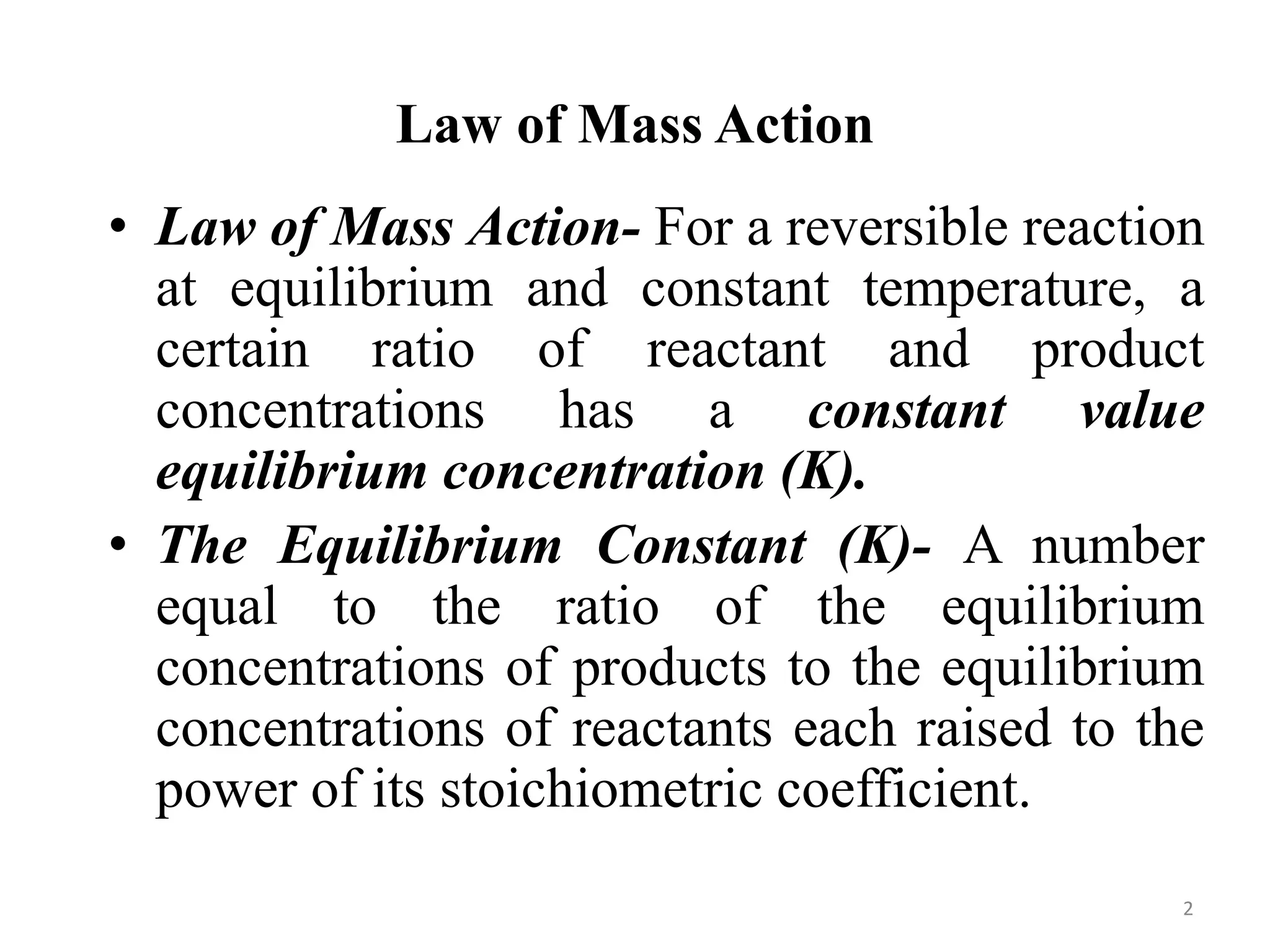
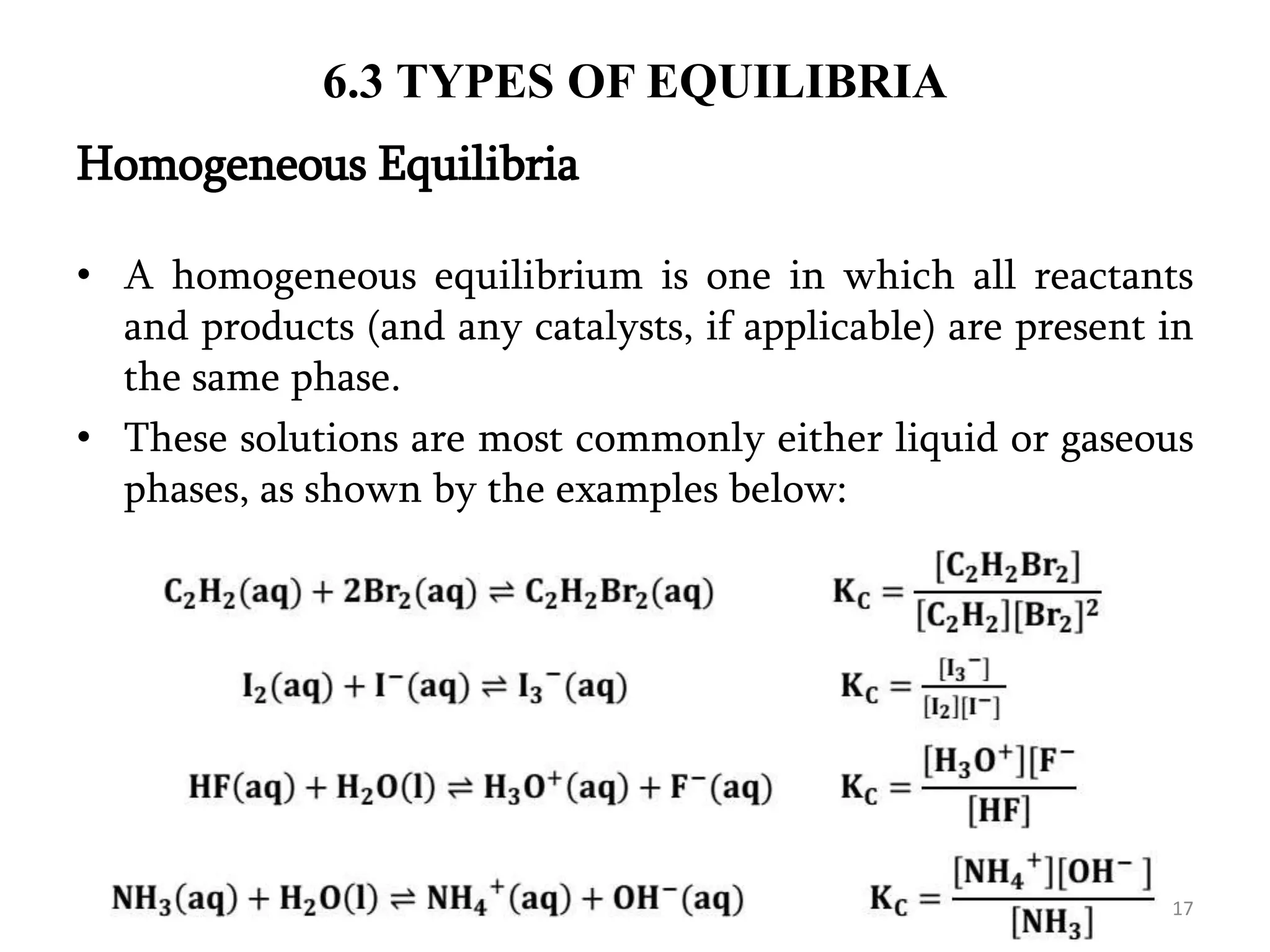
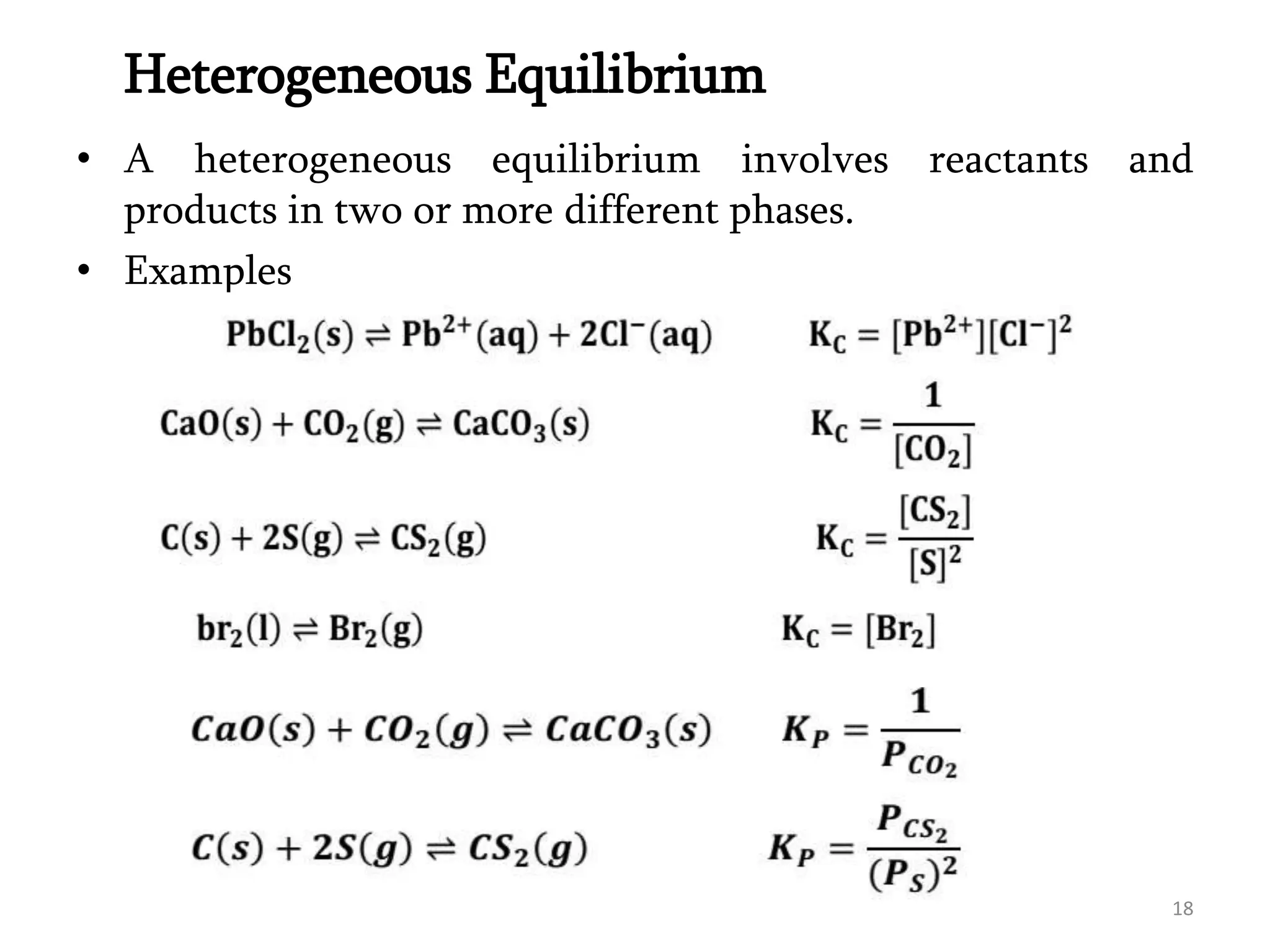
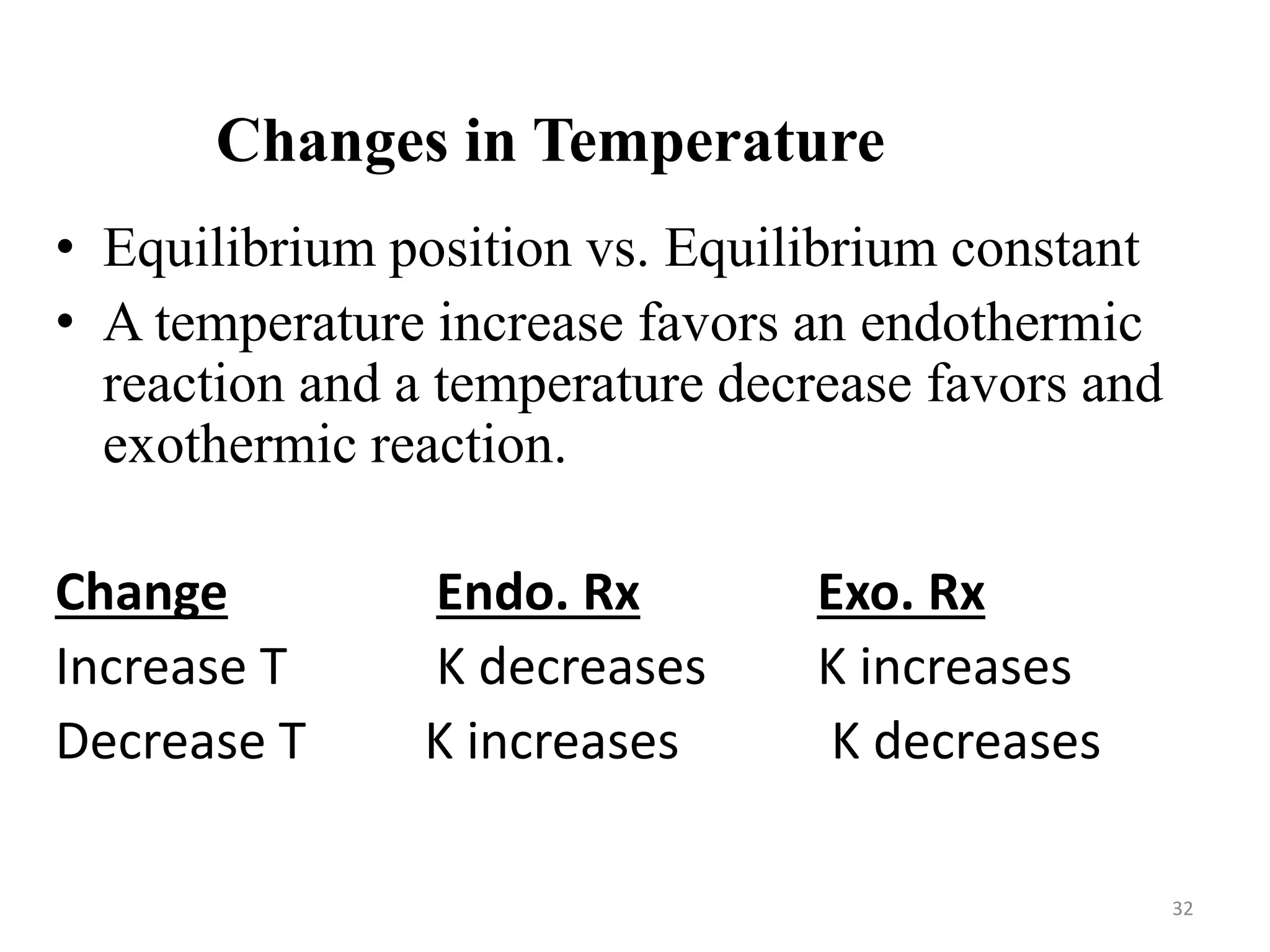
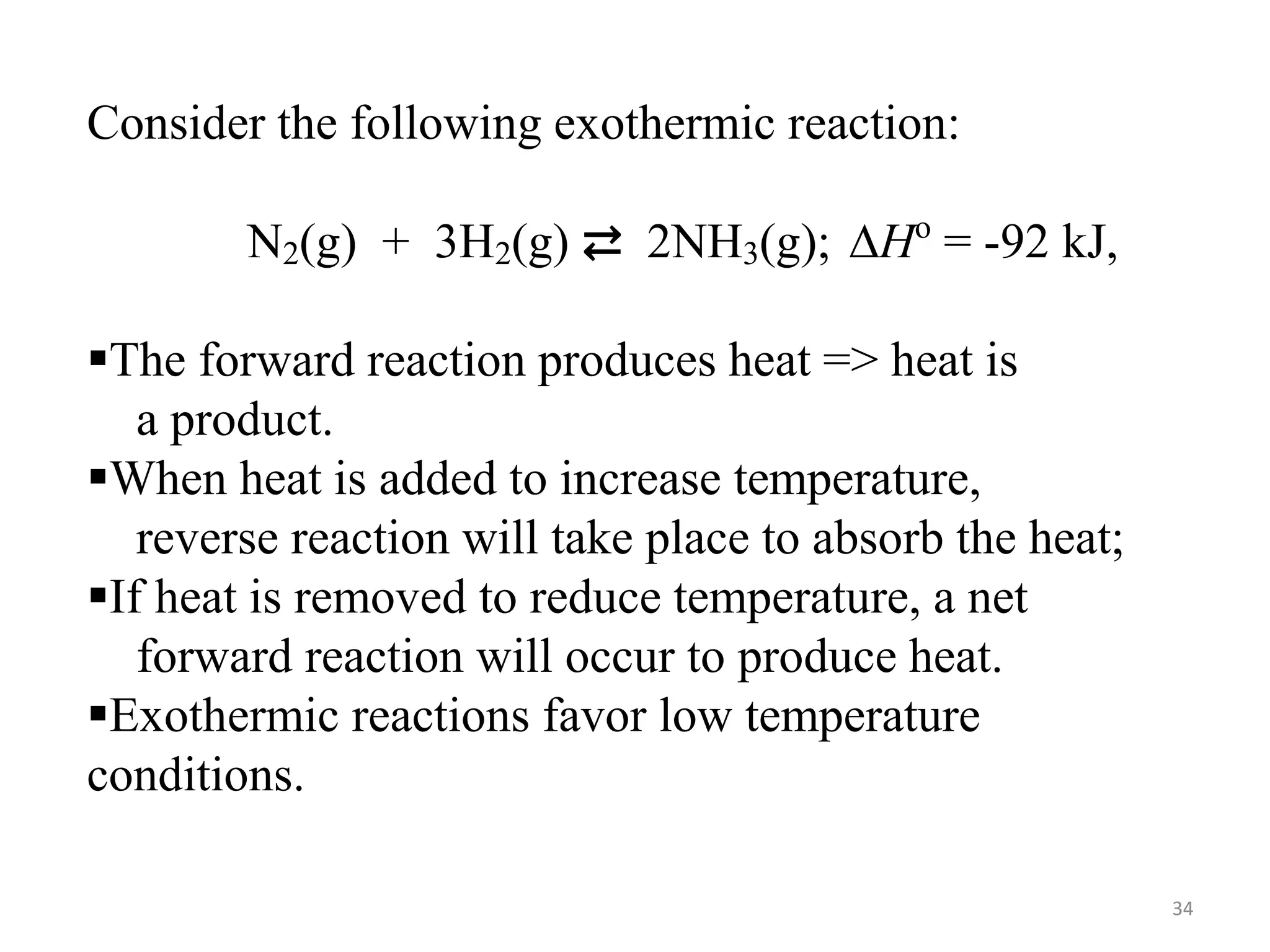
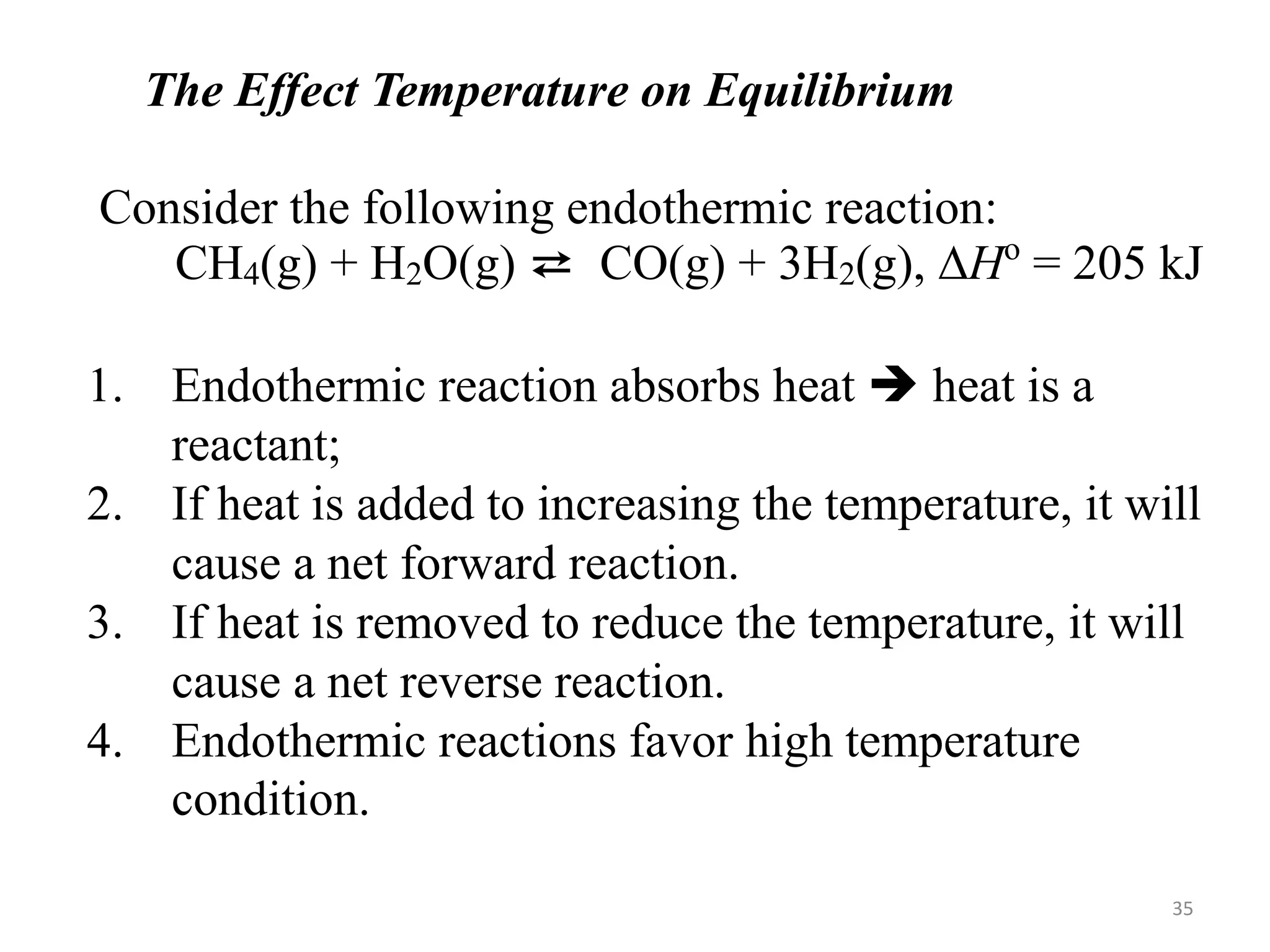
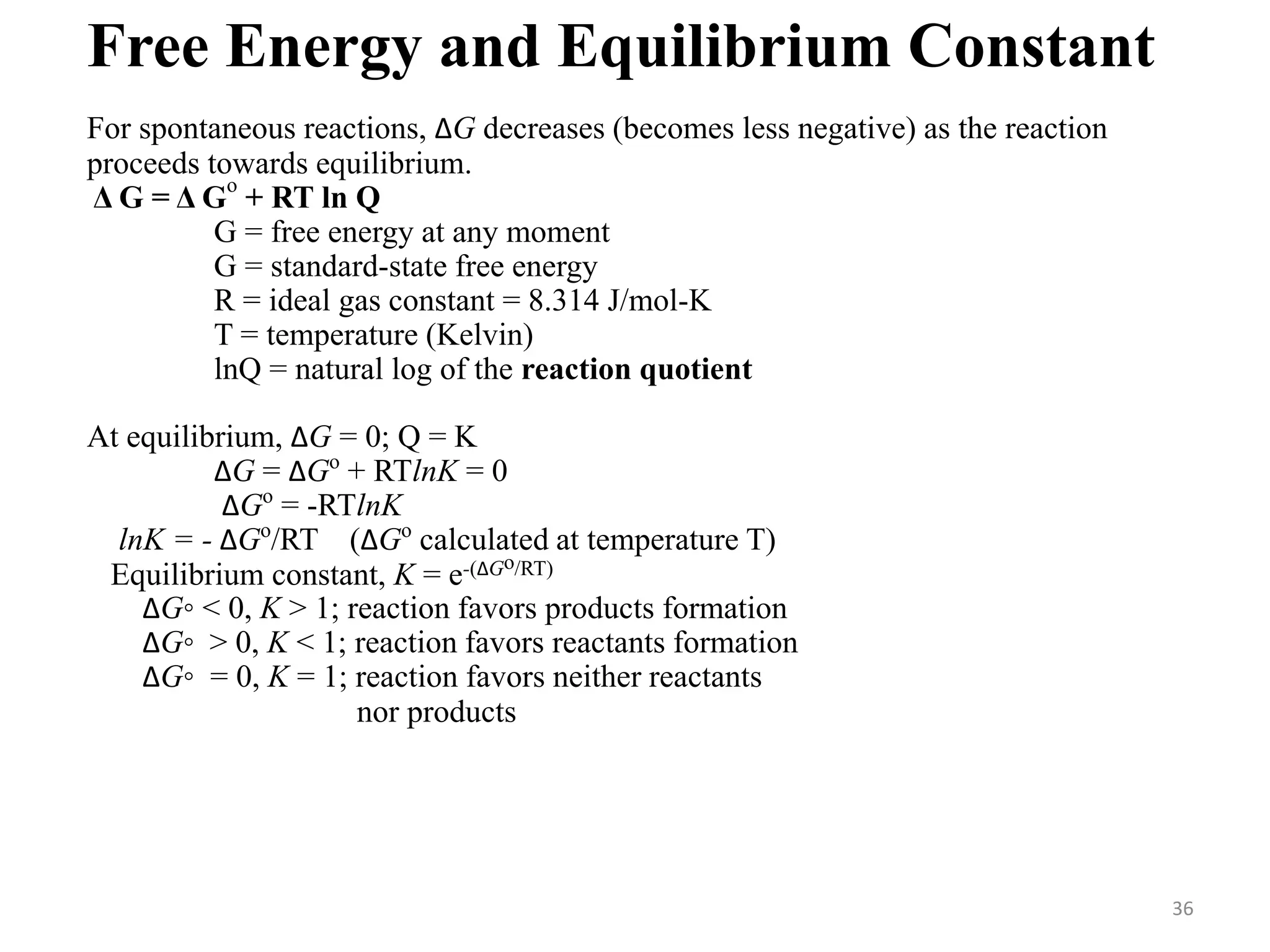
This document discusses chemical equilibrium, including definitions, concepts, and factors that affect equilibrium. It defines equilibrium as a state where the forward and reverse reaction rates are equal, resulting in constant concentrations. The equilibrium constant, K, relates concentrations or pressures of products and reactants. A system at equilibrium adjusts in response to changes in concentration, pressure, volume, or temperature to