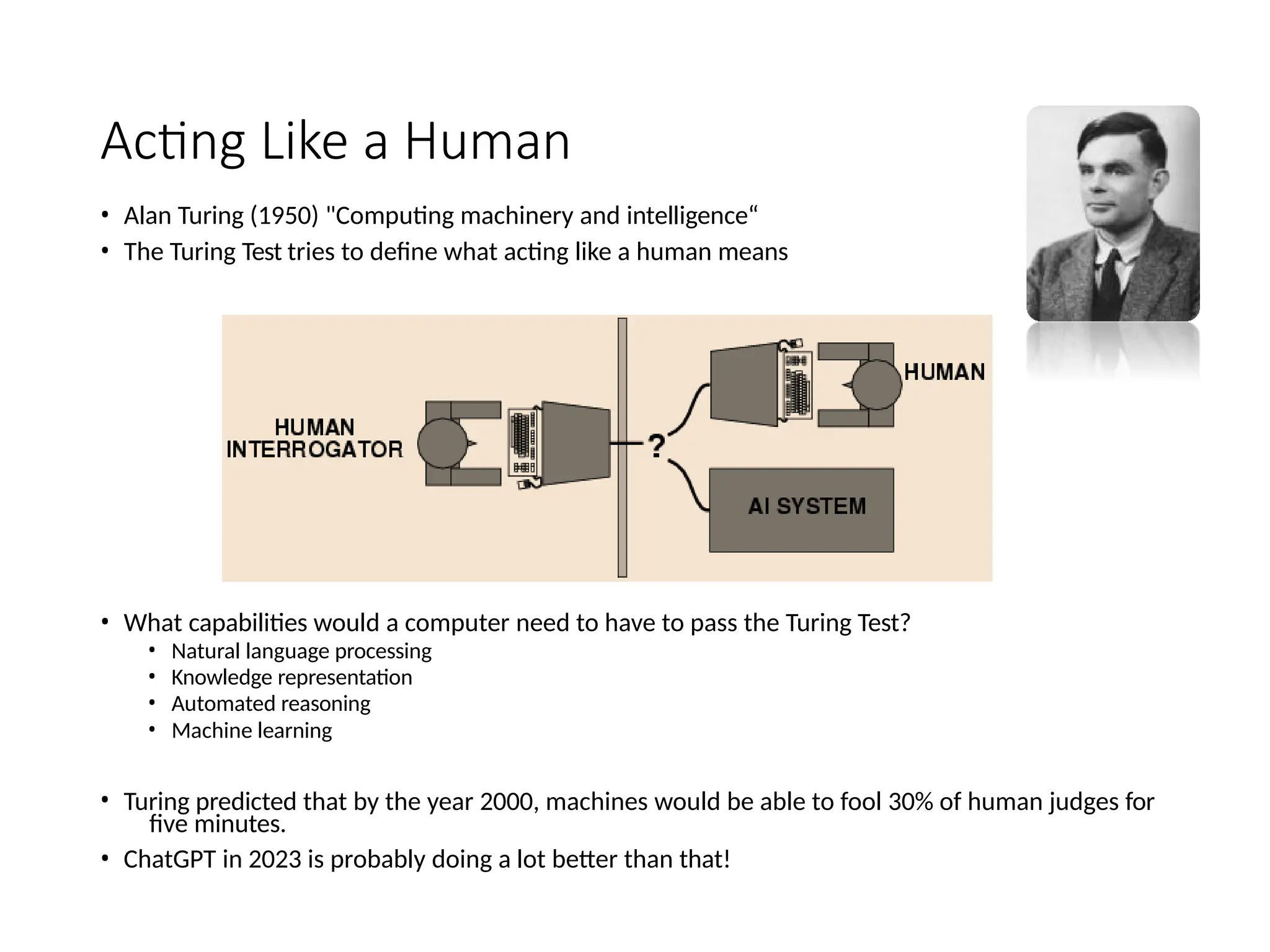
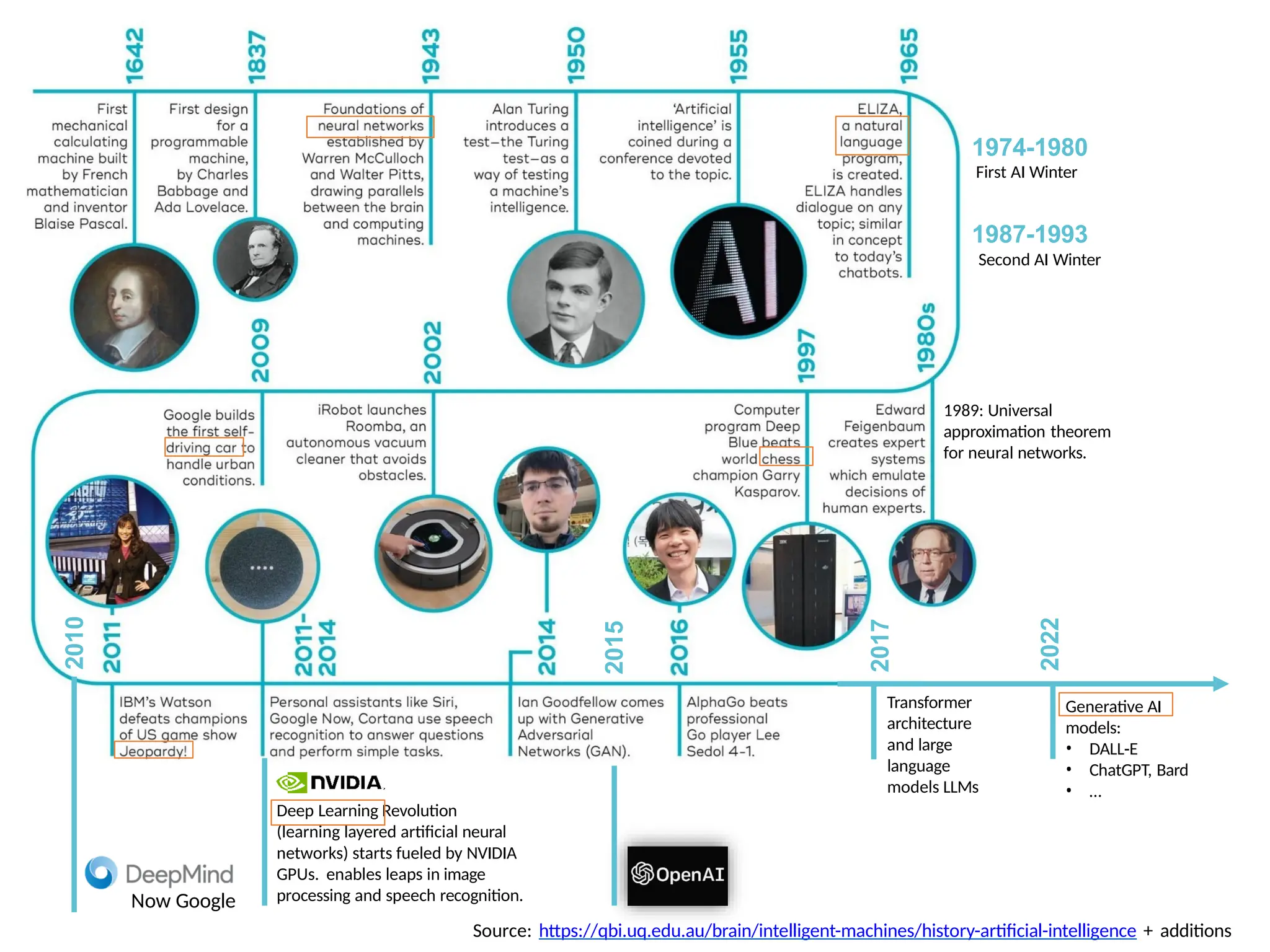
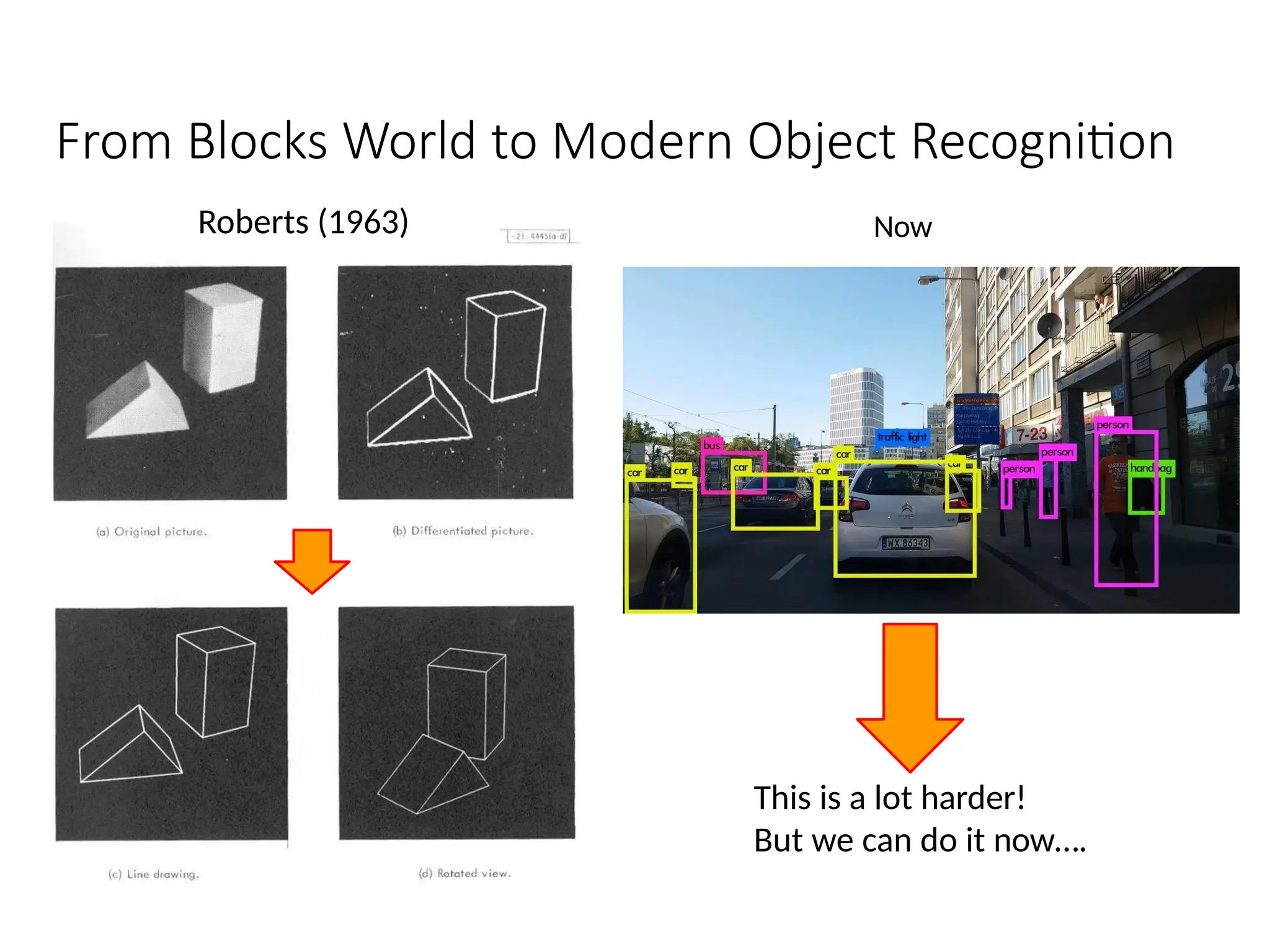
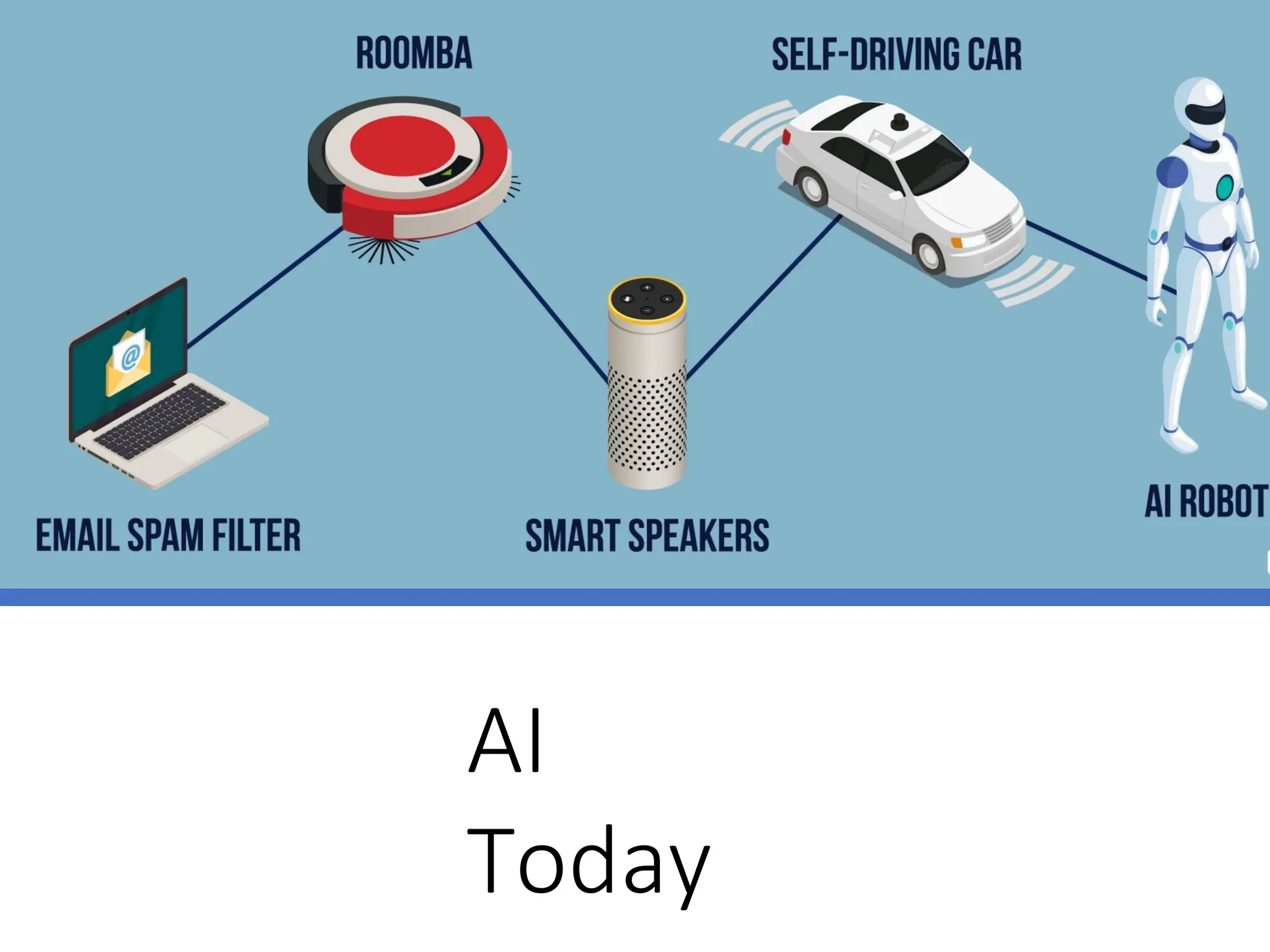
Chapter 1 of 'Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach' introduces the concept of AI, its history, and advancements, particularly narrow AI and artificial general intelligence (AGI). It covers cognitive approaches, Turing's contributions, and the capabilities required for machines to act or think like humans, along with discussions on AI ethics, biases, and real-world applications. Recent advancements stem from powerful hardware, data availability, and machine learning innovations, leading to significant productivity improvements in various sectors.

