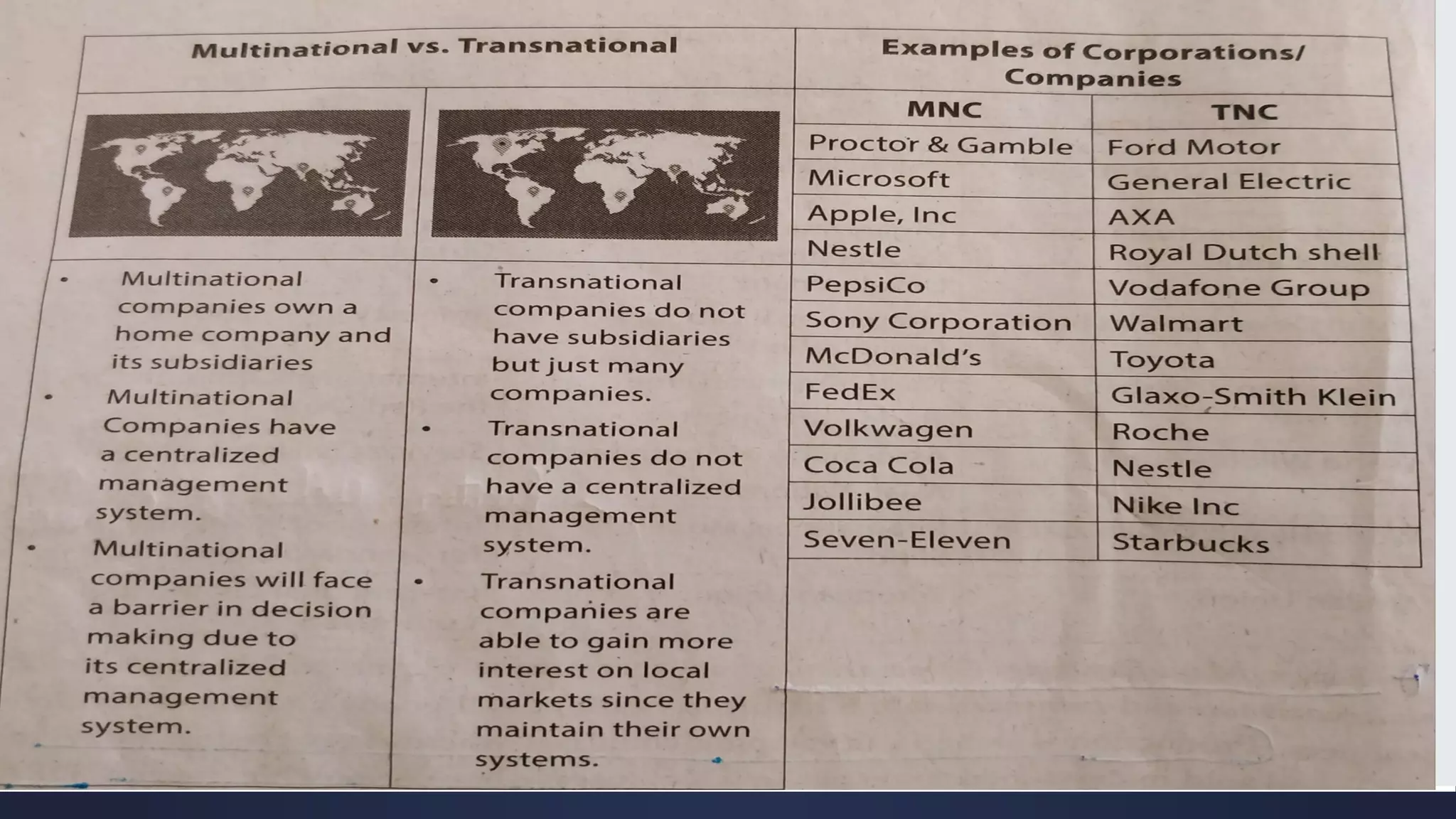
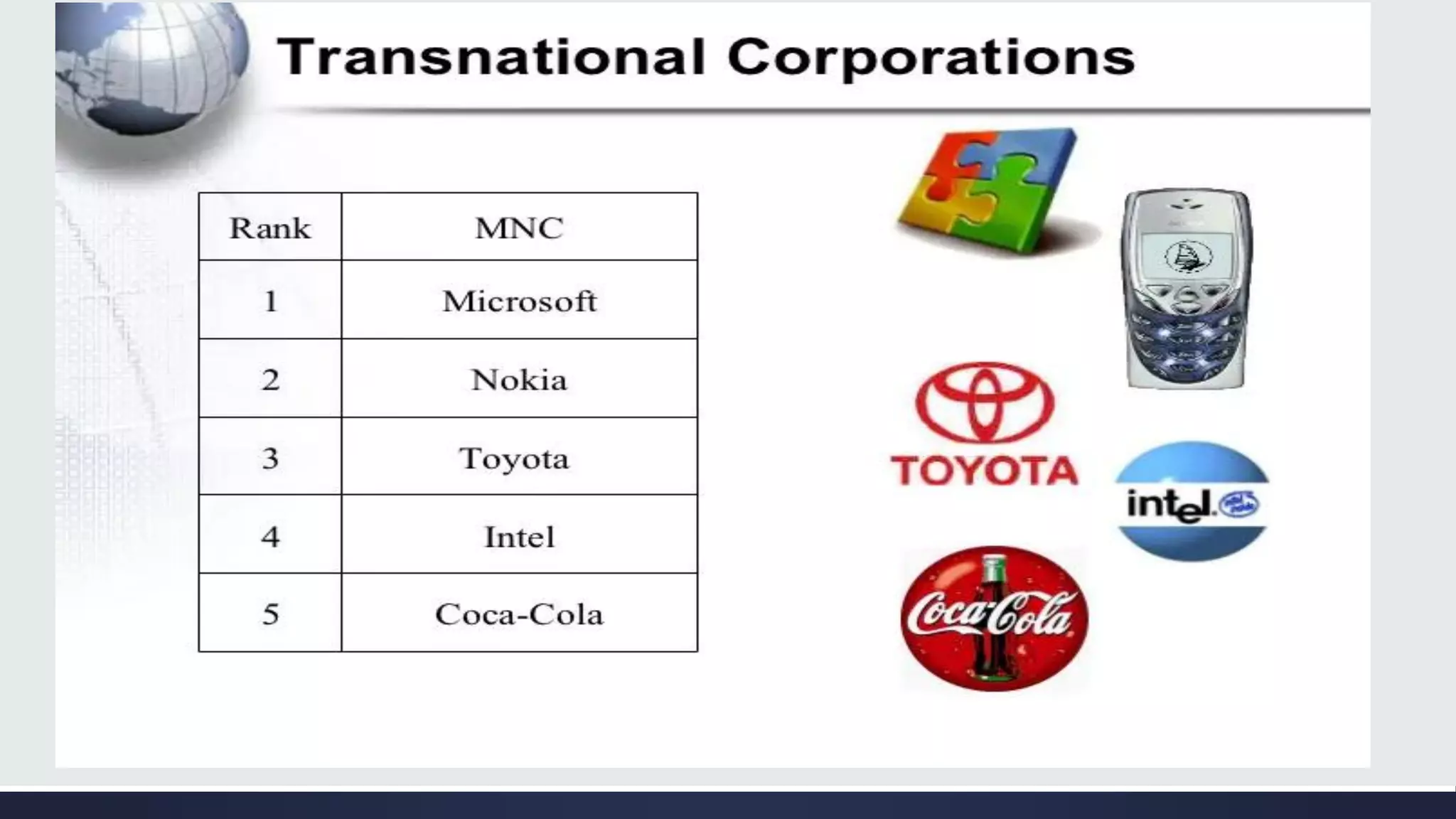
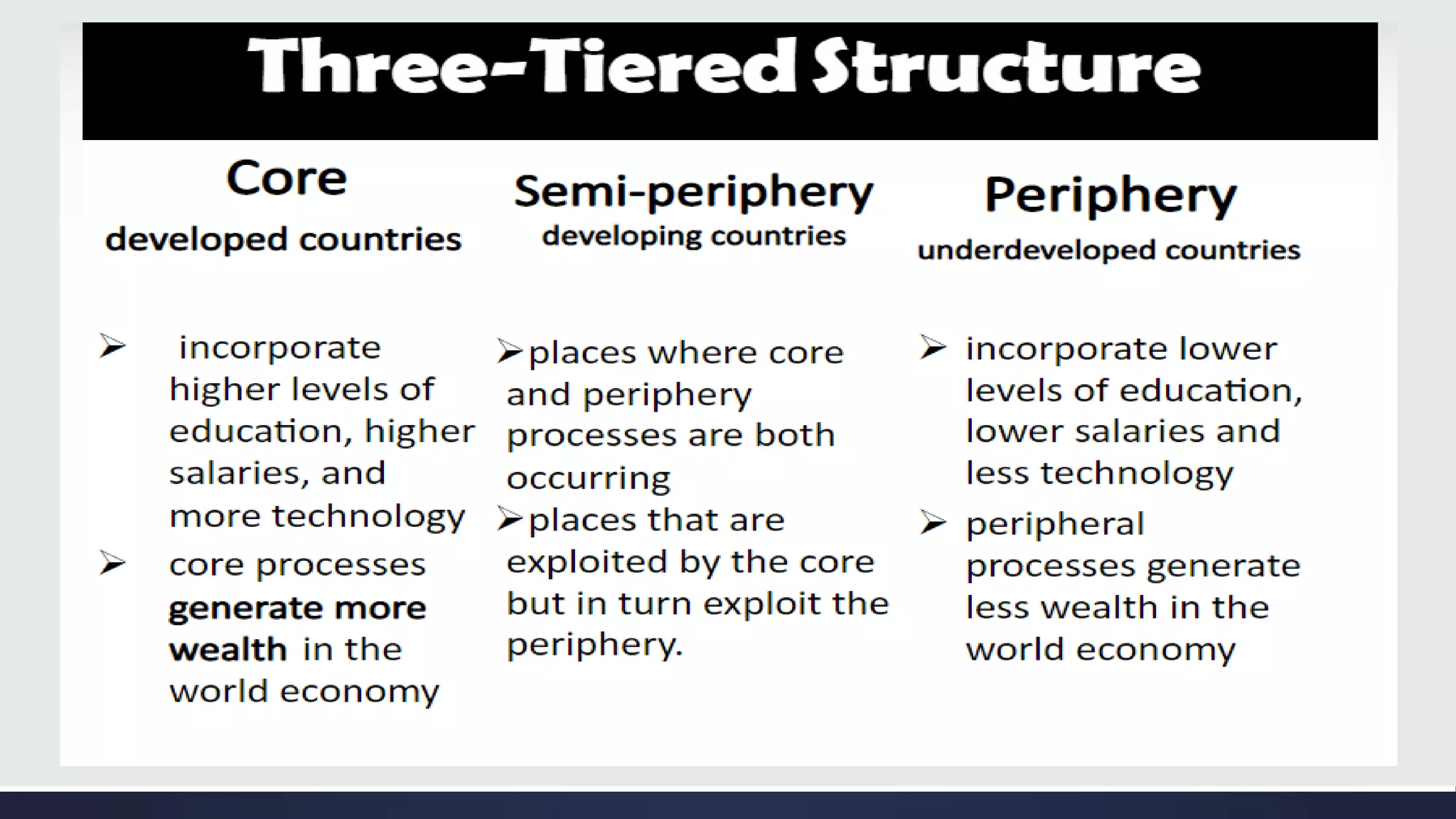
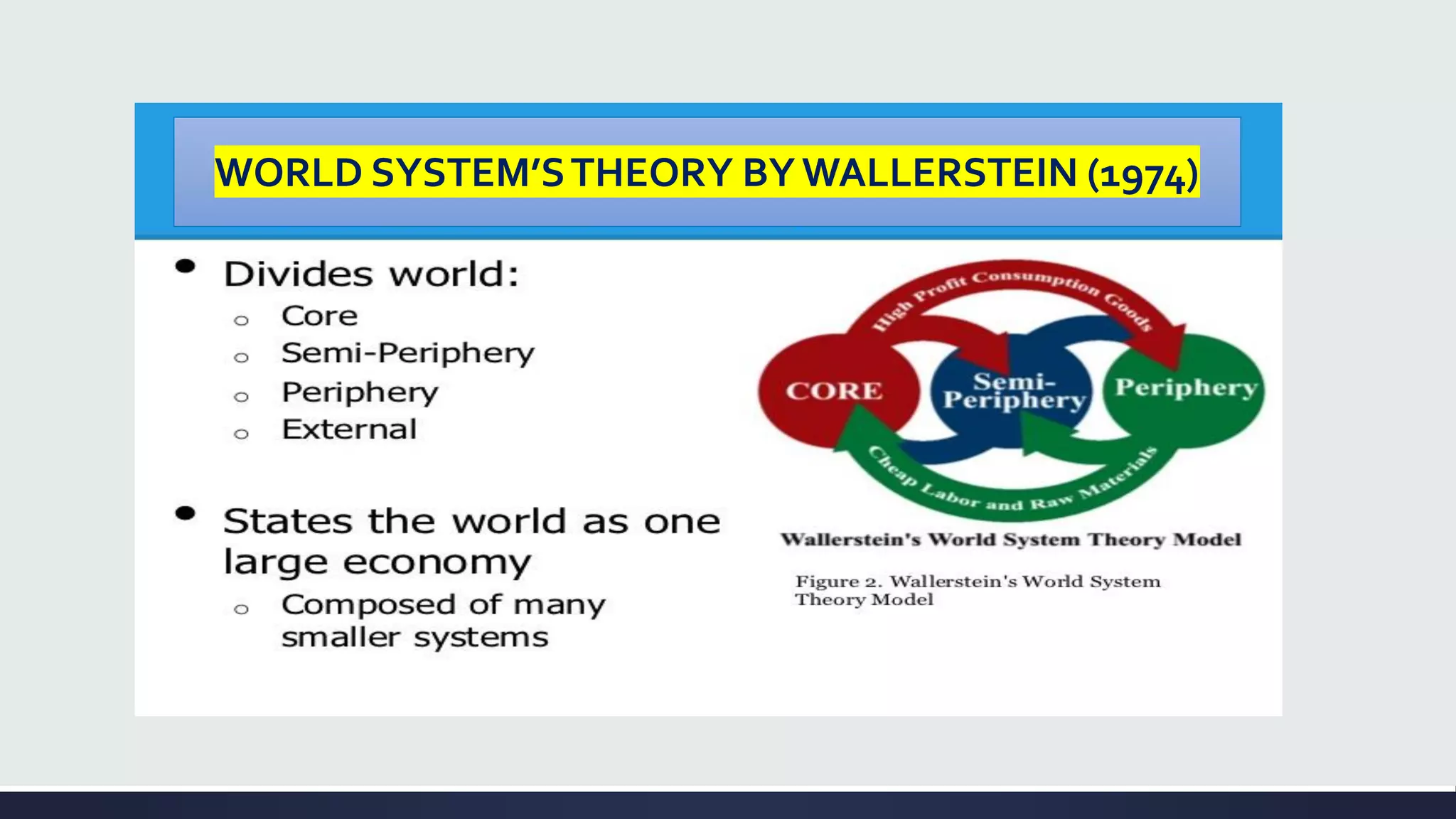
Globalization is a process of increasing integration and interaction between people, companies, and governments around the world. It is driven by international trade and investment and aided by information technology. This process affects many aspects of society including economics, politics, culture, and the environment. Some key aspects of globalization include the liberalization and integration of markets on a global scale, as well as the blending of cultures through increased travel, trade, and information sharing across borders.