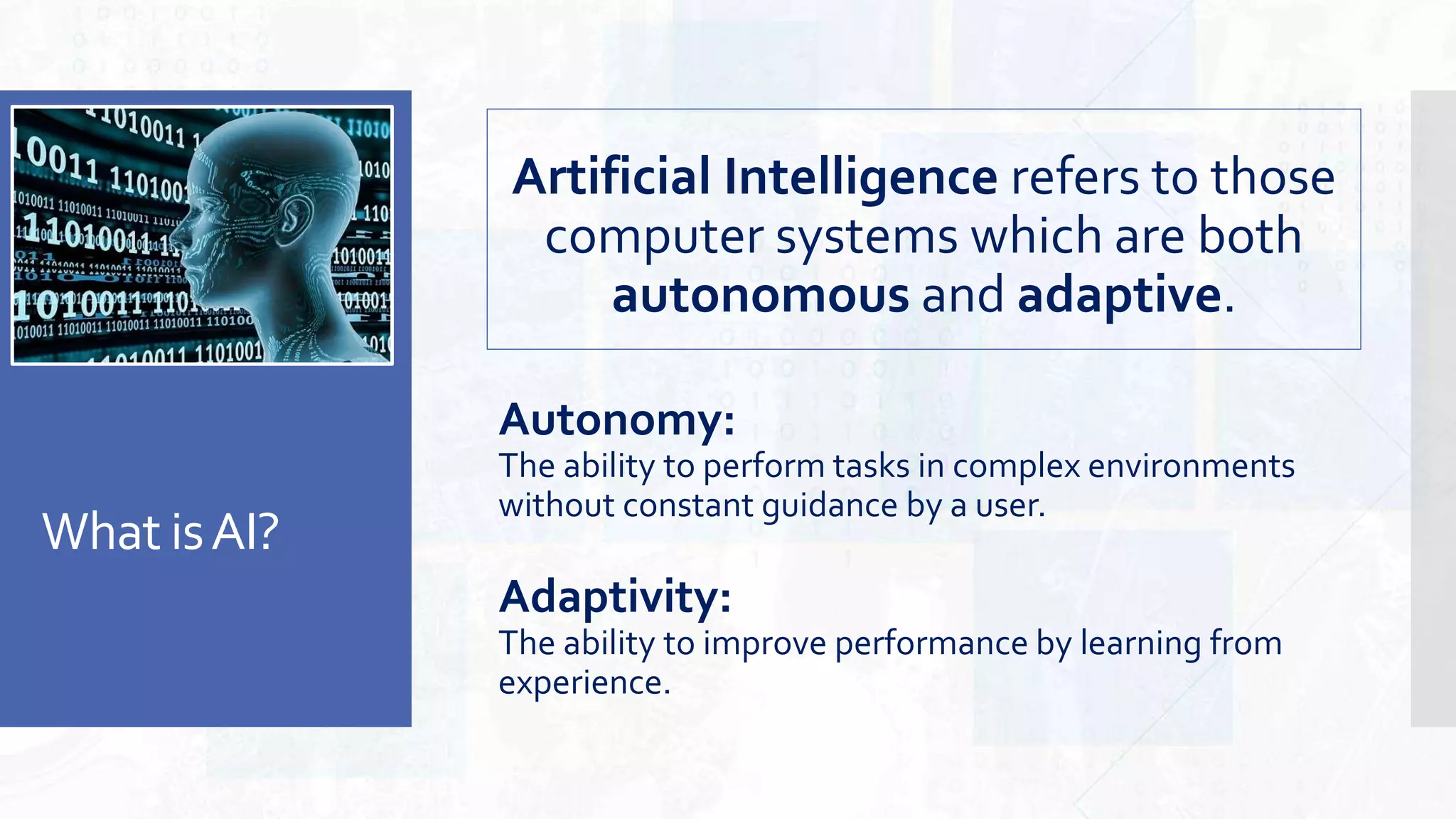
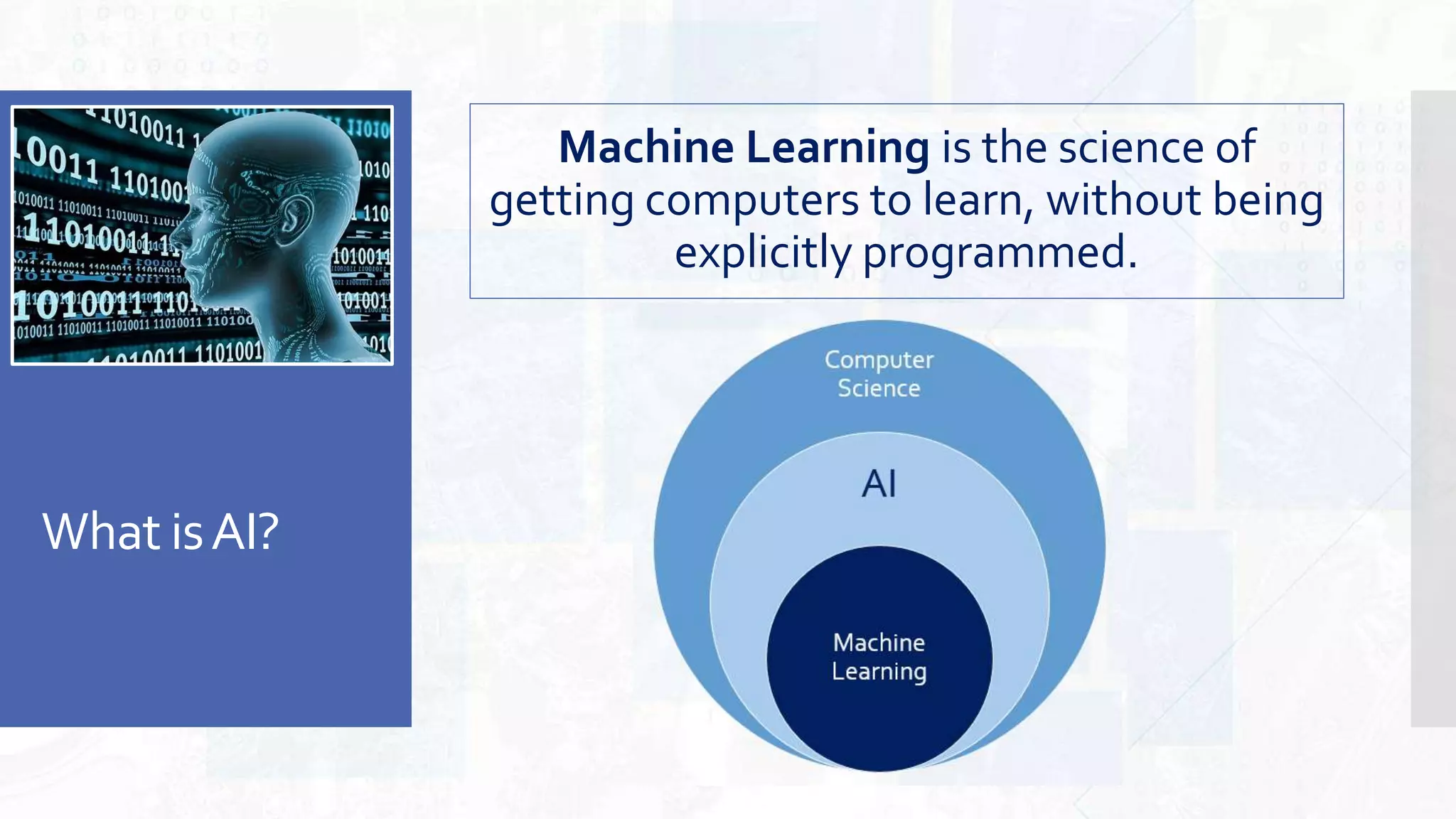
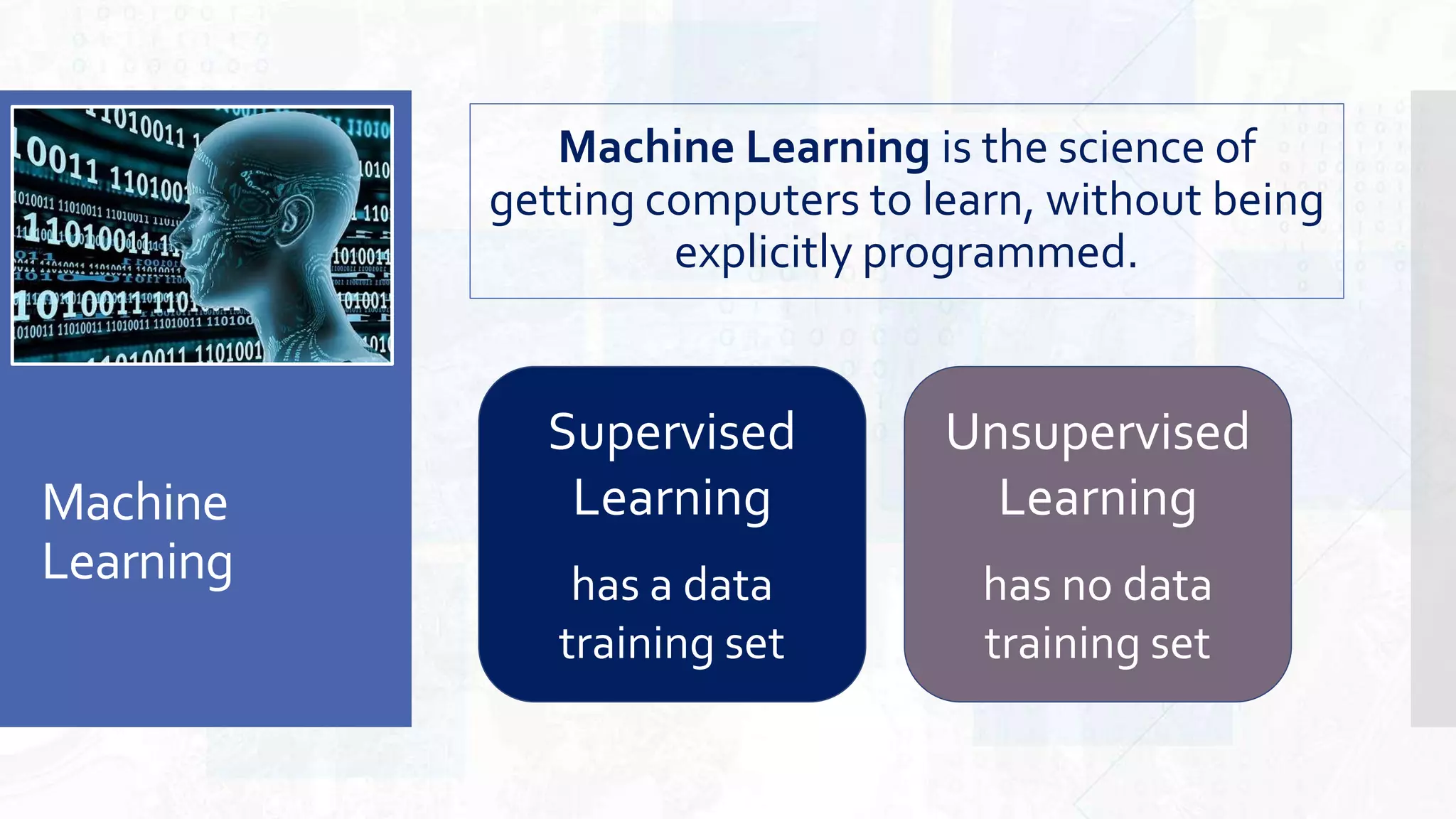
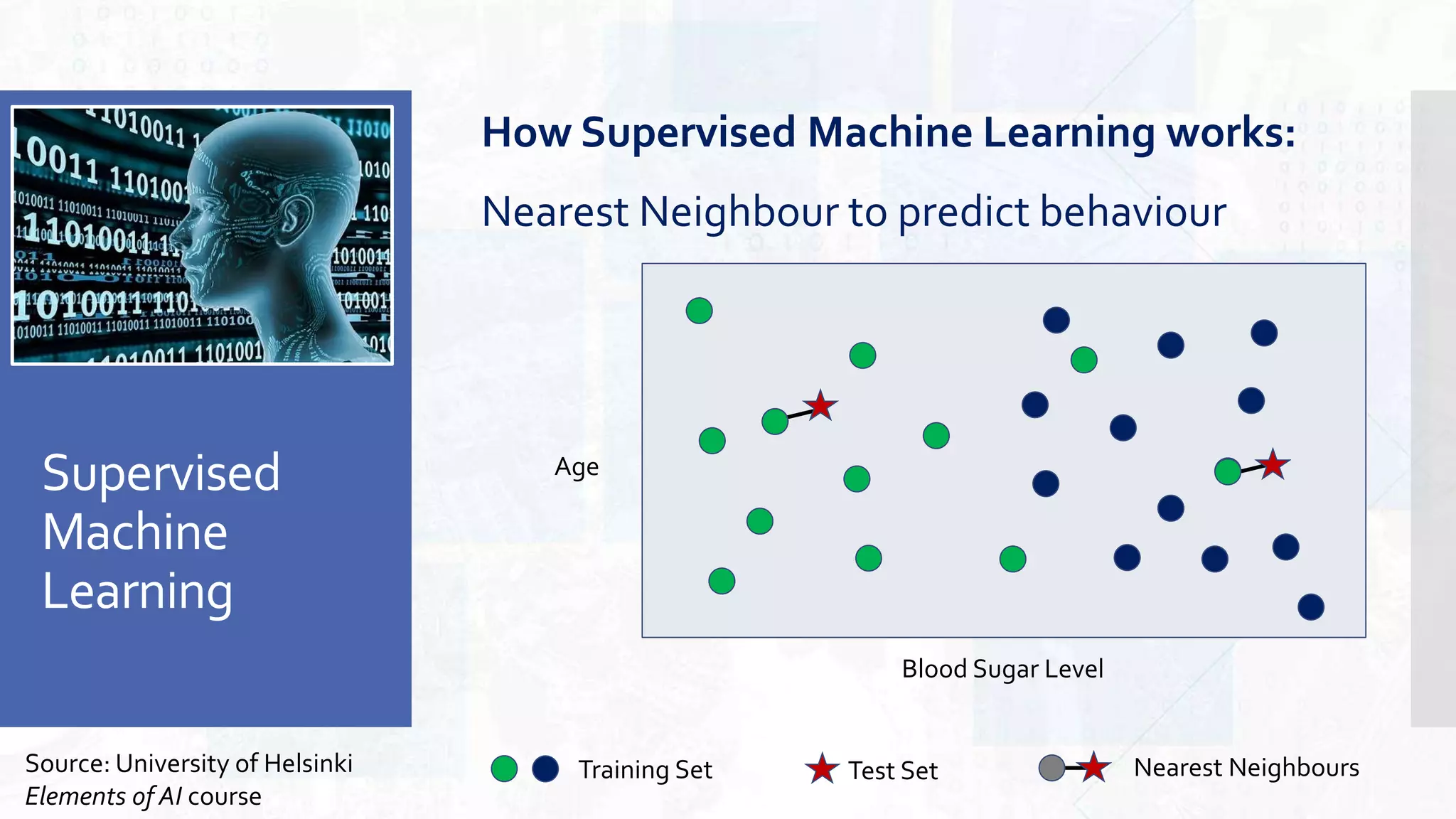