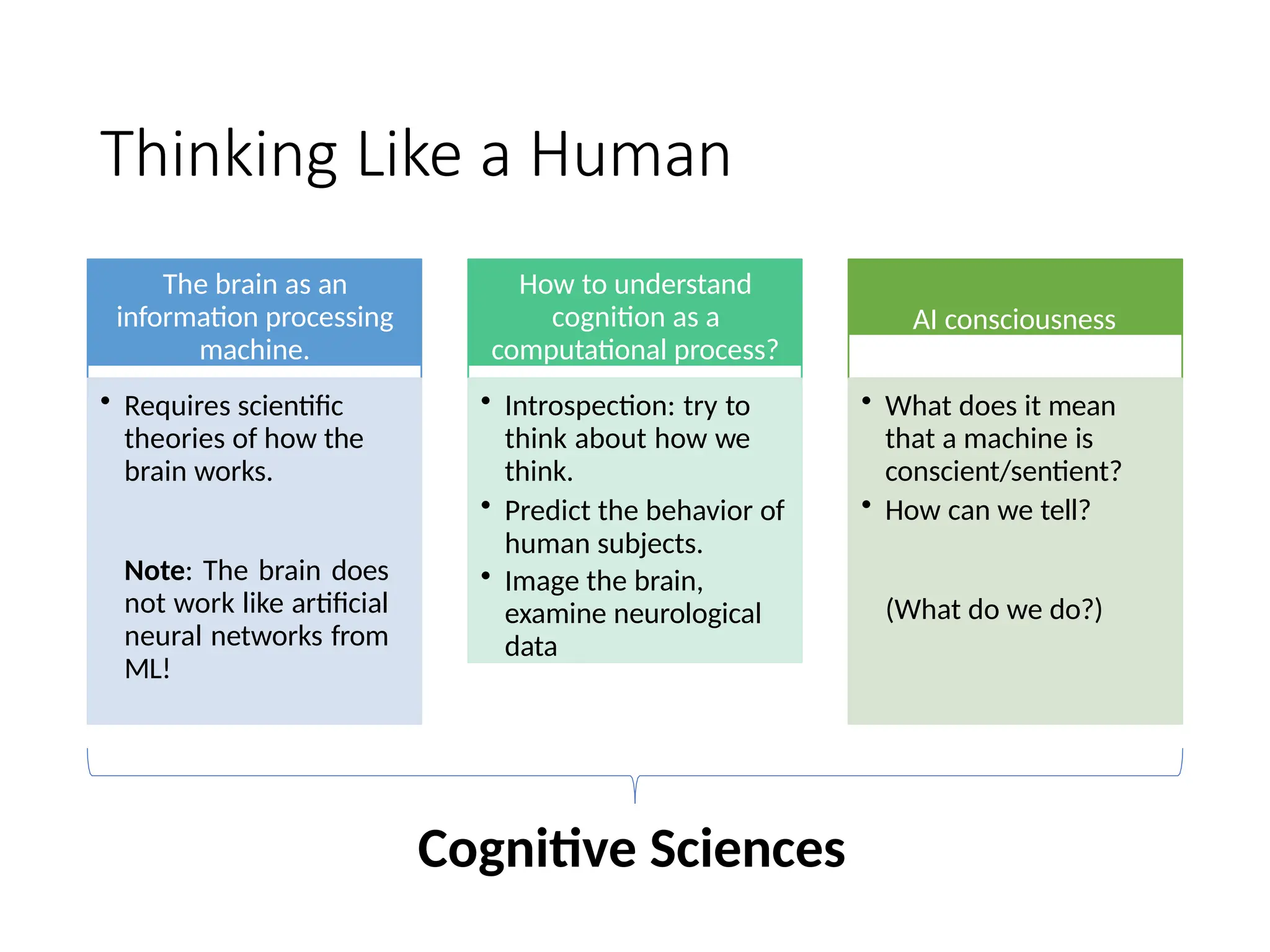
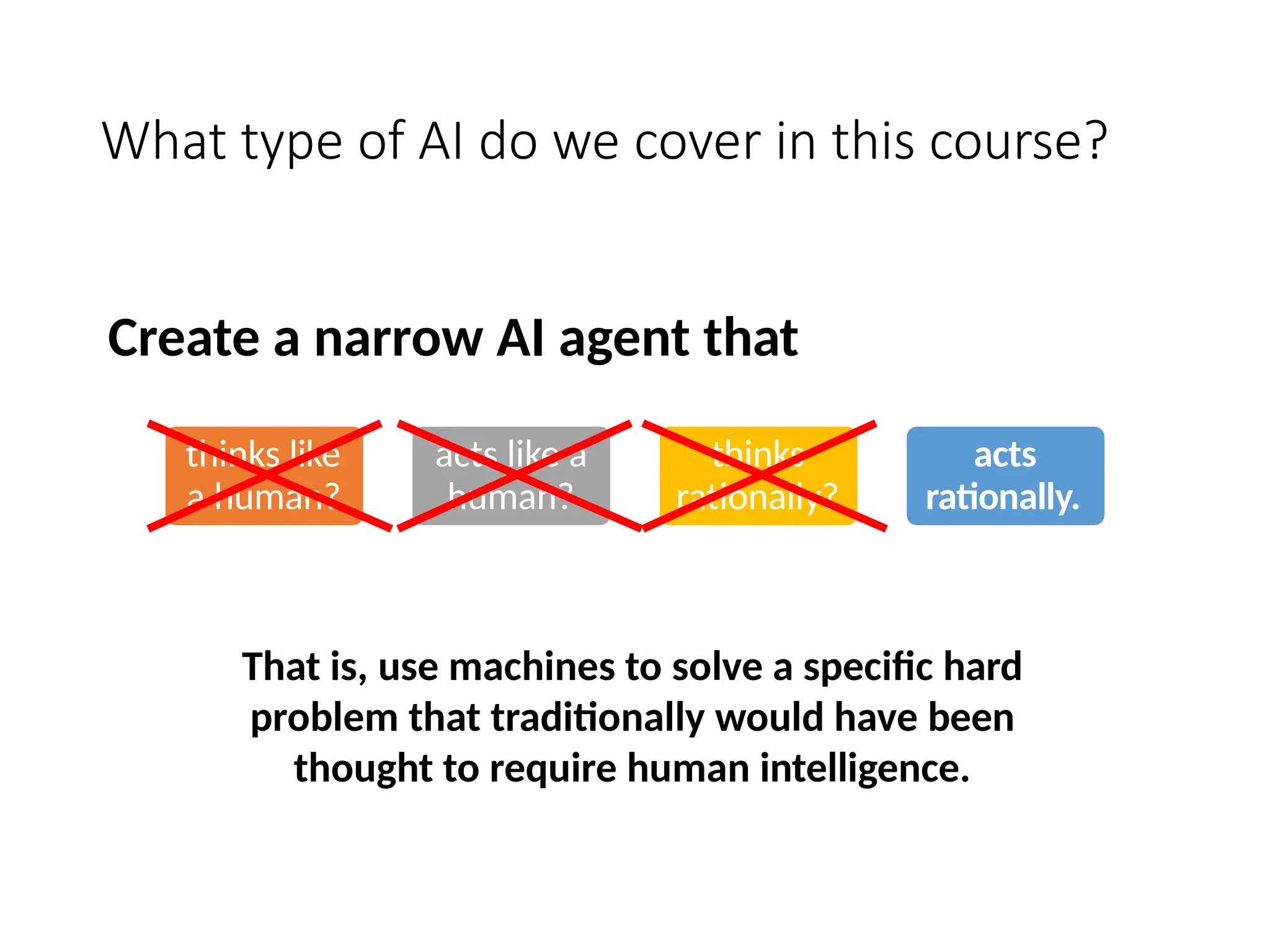
![What is it the Goal of AI?
thinks like
a human?
acts like a
human?
thinks
rationally?
acts
rationally?
“Have machines solve problems that a challenging for humans.”
• Narrow AI focuses on intelligent agents to solve a specific subproblem.
• An artificial general intelligence (AGI) is a hypothetical intelligent agent
which can understand or learn any intellectual task that human beings
or other animals can. [Wikipedia entry on
AGI]
How do we achieve this?
Create an agent that](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01intro-241219150746-08b9d7bd/75/Introduction-to-Artificial-Intelligence-01_intro-pptx-4-2048.jpg)




![What are the Components of an
Intelligent Agent?
