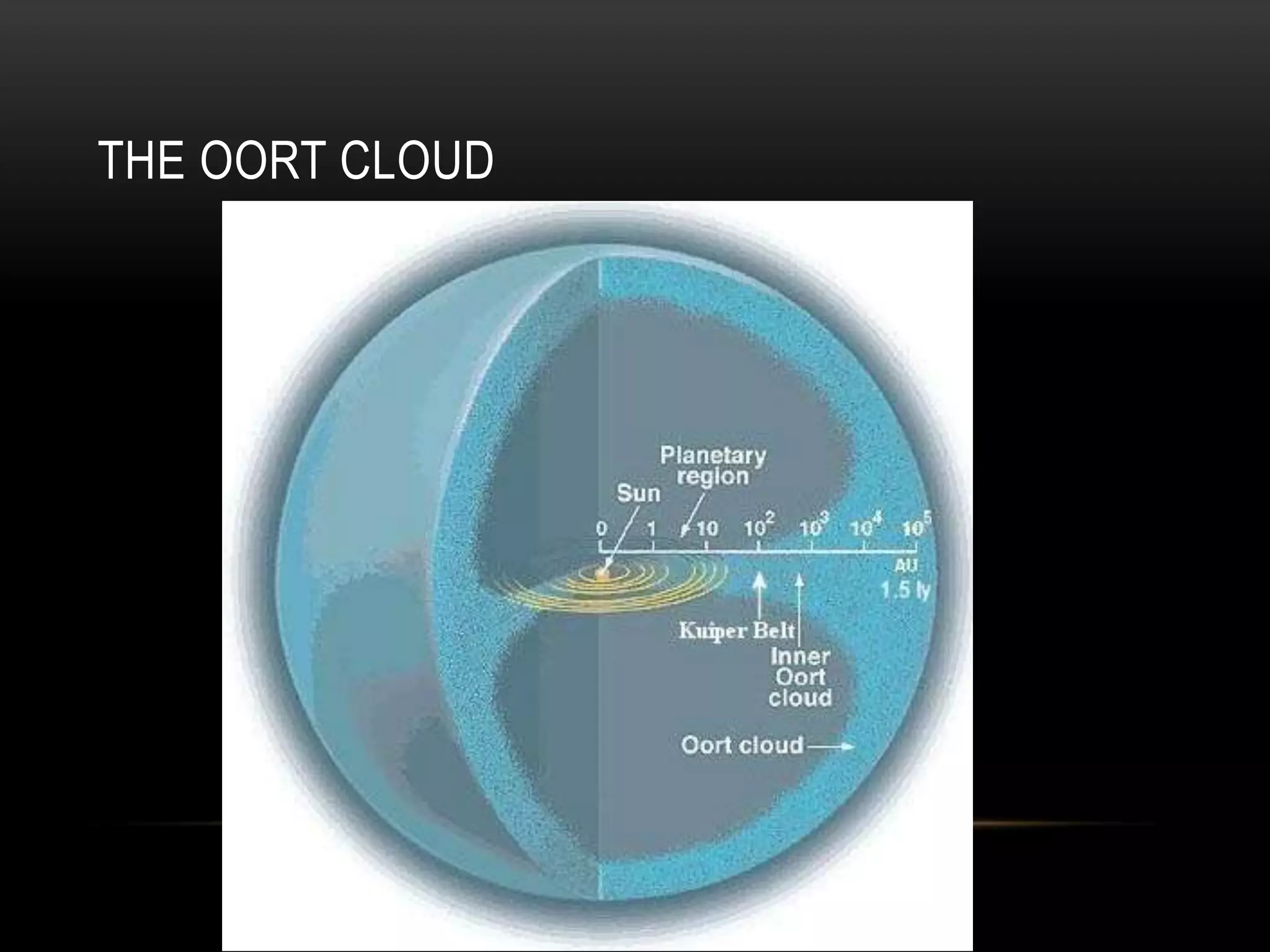
The Oort Cloud is a theorized spherical cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals believed to surround the Sun to as far as halfway to the nearest star. It is thought to be the source of long-period comets. The Kuiper Belt is a disc-shaped region beyond Neptune's orbit populated by numerous icy bodies and extending from 30 to 50 AU from the Sun, including short-period comets and objects like Pluto. New Horizons is an unmanned spacecraft on a mission to conduct the first flyby and study of Pluto and to fly by and study one or more other Kuiper Belt objects after performing a flyby of Jupiter in 2007.