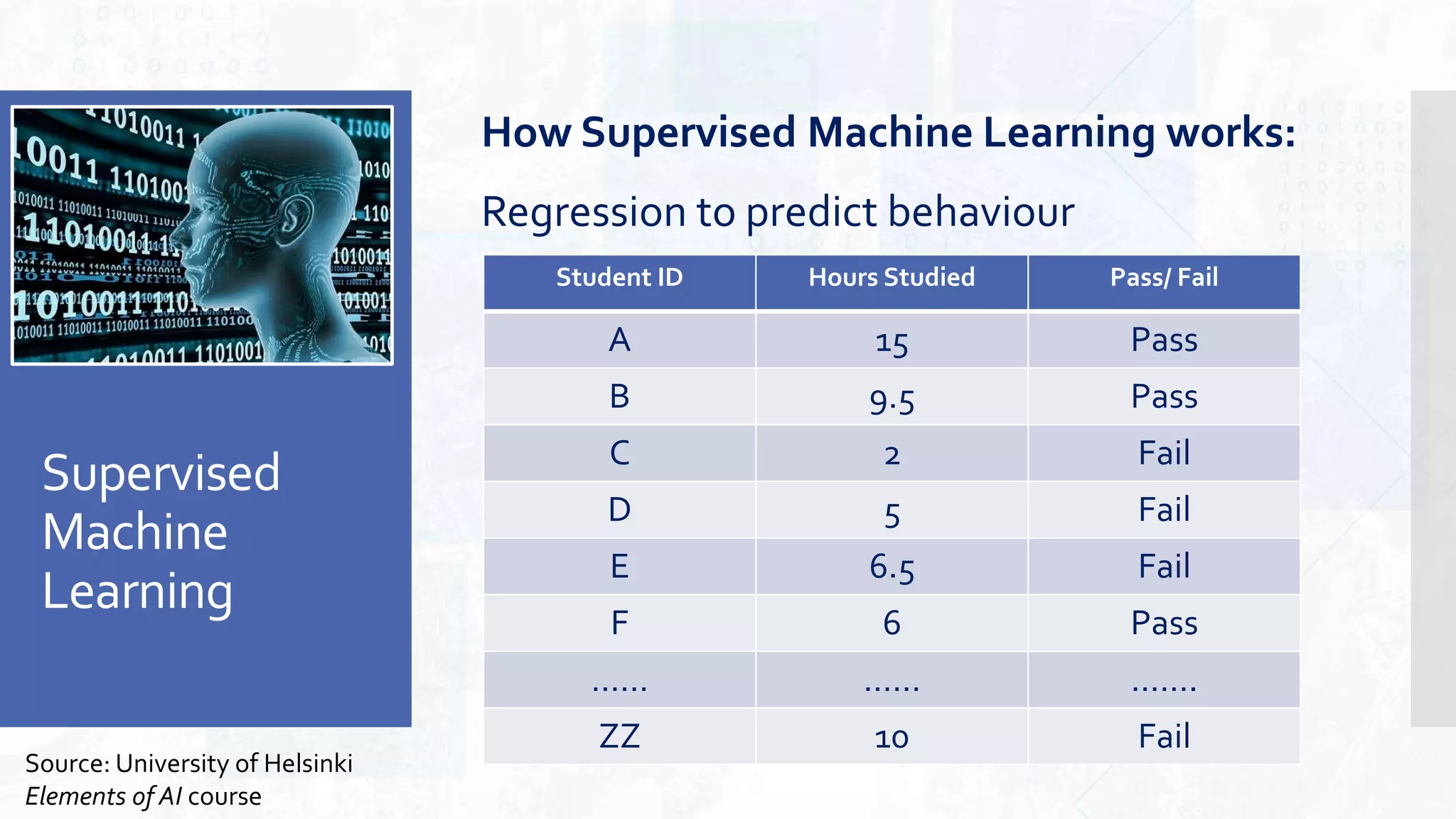
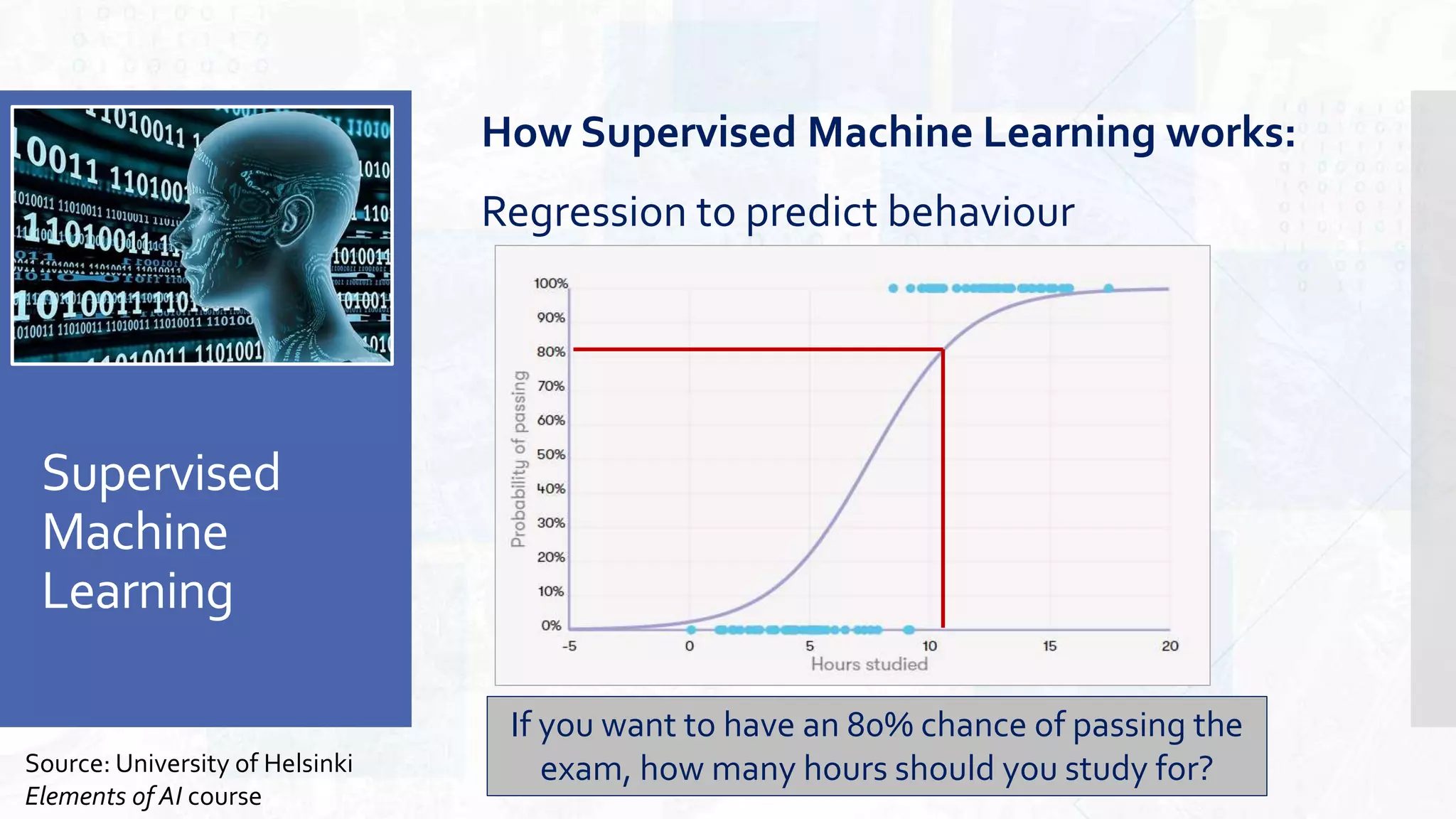
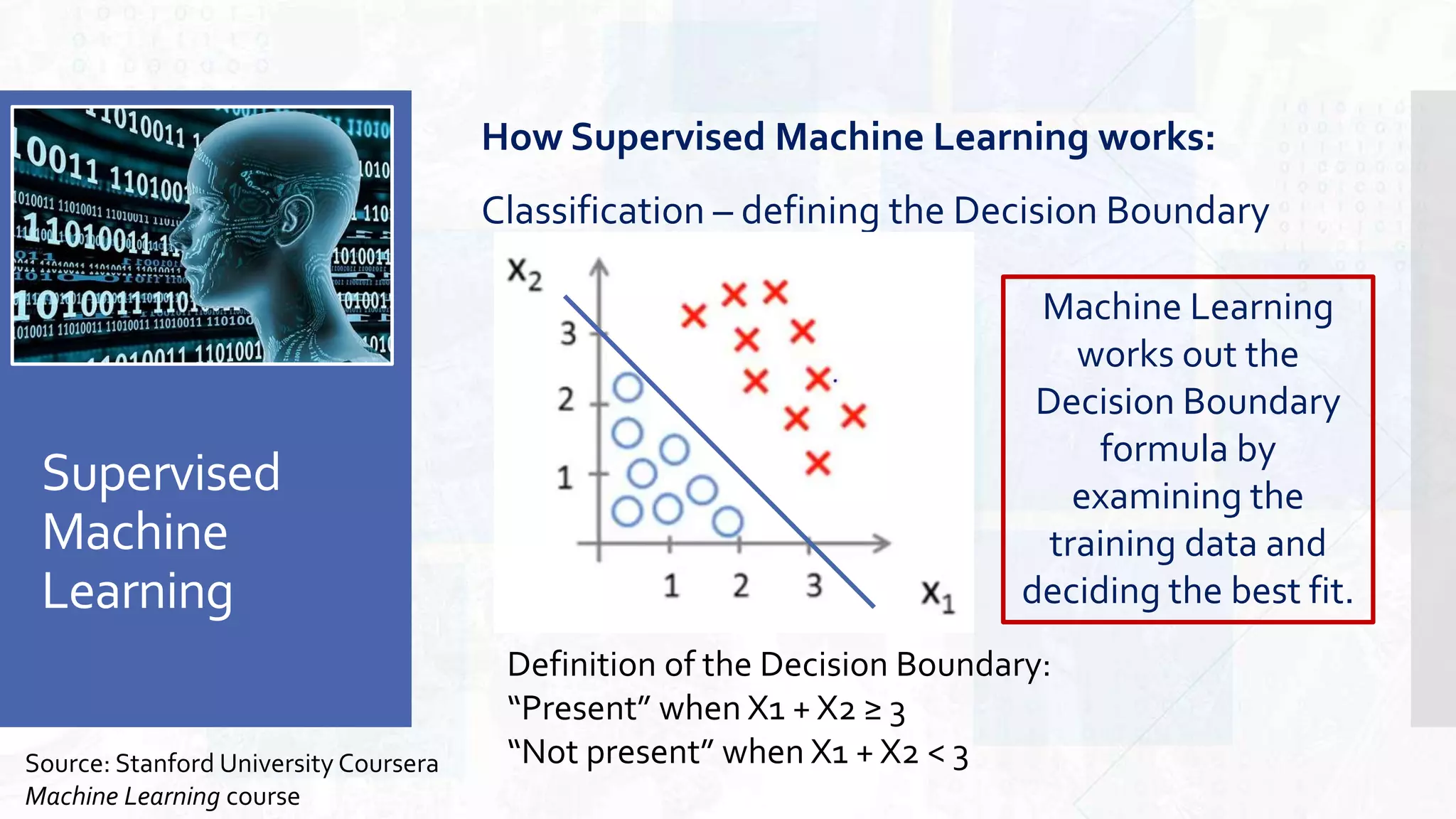
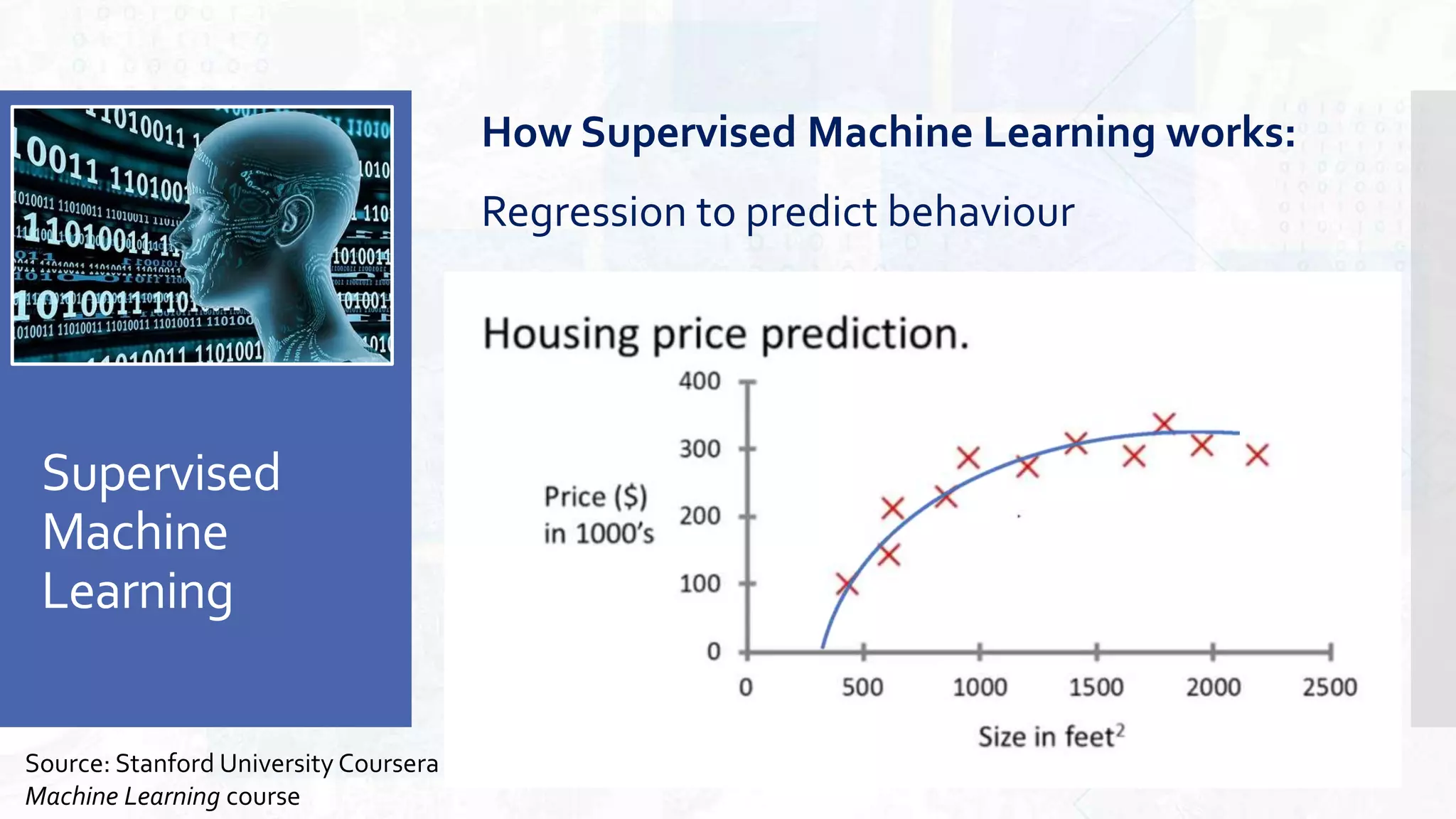
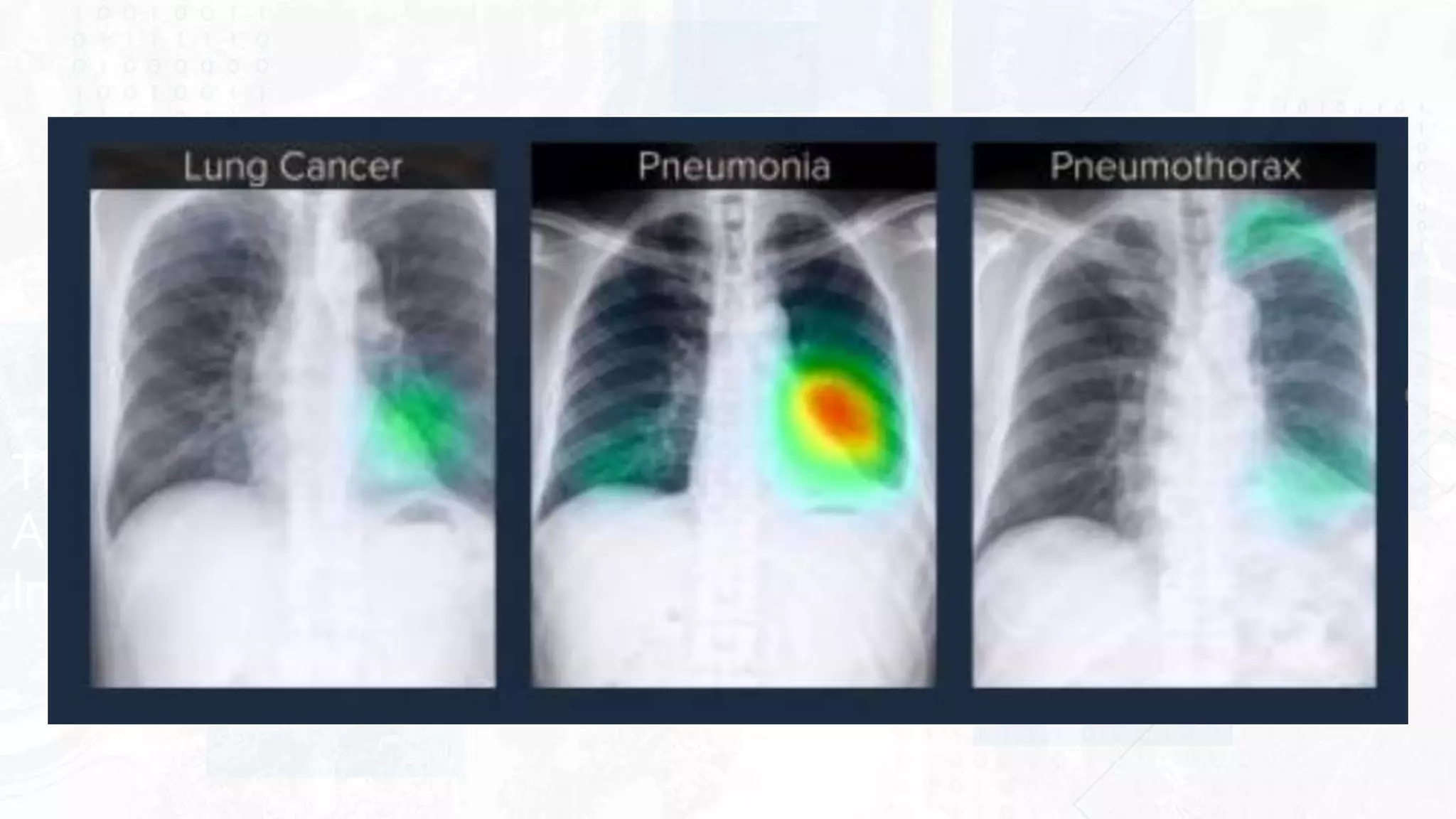
