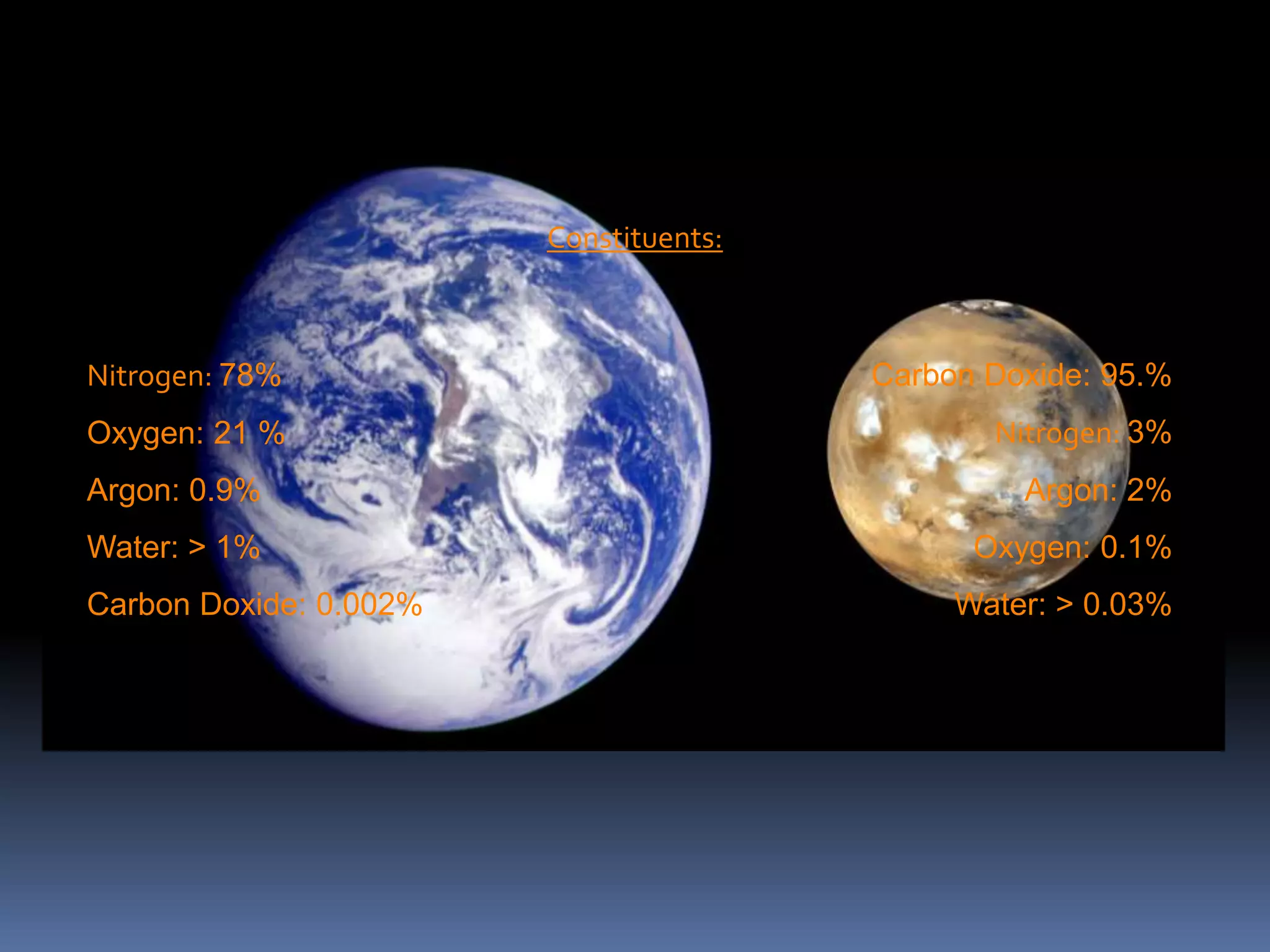
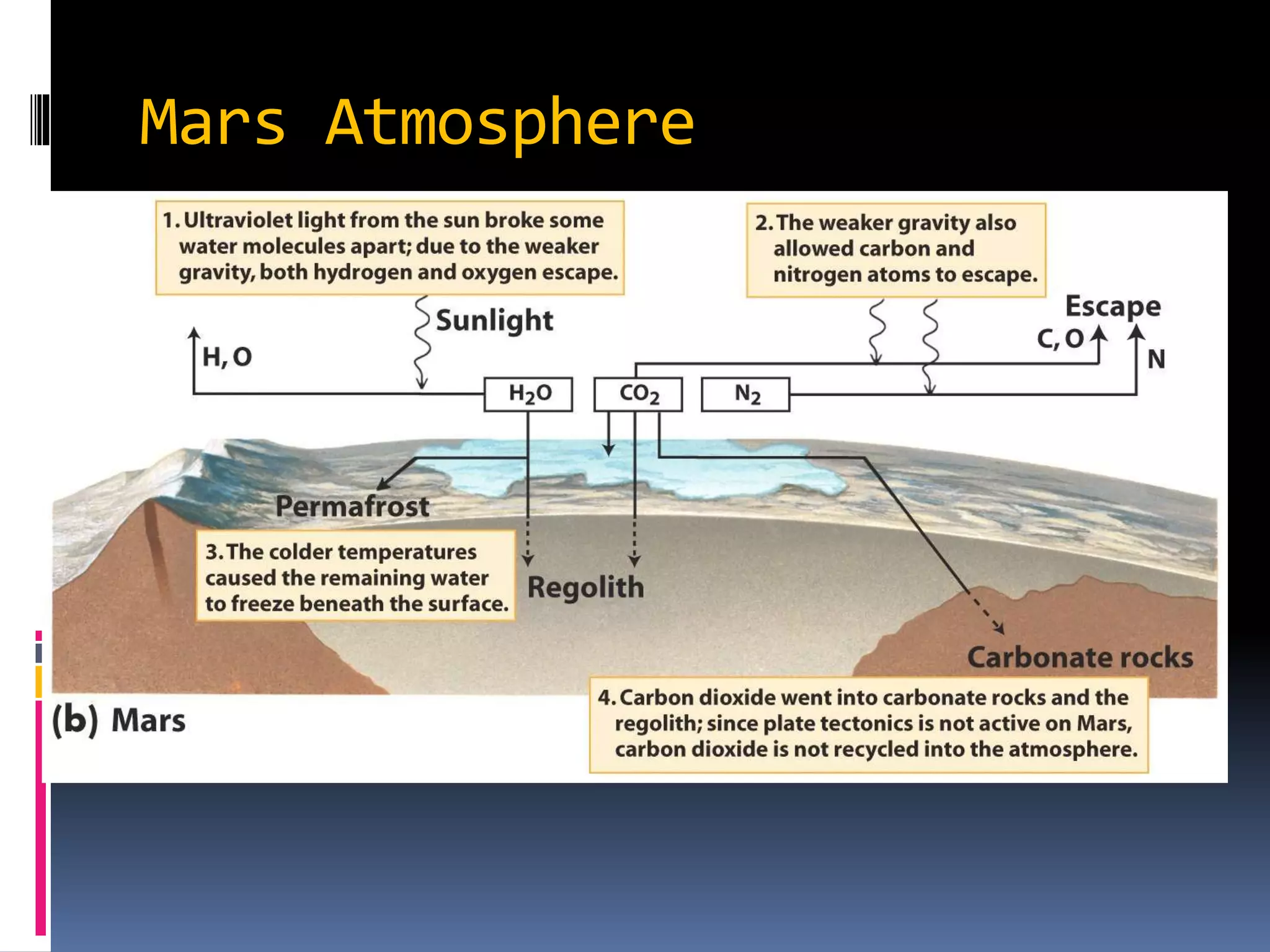
Mars is nicknamed the Red Planet due to the iron oxide in its soil. It has a thin atmosphere composed primarily of carbon dioxide. Mars is about half the diameter of Earth and has a day that is only slightly longer than an Earth day. It has two small moons, Phobos and Deimos, that are irregularly shaped and may be captured asteroids. The largest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons, and deepest canyon, Valles Marineris, are both located on Mars. Water ice is found at the poles and it is possible that liquid water exists underground. Seasonal dust storms can blanket the entire planet. Mars is considered Earth's closest planetary neighbor and is sometimes called the "Red Planet" or