partially counteract the change according to Le Chatelier's principle. Temperature particularly affects equilibrium based on whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.

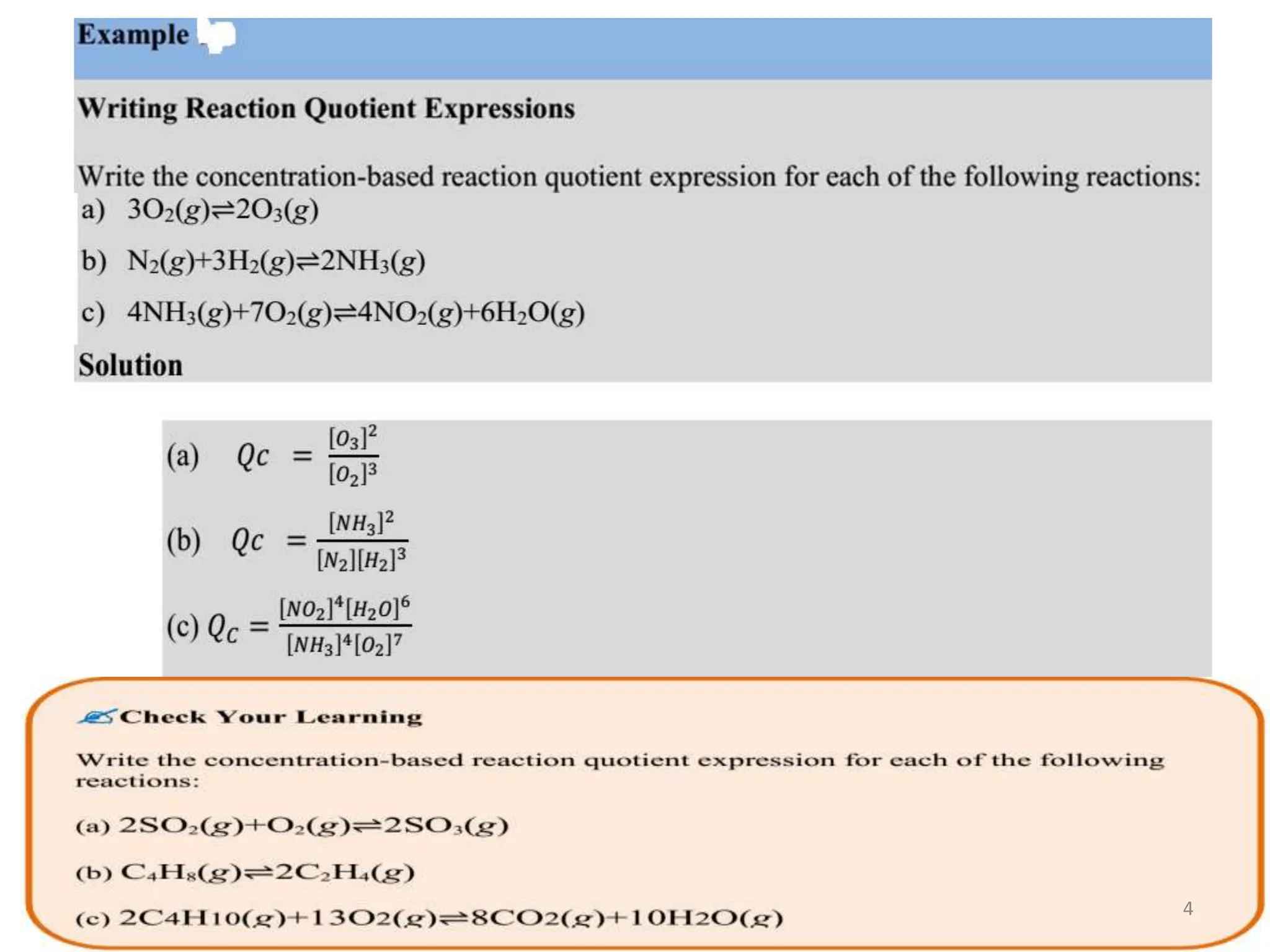
![• Reaction Quotient: Symbol Q, a mathematical
expression relating the concentrations of
reactants and products at any stage of a reaction.
For the general reaction:
At equilibrium:
At any stage
K =
[C]c[D]d
[A]a[B]b
aA (g) + bB (g) c C (g) + d D (g)
Q =
[C]c[D]d
[A]a[B]b
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-3-2048.jpg)
![6.2 Chemical Equilibrium
• Chemical equilibrium is defined by K.
• The magnitude of K will tell us if the
equilibrium reaction favors the reactants or
the products.
