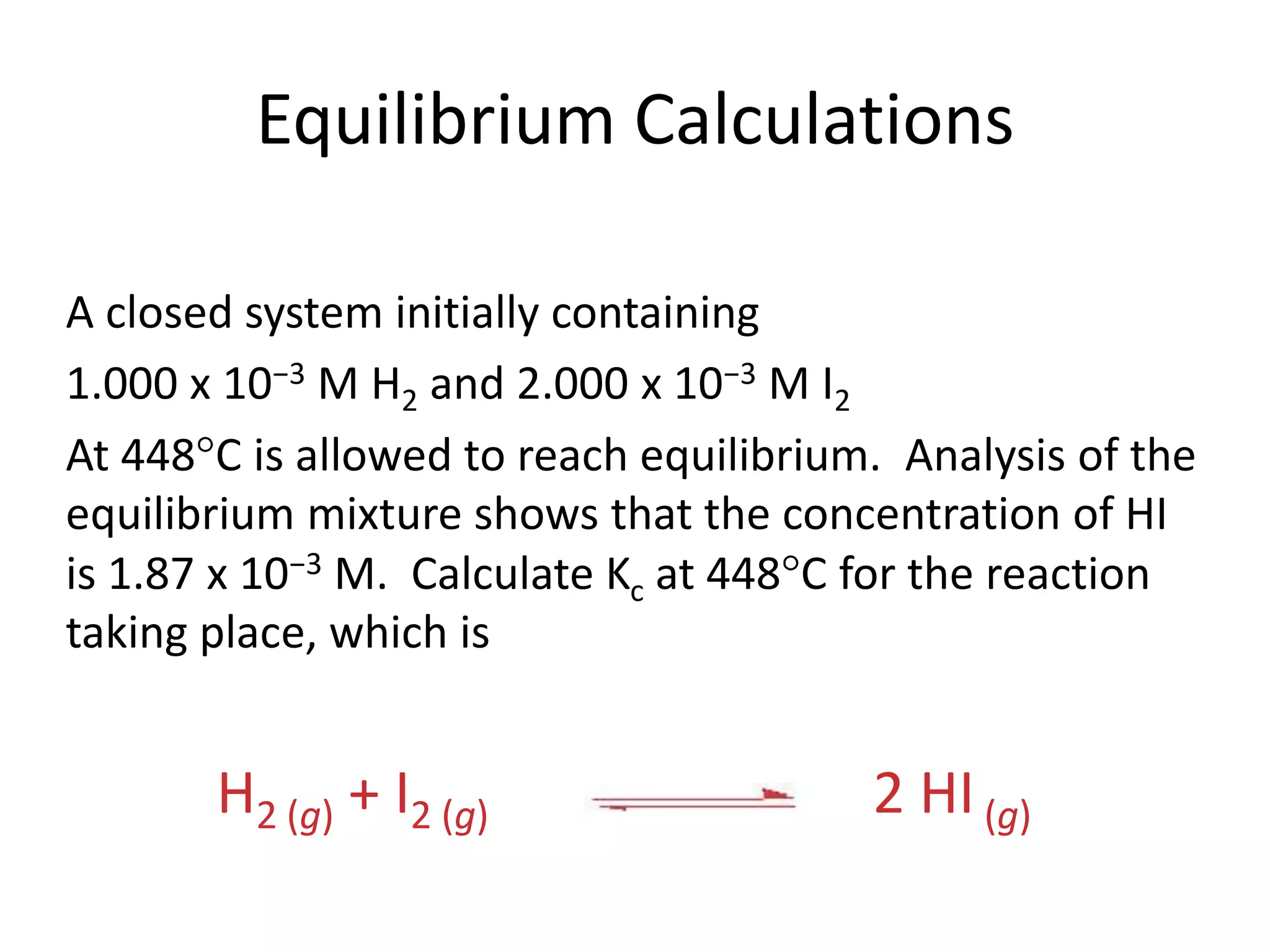
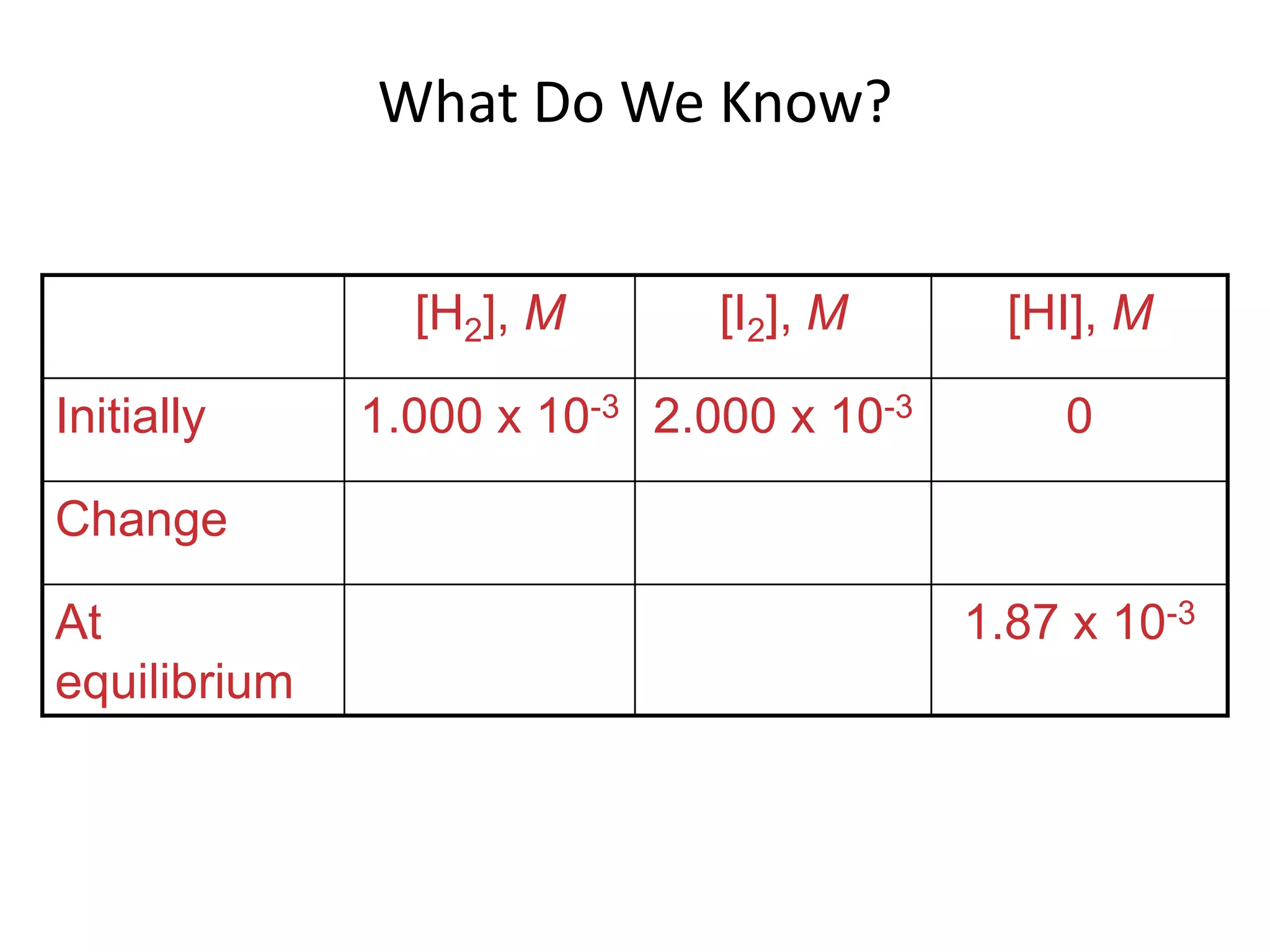
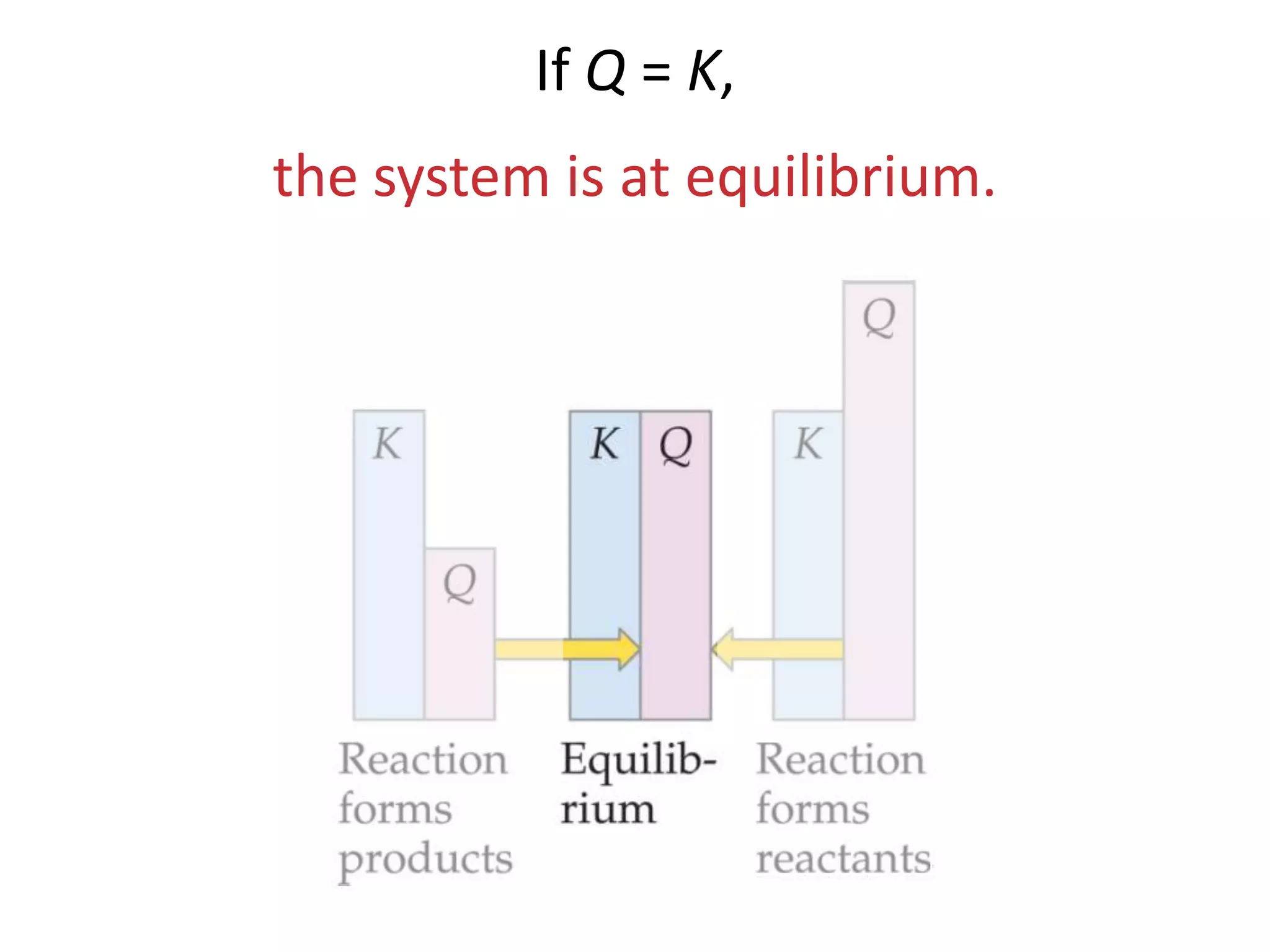
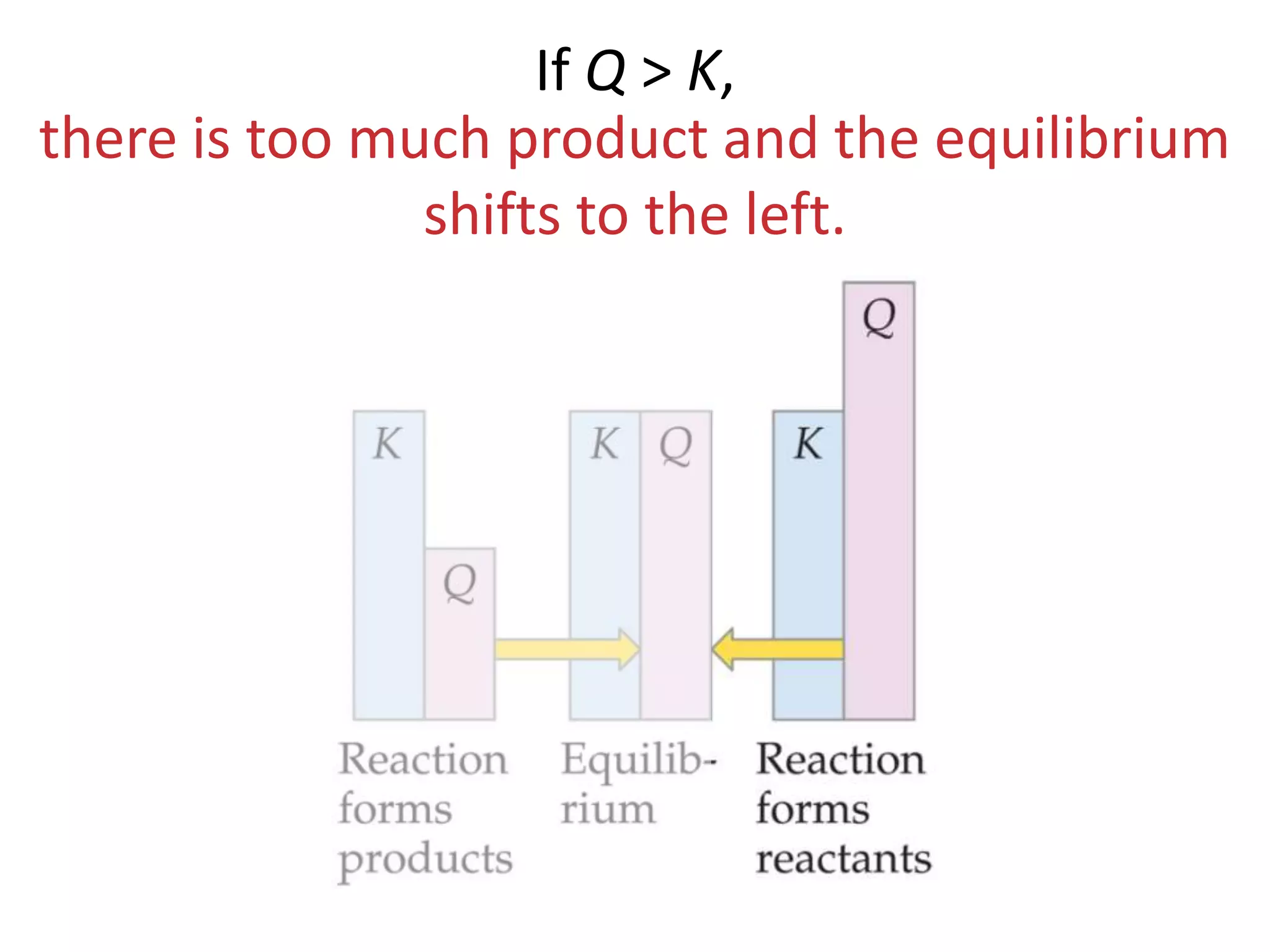