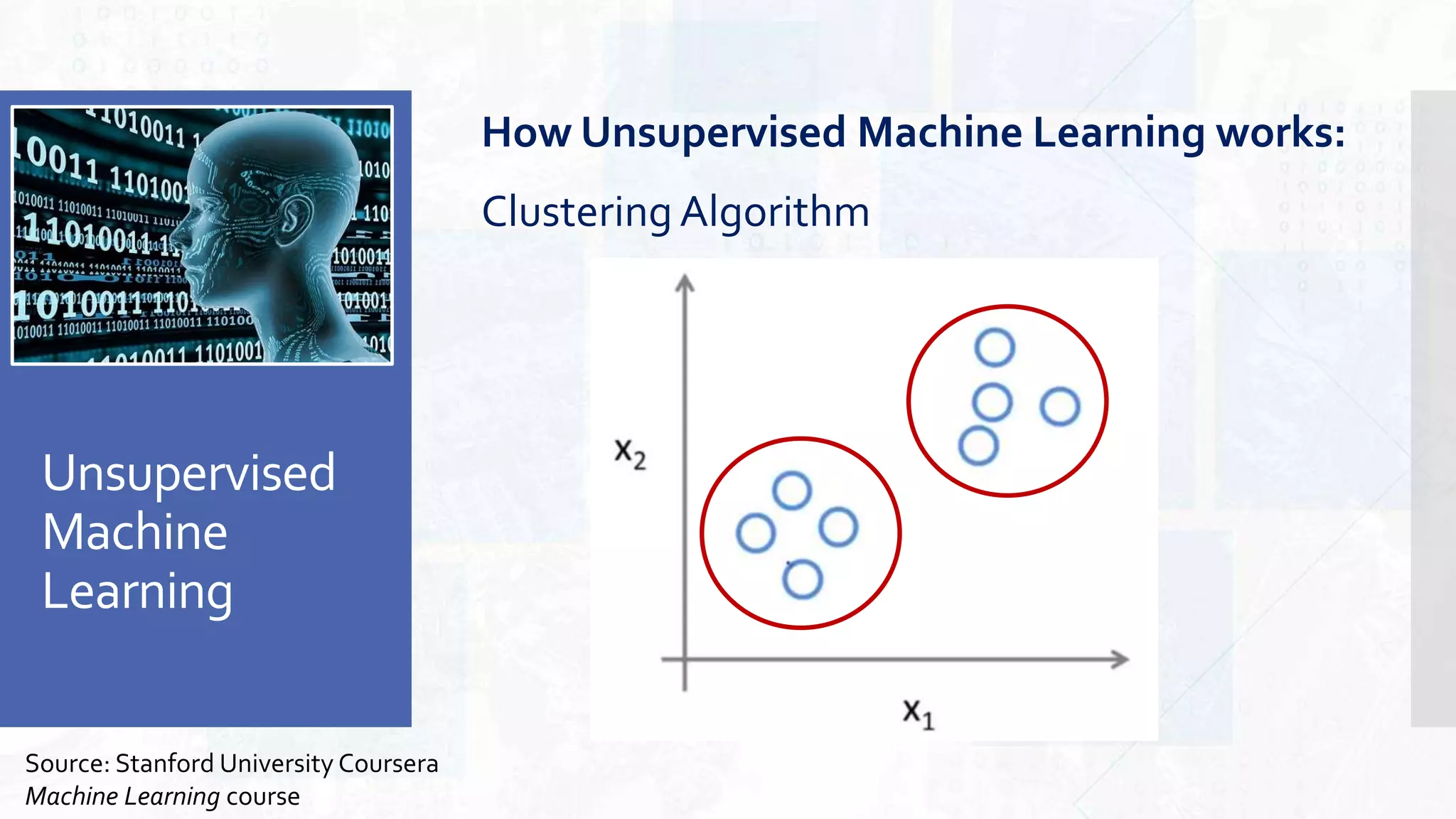
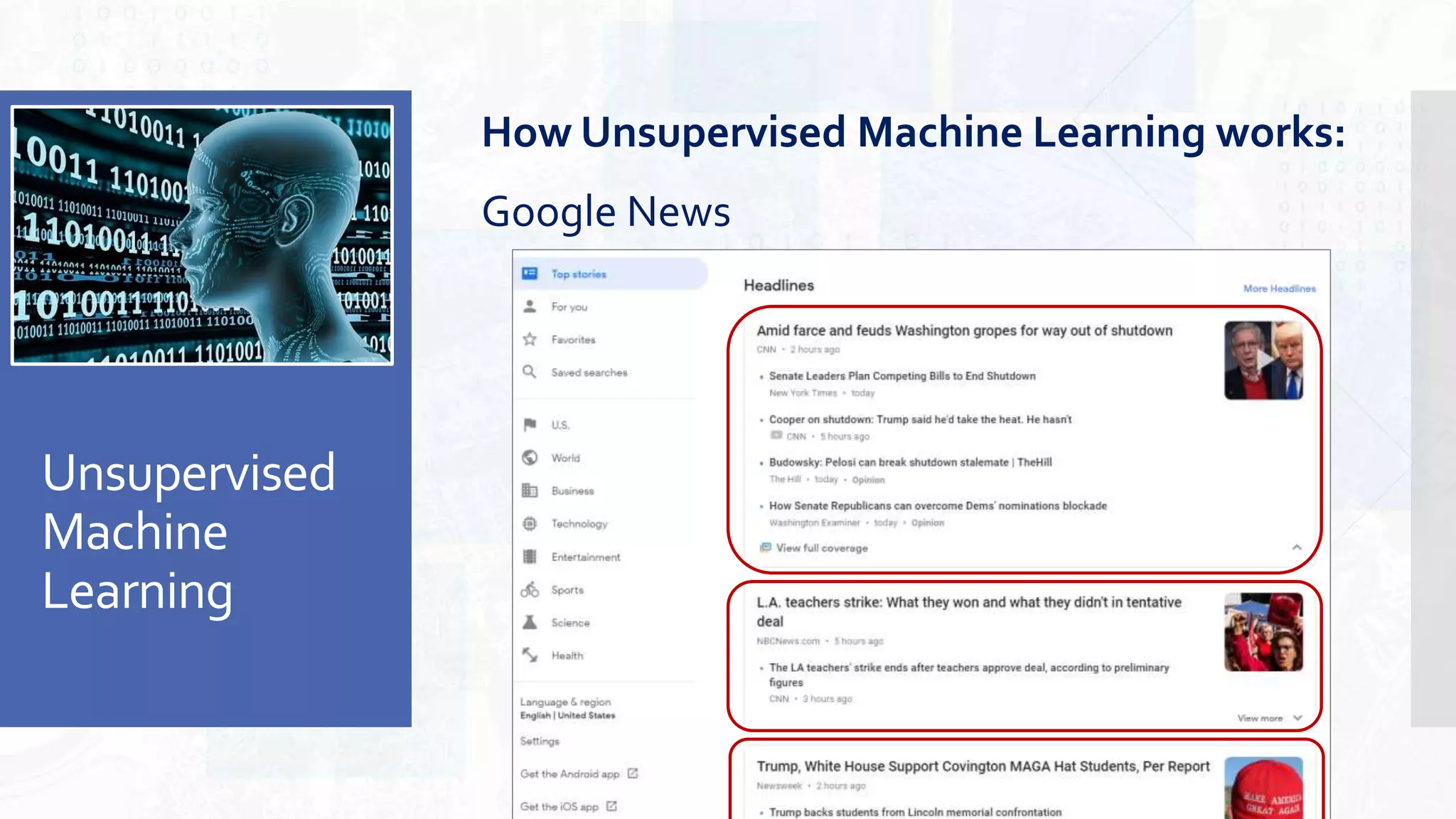
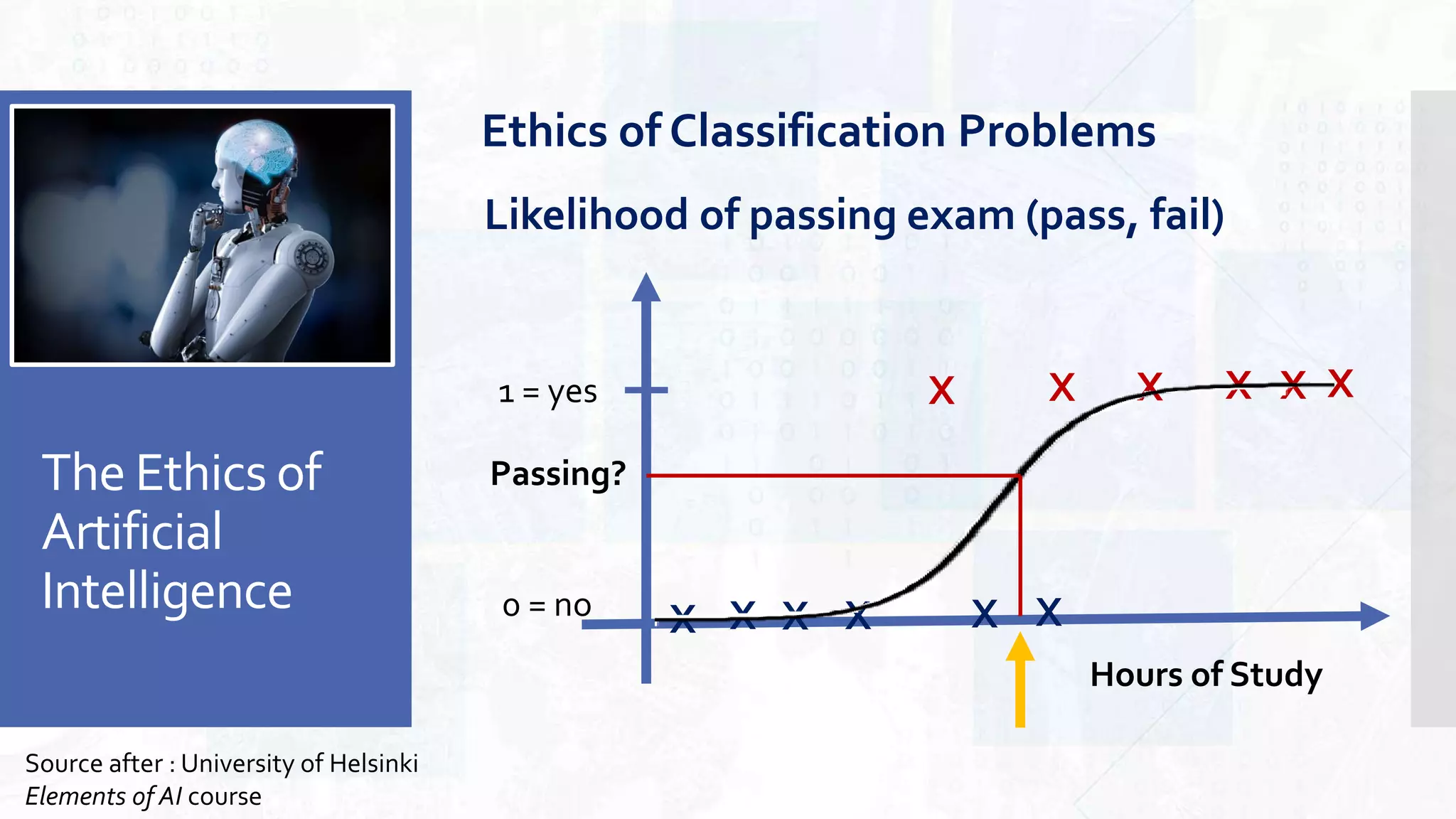
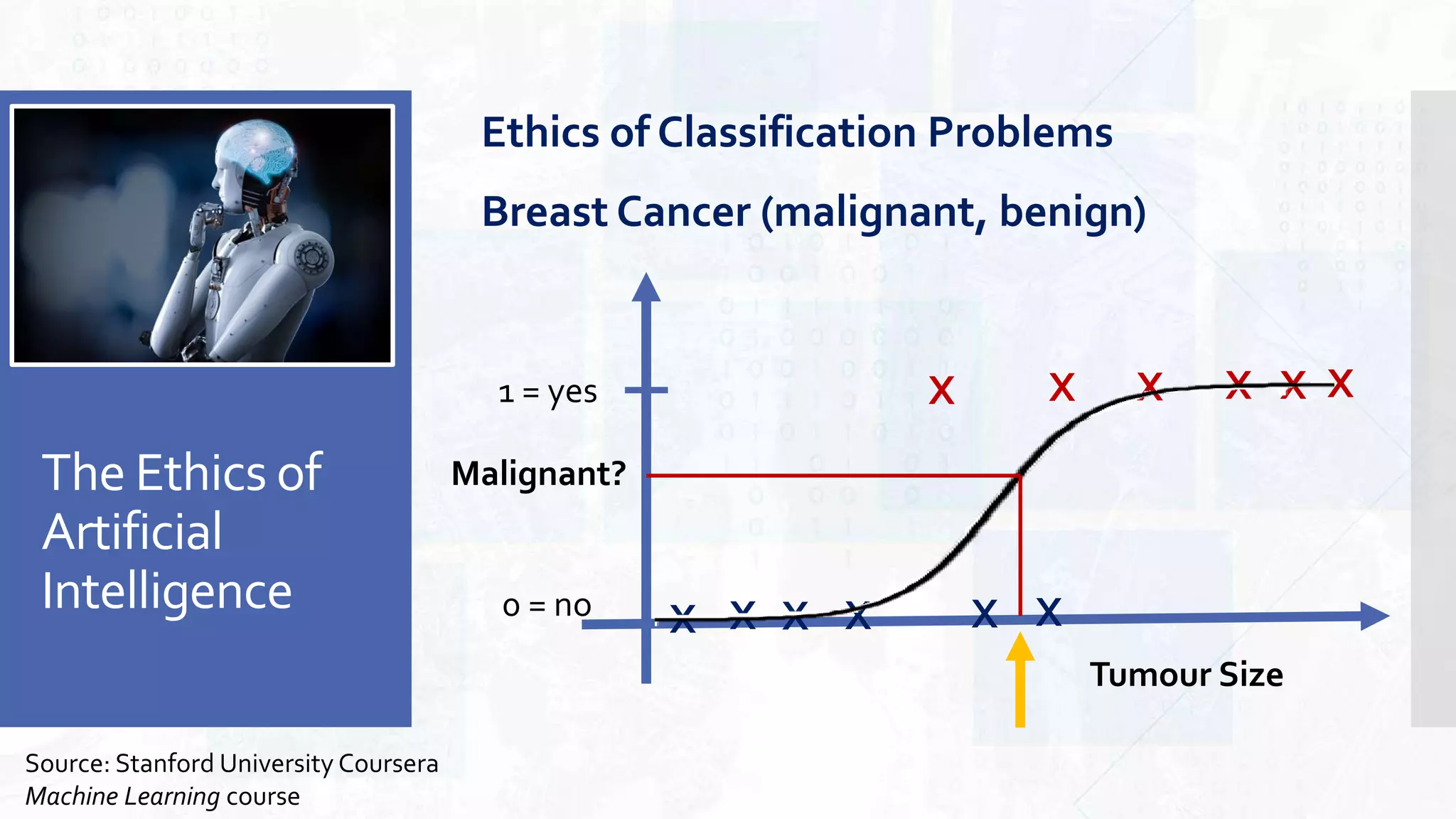
