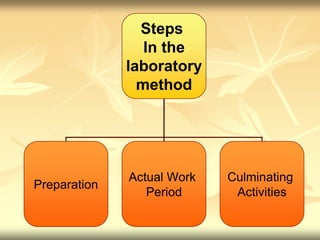
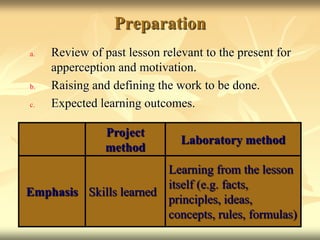
The laboratory method of teaching utilizes hands-on learning with real objects and data to give students a better understanding of course material. It involves defining a problem, gathering information through observation and experimentation, forming a hypothesis, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing conclusions. The key aspects are learning by doing, using reality instead of symbols, and developing scientific skills like observation, reasoning, and applying the scientific method. Some advantages are that students directly engage with materials, better develop problem-solving abilities, and gain experience that can translate to real-life situations. However, it can be more time-consuming and resource-intensive than other methods of instruction.