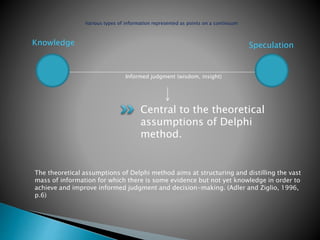
The document discusses the Delphi method, a structured communication process among experts used to gather informed judgments on complex issues through multiple rounds of questionnaires. It emphasizes the advantages of Delphi over traditional group discussions, highlights the importance of expert selection, and describes the iterative nature of the method aimed at reaching consensus. Additionally, it suggests using a straw model to foster deep conversation and clarify underlying assumptions during the process.