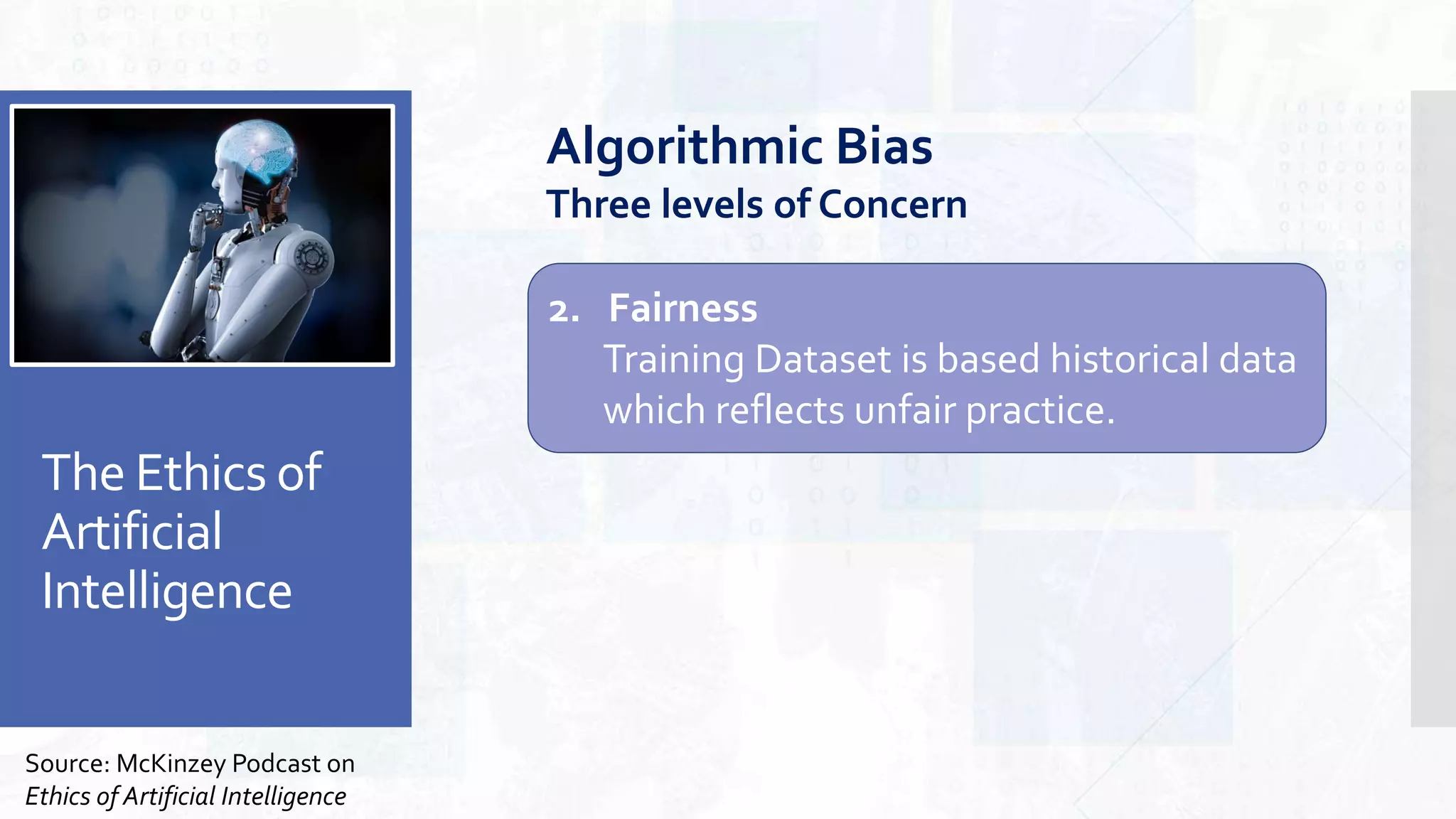
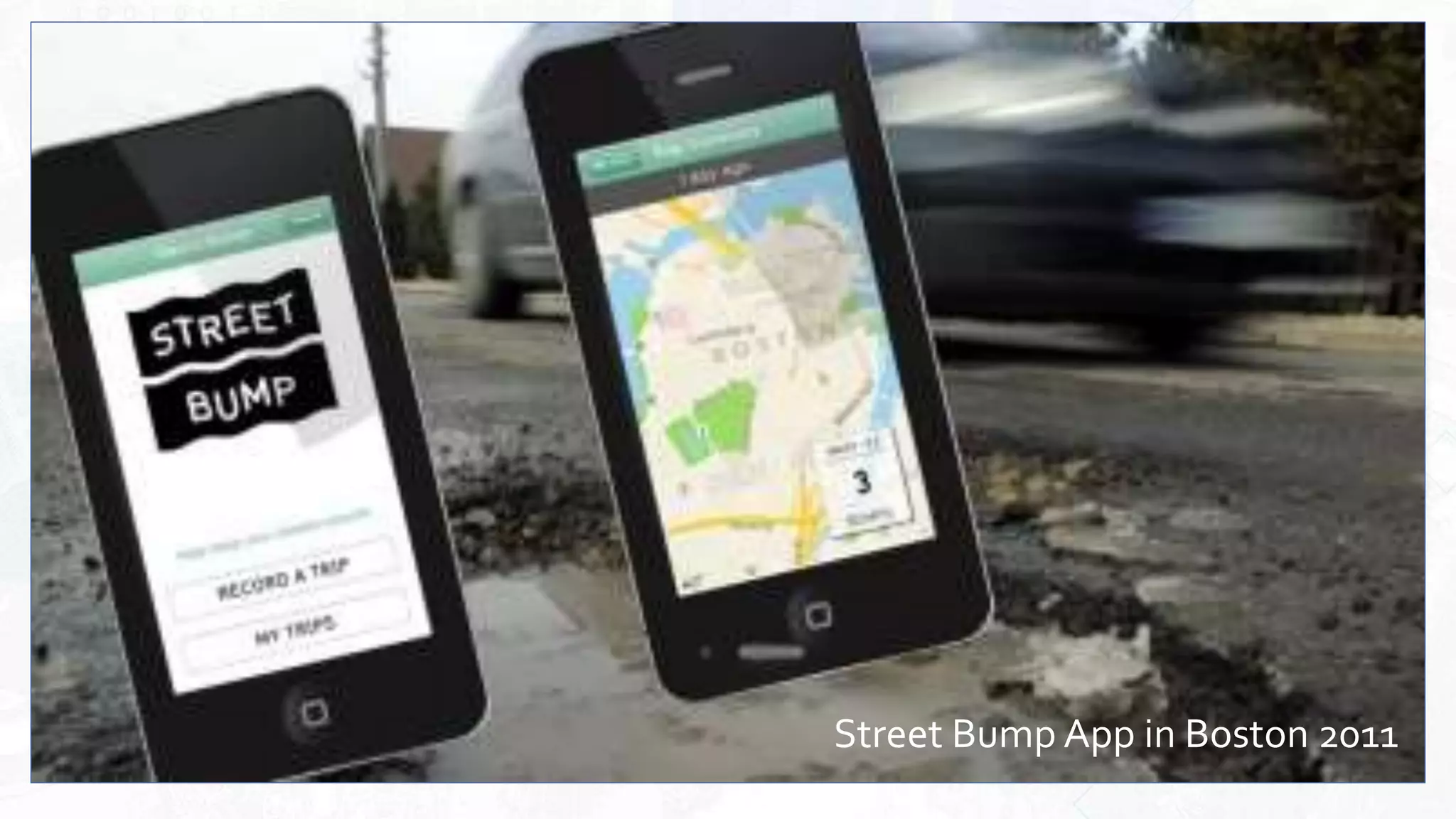
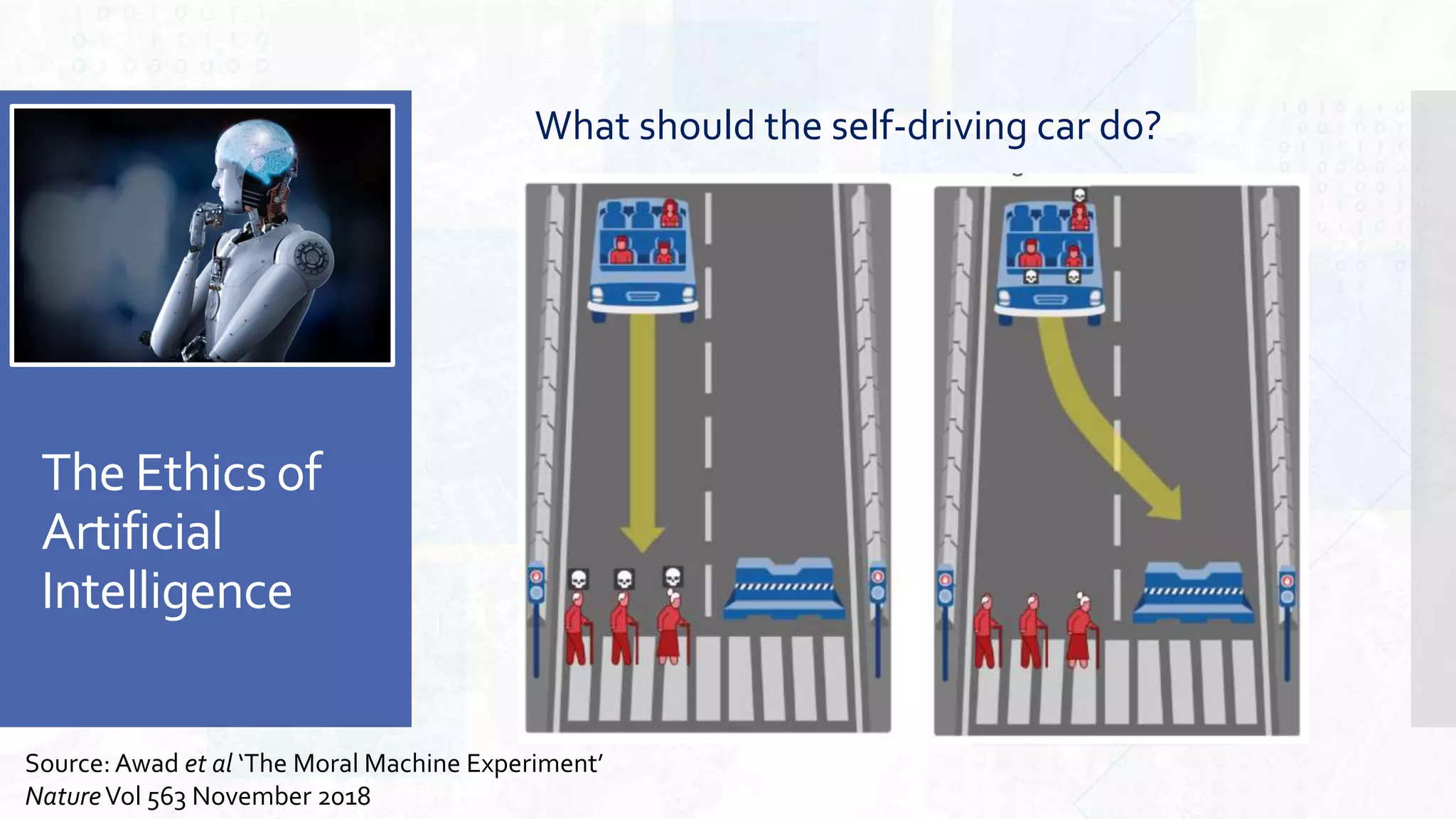
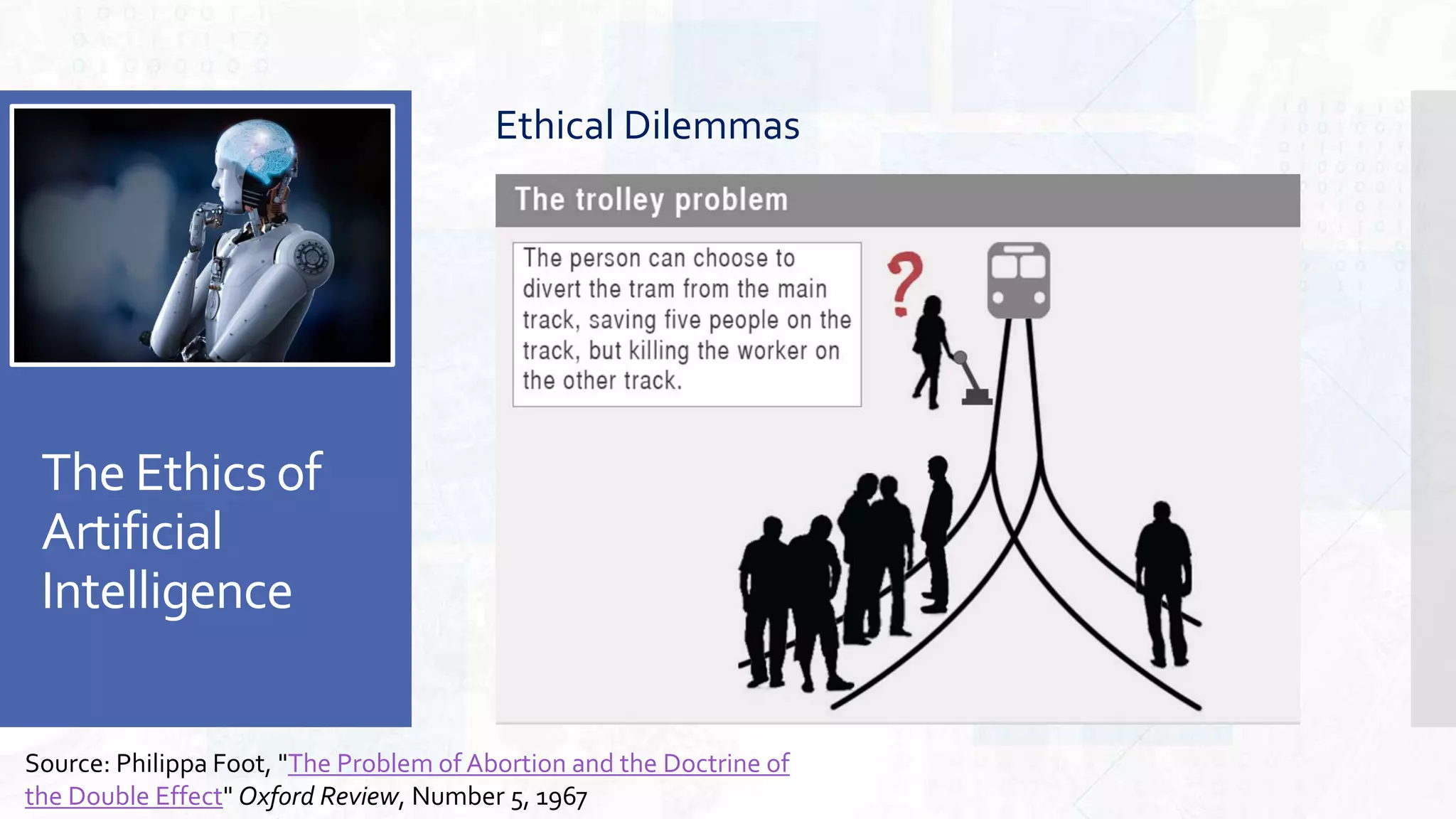
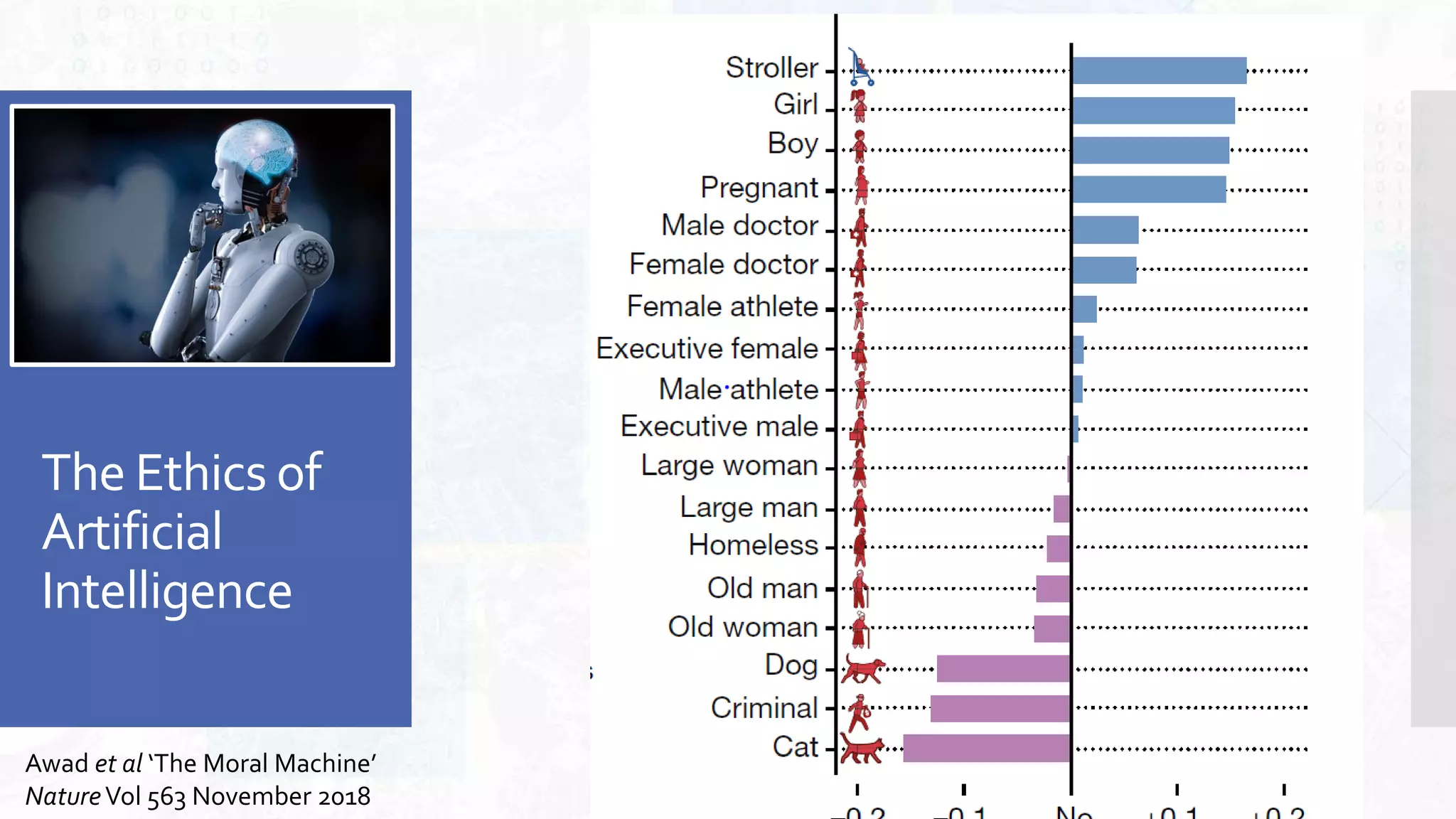
