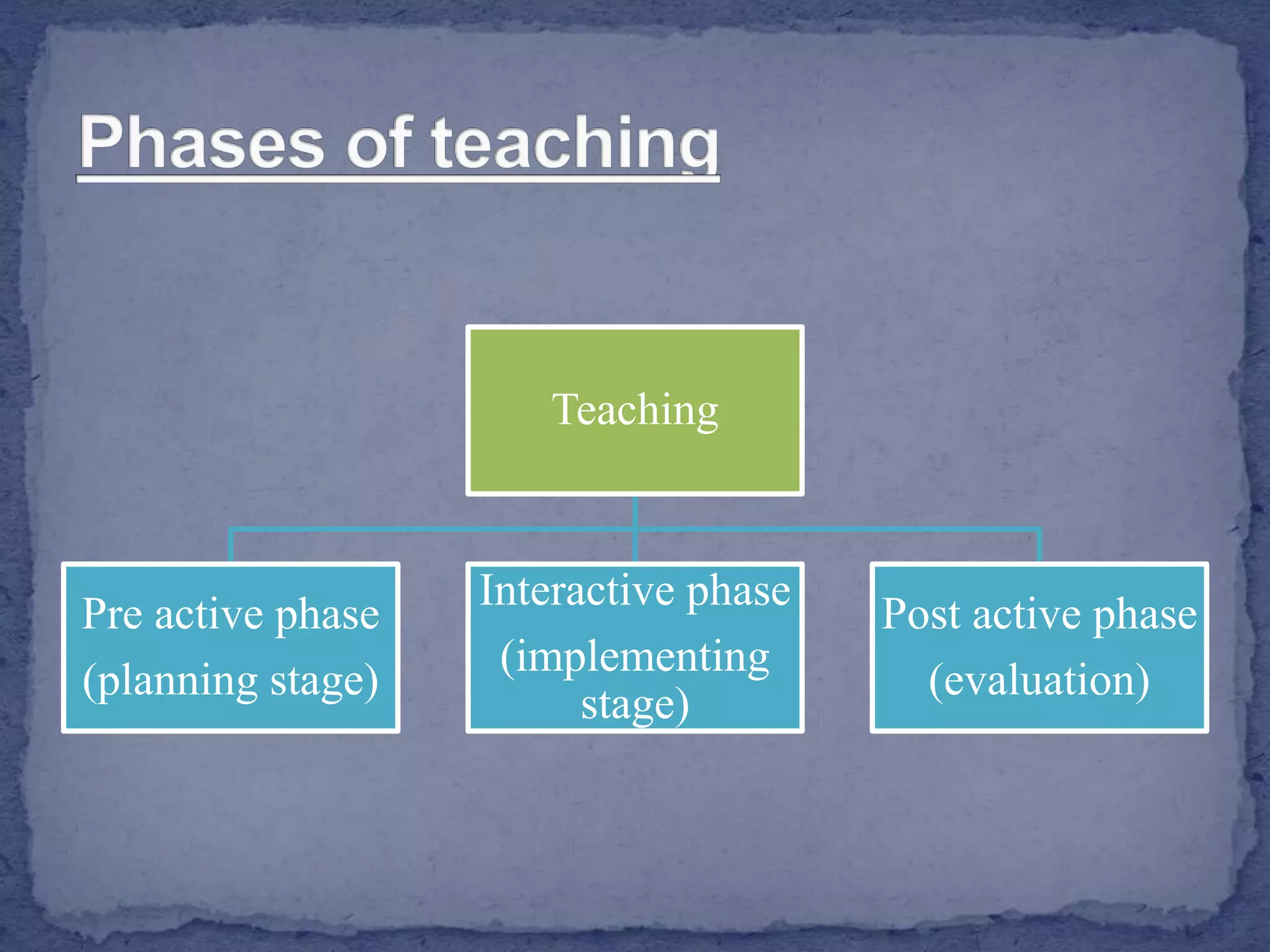
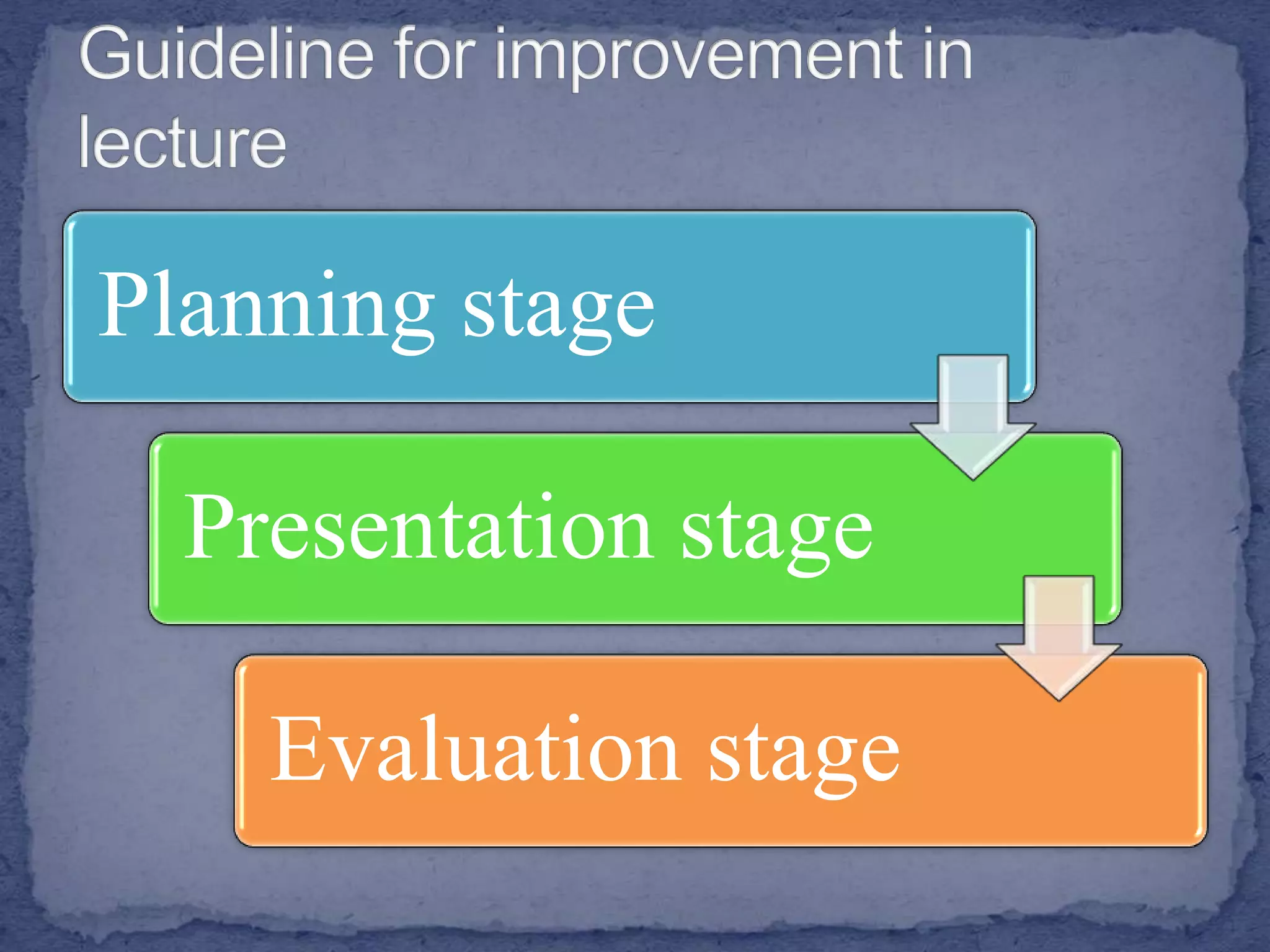
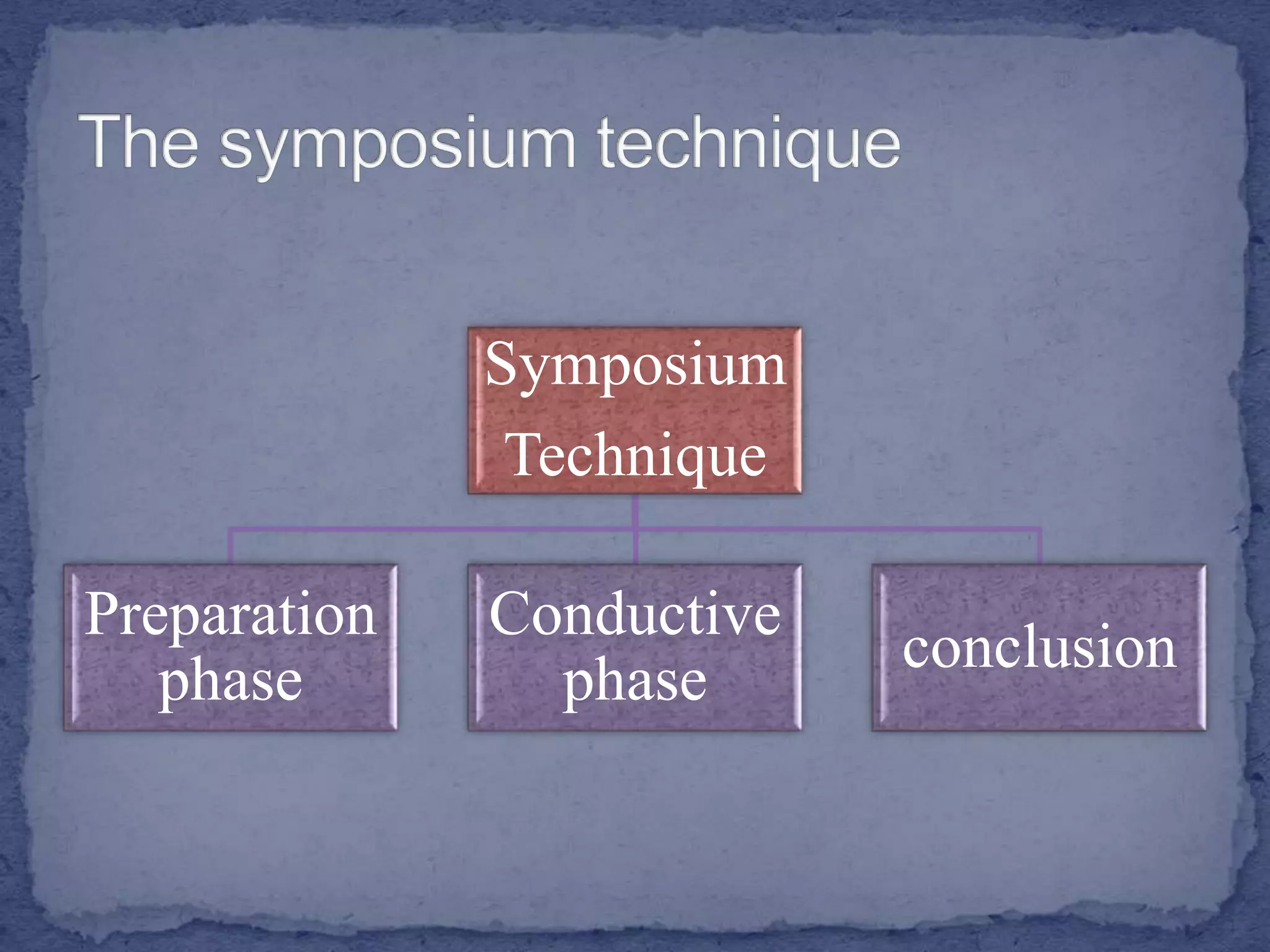
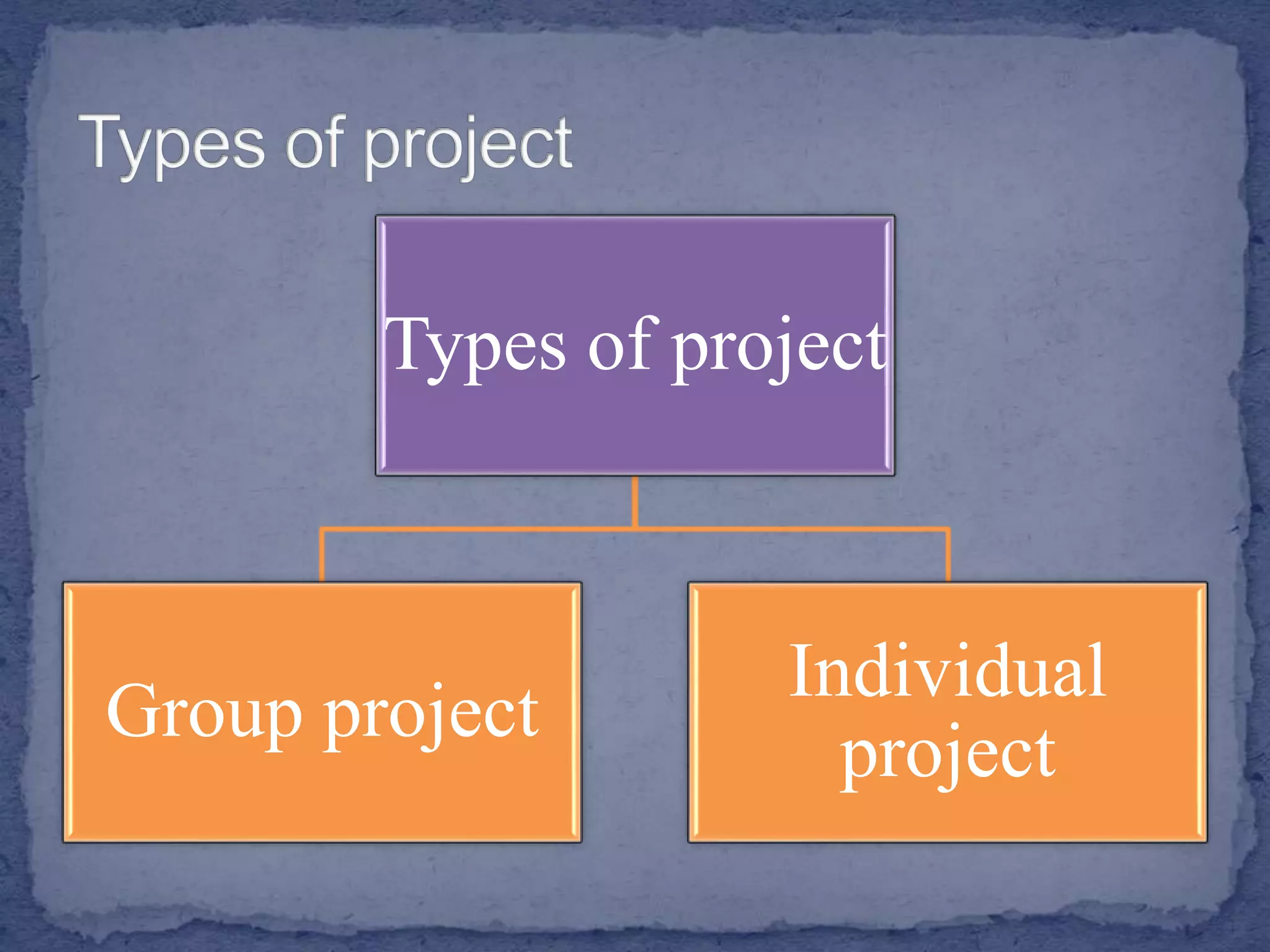
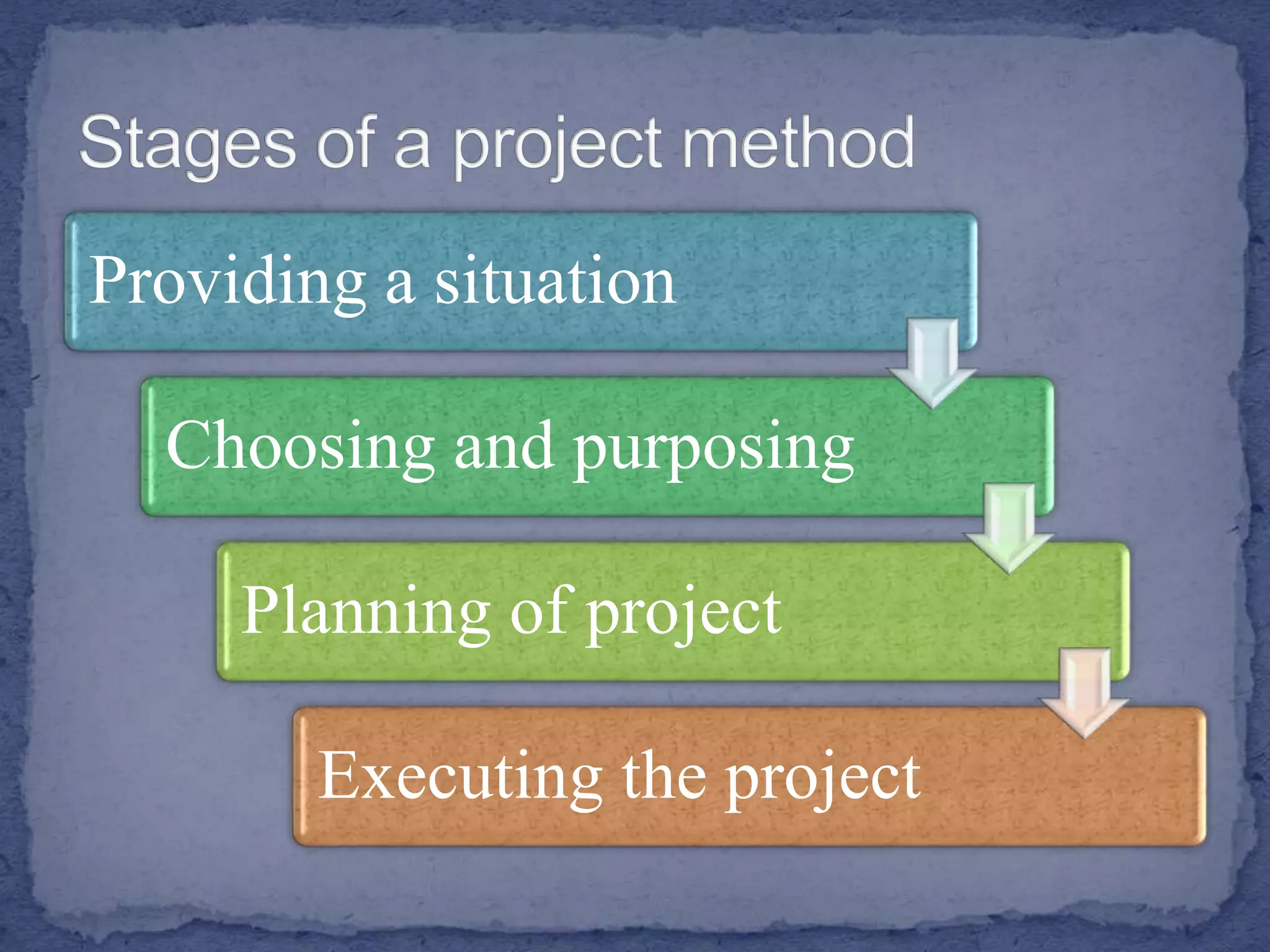
The document discusses various teaching and learning methods. It defines teaching as imparting knowledge or skills, while learning refers to acquiring new information. Some key teaching methods discussed include lectures, demonstrations, discussions, seminars, and microteaching. Lectures allow covering a large group but keep students passive. Demonstrations develop observation skills but have limited student participation. Discussions promote problem solving and peer learning but can be time consuming. Seminars stimulate thinking but require extensive preparation. Microteaching simplifies teaching in a controlled environment to improve skills through feedback. The document also examines learning processes and factors that influence effective instruction.