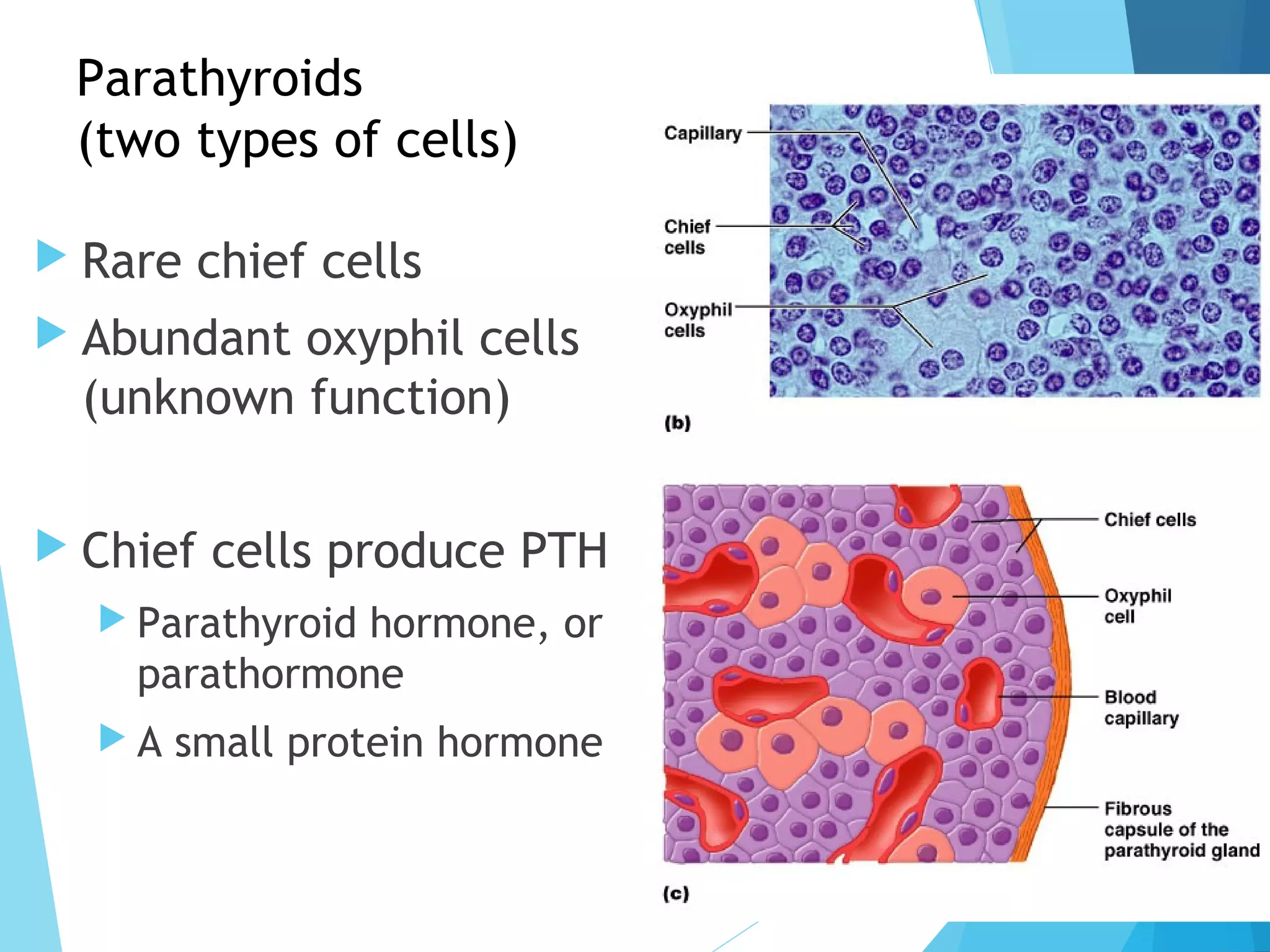
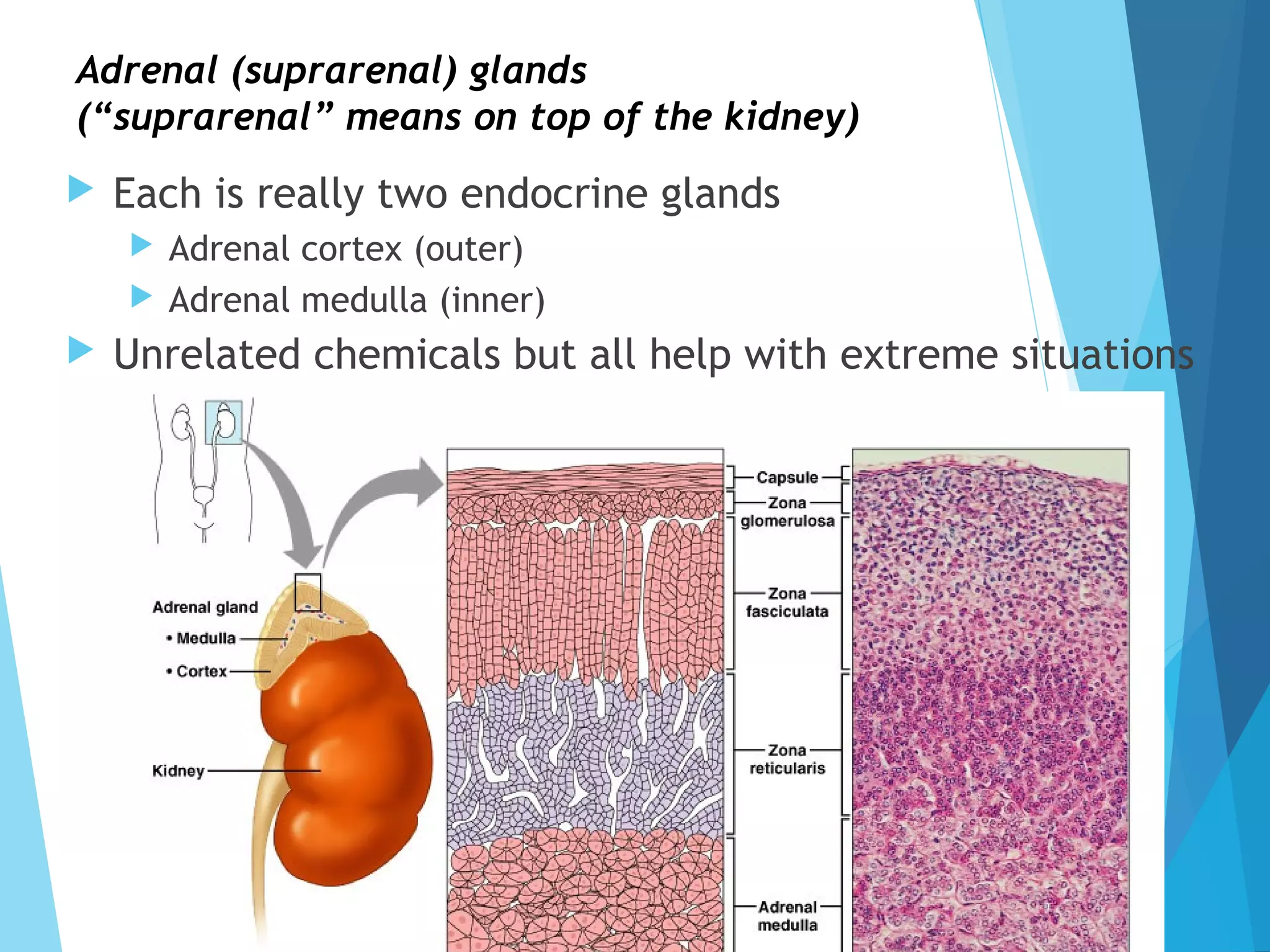
The document provides an overview of the endocrine system, which includes glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate distant target organs and tissues. It describes the major endocrine glands such as the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal and gonads. For each gland, it outlines their location in the body, the hormones they secrete and the primary actions and effects of these hormones on other bodily systems and processes.