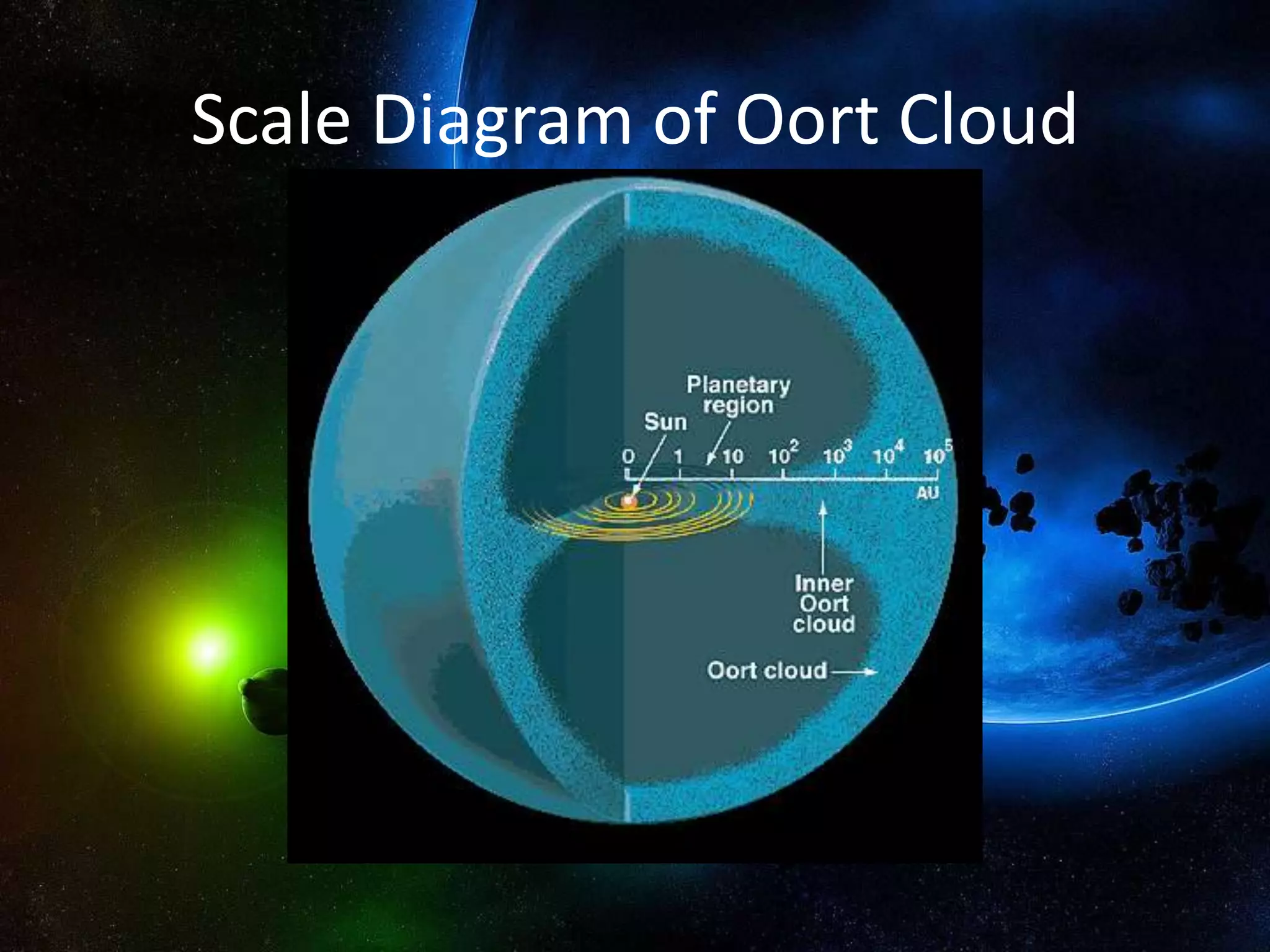
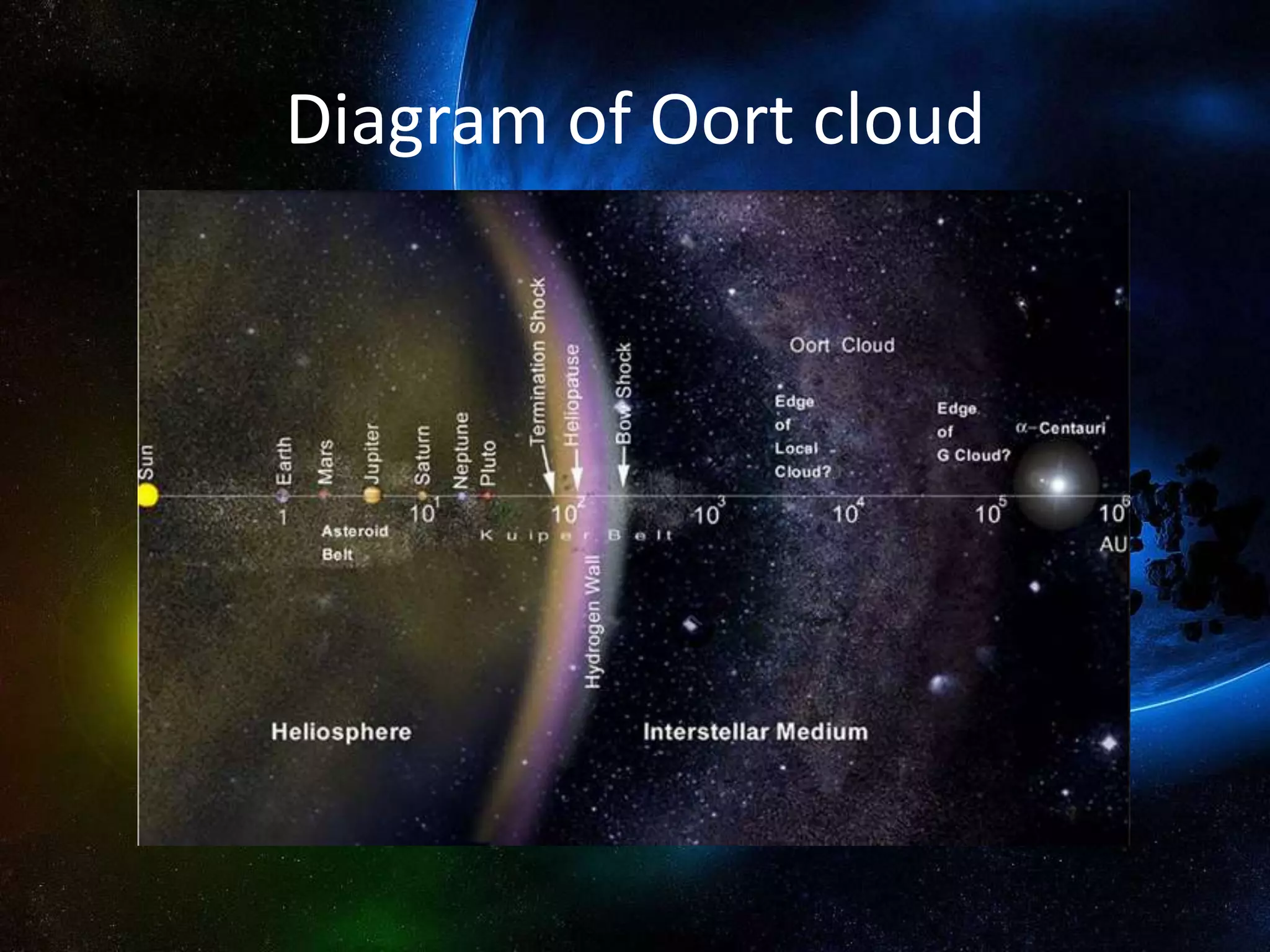
The Oort Cloud is a spherical cloud of predominantly icy objects that is thought to be the source of long-period comets. It is located at the outer edge of the Solar System, beginning around 5,000 AU from the Sun and extending up to 2.1 light years. It is composed mainly of comets and a few rocky objects and is estimated to have a mass 40 times that of Earth. The Oort Cloud was first theorized by Jan Oort in 1950.