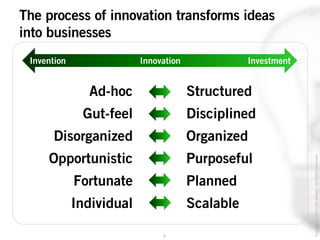
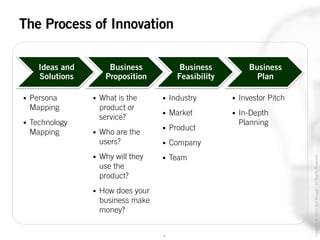
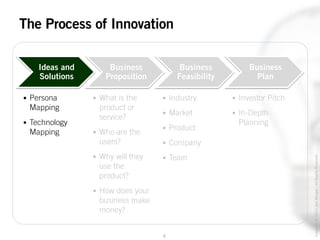
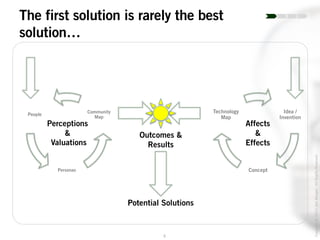
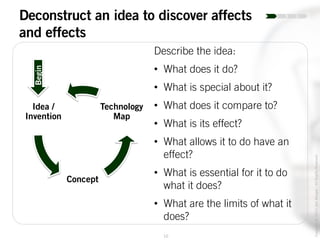
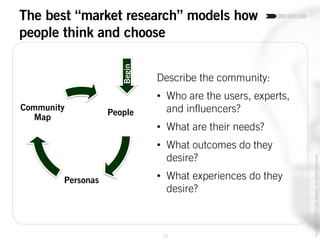
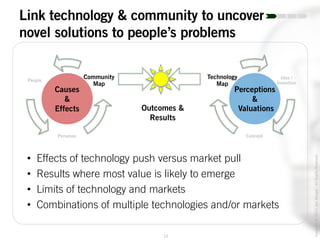
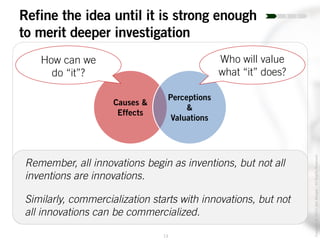
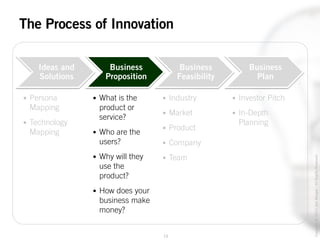
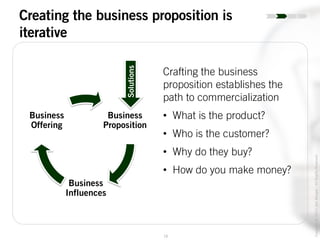
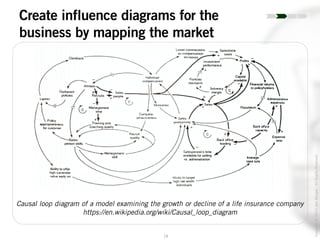
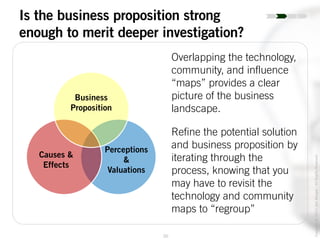
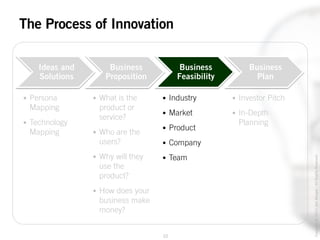
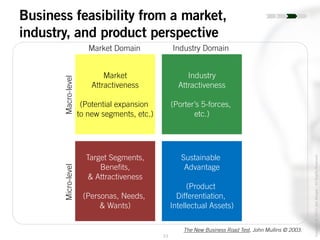
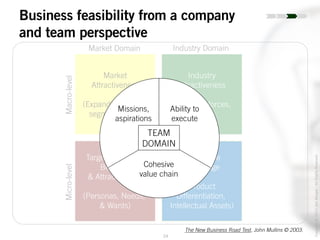
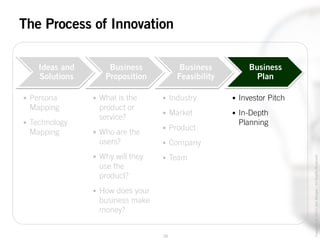
The document outlines the process of innovation, defining it as the link between invention and investment, involving structuring ideas into feasible business propositions. It emphasizes an iterative approach to refining ideas, understanding market needs, and developing a compelling business plan, which is crucial for successful commercialization. Various tools such as persona mapping, technology mapping, and creating influence diagrams are proposed to guide the innovator through identifying viable solutions and establishing market fit.