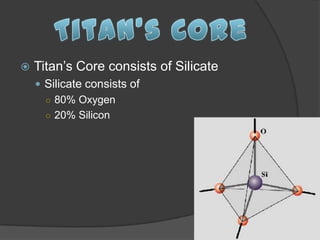
The document summarizes information about the Moon, Titan, and Phobos. It describes the layers that make up each celestial body, including their composition. The Moon has a crust, mantle, outer core, liquid core, and solid inner core composed of elements like iron and oxygen. Titan likely has a thick atmosphere, outer layer of liquid hydrogen, then possible layers of liquid water, high-pressure ice, and a silicate core. Phobos is composed of carbonaceous rock and has the prominent Stickney crater on its dusty surface.