Agent interacting with the environment
[Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, Editions 1-3]
Intelligent agents need to
• Communicate with the
environment
• Represent knowledge,
reason and plan to
achieve a desired
outcome
Optional
• Learn
Developer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01intro-241219150746-08b9d7bd/75/Introduction-to-Artificial-Intelligence-01_intro-pptx-12-2048.jpg)
![Machine Learning vs. Artificial Intelligence
ML
Learning from examples
instead of being programmed
• Supervised learning
• Unsupervised learning
• RL
Deep
Learning
• Vision
• Sensors
• Motion
• NLP
• Knowledge
representation
• Planning
• Goals
AI
Designing an intelligent
agent
ML
ML
ML
Agent interacting with the environment
[Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, Editions 1-3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01intro-241219150746-08b9d7bd/75/Introduction-to-Artificial-Intelligence-01_intro-pptx-13-2048.jpg)





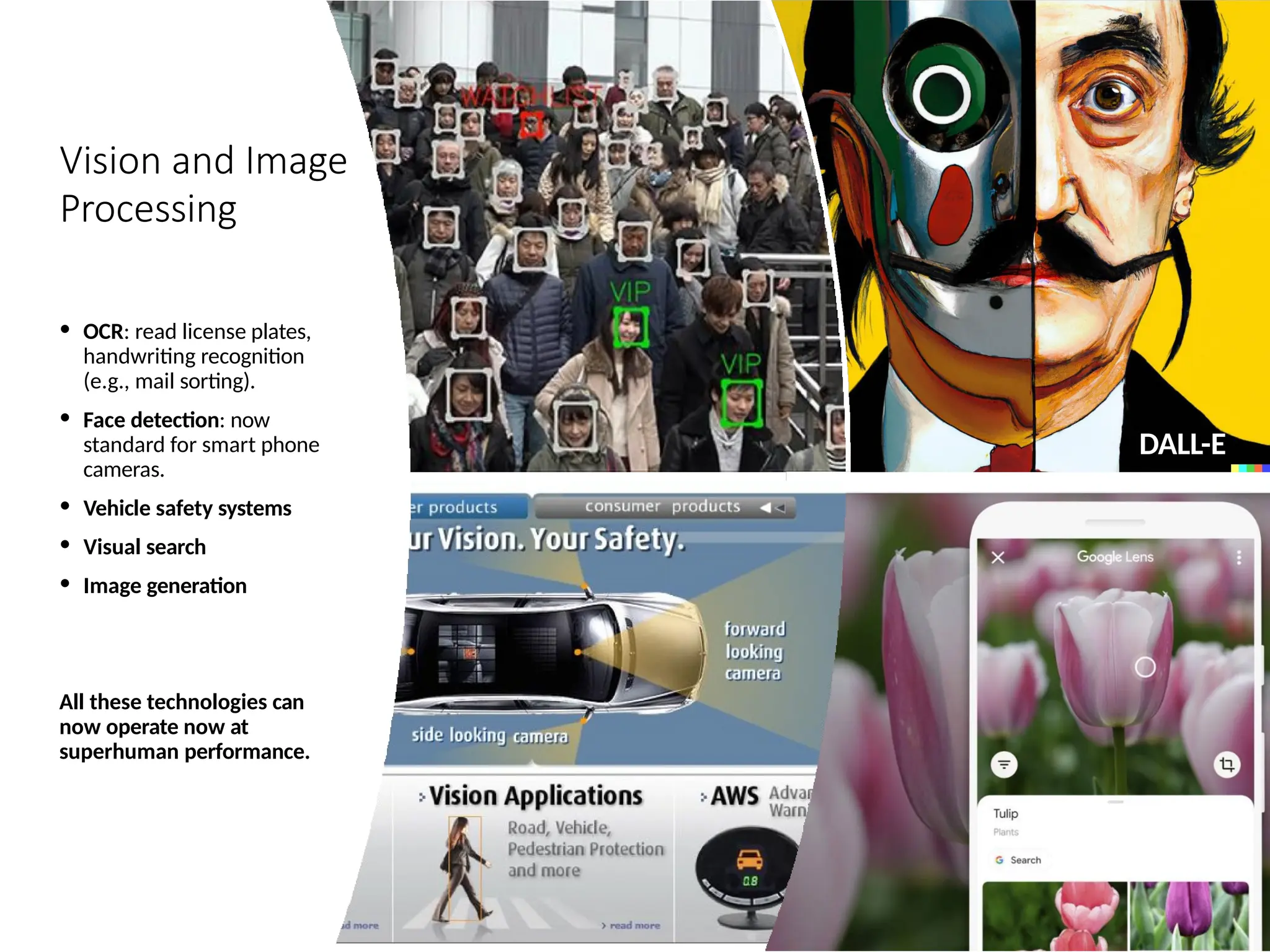


