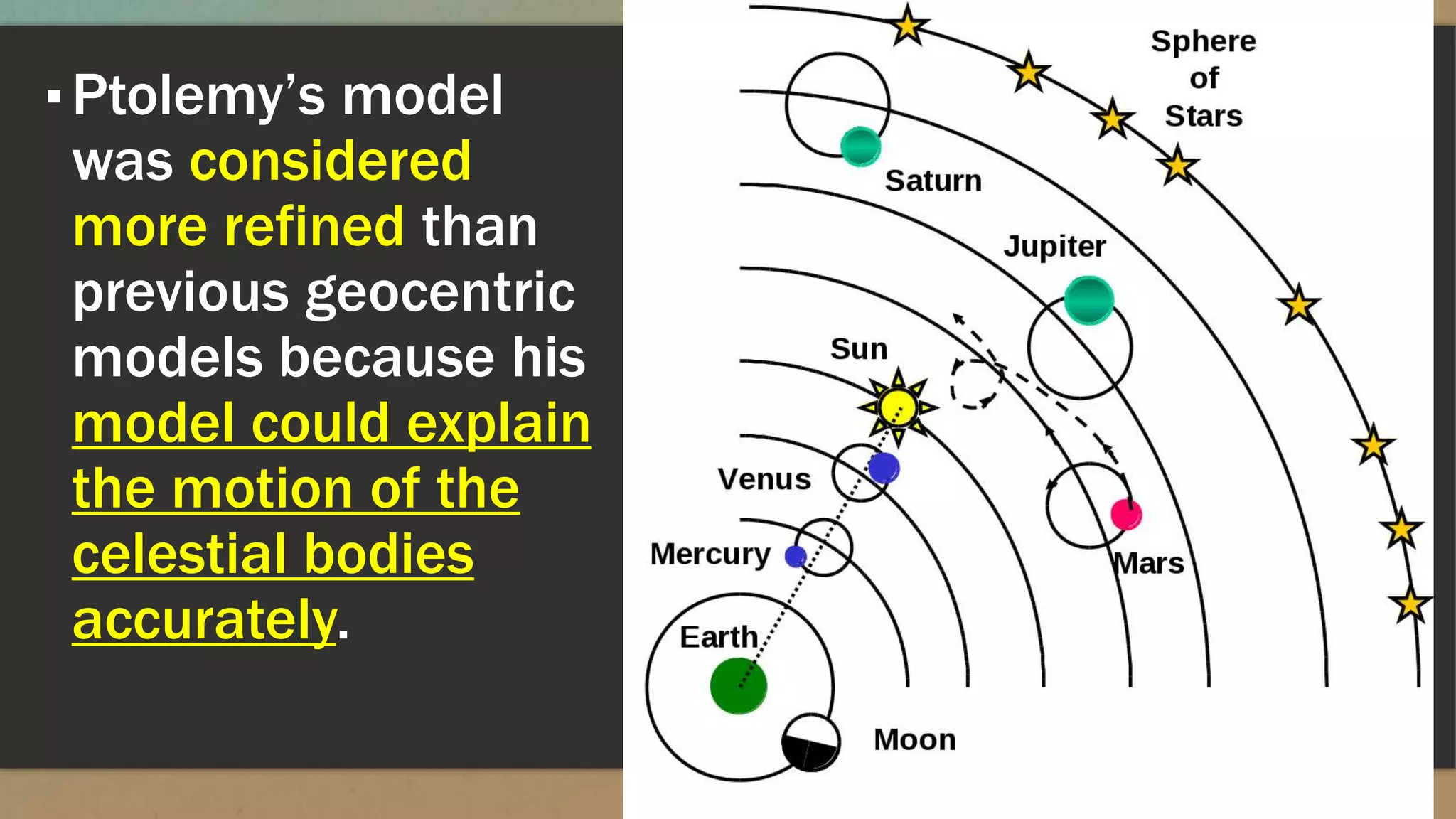
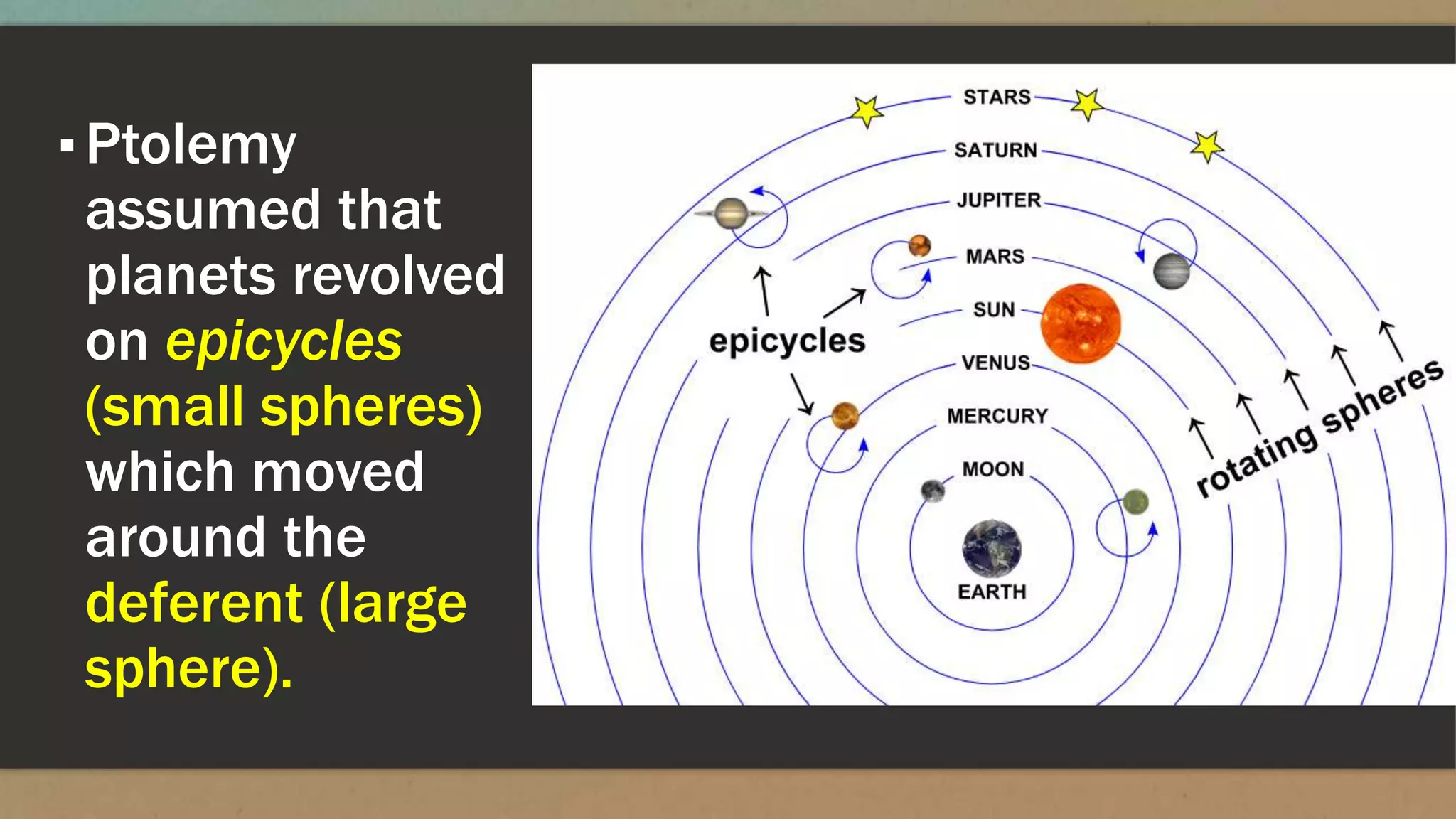
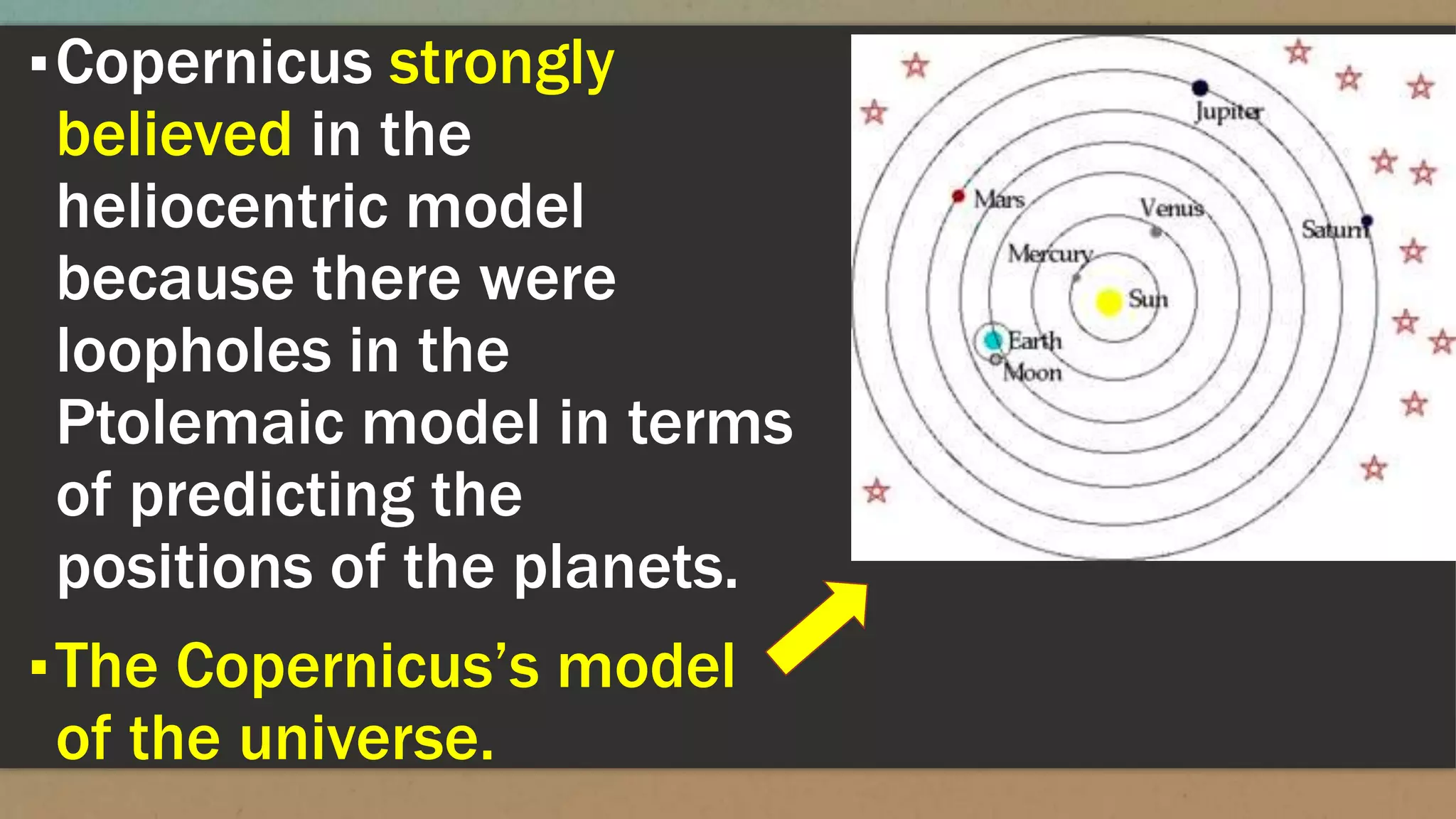
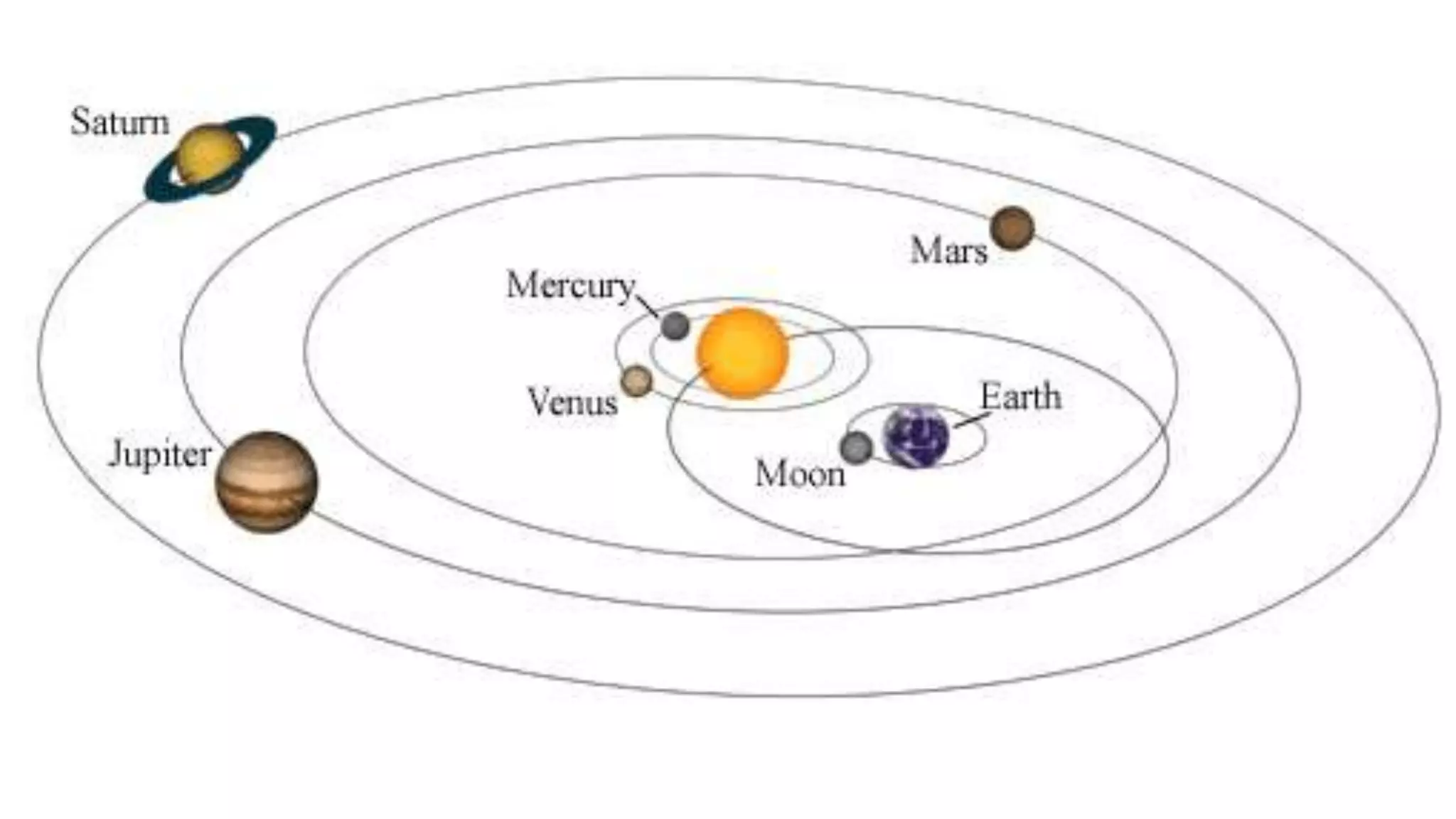
The document discusses early models of the universe including the ideas that the Earth was flat and then spherical. It describes models from Greek philosophers like Aristotle who believed the Earth was at the center of the universe and surrounded by spheres carrying the planets and stars. Later models from Copernicus, Brahe and Kepler placed the Sun at the center with Earth and other planets orbiting around it, moving astronomy toward a heliocentric understanding of the solar system.