• If K » 1……..favors products
• If K « 1……..favors reactants
• If K = 0…….. At equilibrium
If Q < K, the reaction goes forward | to increase [product]
if Q = K, the system is at equilibrium |the law of mass action
if Q > K, the reaction goes backward | to decrease [product] 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-5-2048.jpg)




![The relation between Kc and Kp
• Equilibrium Constant Equations
• But from equations of ideal gases we have ,
PV= nRT, P = n/V RT
P = cRT
aA (g) + bB (g) cC (g) + dD (g)
Kc =
[C]c[D]d
[A]a[B]b
Kp =
PcCPd
PaAPbB
D
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-12-2048.jpg)
![Equilibrium Constant Expressions
Kp = Kc(RT)Dn
Dn = moles of gaseous products – moles of gaseous reactants
Dn = (c + d) – (a + b)
Kp =
[RTC]c [RTD]d
[RTA]a[RTB]b
Kp =KC
[RT]c [RT]d
[RT]a[RT]b
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-13-2048.jpg)
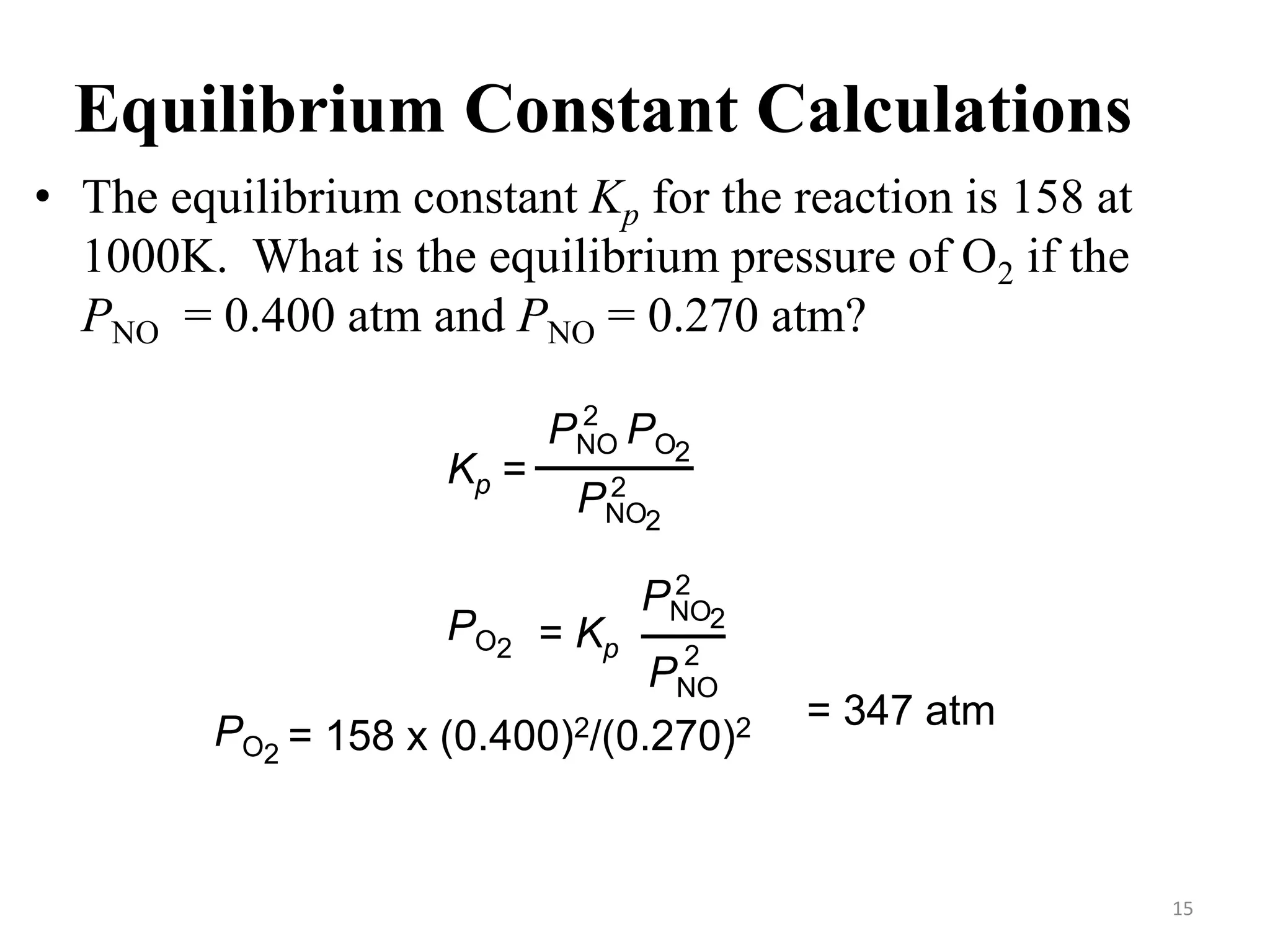
![Equilibrium Constant Calculations
The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction between carbon
monoxide and molecular chlorine to form COCl2 (g) at 740C
are [CO] = 0.012 M, [Cl2] = 0.054 M, and [COCl2] = 0.14 M.
Calculate the equilibrium constants Kc and Kp.
CO (g) + Cl2 (g) COCl2 (g)
Kc = [COCl2]
[CO][Cl2] =
0.14
0.012 x 0.054
= 220
Kp = Kc(RT)Dn
Dn = 1 – 2 = -1 R = 0.0821 T = 273 + 74 = 347 K
Kp = 220 x (0.0821 x 347)-1 = 7.7
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-14-2048.jpg)

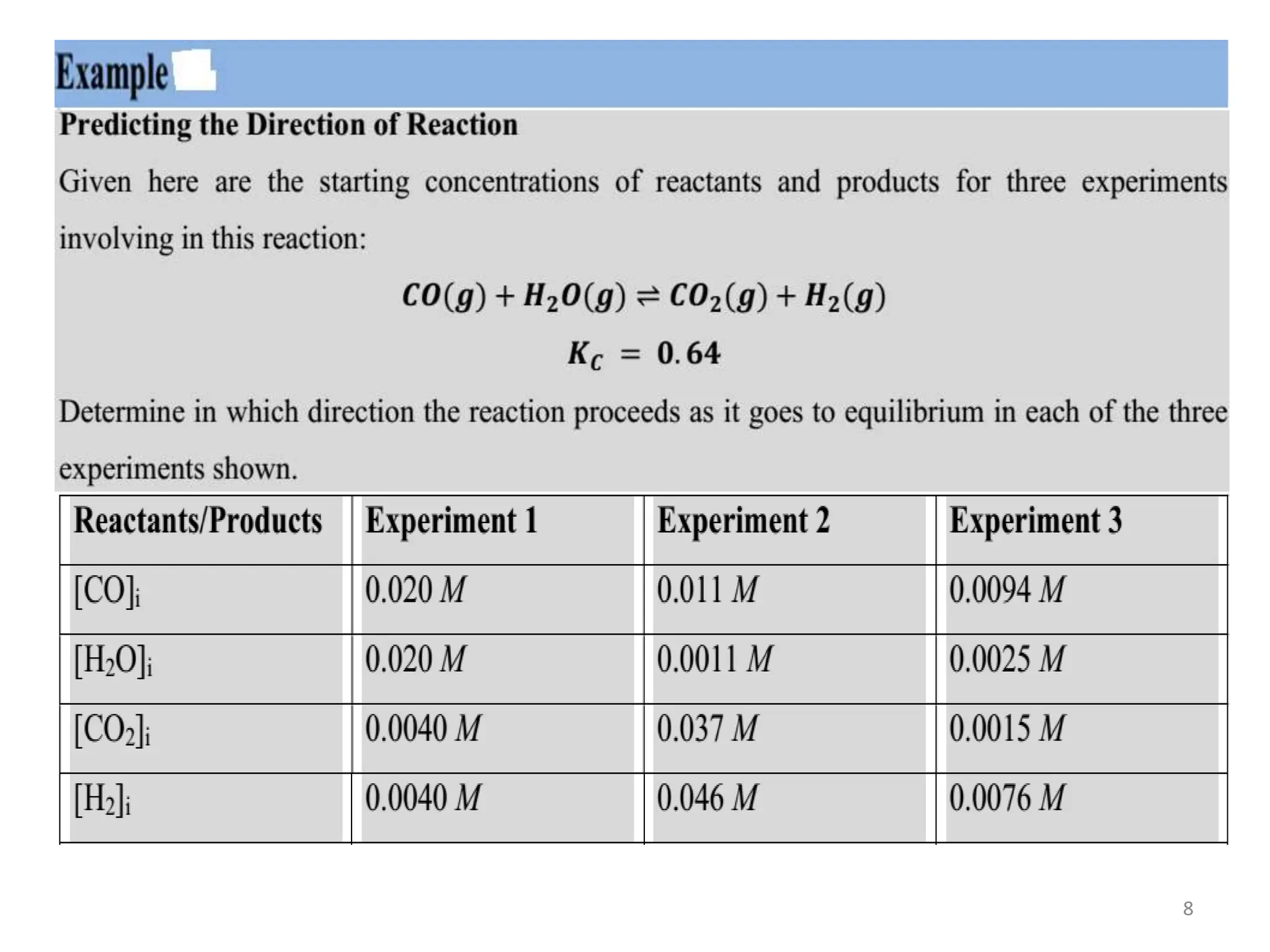
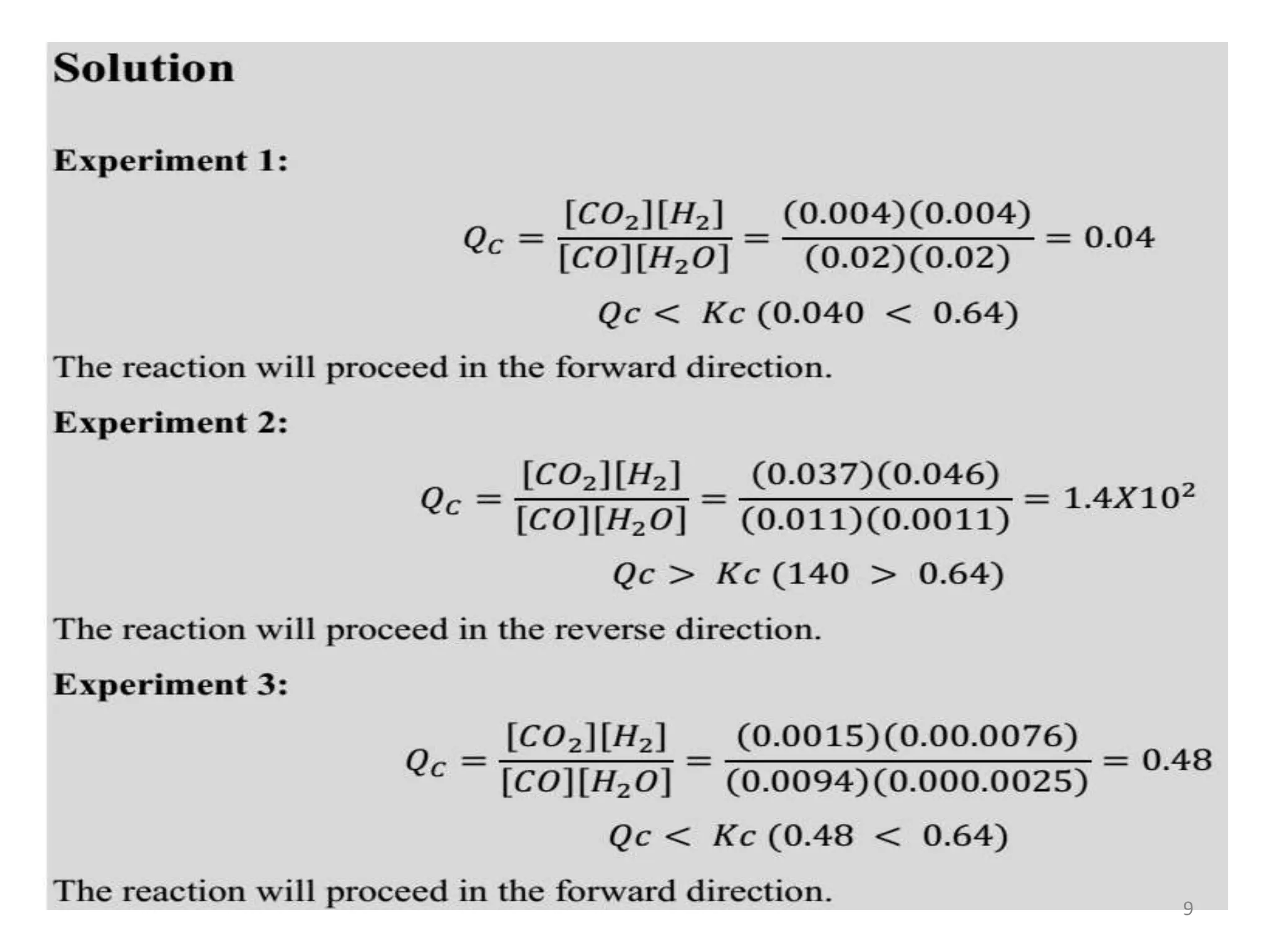
![Predicting the Direction of a Reaction
• The Kc for hydrogen iodide in the following
equation is 53.4 at 430ºC. Suppose we add
0.243 mol H2, 0.146 mol I2 and 1.98 mol HI to
a 1.00L container at 430ºC. Will there be a net
reaction to form more H2 and I2 or HI?
H2 (g) + I2 (g) → 2HI (g)
[HI]0
2
[H2]0 [I2]0
Kc =
[1.98]2
[0.243][0.146]
Kc = Kc = 111
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-20-2048.jpg)
![Calculating Equilibrium Concentrations
• At 1280ºC the equilibrium constant (Kc) for
the reaction is 1.1 x 10-3. If the initial
concentrations are [Br2] = 0.063 M and [Br] =
0.012 M, calculate the concentrations of these
species at equilibrium.