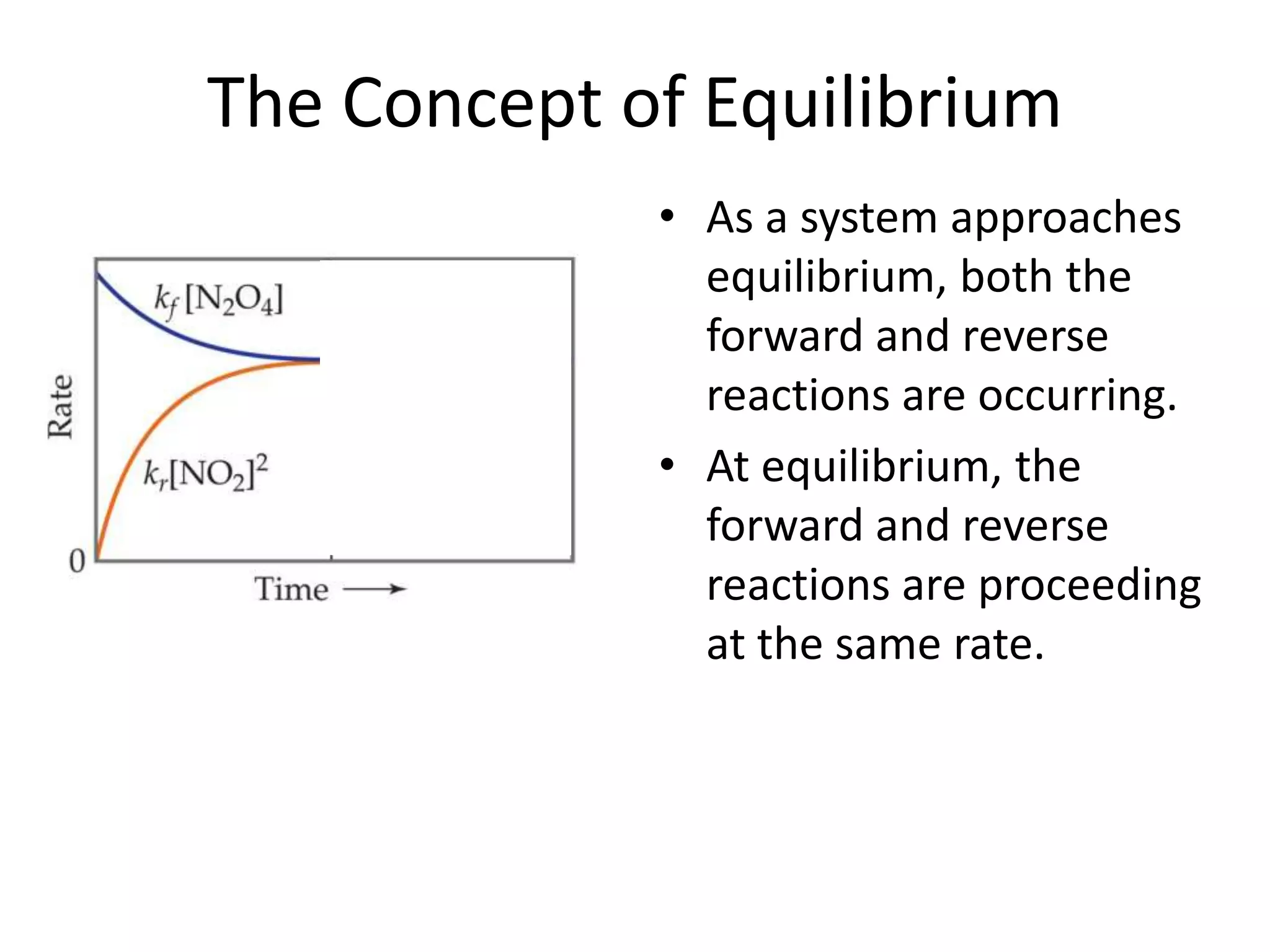
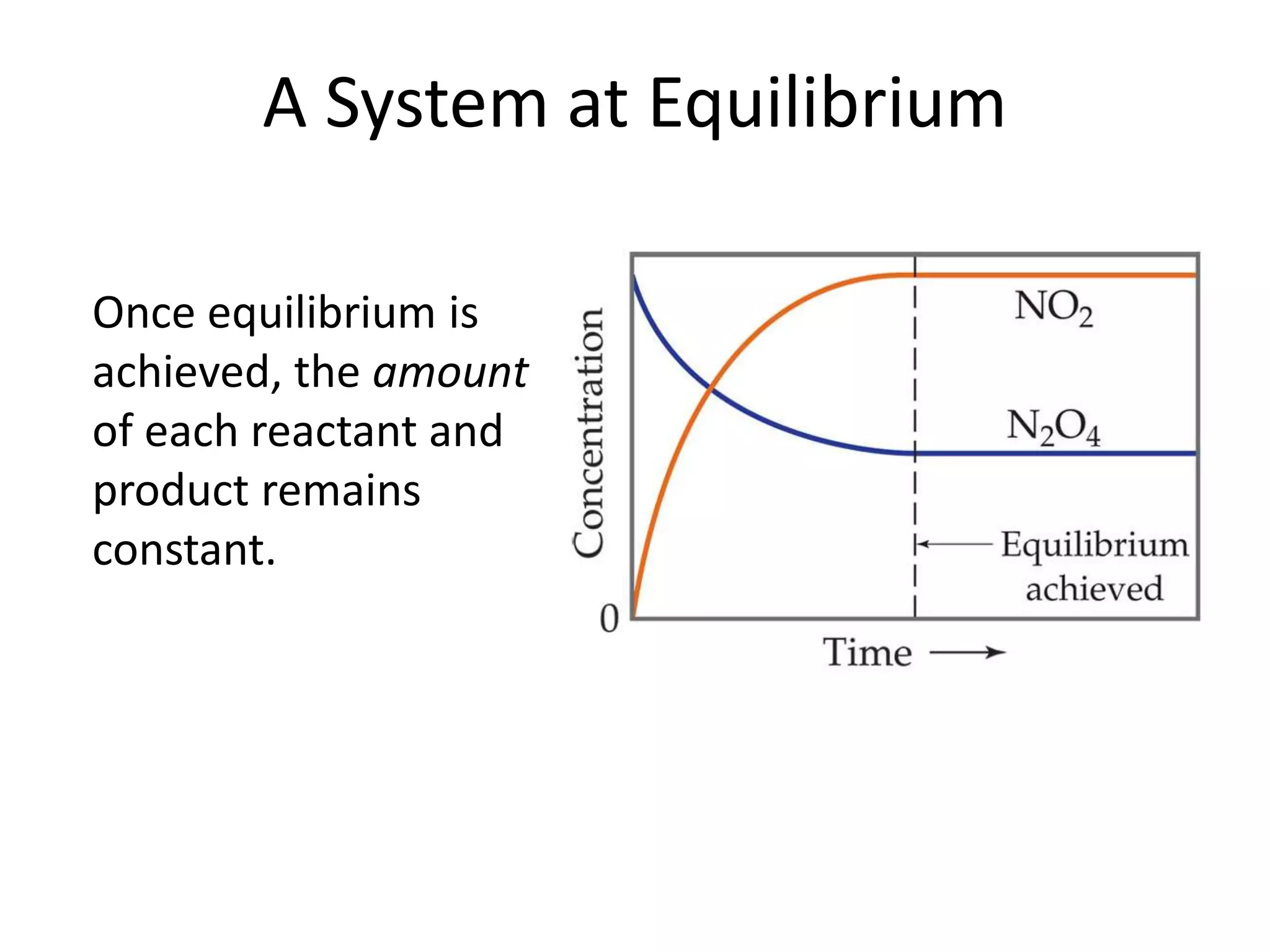
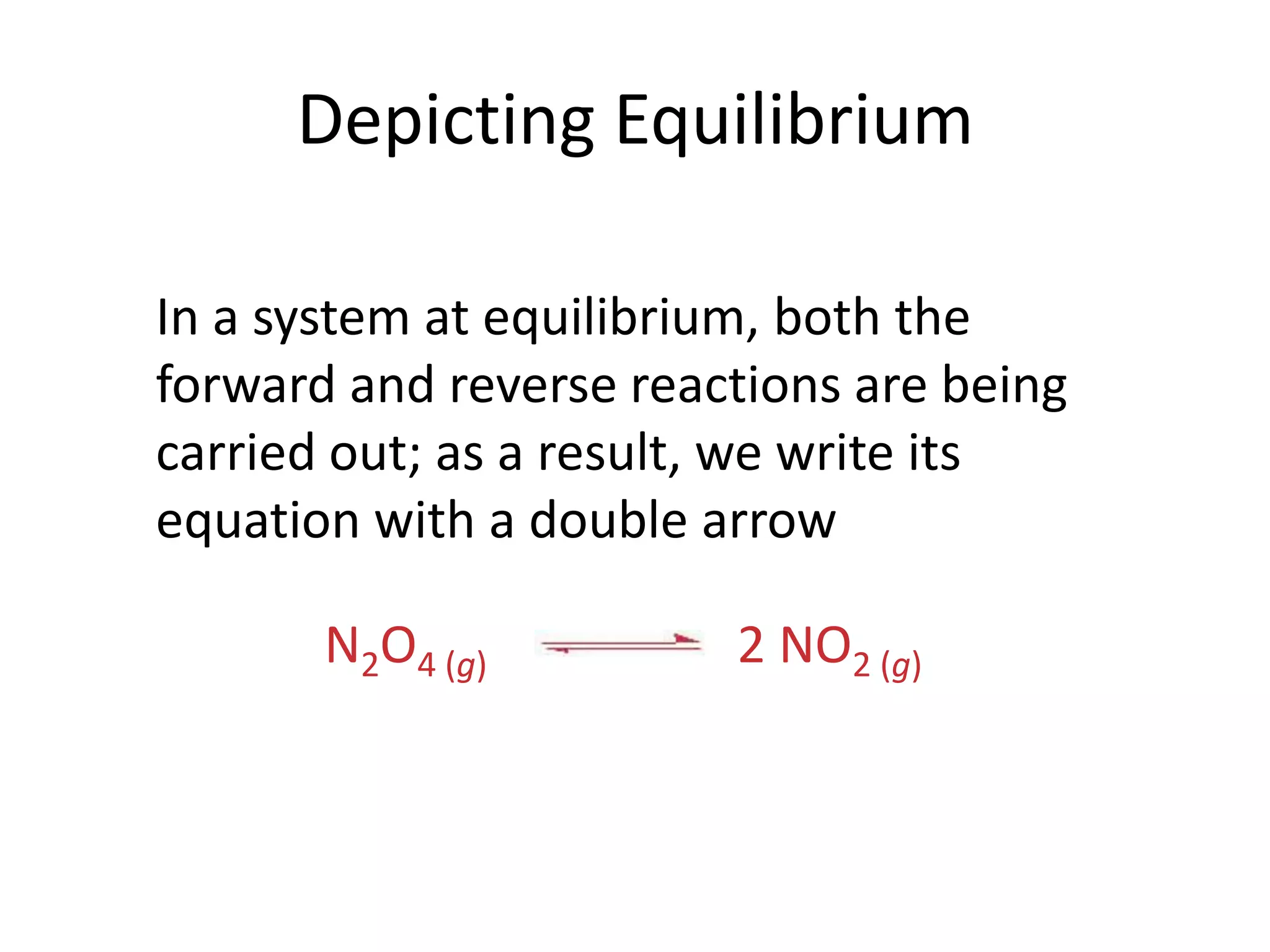
The document discusses chemical equilibrium, which occurs when the forward and reverse reactions of a chemical reaction proceed at the same rate. At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. The equilibrium constant, K, is a ratio of products over reactants that characterizes the position of equilibrium. A large K value indicates the reaction favors products, while a small K value indicates the reaction favors reactants.

