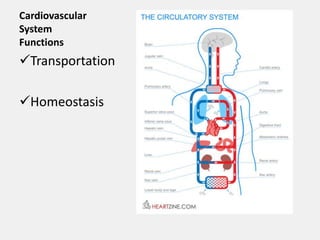
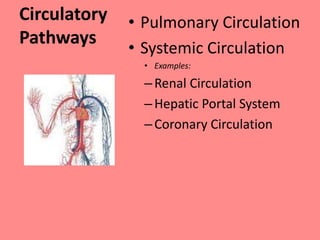
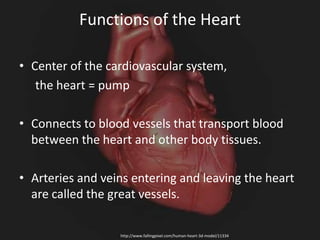
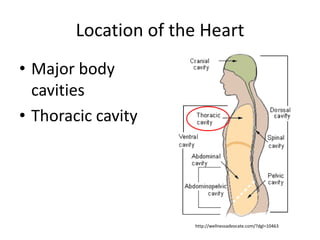
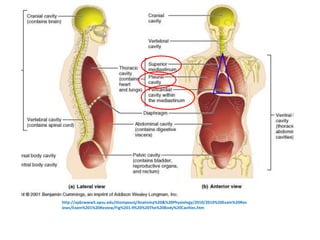
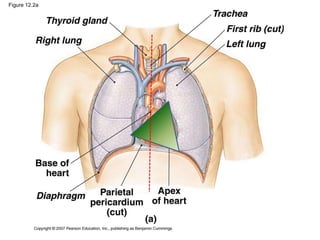
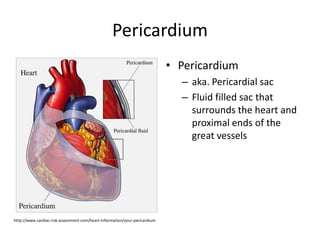
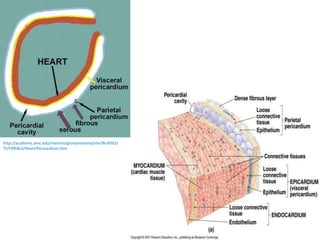
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and blood vessels, and functions to transport blood throughout the body and maintain homeostasis. The heart acts as a pump located in the thoracic cavity, surrounded by the pericardium. It has four chambers and ensures unidirectional blood flow through the pulmonary and systemic circulations, developing blood pressure through cycles of contraction and relaxation. Arteries and veins connect the heart to other tissues to circulate oxygenated blood.