This document provides an overview of chemical equilibria, including:
- Equilibrium is the state where concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time. Reactions at equilibrium are reversible.
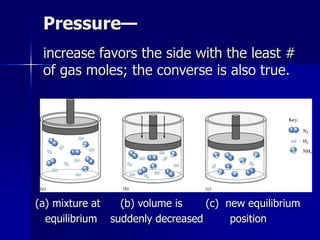
- The equilibrium position depends on initial concentrations, relative energies of reactants/products, and degree of organization.
- The equilibrium constant K relates concentrations of products over reactants at equilibrium. K values indicate whether a reaction favors products or reactants.
- The reaction quotient Q is similar to K but used when a system is not at equilibrium to predict the direction of the shift to reach equilibrium.
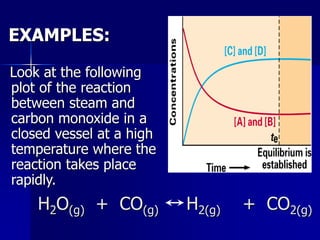
Several examples are provided to demonstrate calculating equilibrium concentrations and values of K using balanced reactions, initial concentrations, and equilibrium expressions.













![EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
EXPRESSION
For the general reaction:
aA + bB cC + dD
Equilibrium constant:
K = [C]c[D]d
[A]a[B]b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-15-320.jpg)


![[ ] indicates concentration in Molarity
Kc -- is for concentration (aqueous)
Kp -- is for partial pressure (gases)
“K” values are often written without
units](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-18-320.jpg)



![Solution
K = [NO2]4[H2O]6
[NH3]4[O2]7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-22-320.jpg)


![Solution
a: K = [Cl2]
Kp = PCl2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-25-320.jpg)

![Solution
b: K = [H2O]5
Kp = PH2O
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-27-320.jpg)


![Exercise 2
Calculating the Values of K
The following equilibrium
concentrations were observed for the
Haber process at 127°C:
[NH3] = 31 X 10-2 mol/L
[N2] = 8.5 X 10-1 mol/L
[H2] = 3.1 X 10-3 mol/L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-30-320.jpg)






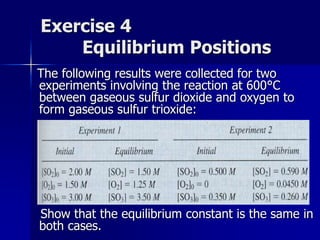






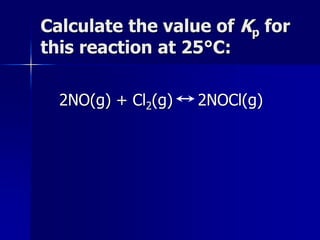










![For the general reaction:
aA + bB cC + dD
Reaction quotient = Qc = [C]c[D]d
[A]a[B]b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-55-320.jpg)






![Exercise 7, cont.
[NH3]0 = 1.0 X 10-3 M
[N2]0 = 1.0 X 10-5 M
[H2]0 = 2.0 X 10-3 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-62-320.jpg)

![Exercise 7, cont.
[NH3]0 = 2.00 X 10-4 M
[N2]0 = 1.50 X 10-5 M
[H2]0 = 3.54 X 10-1 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-64-320.jpg)

![Exercise 7, cont.
[NH3]0 = 1.0 X 10-4 M
[N2]0 = 5.0 M
[H2]0 = 1.0 X 10-2 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-66-320.jpg)
















![Solution
[Cl2] = 2.00 X 10-3 M
[PCl3] = 0.300 M
[PCl5] = 6.70 X 10-3 M
K = 8.96 X 10-2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-83-320.jpg)


![Solution
[CO] = [H2O] = 0.613 M
[CO2] = [H2] = 1.387 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-86-320.jpg)


![Solution
[H2] = [F2] = 0.472 M
[HF] = 5.056 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apch13generalequilibrium-240410114608-51e0a9a3/85/General-Equilibrium-ppt-chemistry-first-year-89-320.jpg)