![The Equilibrium ConstantForward reaction:N2O4 (g) 2 NO2 (g)Rate law:Rate = kf [N2O4]Reverse reaction:2 NO2 (g) N2O4 (g)Rate law:Rate = kr [NO2]2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theconceptofequilibrium-100415122225-phpapp01/75/The-concept-of-equilibrium-5-2048.jpg)
![The Equilibrium Constant[NO2]2[N2O4]kfkr=Therefore, at equilibriumRatef = Raterkf [N2O4] = kr [NO2]2Rewriting this, it becomes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theconceptofequilibrium-100415122225-phpapp01/75/The-concept-of-equilibrium-6-2048.jpg)
![The Equilibrium Constant[NO2]2[N2O4]Keq =kfkr= The ratio of the rate constants is a constant at that temperature, and the expression becomes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theconceptofequilibrium-100415122225-phpapp01/75/The-concept-of-equilibrium-7-2048.jpg)
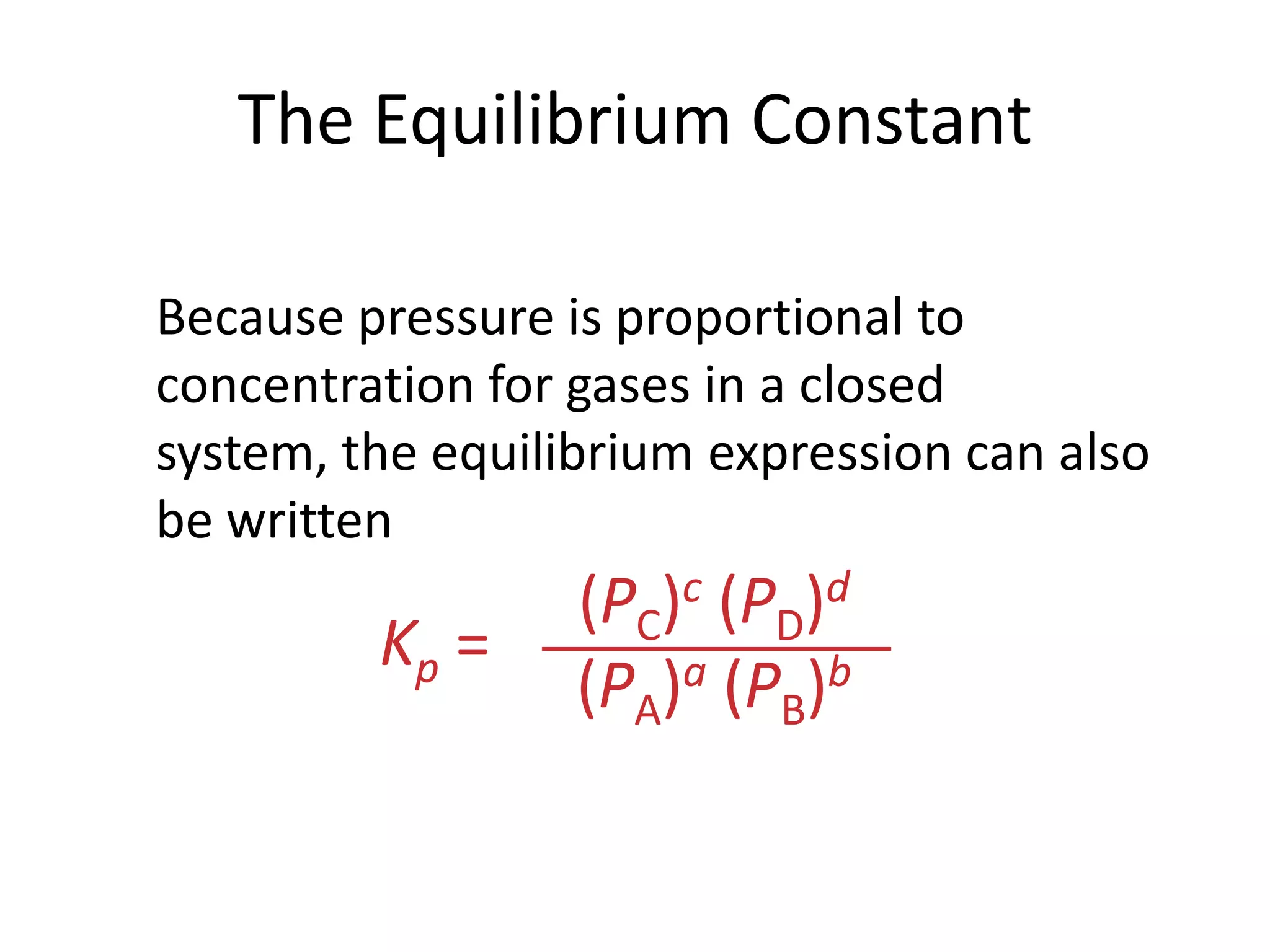
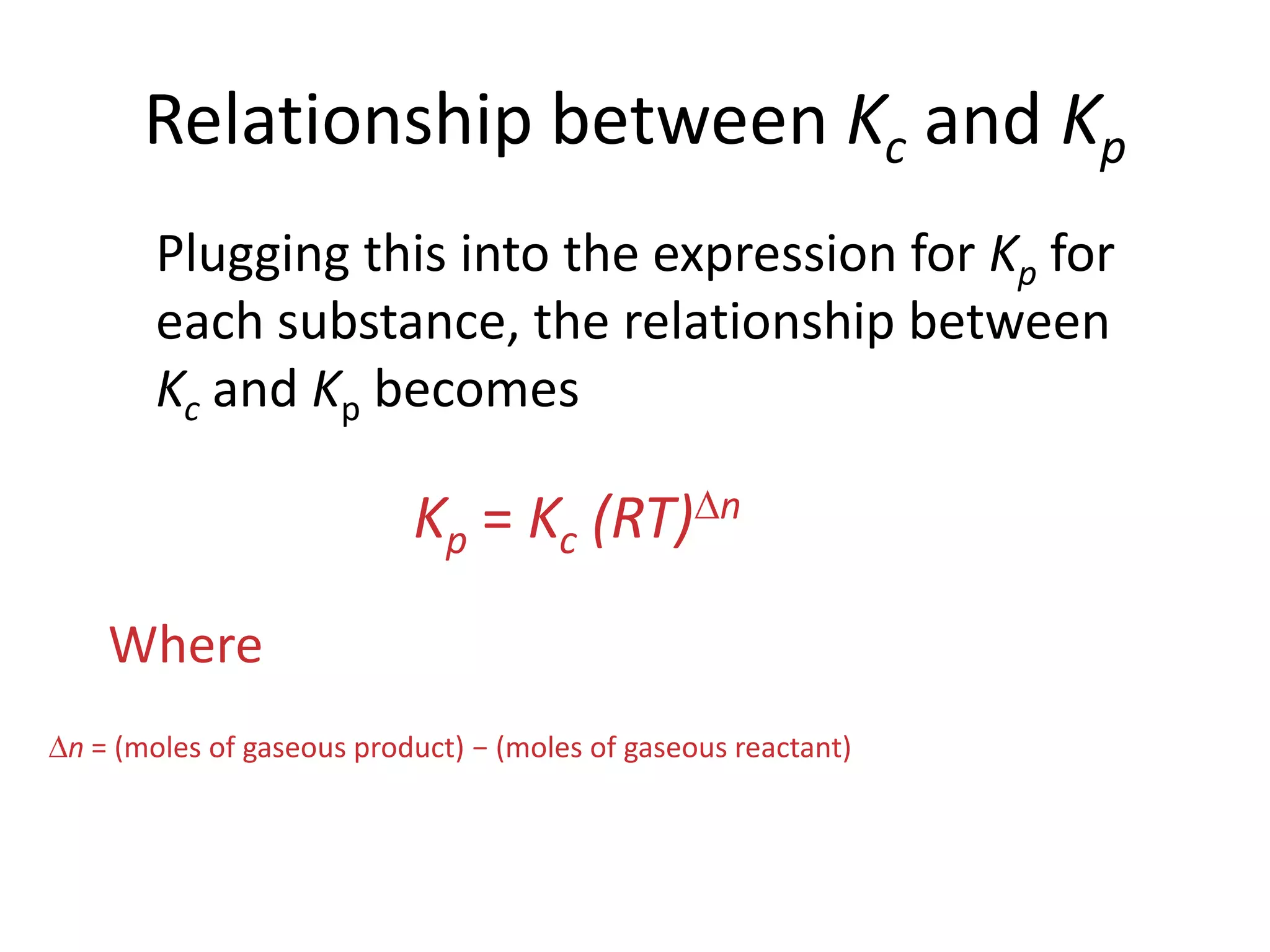
![The Equilibrium ConstantaA + bBcC + dD[C]c[D]d[A]a[B]bKc = To generalize this expression, consider the reactionThe equilibrium expression for this reaction would beWhat Are the Equilibrium Expressions for These Equilibria?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theconceptofequilibrium-100415122225-phpapp01/75/The-concept-of-equilibrium-8-2048.jpg)
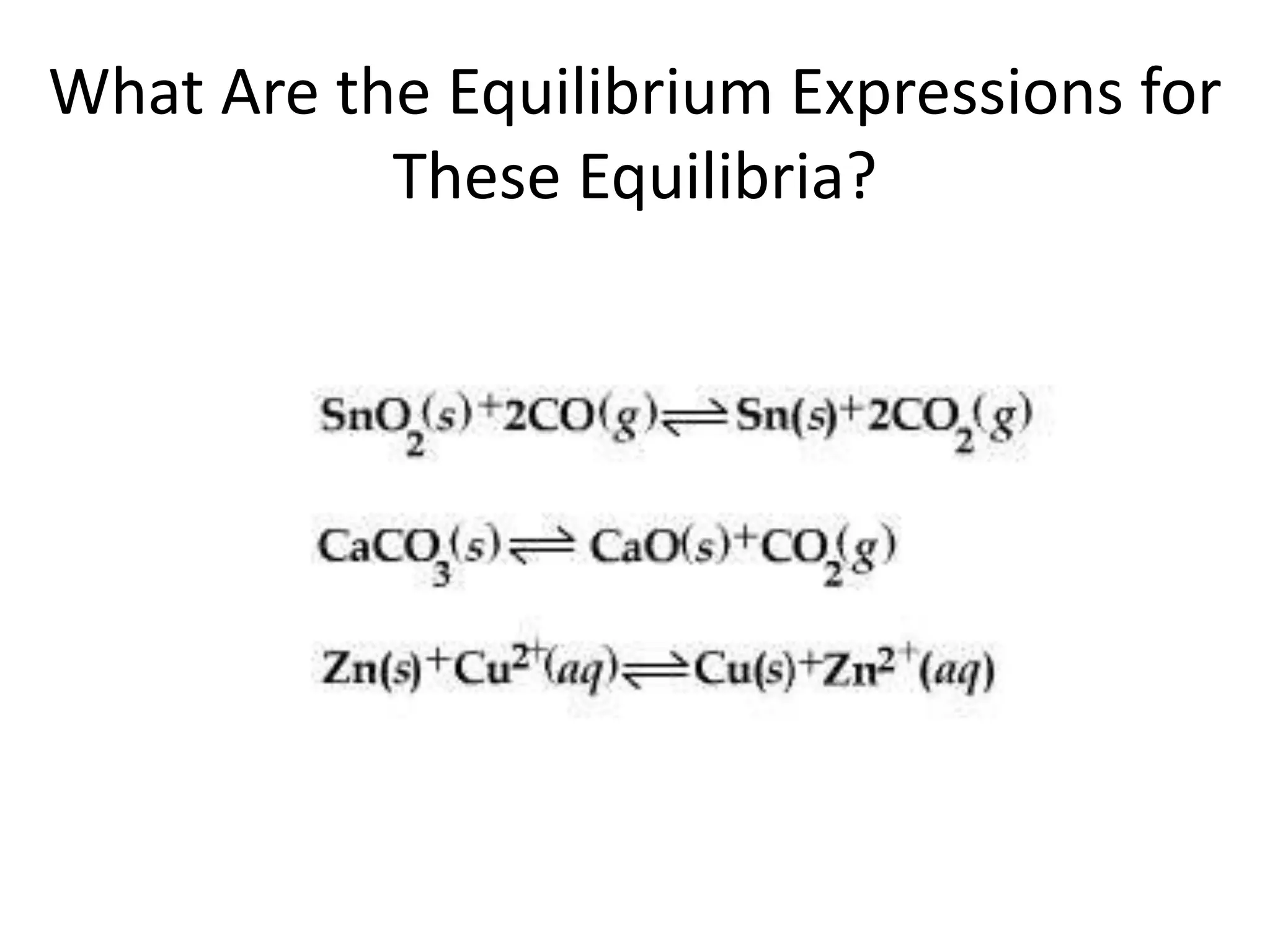
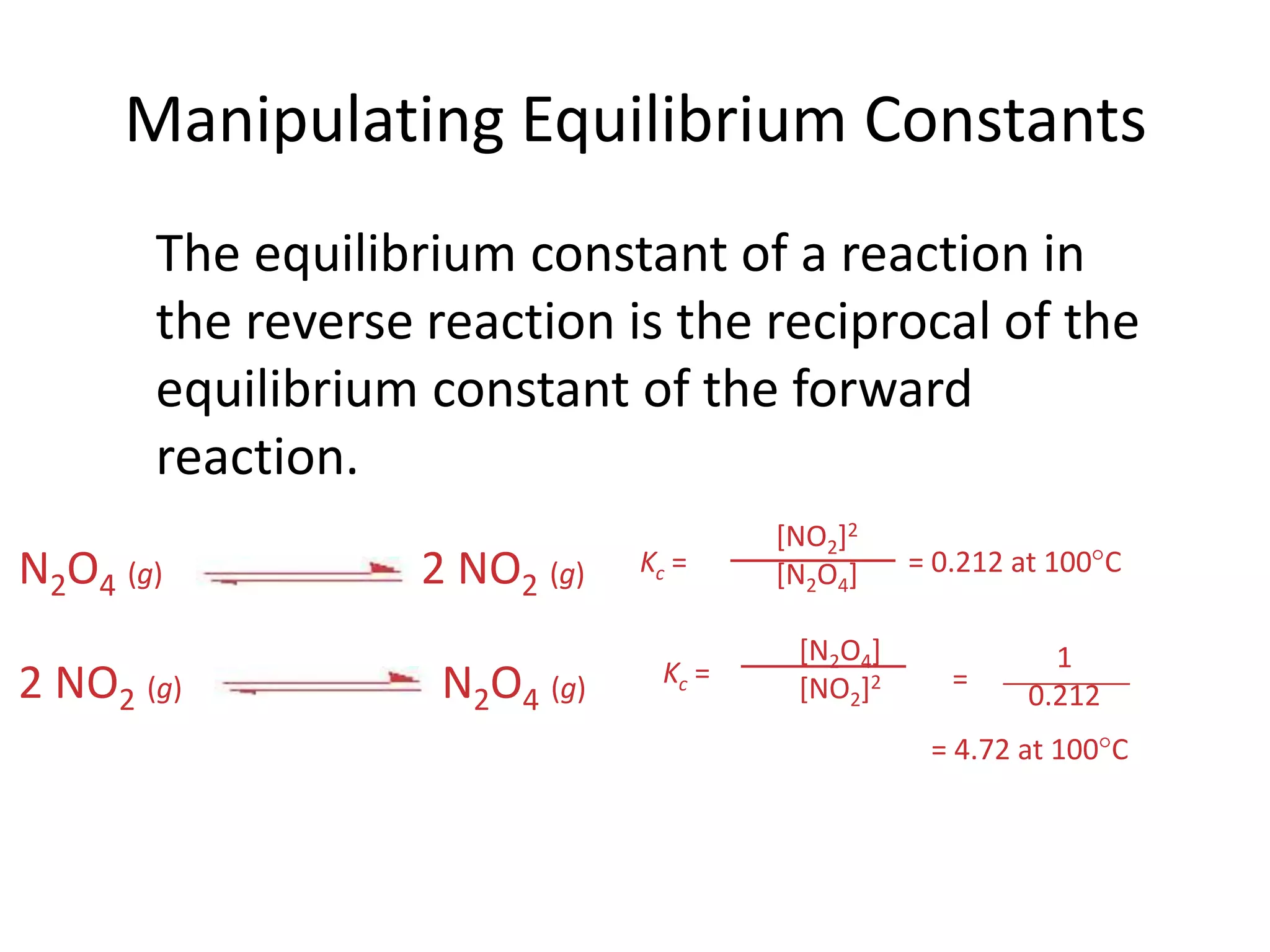
