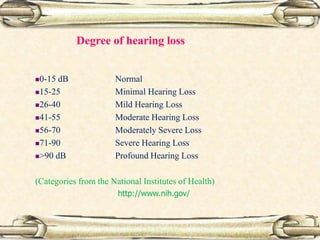
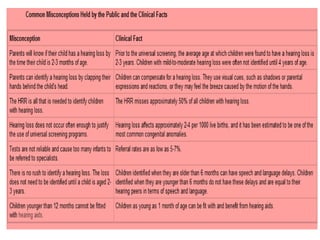
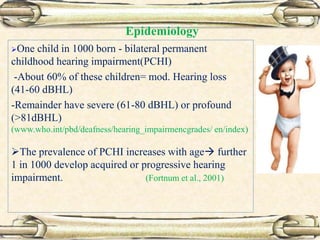
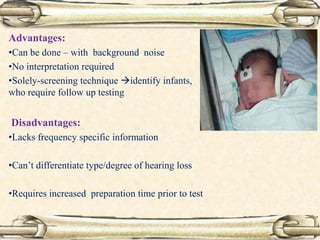
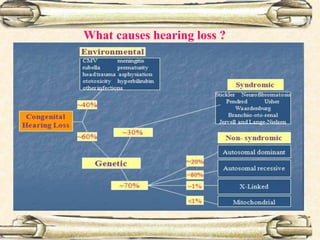
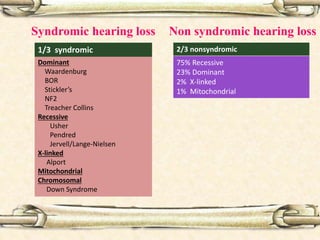
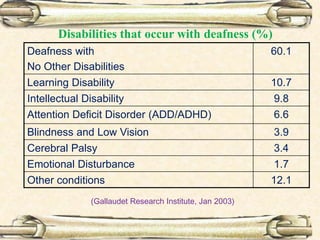
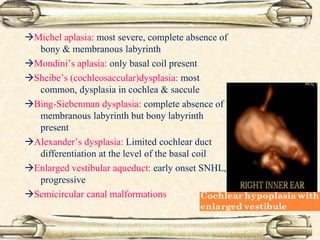
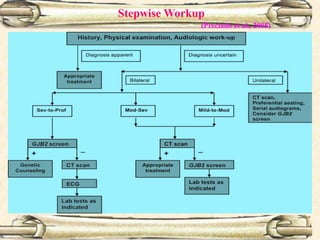
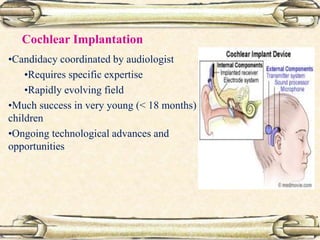
This document discusses evaluation and management of deaf children. It begins by defining different types and degrees of childhood hearing loss. Early diagnosis is important as it allows for early intervention, which research shows improves outcomes for language development and education. Universal newborn hearing screening within the first 3 months of life is now standard practice. Diagnostic tests include otoacoustic emissions testing and auditory brainstem response testing. Causes of childhood hearing loss can be genetic syndromic or non-syndromic causes. Proper evaluation involves history, physical exam, and potential genetic or imaging studies to determine the etiology.