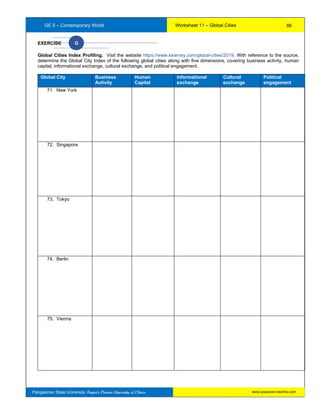
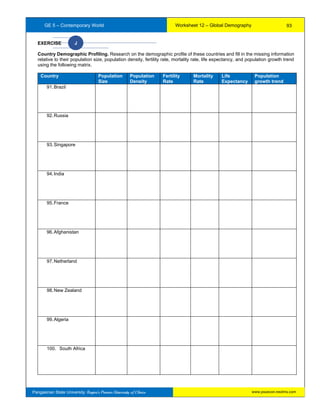
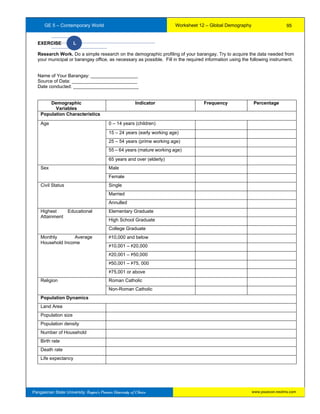
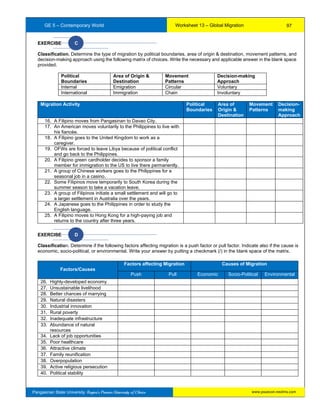
The document provides information about a workbook intended for use by students taking Contemporary World at Pangasinan State University. It begins with background on the GE5 course which introduces students to contemporary world issues through examining globalization using various social science disciplines. The workbook aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of microeconomics and serves as a learning and assessment tool. It covers exercises building on 16 course outcomes related to understanding global issues like economic and cultural globalization, trade, governance, and citizenship. The workbook requires sustained effort but will help students answer its exercises and learn about the contemporary world.