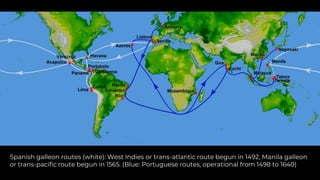
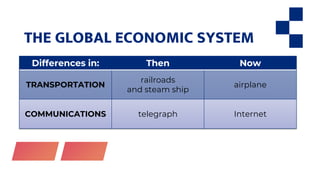
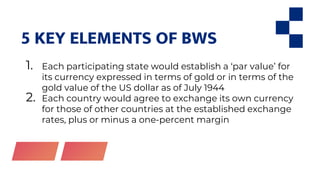
This document discusses economic globalization and related topics through four main sections. It begins by defining economic globalization and its emergence in the 1500s. It then examines the Bretton Woods system established in 1944 to regulate international monetary systems and addresses organizations it created like the IMF and World Bank. Other economic organizations are also outlined. Finally, it explores the role of multinational corporations in globalization through foreign direct investment and other activities.