![What Does the Value of K Mean?If K >> 1, the reaction is product-favored; product predominates at equilibrium.If K << 1, the reaction is reactant-favored; reactant predominates at equilibrium.Manipulating Equilibrium ConstantsKc = = 4.72 at 100CKc = = 0.212 at 100CN2O4(g)2 NO2(g)N2O4(g)2 NO2(g)[NO2]2[N2O4][N2O4][NO2]210.212= The equilibrium constant of a reaction in the reverse reaction is the reciprocal of the equilibrium constant of the forward reaction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theconceptofequilibrium-100415122225-phpapp01/75/The-concept-of-equilibrium-12-2048.jpg)
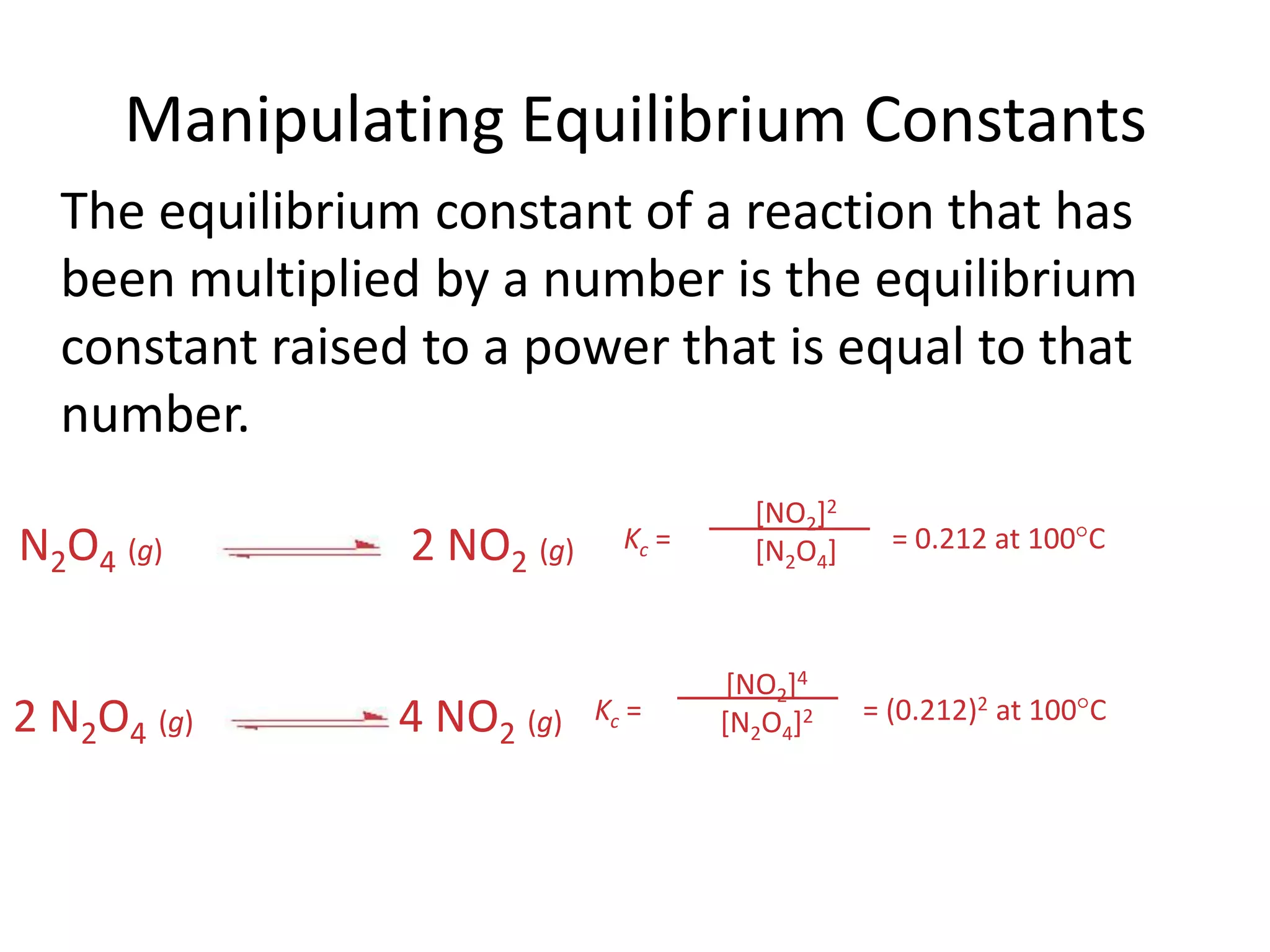
![Manipulating Equilibrium ConstantsKc = = 0.212 at 100CKc = = (0.212)2 at 100CN2O4(g)2 NO2(g)2 N2O4(g)4 NO2(g)[NO2]2[N2O4][NO2]4[N2O4]2 The