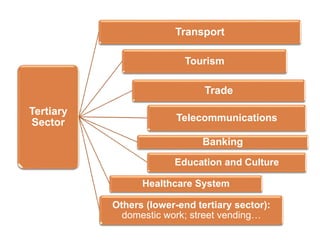
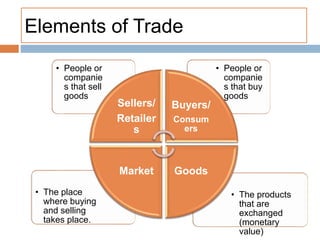
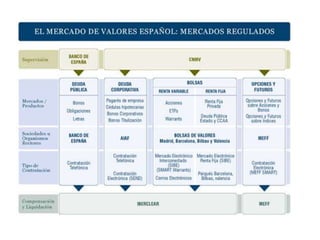
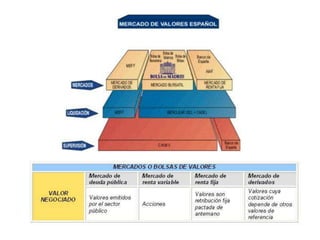
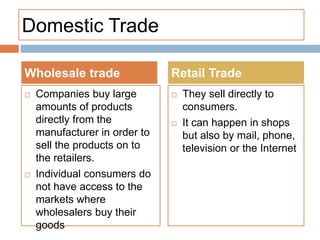
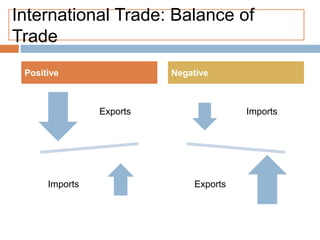
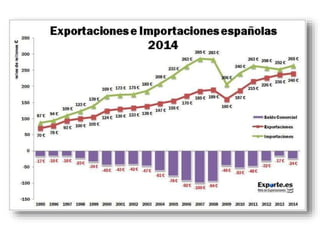
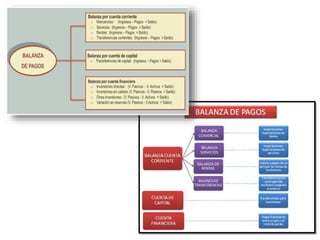
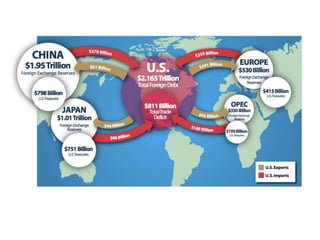
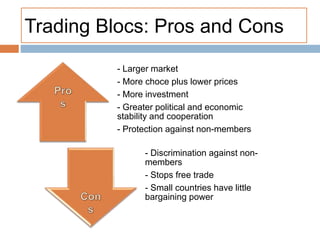
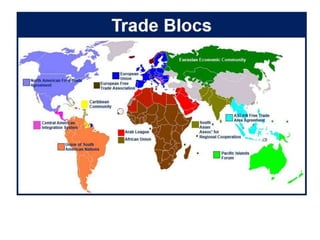
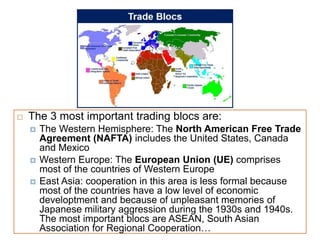
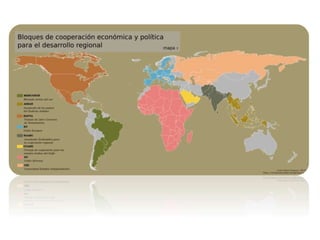
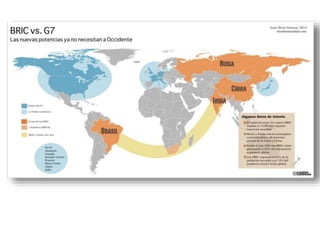
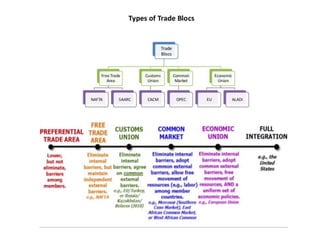
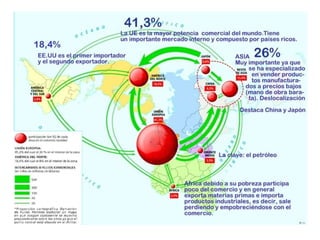
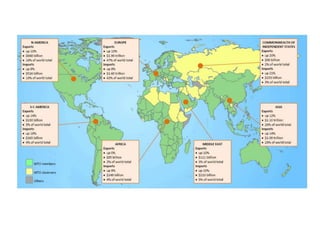
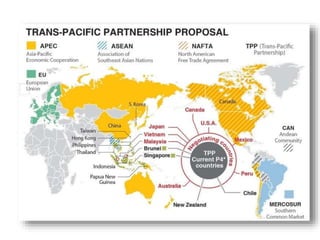
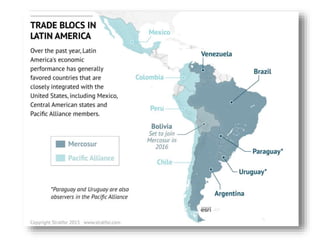