Br2 (g) 2Br (g)
Let x be the change in concentration of Br2
Br2 (g) 2Br (g)
Initial (M)
Change (M)
Equilibrium (M)
0.063
-x
0.063 - x
0.012
+2x
0.012 + 2x
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-21-2048.jpg)
![Calculating Equilibrium Concentrations
[Br]2
[Br2]
Kc =
Kc =
(0.012 + 2x)2
0.063 - x
= 1.1 x 10-3
4x2 + 0.048x + 0.000144 = 0.0000693 – 0.0011x
4x2 + 0.0491x + 0.0000747 = 0
ax2 + bx + c = 0 -b ± b2 – 4ac
2a
x =
x = -0.00178
x = -0.0105
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-22-2048.jpg)
![Br2 (g) 2Br (g)
Initial (M)
Change (M)
Equilibrium (M)
0.063 0.012
-x +2x
0.063 - x 0.012 + 2x
At equilibrium, [Br] = 0.012 + 2x = -0.009 M
At equilibrium, [Br2] = 0.063 – x = 0.0648 M
or 0.00844 M
Calculating Equilibrium Concentrations
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-23-2048.jpg)


![Changes in Concentration
Change Shift in Equilibrium
Increase in [Products] left
Decrease in [Products] right
Increase in [Reactants] right
Decrease in [Reactants] left
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-26-2048.jpg)







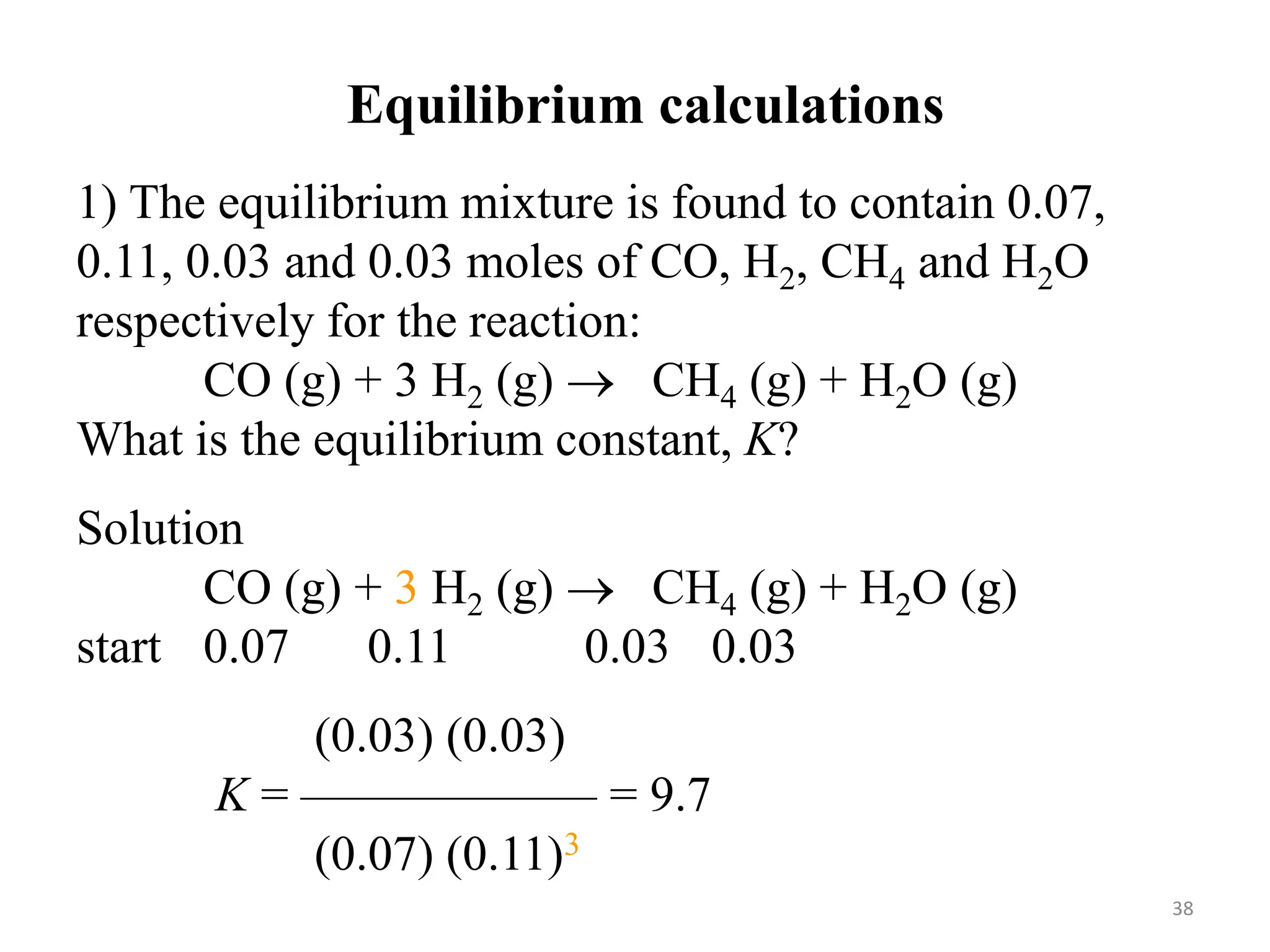

![Solution:
——————————————————————————
H2(g) + I2(g) ⇄ 2 HI(g)
——————————————————————————
Initial [ ], M: 0.200 0.200 0.000
Change in [ ], M: -0.158 -0.158 + 0.316
Equilibrium [ ], M 0.042 0.042 0.316
——————————————————————————
]
][I
[H
[HI]
2
2
2
2
2
(0.316)
0.042
( )
=
Kc = = 57
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-40-2048.jpg)
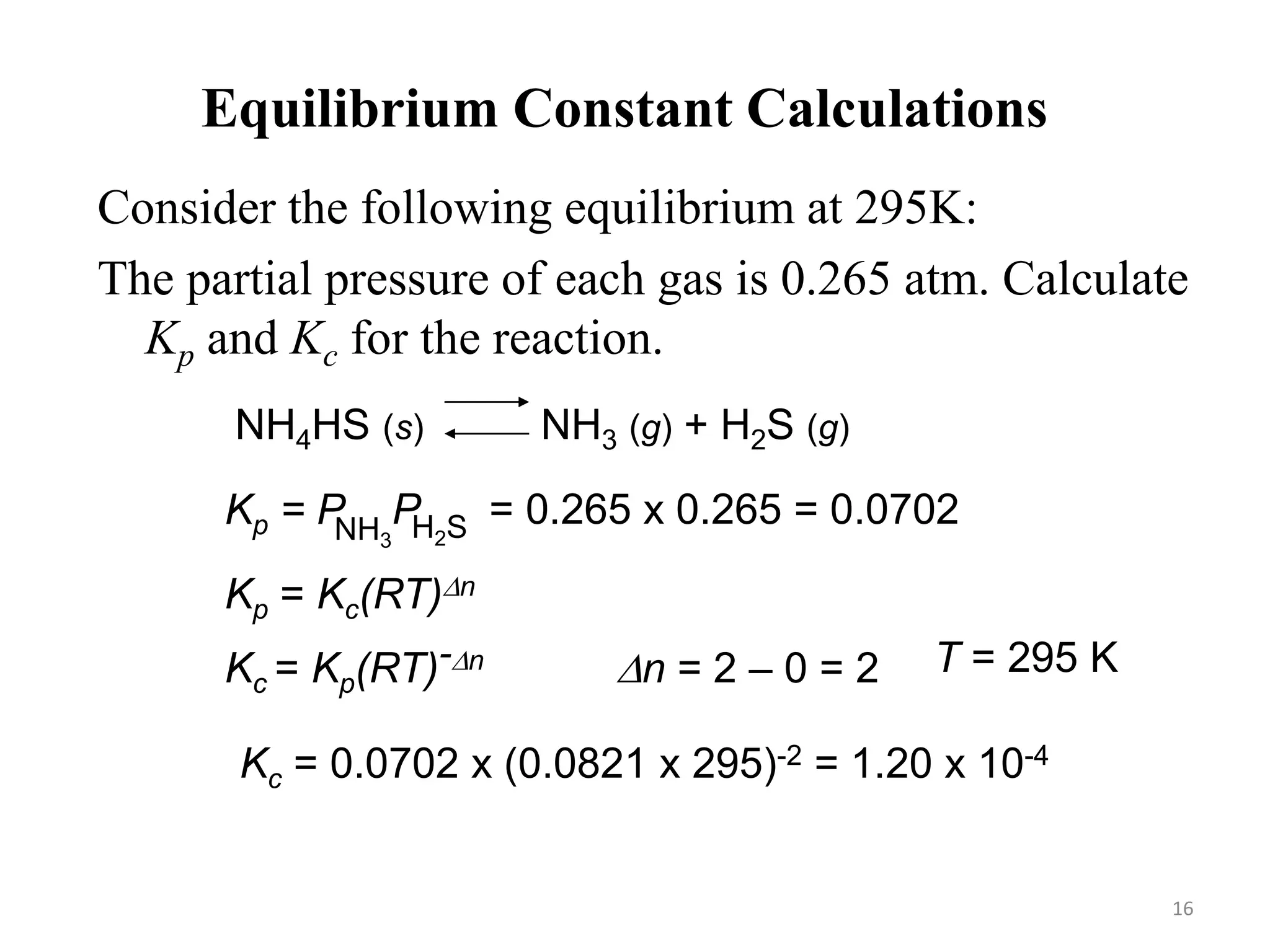
![3) The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction
between carbon monoxide and molecular chlorine
to form COCl2 (g) at 74◦C are [CO] = 0.012 M,
[Cl2] = 0.054 M, and [COCl2] = 0.14 M. Calculate
the equilibrium constants Kc and Kp.
CO (g) + Cl2 (g) ⇄ COCl2 (g)
Kc =
[COCl2]
[CO][Cl2]
=
0.14
0.012 x 0.054
= 220
Kp = Kc(RT) ∆n
Dn = 1 – 2 = -1 R = 0.0821 L-atm mol-1 K-1
T = 273 + 74 = 347 K