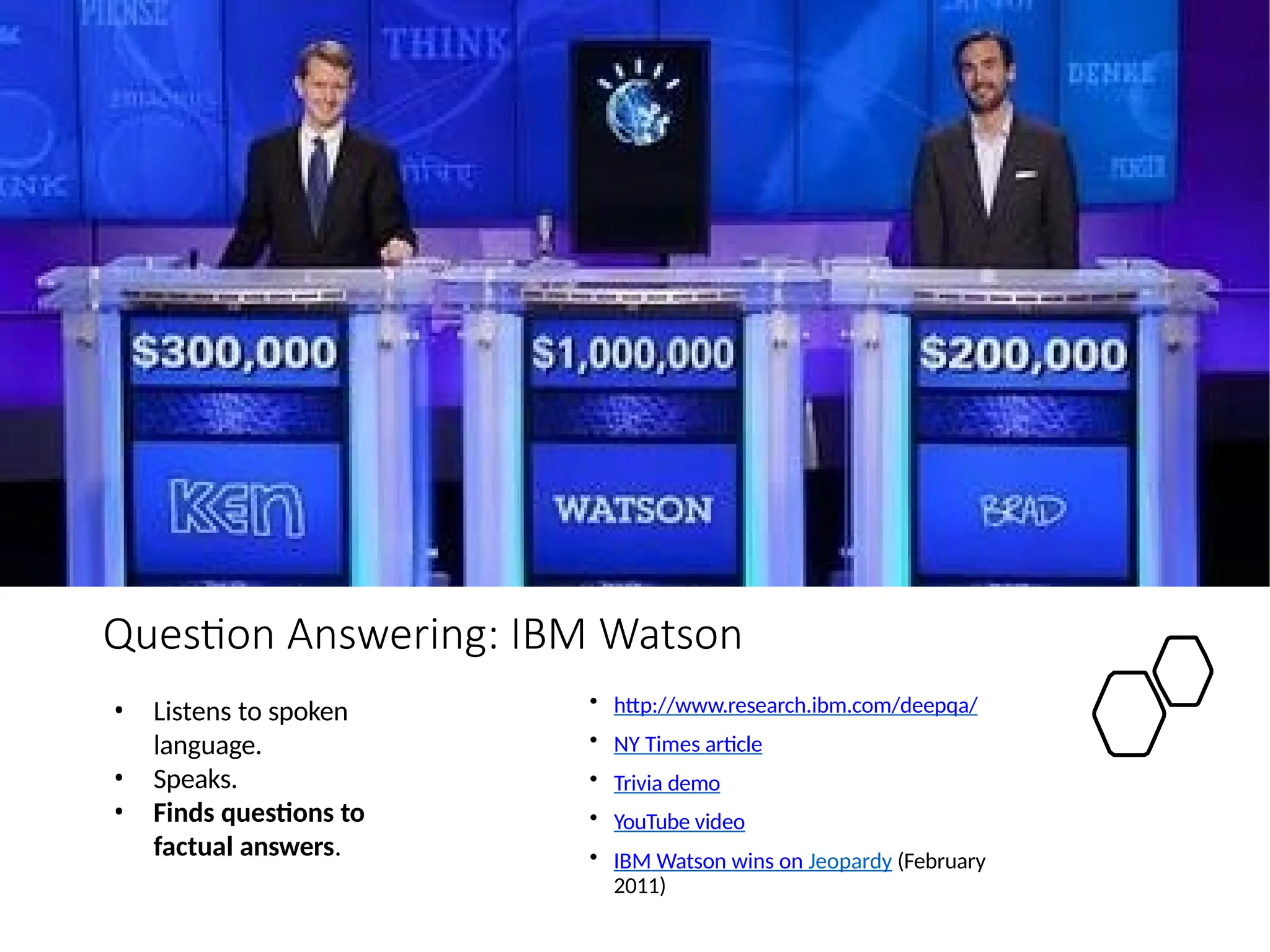
![Math, Games and Puzzles
• 1996: A computer program written by researchers at Argonne
National Laboratory proved a mathematical conjecture
(Robbins conjecture) unsolved for decades
• NY Times story: “[The proof] would have been called
creative if
a human had thought of it”
• 1996/97: IBM’s Deep Blue defeated the reigning world chess
champion Garry Kasparov in 1997
• 1996: Kasparov Beats Deep Blue
“I could feel --- I could smell --- a new kind
of intelligence across the table.”
• 1997: Deep Blue Beats Kasparov
“Deep Blue hasn't proven anything.”
• 2007: Checkers was “solved” --- a computer system that never loses
was developed. Science article
• 2017+: AlphaZero learns chess, shogi and go by playing itself. Science
article
• 2019: MuZero learns to play Atari computer games.
AI exhibits superhuman performance on almost all games.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01intro-241219150746-08b9d7bd/75/Introduction-to-Artificial-Intelligence-01_intro-pptx-26-2048.jpg)