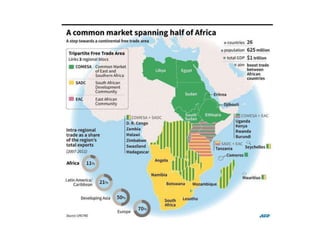
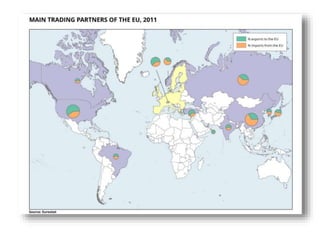
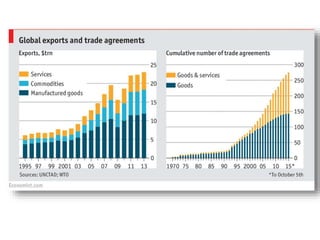
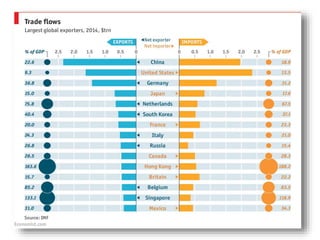
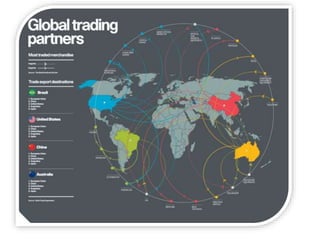
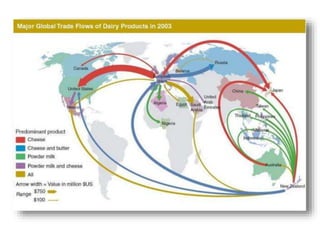
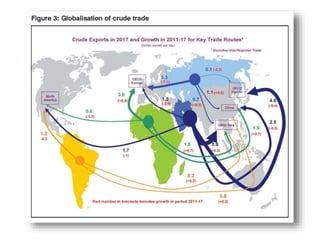
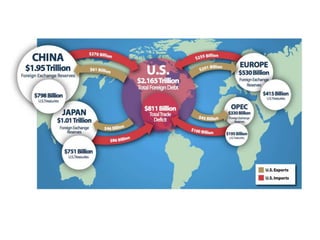
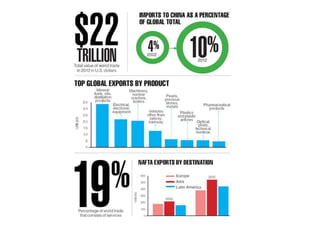
The document discusses the tertiary sector, emphasizing its services, including transport, tourism, trade, telecommunications, banking, education, and healthcare. It contrasts the tertiary sector with the quaternary sector and highlights the characteristics and types of trade, including domestic and international trade. Additionally, it outlines trading blocs, their benefits, drawbacks, and key examples like NAFTA and the EU.