Kp = 220 x (0.0821 x 347)-1 = 7.7 41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-41-2048.jpg)
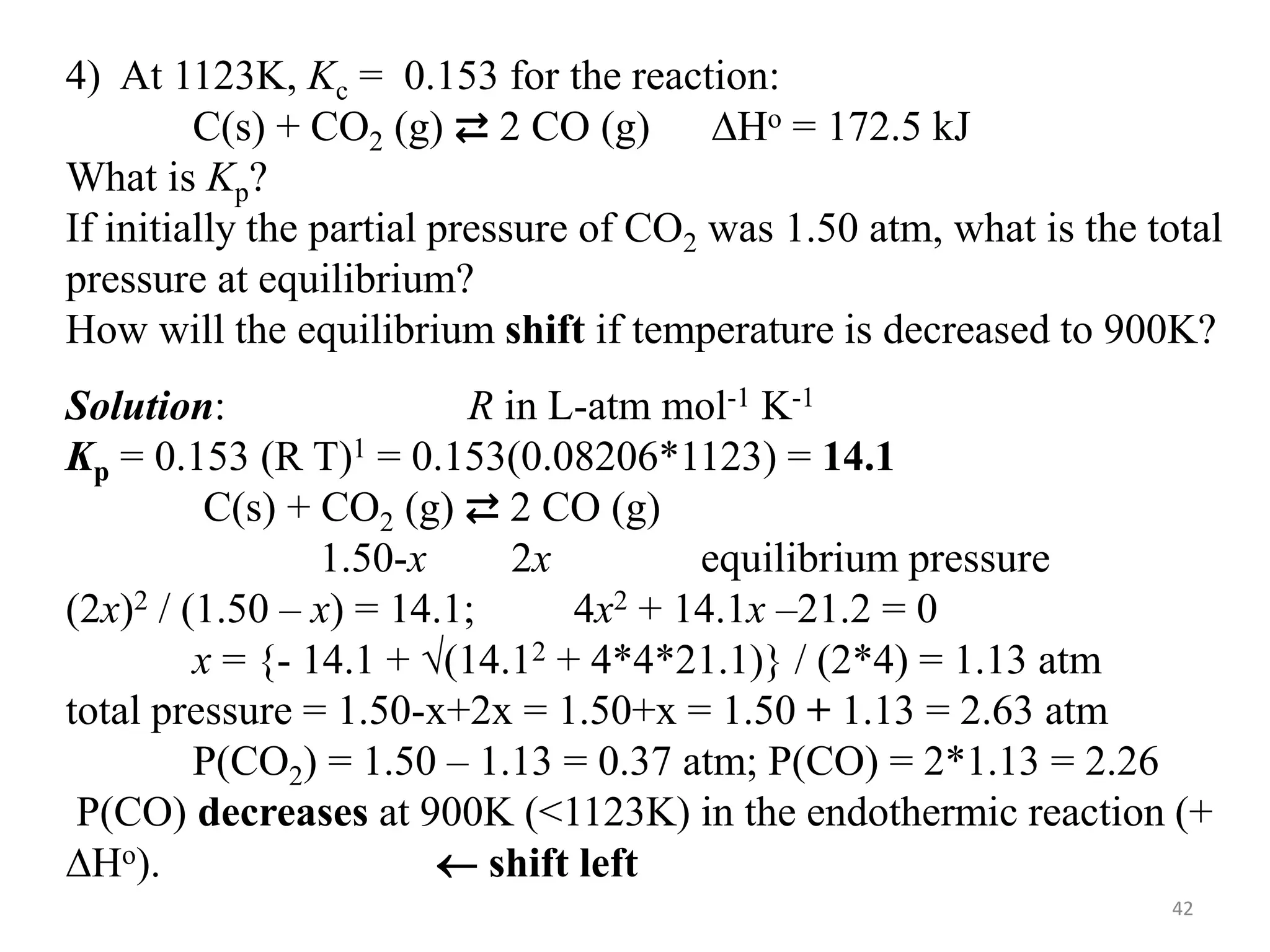
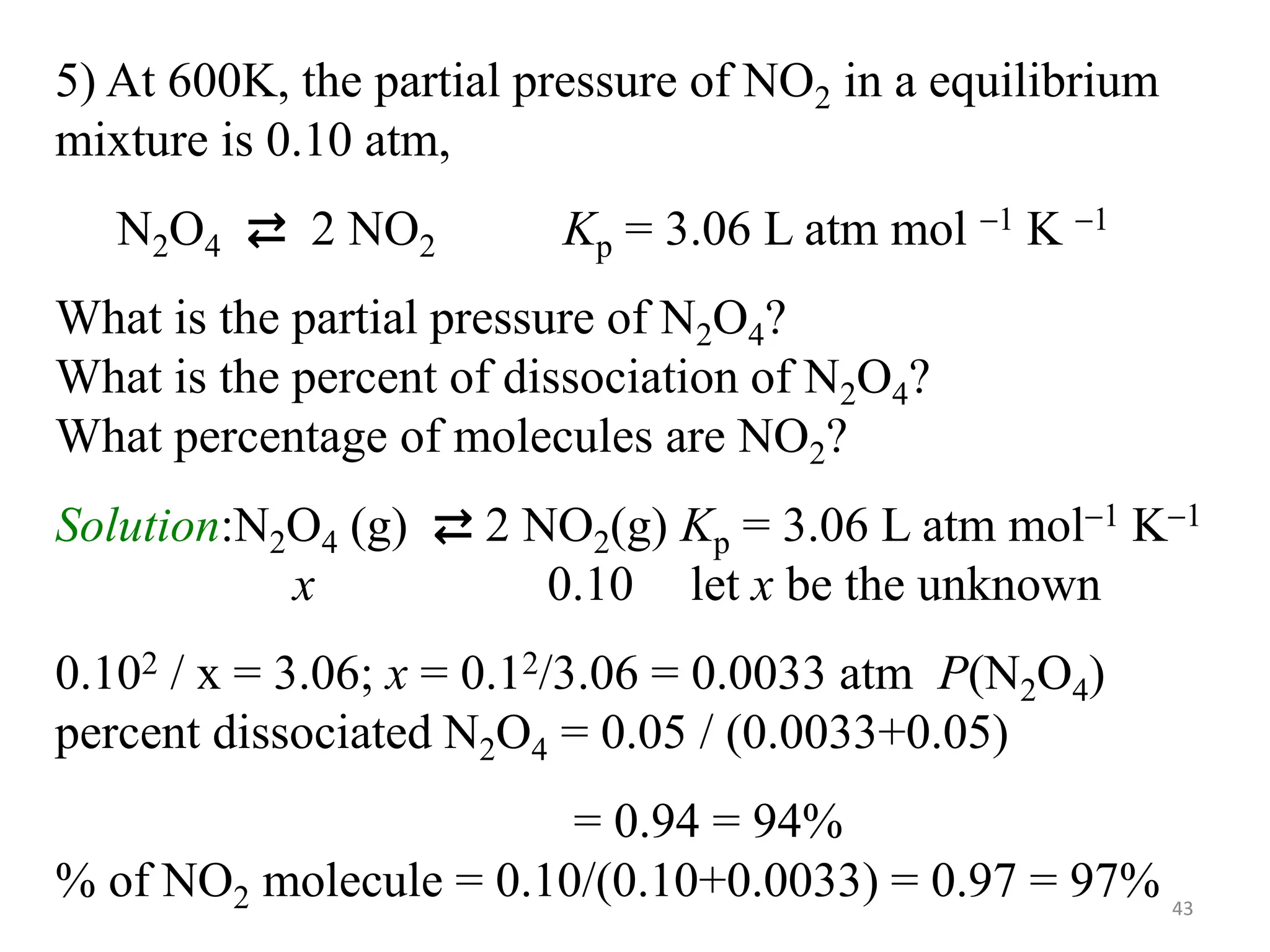

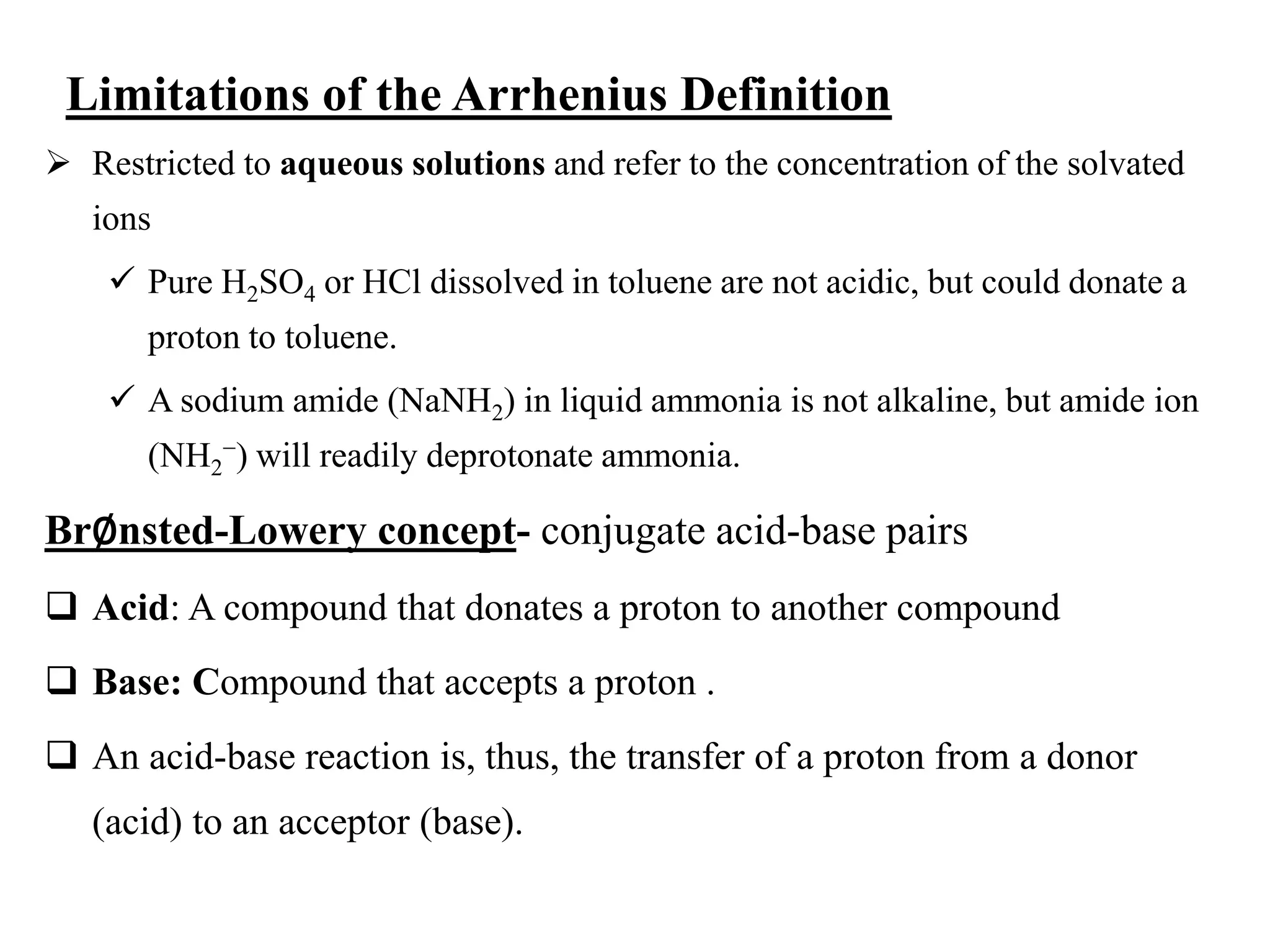
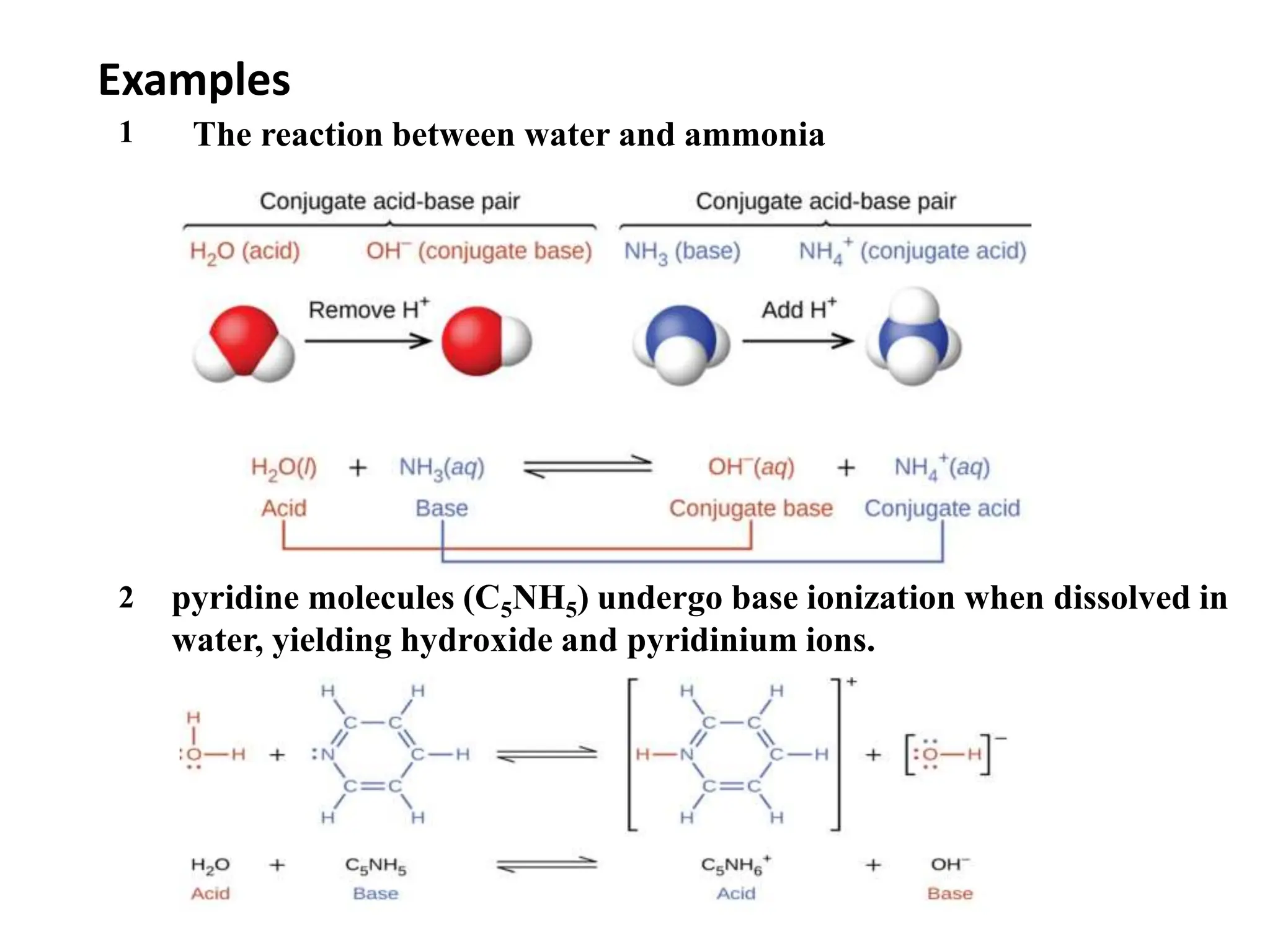
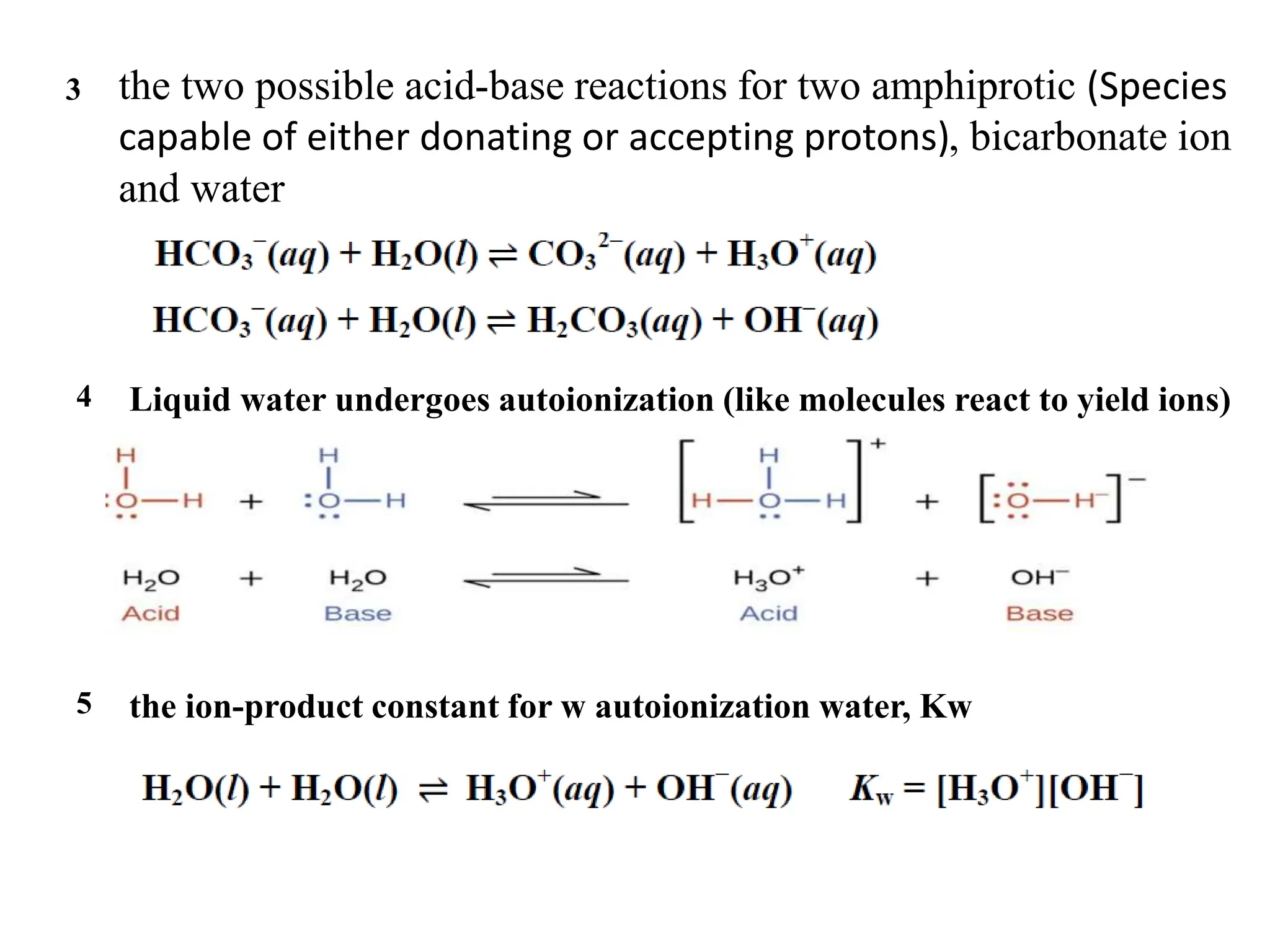
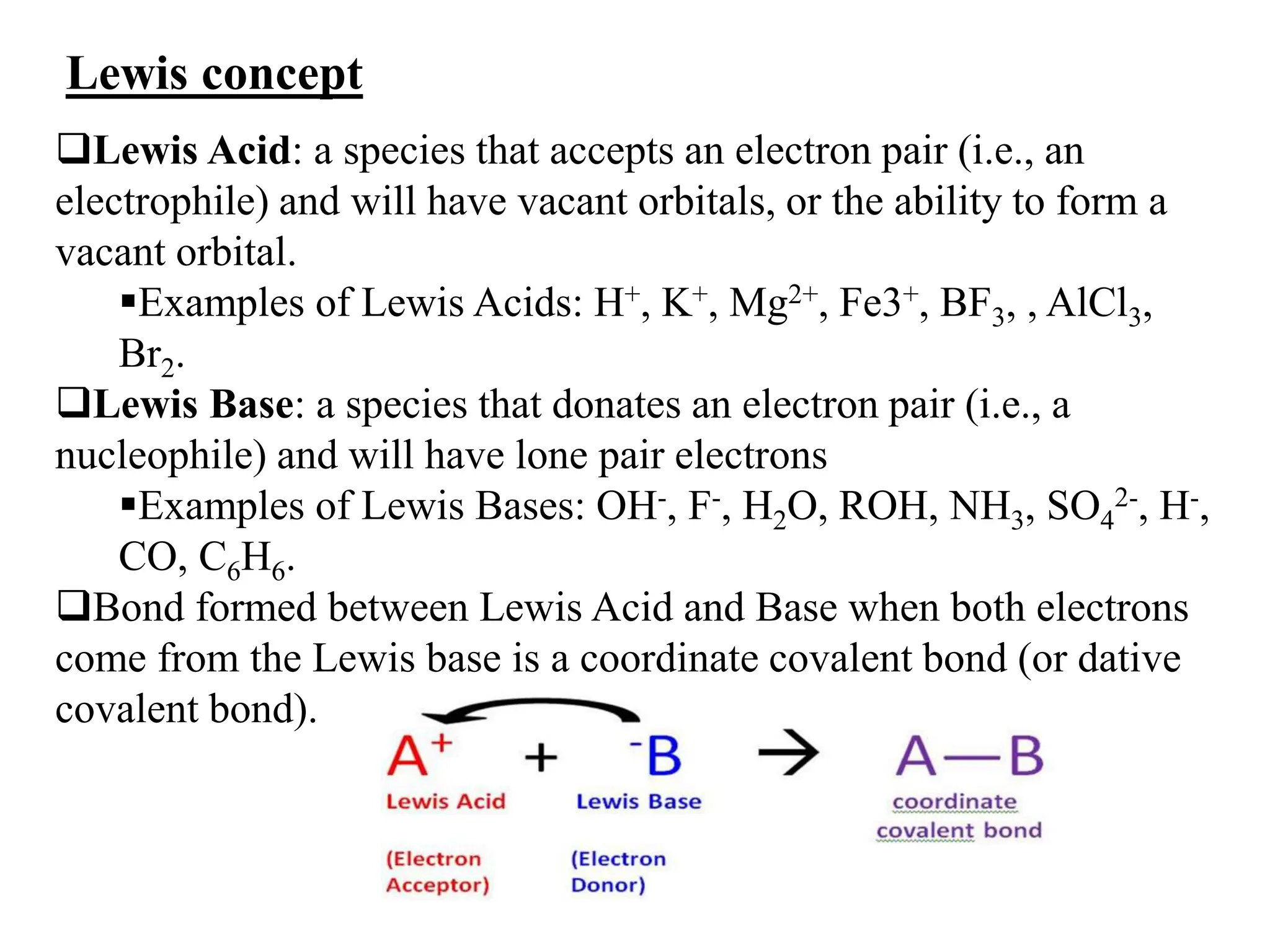
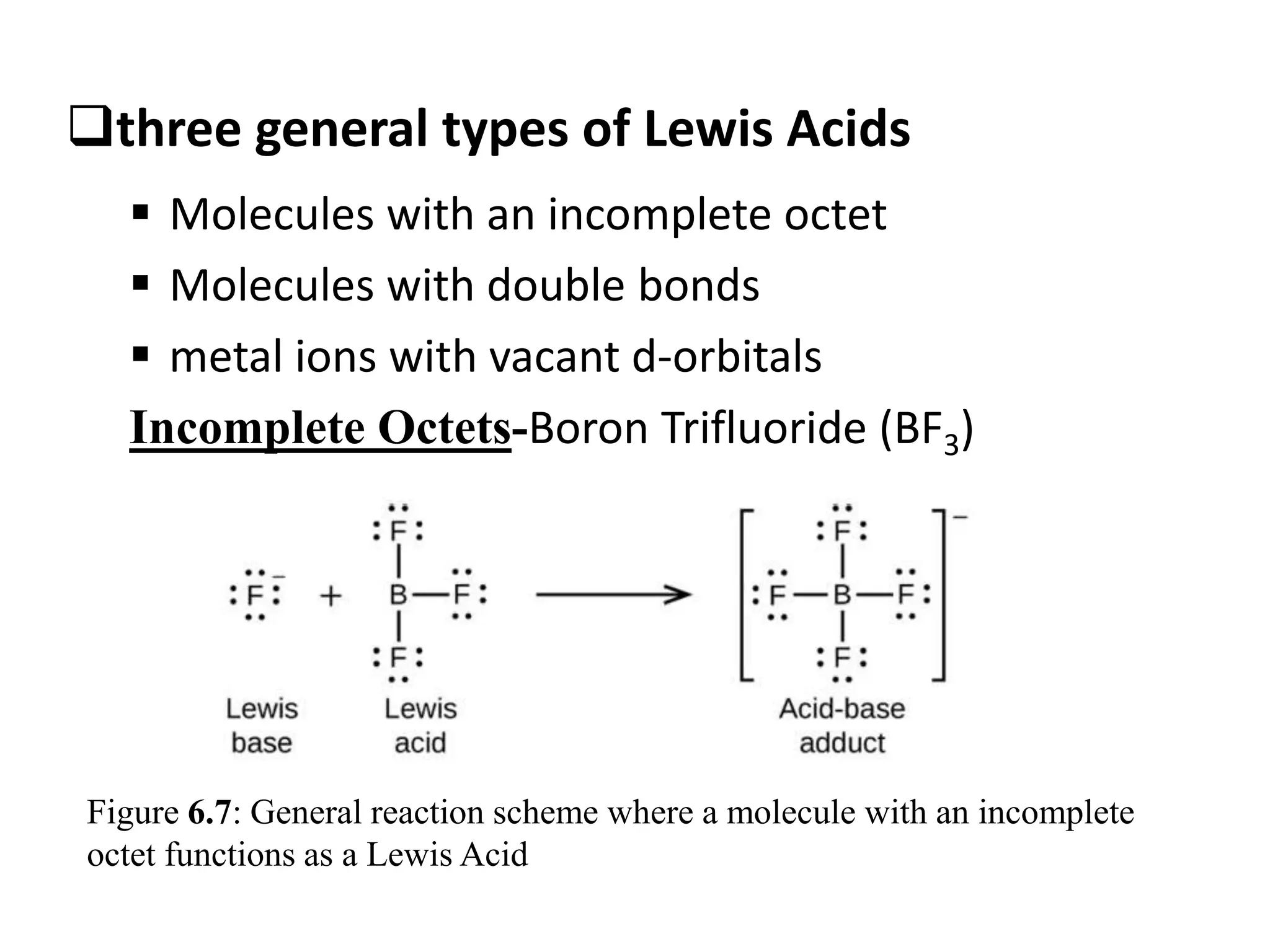
![…Cont’d
● The pH of a solution is defined as
pH = -log[H3O+] ⇨ [H3O+] = 10-pH
● Likewise, the hydroxide ion molarity may be expressed as a p-function, or
pOH:
pOH = -log[OH-] ⇨ [OH-] = 10-pOH
● The relationship between ionic product of water (KW) and, [H3O+] and [OH-]
is
KW = [H3O+][OH-] ; KW = 1..0 x 10-14 at 25 oC
-log KW = -log([H3O+][OH-]) = -log[H3O+] + -(log[OH-]
pKW = pH + pOH ⇨ 14.00 = pH + pOH at 25 oC
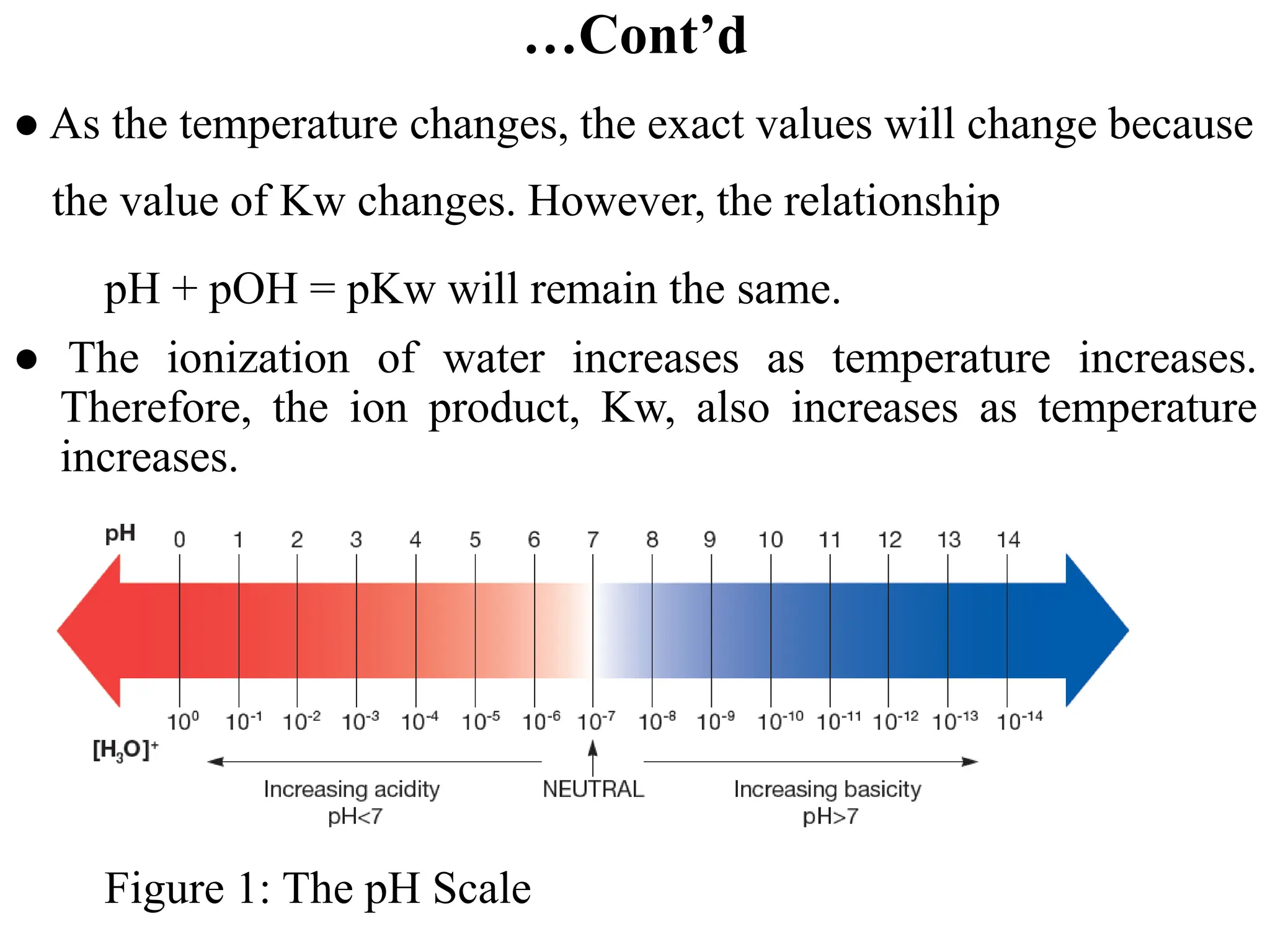
● The sum of a solution’s pH and pOH is not always 14. It depends on
temperature.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-52-2048.jpg)
![…Cont’d
● Summary of relations for acidic, basic and neutral solutions
Acidic: [H3O+] > [OH-], [H3O+] < 1.0x10-7 M, pH < 7
Neutral: [H3O+] = [OH−], [OH−] = 1.0x10-7 M, pH = 7
Basic: [H3O+] < [OH-], [OH−] > 1.0x10-7 M, pH > 7
Table 2: Approximate pH range of some common materials at 25 oC
Material pH Material pH Material pH
1 M HCl 0 Cherries 3.2–4.7 Saliva 6.5–7.5
Gastric juice 1.0–3.0 Tomatoes 4.0–4.4 Pure water 7.0
Lemons 1.8–2.4 Beer 4-4.5 Blood 7.3–7.5
Vinegar 2.4–3.4 Bananas 4.5–5.7 Eggs 7.6–8.0
Soft drinks 2.0–4.0 Bread 5.0–6.0 Urine 5-7
Apples 2.9–3.3 Rainwater 5.5–5.8 Sea water 8.0–8.5
Grapefruit 2.9–3.4 Potatoes 5.6–6.0 Milk of magnesia 10.5
Oranges 3.0–4.0 Milk 6.3–6.6 Household ammonia 11.9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-54-2048.jpg)
![…Cont’d
Example 1: What is the pH of a 1.0 x 10-3 M NaOH solution?
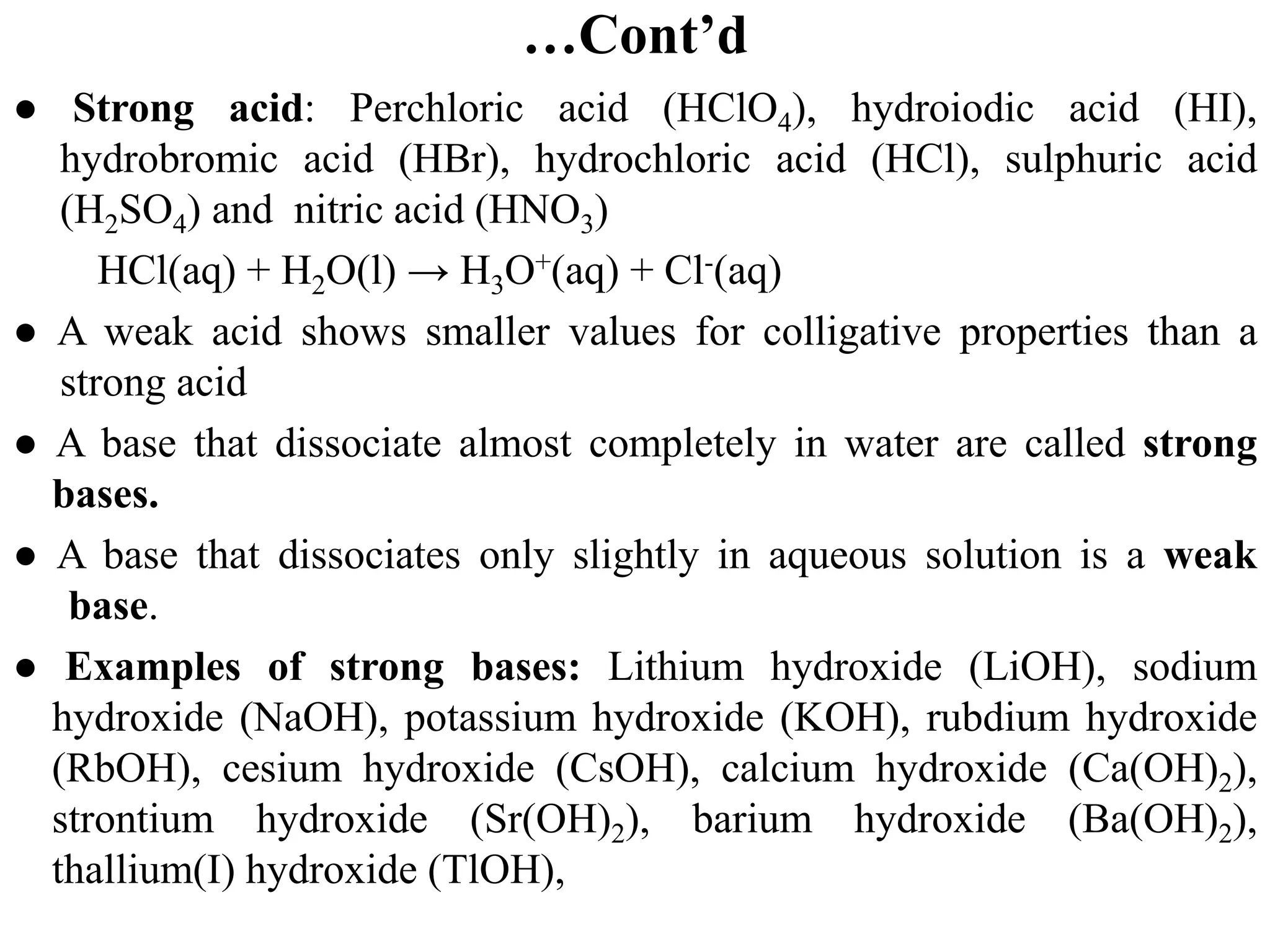
Solution: NaOH is a strong base that dissociates completely. Thus,
