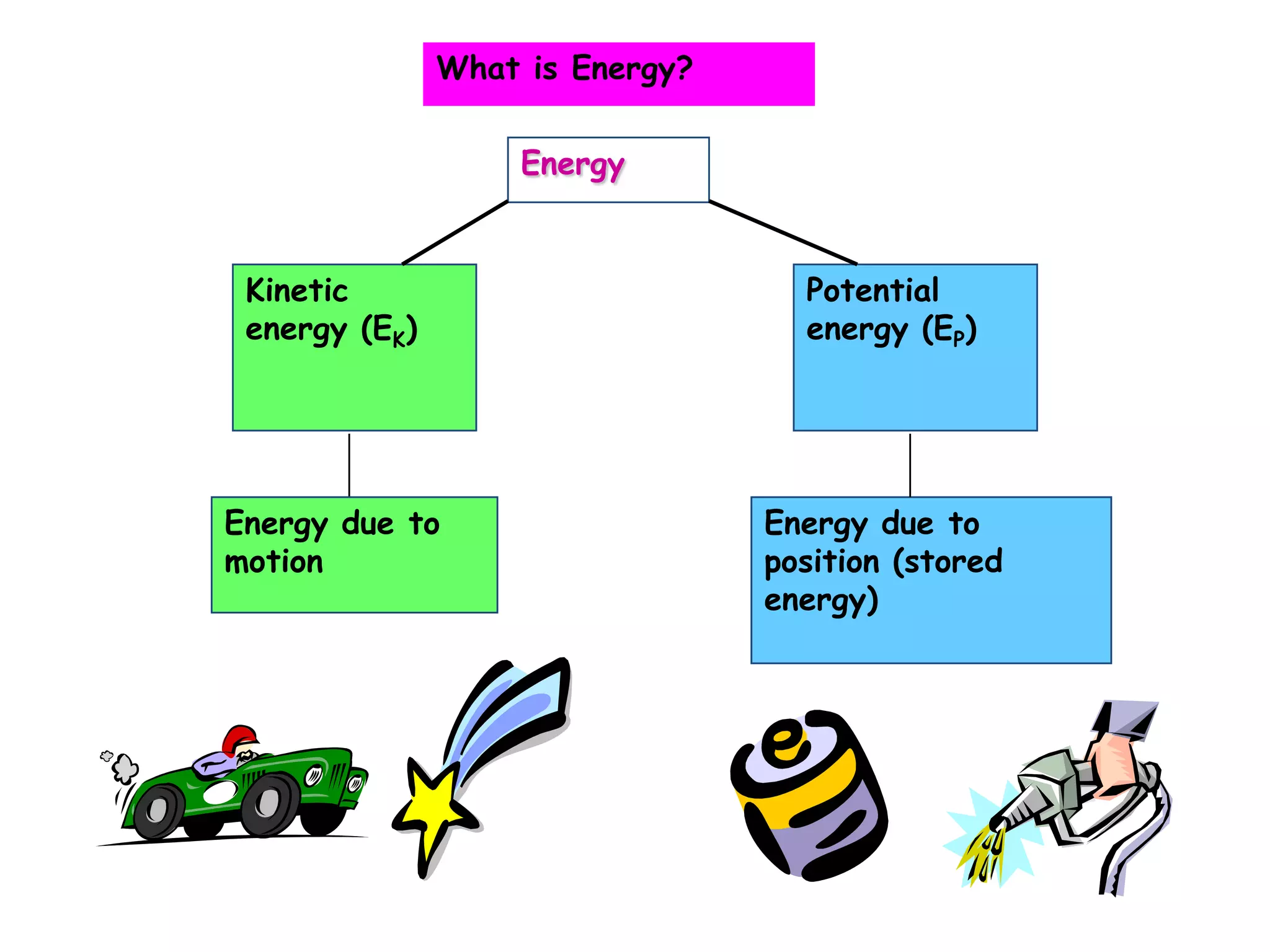
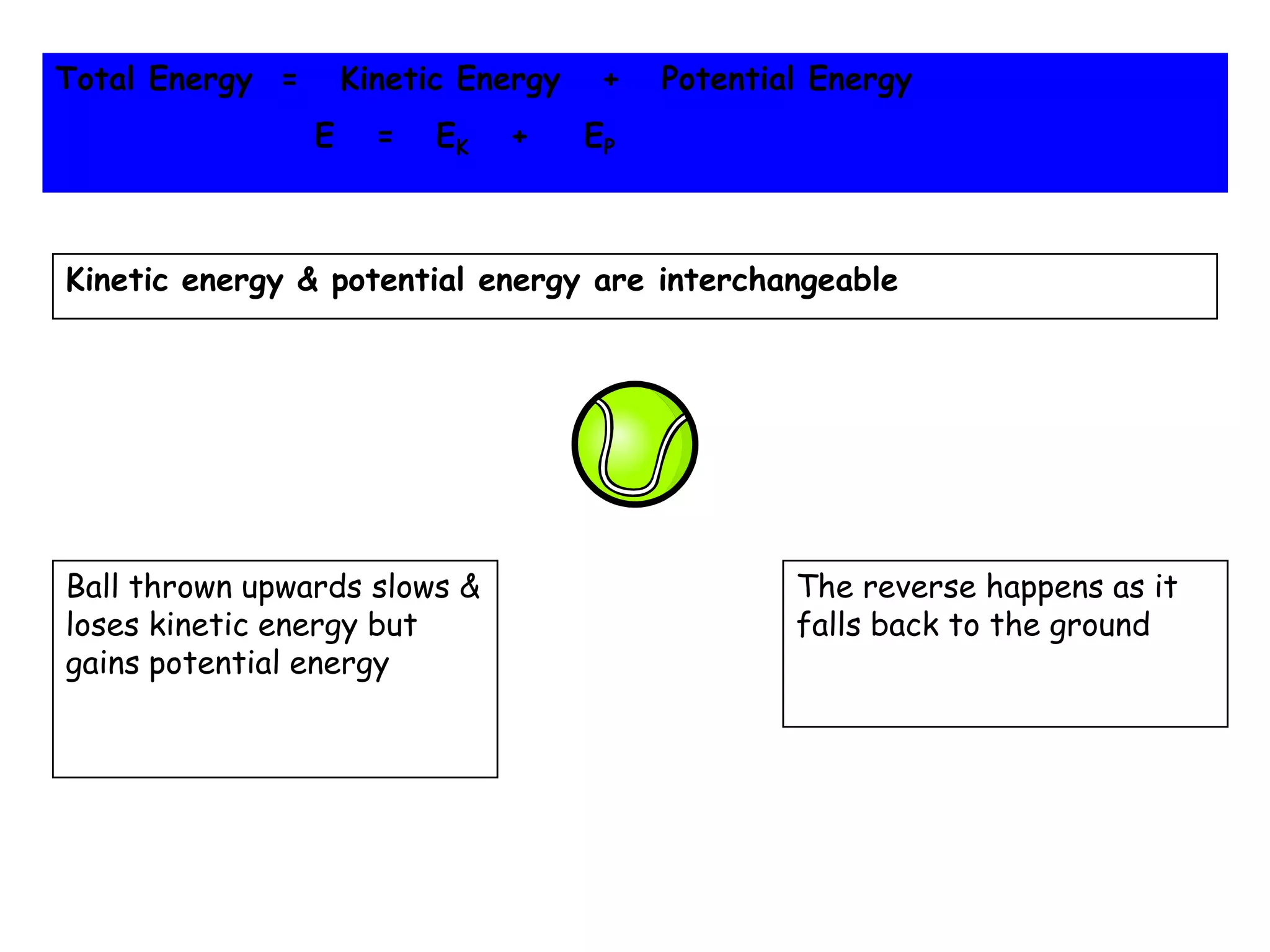
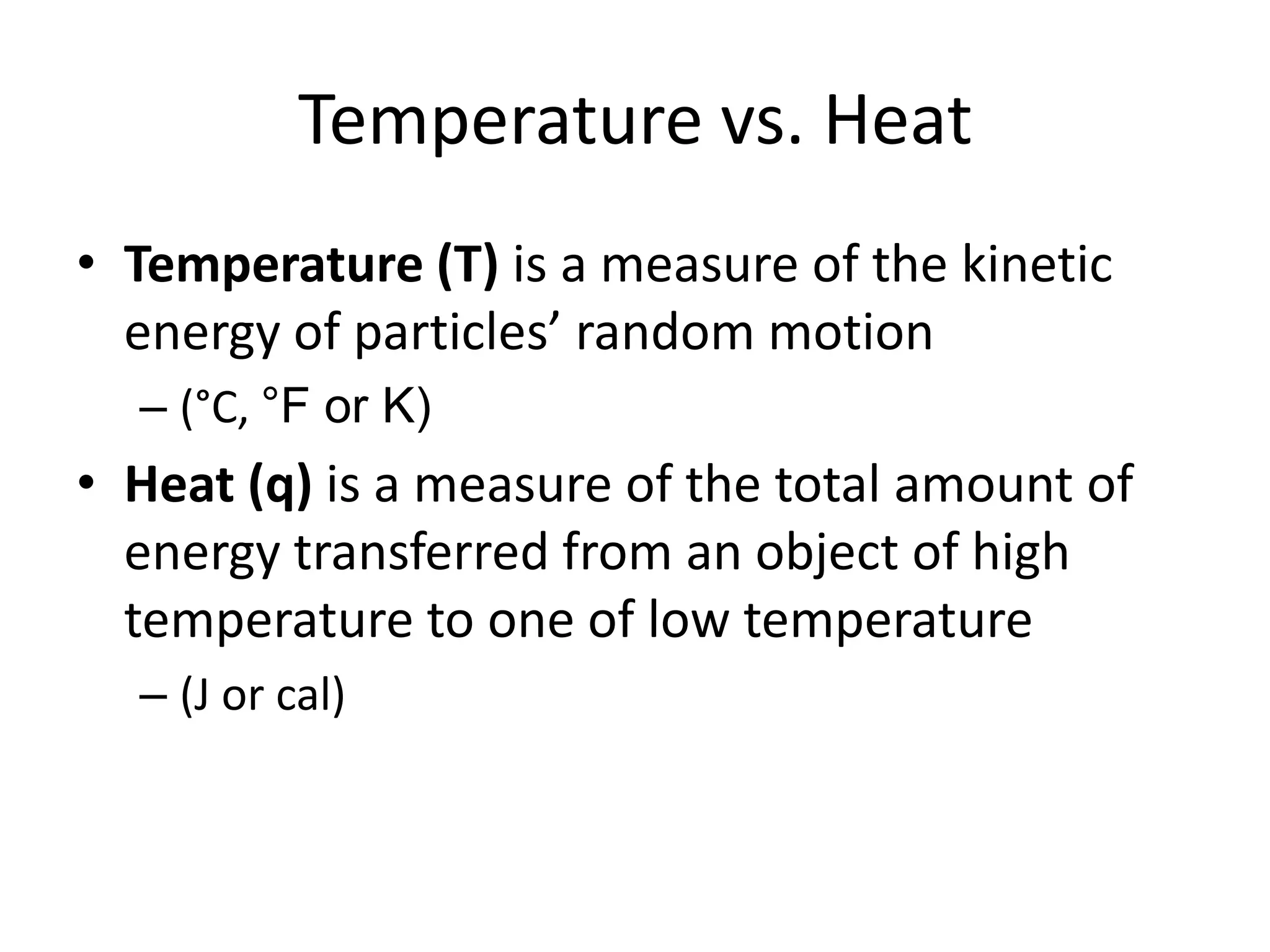
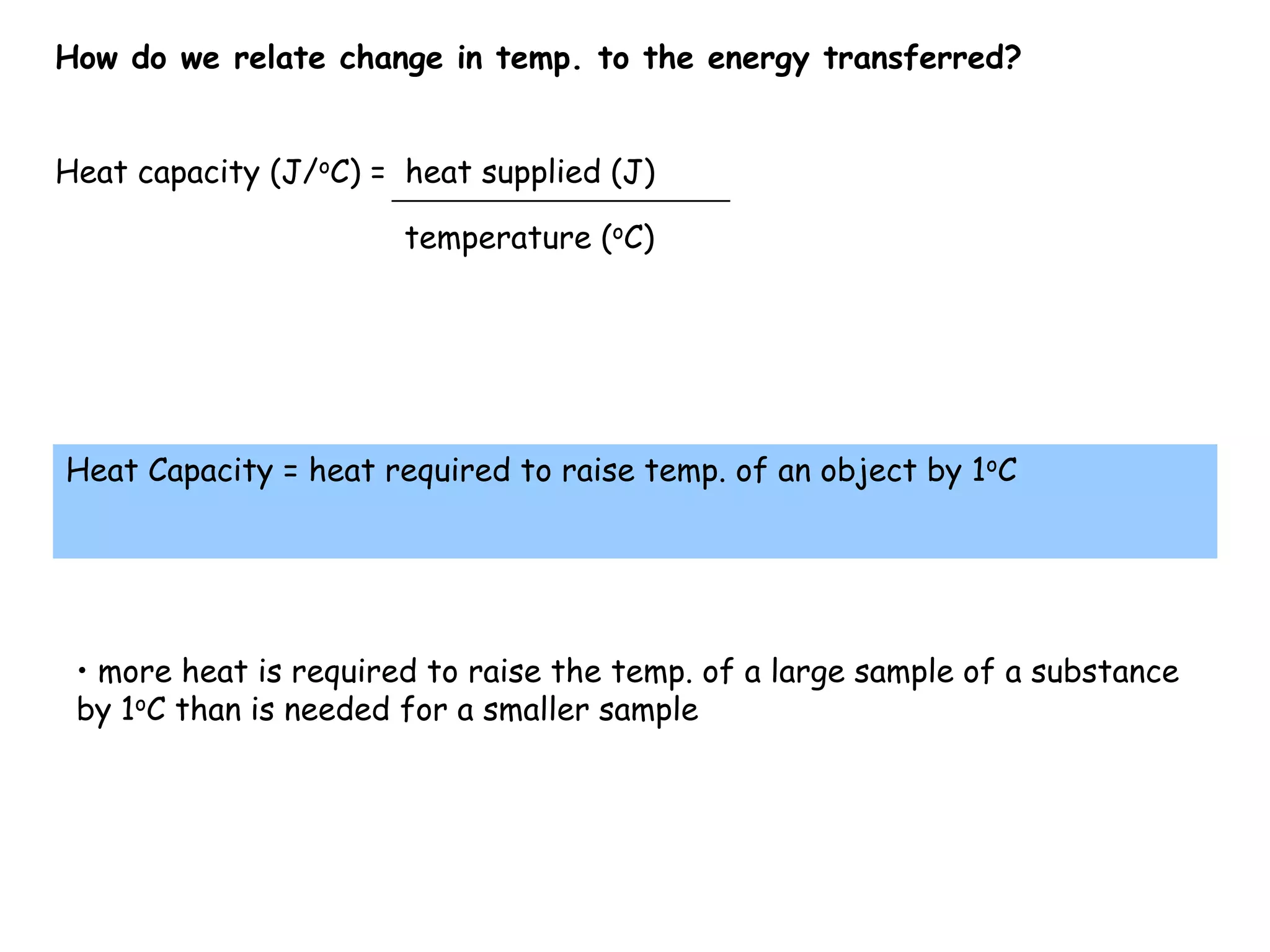
Energy exists in two main forms - kinetic energy, which is energy due to motion, and potential energy, which is stored energy due to position. The total energy of a system is the sum of its kinetic and potential energies, and the total energy of the universe remains constant according to the law of conservation of energy. Heat is a transfer of energy between objects due to a temperature difference, while temperature measures the average kinetic energy of particles. The amount of heat required to change an object's temperature depends on its heat capacity, which relates the heat supplied to the temperature change.