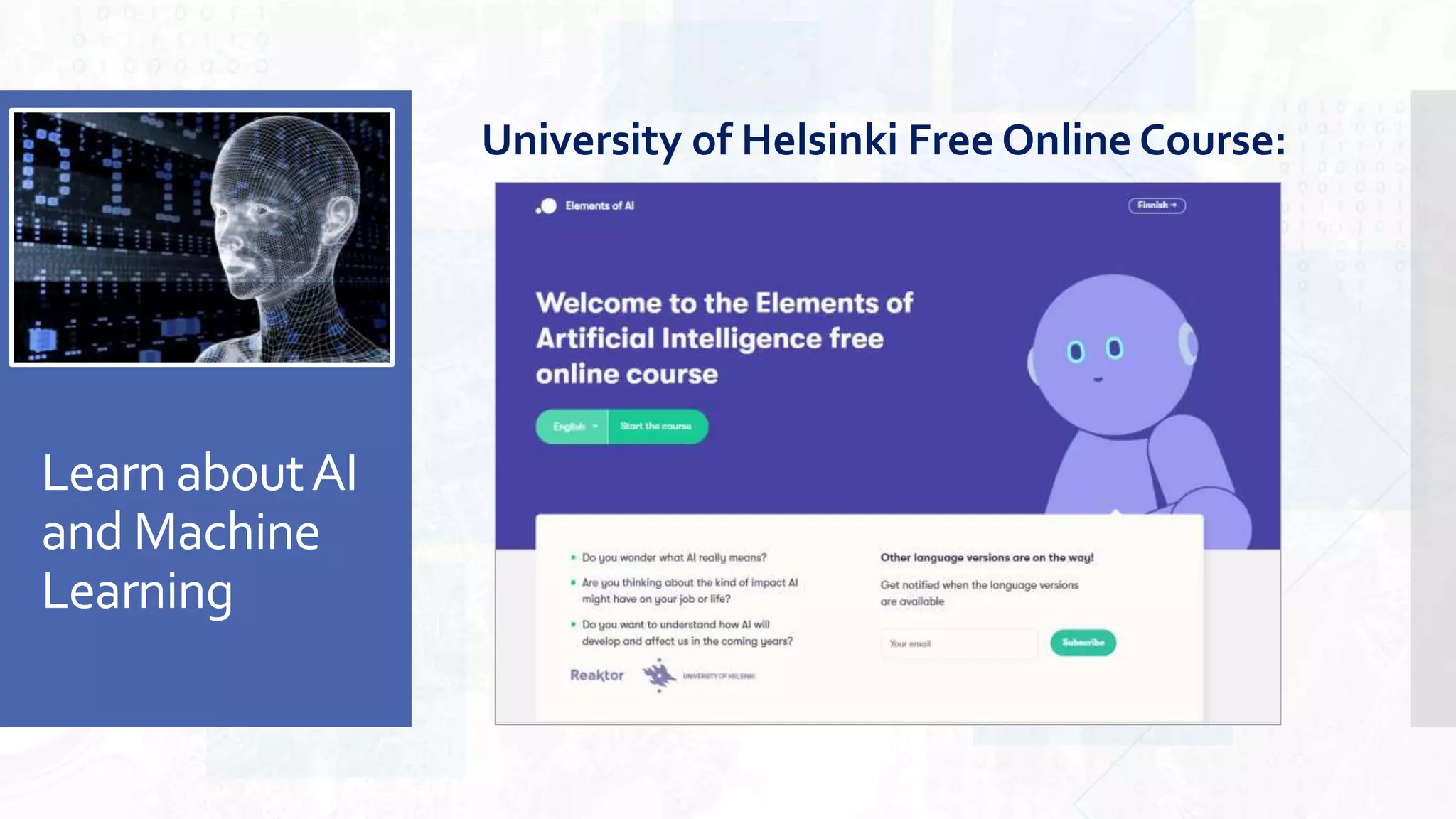
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence and machine learning. It begins by defining AI as computer systems that can perform tasks autonomously and adaptively. Machine learning is described as getting computers to learn without being explicitly programmed. Examples of machine learning in daily life are discussed. The basics of supervised and unsupervised learning are explained. Ethical issues around AI like bias, fairness, and determining appropriate use are then discussed. Options for addressing these issues like ensuring diversity of data and viewpoints are presented. The document concludes by providing recommendations for further learning.