[OH−] = 1.0 x 10–3 M ⇨ pOH = -log[OH-] = -log(1.0 x 10–3 ) = 3
pH + pOH = 14.0 at 25 oC ⇨ pH = 14.0-pOH = 14.0-3 = 11
Example 2: The pH of household ammonia was measured to
be 11.28. Determine its [H3O+]?
Solution: pOH = 14.00 - pH = 14.00 - 11.28 = 2.72
pOH = -log[OH-]. ⇨ log[OH-] = 10-pOH
[OH-] = 10-2.72 = 1.9 x 10-3 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-55-2048.jpg)
![…Cont’d
Exercises: 1) The pH of an aqueous solution is 3.67. Determine its
[H3O+].
2) Determine the pH, [H3O+], [NO3
-], and [OH−] at 25 oC in a 0.60 M
aqueous solution of HNO3(aq), a strong acid.
Answer: [H3O+] = [NO3
-] = 0.60 M; [OH-] = 1.7 x 10-14 M, pH = 778
3) Arrange the following solutions in order from lowest to highest pH:
0.10 M HCl, 0.10 M H2SO4, and 0.10 M HF.
4) Calculate [Ba2+], [OH−], and [H3O+] at 25 oC in a 0.25 M aqueous
solution of barium hydroxide, a strong base.
Answer: [Ba2+] = 0.25 M; [OH−] = 0.50 M; [H3O+] = 2.0 x 10−14 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-56-2048.jpg)

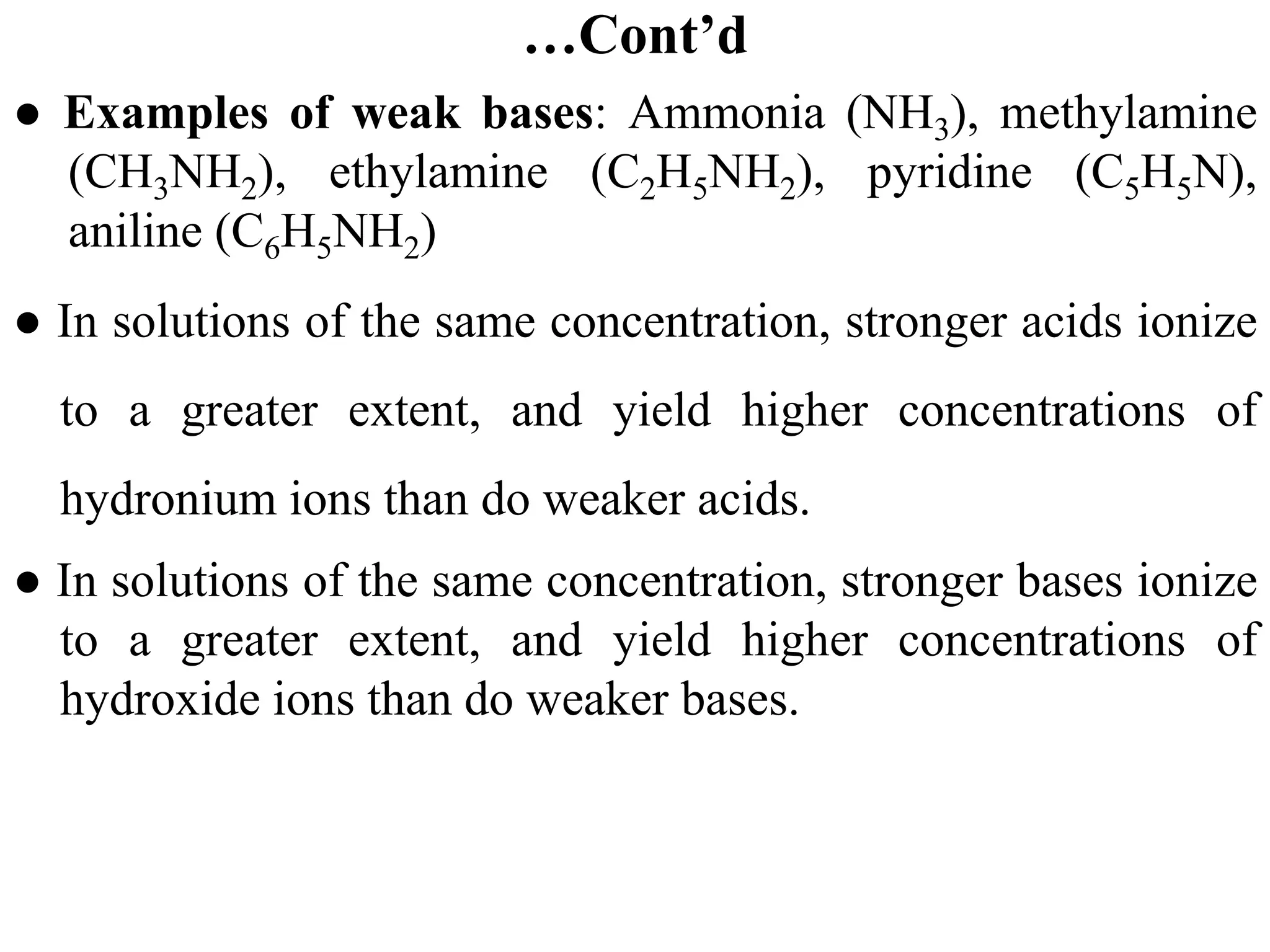
![6.6.1 Ionization of weak acids
● The strength of a weak acid, that is, extent of dissociation of
a weak acid is quantified by the acid dissociation constant
(Ka) which is the equilibrium constant for the ionization of
the weak acid.
● For a weak acid HA, HA + H2O ⇋ H3O+ + A-
● Note that water has been omitted from the equilibrium
equation because its concentration in dilute solutions is
essentially the same as that in pure water (55.5 M) and pure
liquids are always omitted from equilibrium equations.
+ -
3
a
[H O ][A ]
K =
[HA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-60-2048.jpg)
![…Cont’d
● The larger the Ka, the stronger the acid.
● Strong acids can be assumed, for practical purposes, to
ionize completely in water, and [HA] is zero and the acid
ionization constant is immeasurably large (Ka ≈ ∞).
● For weak acid, Ka is small and they mainly exist in the form
of undissociated molecule.
