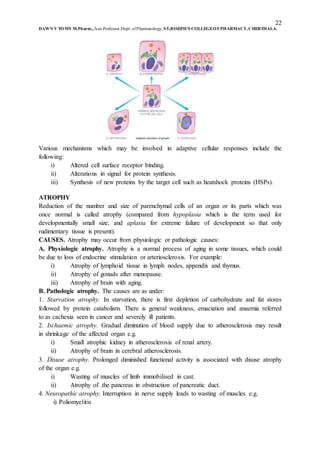
The document discusses cell injury and its causes. It defines cell injury as damage to cells from changes in their internal or external environment. There are two main types of causes of cell injury - genetic and acquired. Acquired causes are more common and include hypoxia/ischemia, physical agents, chemicals/drugs, microbes, immunological factors, nutritional imbalances, aging, and psychological stress. The severity and reversibility of cell injury depends on factors like the injurious agent, duration of exposure, cell type, and underlying intracellular changes. Reversible cell injury from short-term hypoxia/ischemia involves decreased ATP production, lactic acidosis, and damage to membrane pumps causing swelling.