equilibrium constant of a reaction that has been multiplied by a number is the equilibrium constant raised to a power that is equal to that number.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theconceptofequilibrium-100415122225-phpapp01/75/The-concept-of-equilibrium-13-2048.jpg)
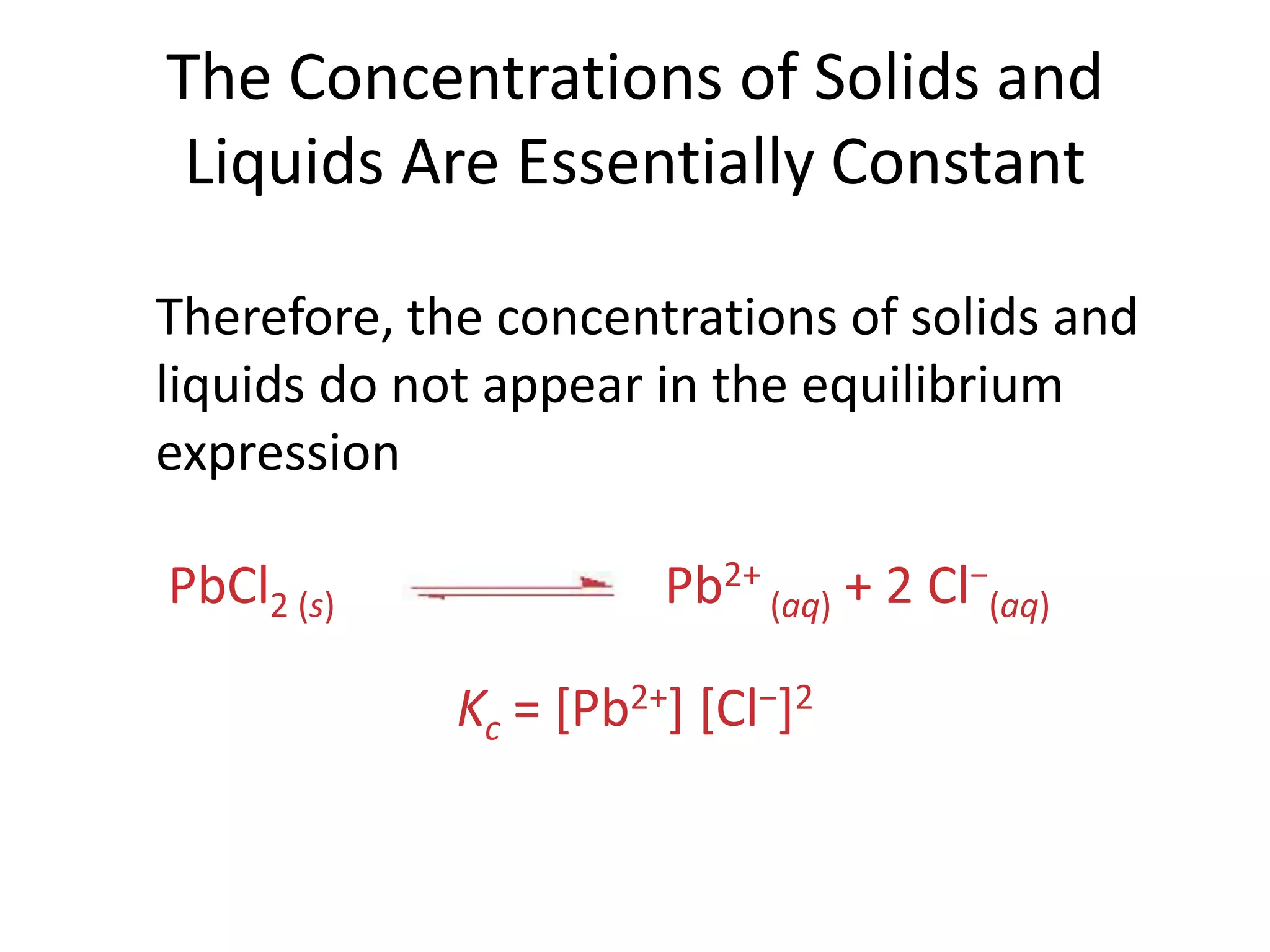
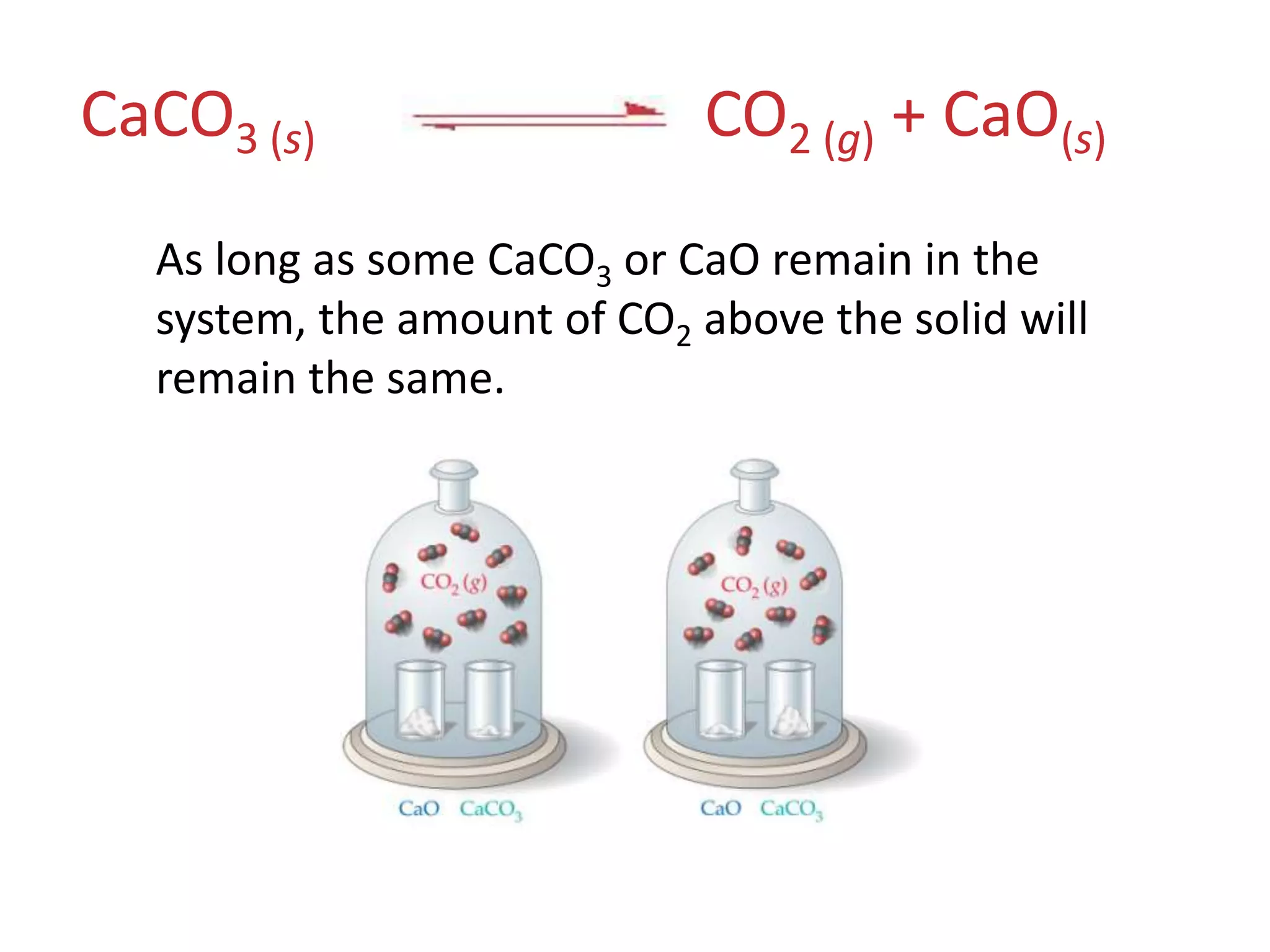
![The Concentrations of Solids and Liquids Are Essentially ConstantPbCl2 (s)Pb2+ (aq) + 2 Cl−(aq) Therefore, the concentrations of solids and liquids do not appear in the equilibrium expressionKc = [Pb2+] [Cl−]2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theconceptofequilibrium-100415122225-phpapp01/75/The-concept-of-equilibrium-16-2048.jpg)