● For example, about 1.3% of the solute molecules in a 0.1 M
acetic acid solution are ionized at room temperature. The
remaining 98.7% of the acetic acid molecules, CH3COOH,
remain nonionized.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-61-2048.jpg)
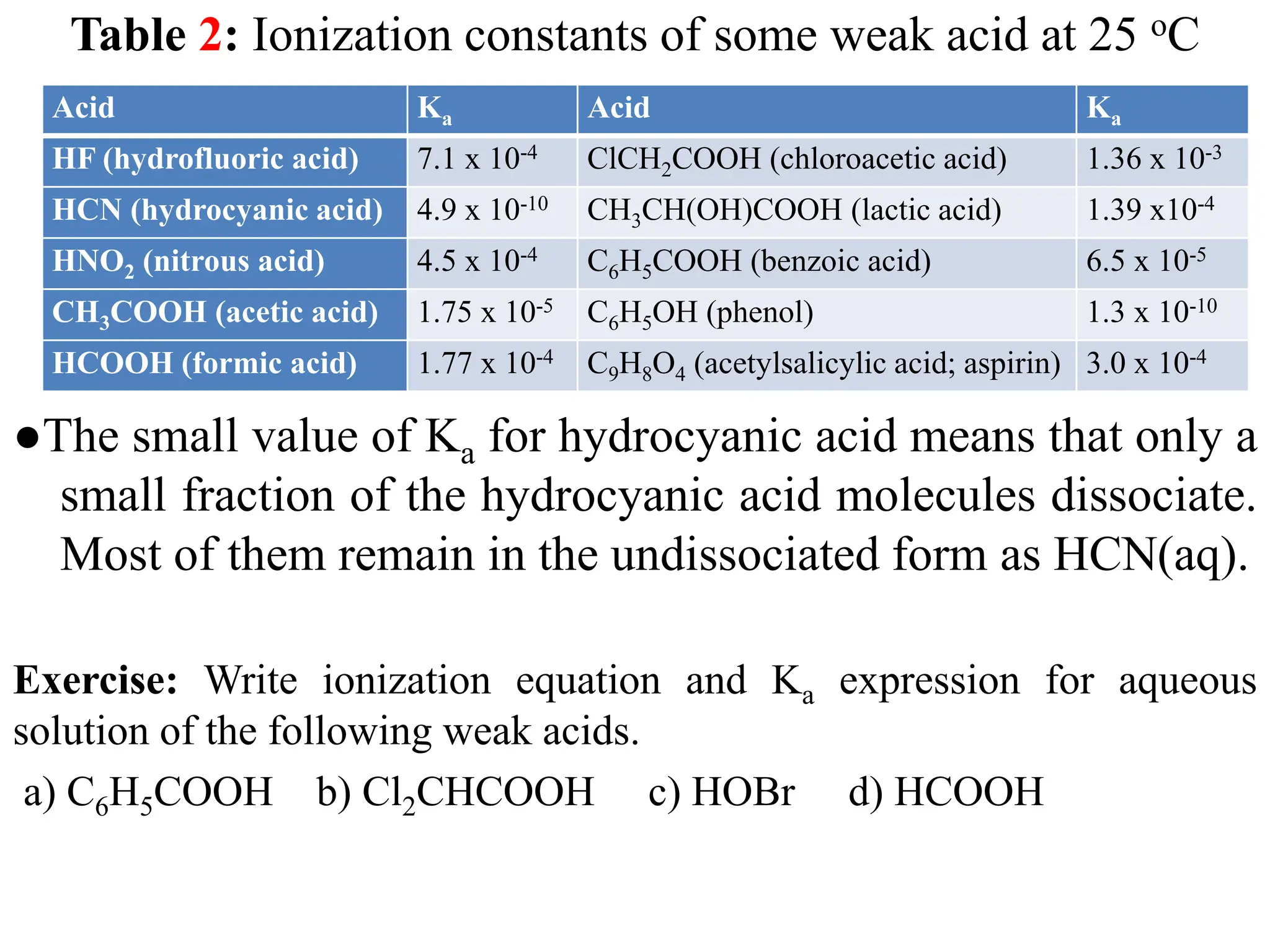
![6.6.1.1 Percent ionization of weak acids
● The magnitude of Ka indicates the strength of an acid (as Ka increases,
so does the strength of the acid). Another measure of the strength of
an acid is its percent ionization (%α), which is defined as
● The stronger the acid, the greater the percent ionization. For a
monoprotic acid HA, the concentration of the acid that undergoes
ionization is equal to the concentration of the H+ ions or the
concentration of the A- ions at equilibrium. Therefore, we can write
the percent ionization as
ionized acid concentration at equilibrium
Percent ionization = x 100
initial concentration of acid
+ -
3 eq eq
o o
[H O ] [A ]
Percent ionization (%α) = x 100 = x 100
[HA] [HA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-63-2048.jpg)
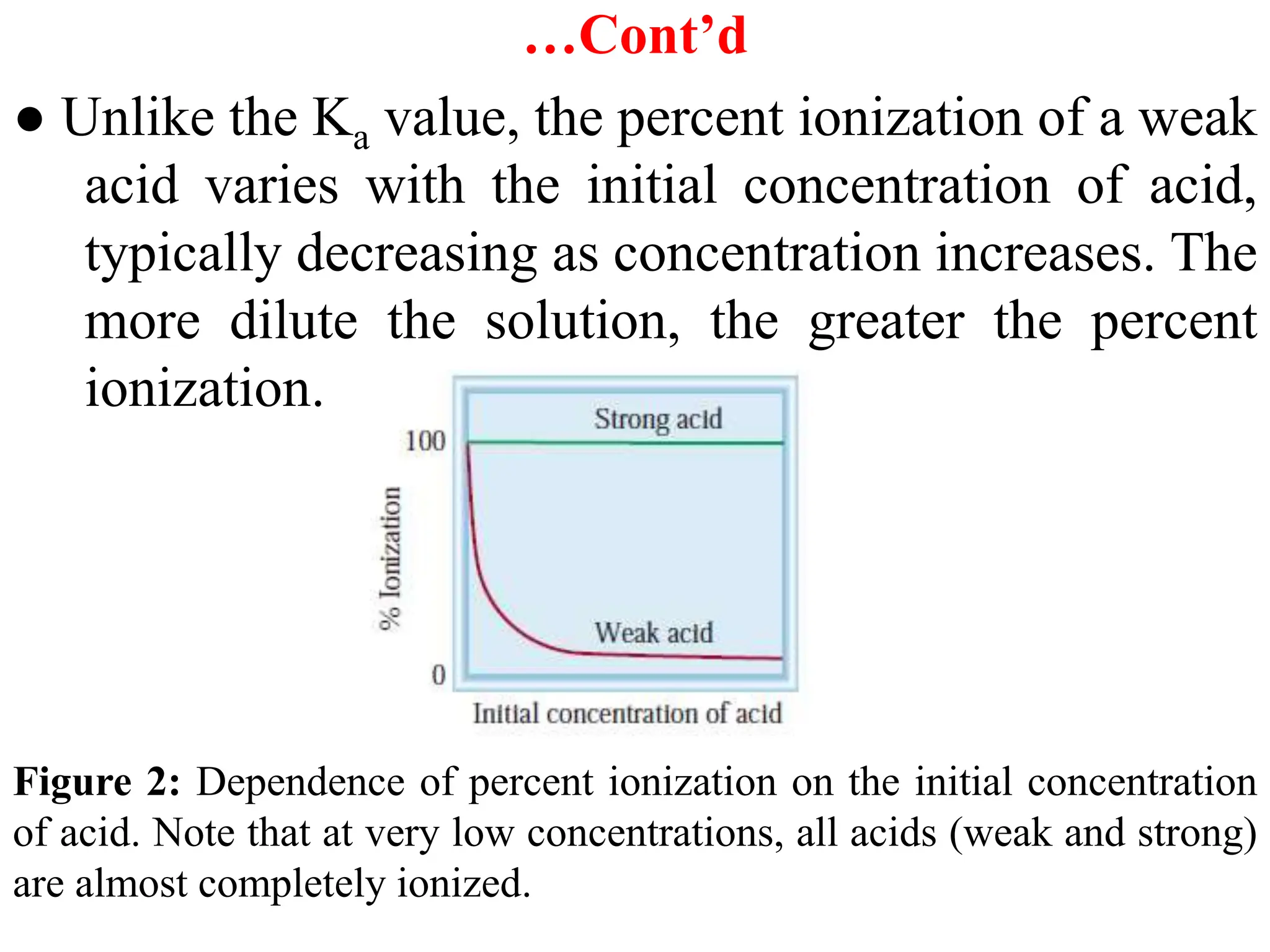
![…Cont’d
Example: Calculate the pH and the concentrations of all the
species in a 0.250 M aqueous solution of benzoic acid,
C6H5COOH(aq). The value of Ka for benzoic acid is 6.3 x 10-5
M.
Solution: C6H5COOH + H2O ⇋ H3O+ + C6H5COO-
Ka= [C6H5COO-][H3O+]/[C6H5COOH] = [H3O+]2/[C6H5COOH]
[H3O+] = [C6H5COO-] = 3.968x10-3 M
[C6H5COOH]eq = (0.250 - 3.968x10-3) M = 0.246 M
pH = -log [H3O+] = -log (3.968x10-3) = 2.40
+ -5 -3
3 a 6 5
[H O ] = K [C H COOH] = 6.3 x 10 x 0.250 = 3.968x10 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-65-2048.jpg)
![…Cont’d
Percent ionization = 1.59%
Exercises: 1) The pH of a 0.40 M solution of formic acid,
HCOOH(aq), is 2.08 and that of a 0.40 M solution of
hydrocyanic acid, HCN(aq), is 4.80. Compare the percentages
of acid molecules that are dissociated in the two solutions.
Answer: HCOOH, 2.1%; HCN, 0.0040%
2) Calculate the percent ionization of acetic acid in the
following solutions. a) 1.0 M acetic acid solution with a pH
of 2.40 b) 0.10 M acetic acid solution with a pH of 2.90
c) 0.010 M acetic acid solution with a pH of 3.40
- + -3
6 5 eq 3 eq
6 5 o o
[C H COO ] [H O ] 3.968x10 M
Percent ionization (%α) = x 100 = x 100 = x 100
[C H COOH] [HA] 0.250 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-66-2048.jpg)
![6.6.2 Ionization of weak bases
● Weak bases accept a proton from water to give the conjugate acid of
the base and OH- ions.
● The reaction for ionization of a weak base (B) in aqueous solution can
be written as
B(aq) + H2O(l) ⇋ BH+(aq) + OH-(aq)
● The expression for the equilibrium constant is written as
Kb = [BH+][OH-]/[B]
● The higher the Kb the stronger the base is.
● Some examples of reactions of weak bases are as follows:
NH3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇋ NH4
+(aq) + OH-(aq)
HOCH2CH2NH2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇋ HOCH2CH2NH3
+(aq) + OH-(aq)
CN-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇋ HCN(aq) + OH-(aq)
IO3
-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇋ HIO3(aq) + OH-(aq)
Exercise: Write ionization equation and Kb expression for aqueous
solution of the following weak bases
a) CH3NH2 b) NH3 c) C5H5N](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-67-2048.jpg)
![…Cont’d
Example: Find the concentration of hydroxide ion, in a 0.25 M solution
of trimethylamine, a weak base. Calculate the pH and the percent
ionization (the fraction ionized) of trimethylamine,. Kb = 7.4 x 10−5
Solution: (CH3)3N(aq) + H2O(l) ⇋ (CH3)3NH+(aq) + OH−(aq)
Kb = [CH3)3NH+][OH-]/[CH3)3N] = [OH-]2/[CH3)3N]
[CH3)3NH+] = [OH−] =
This is less than 5% of the initial concentration (0.25), so the assumption
is justified/acceptable.
pOH = -log[OH−] = -log(4.3x10-3) = 2.37
pH + pOH = 14 ⇨ pH = 14-pOH = 14-2.37 = 11.63
Percent ionization = ([OH−]eq/[CH3)3N]o) x 100
Percent ionization = (4.3x10-3/0.25) x 100 = 1.72%
+ -
eq eq
o o
[BH ] [OH ]
Percent ionization of base = x 100 = x 100
[B] [B]
-5 -3
b 3
K [(CH ) N] = 7.4 x 10 x 0.25 = 4.3x10 M
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-68-2048.jpg)
![….Cont’d
Exercises: 1) Aniline, C6H5NH2(l), is used in the
manufacture of dyes and various pharmaceuticals. The
solubility of aniline in water at 25 °C is 3.50 grams per
100.0 mL of solution. Calculate the pH and the
concentrations of all the species in a saturated aqueous
solution of aniline at 25 oC.
Answer: [OH−] = [C6H5NH3
+] = 1.7 x 10-5 M
[C6H5NH2] = 0.376 M
[H3O+] = 5.9 x 10−10 M; pH = 9.23
2) CH3NH2 has a pKb value of 3.34. What is the pH of an
aqueous solution of CH3NH2 of concentration 0.10
mol.dm-3?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-69-2048.jpg)
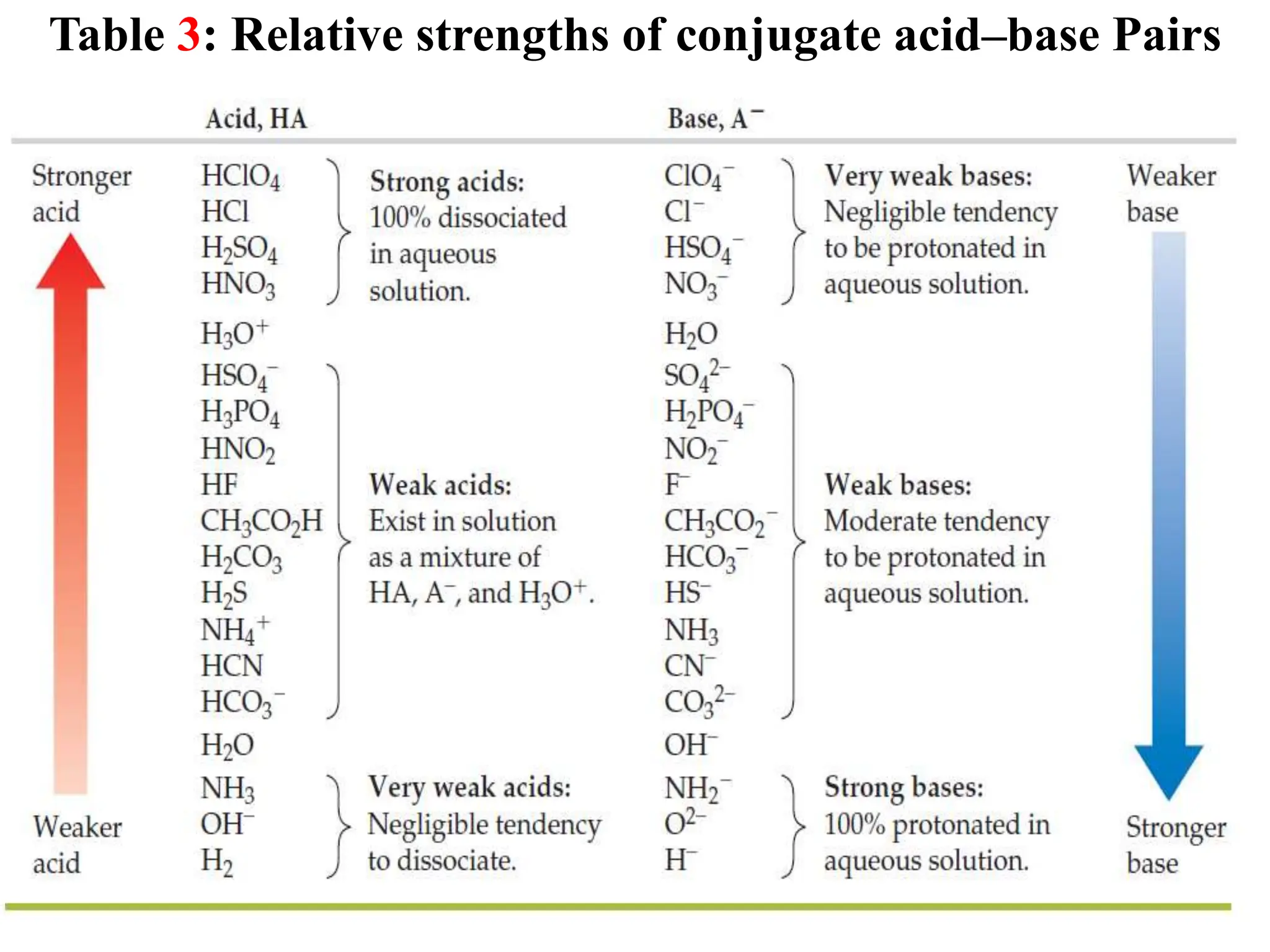
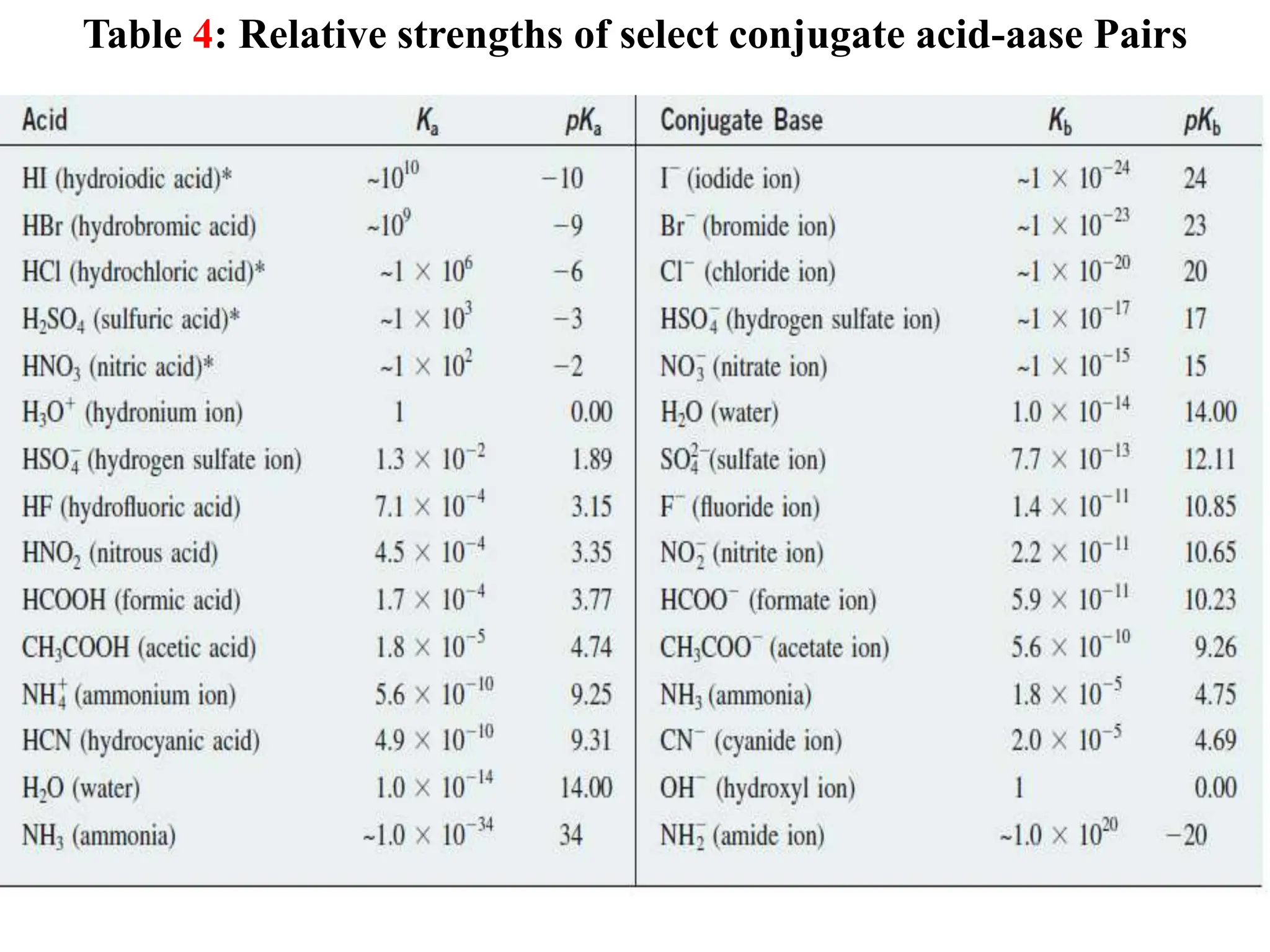
![6.6.3 Relative strengths of conjugate acid-base pairs
● An acid transfers a proton to a base to form the conjugate base of the original
acid and the conjugate acid of the original base.
● Conjugate acid-base pairs differ by a proton, which is present in the acid form
and missing in the base form.
● Consider a conjugate acid-base pair HA/A- whose ionization equilibrium
equations and ionization constant expressions are:
HA(aq) + H2O(l) ⇋A-(aq) + H3O+(aq) Ka = [A-][H3O+]/[HA]
A-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇋ OH-(aq) + HA(aq) Kb = [OH-][HA]/[A-]
2H2O(l) ⇋ OH-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
● Thus, adding the above two chemical equations yields the equation for the
autoionization for water. The equilibrium constant for a summed reaction is
equal to the product of the equilibrium constants for the added reactions,
and so
Ka x Kb = ([A-][H3O+]/[HA]) x ([OH-][HA]/[A-])
Ka x Kb = [H3O+][OH-] = KW
● For any conjugate acid–base pair, the product of the acid-dissociation
constant for the acid and the base-dissociation constant for the base always
equals the ion-product constant for water:
Ka x Kb = Kw](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-70-2048.jpg)
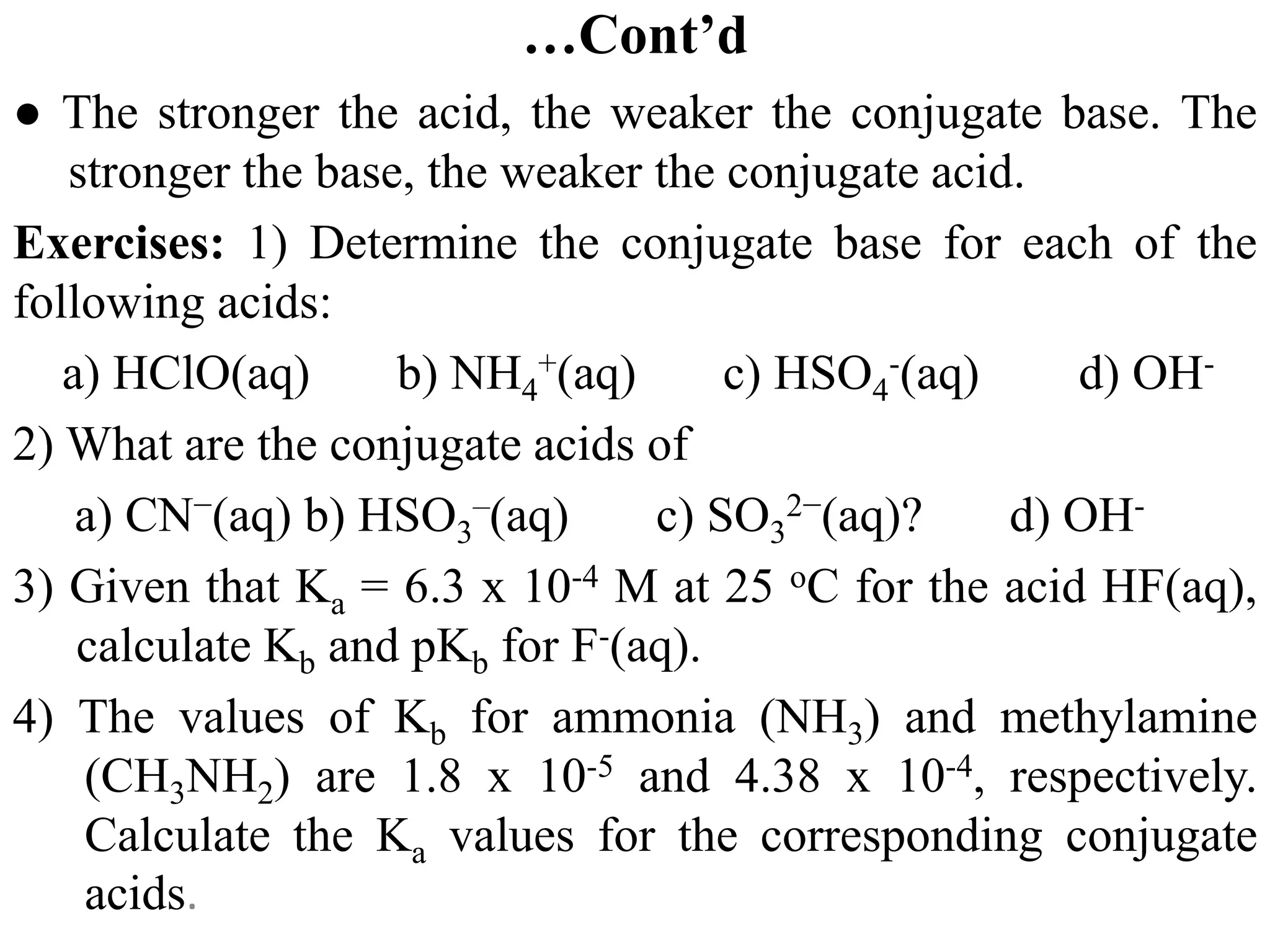








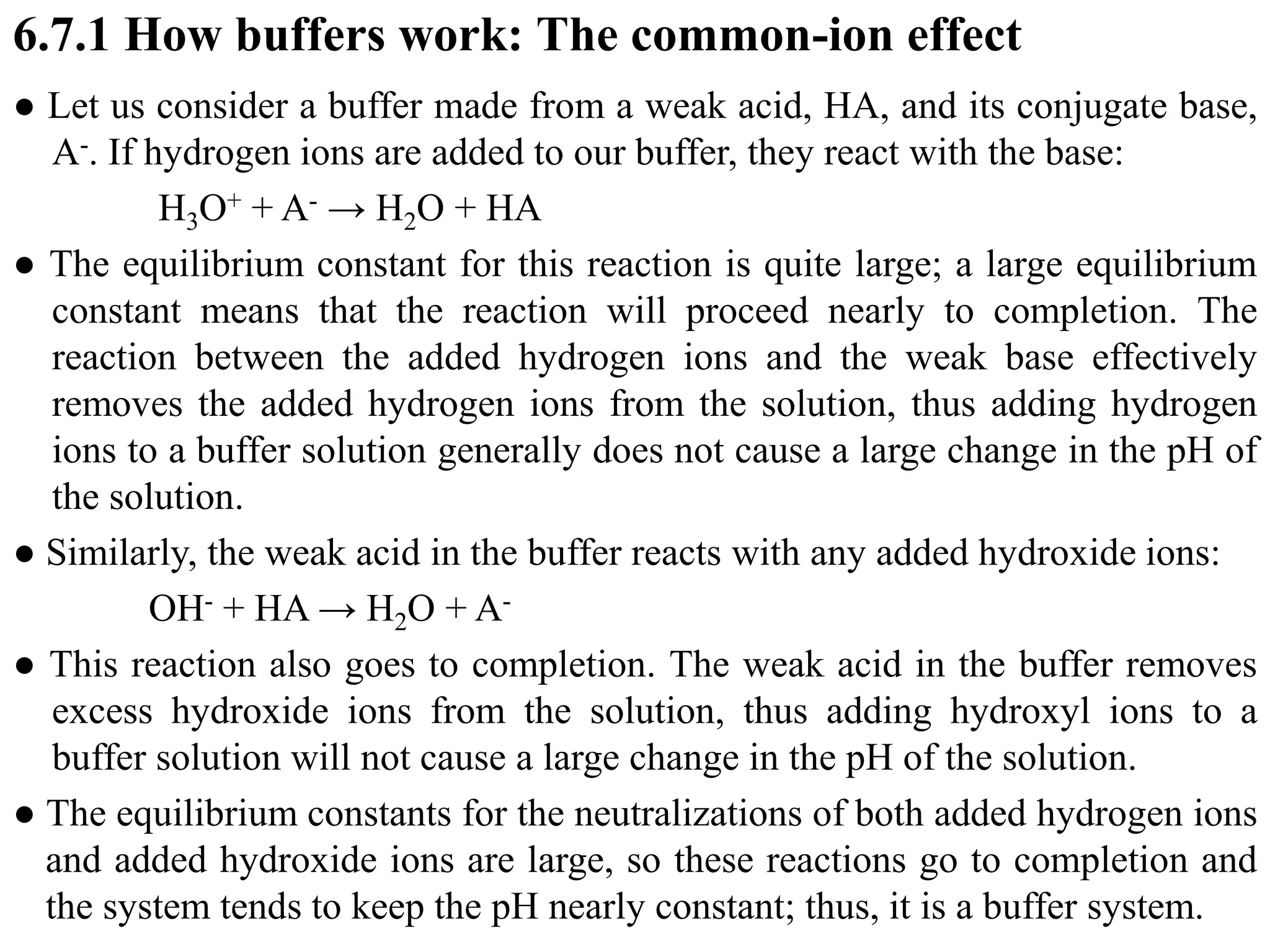

![6.7.2 Henderson–Hasselbalch equation
● This equation is used for calculating pH of a buffer solution.
● For a solution consisting of a weak acid and a salt of the weak acid:
pH = pKa + log([salt]/[acid]
where pKa refers to the weak acid.
● For a solution consisting of a weak base and a salt of the weak acid:
pOH = pKb + log([salt]/[base]
where pKb refers to the weak base.
● In general, pH of a buffer solution is given by
pH = pKa + log([base]/[acid]
● In general, if Ka for the acid is larger than 1x10-7, the buffer will be
acidic. If Kb is larger than 1x10-7, the buffer is basic.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-84-2048.jpg)
![6.7.3 Preparing a buffer solution of specified pH
● To prepare a buffer solution of a given pH, the procedure is as follows:
i) Choose a weak acid with a pKa value close to the required pH of the
buffer; the weak acid may be the salt of a polybasic acid, e.g.
NaH2PO4.
ii) Choose an appropriate salt of the weak acid.
iii) Use the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation to determine the
[base]/[acid] ratio needed to attain the correct pH.
iv) Remember that for maximum buffering capacity, [base]/[acid] = 1.
Exercise: A buffer solution of pH 7.23 is required. Choose a suitable
weak acid and calculate the ratio of [base]/[acid] required. Suggest what
acid and base combination might be appropriate.
Answer: Possible components for the buffer solution are NaH2PO4
(acid) and Na2HPO4 (base) with [base]/[acid] ratio of 1.05.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-85-2048.jpg)
![...Cont’d
Example: Consider 100 mL of an acetate buffer that is 0.120 M acetic
acid and 0.120 M sodium acetate. a) Calculate the pH of the buffer
b) Calculate the change in pH observed when 5.0 mL of 0.050 M HCl is
added to 100.0 mL of the buffer
c) Calculate the change in pH observed when 5.0 mL of 0.050 M NaOH
is added to 100.0 mL of the buffer. Ka of HAc = 1.8x10-5
Solution: a) pH = pKa + log([salt]/[acid]
pH = pKa + log([CH3COO-]/[CH3COOH]
pH = -log(1.8x10-5) + log(0.120/0.120) = 4.74
b) H3O+ + CH3COO- → H2O + CH3COOH
mmol of acid added = 0.050 M x 5.0 mL = 0.25 mmol
mmol of CH3COO- after adding acid = 0.120 Mx100 mL- 0.050 M x 5.0 mL
mmol of CH3COO- after adding acid = 11.75 mmol
[CH3COO-] after adding acid = 11.75 mmol/(100 mL + 5 mL) = 0.1119 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-86-2048.jpg)
![...Cont’d
mmol of CH3COOH after adding acid = 0.120 Mx100 mL + 0.050 M x 5.0 mL
mmol of CH3COOH after adding acid = 12.25 mmol
[CH3COOH] after adding acid = 12.25 mmol/(100 mL + 5 mL) = 0.1167 M
pH = pKa + log([CH3COO-]/[CH3COOH]
pH = -log(1.8x10-5) + log(0.1119/0.1167) = 4.72
c) OH- + CH3COOH → H2O + CH3COO-
mmol of base added = 0.050 M x 5.0 mL = 0.25 mmol
mmol of CH3COOH after adding base = 0.120 Mx100 mL - 0.050 M x 5.0 mL
mmol of CH3COOH after adding base = 11.75 mmol
[CH3COOH] after adding base = 11.75 mmol/(100 mL + 5 mL) = 0.1119 M
mmol of CH3COO- after adding base = 0.120 Mx100 mL+ 0.050 M x 5.0 mL
mmol of CH3COO- after adding base = 12.25 mmol
[CH3COO-] after adding base = 12.25 mmol/(100 mL + 5 mL) = 0.1167 M
pH = pKa + log([CH3COO-]/[CH3COOH]
pH = -log(1.8x10-5) + log(0.1167/0.1119) = 4.76](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-6-240321065315-a0d5f7fb/75/Unit-6-pptEquilibrium-concept-and-acid-base-equilibrium-87-2048.jpg)
