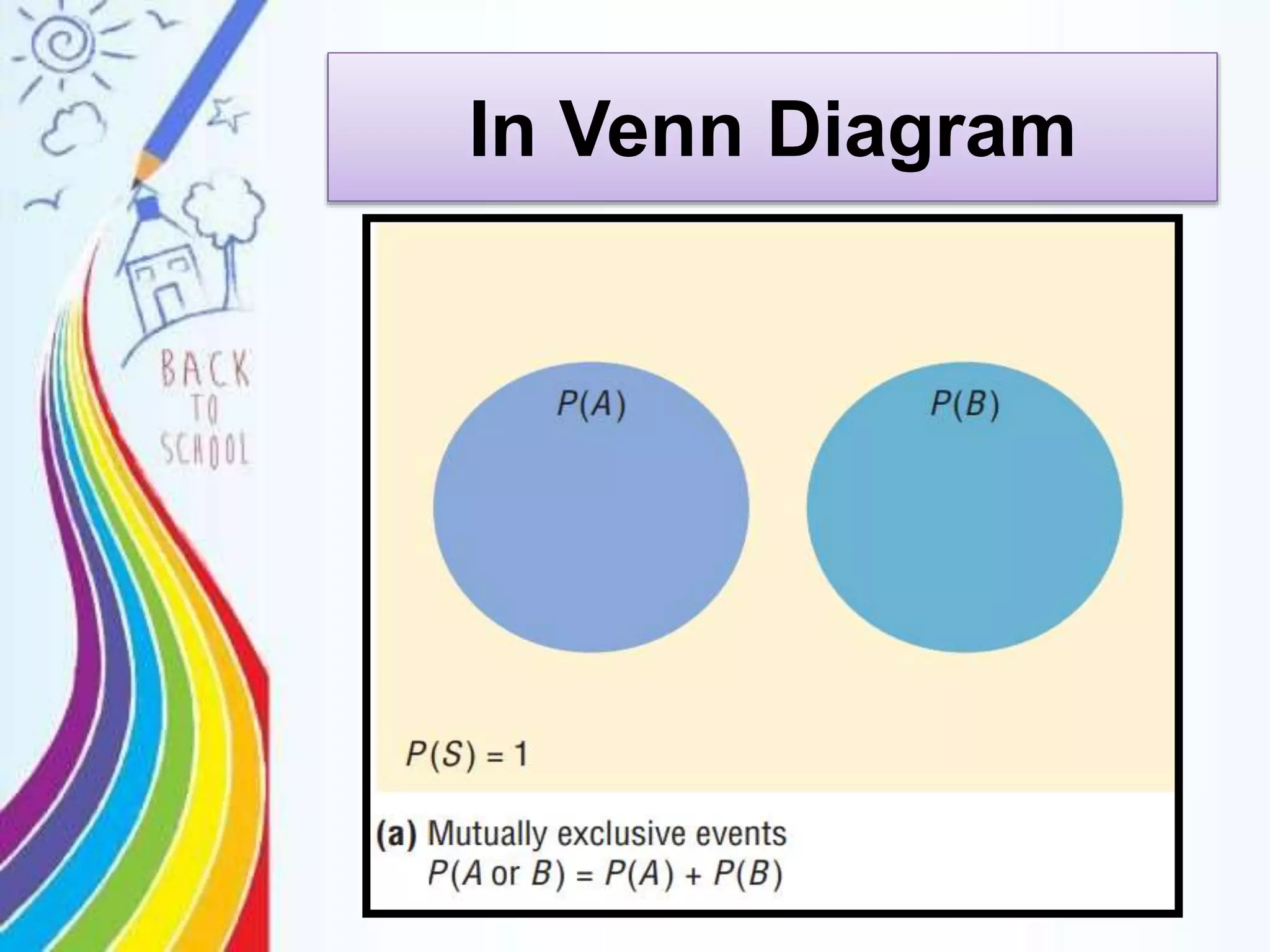
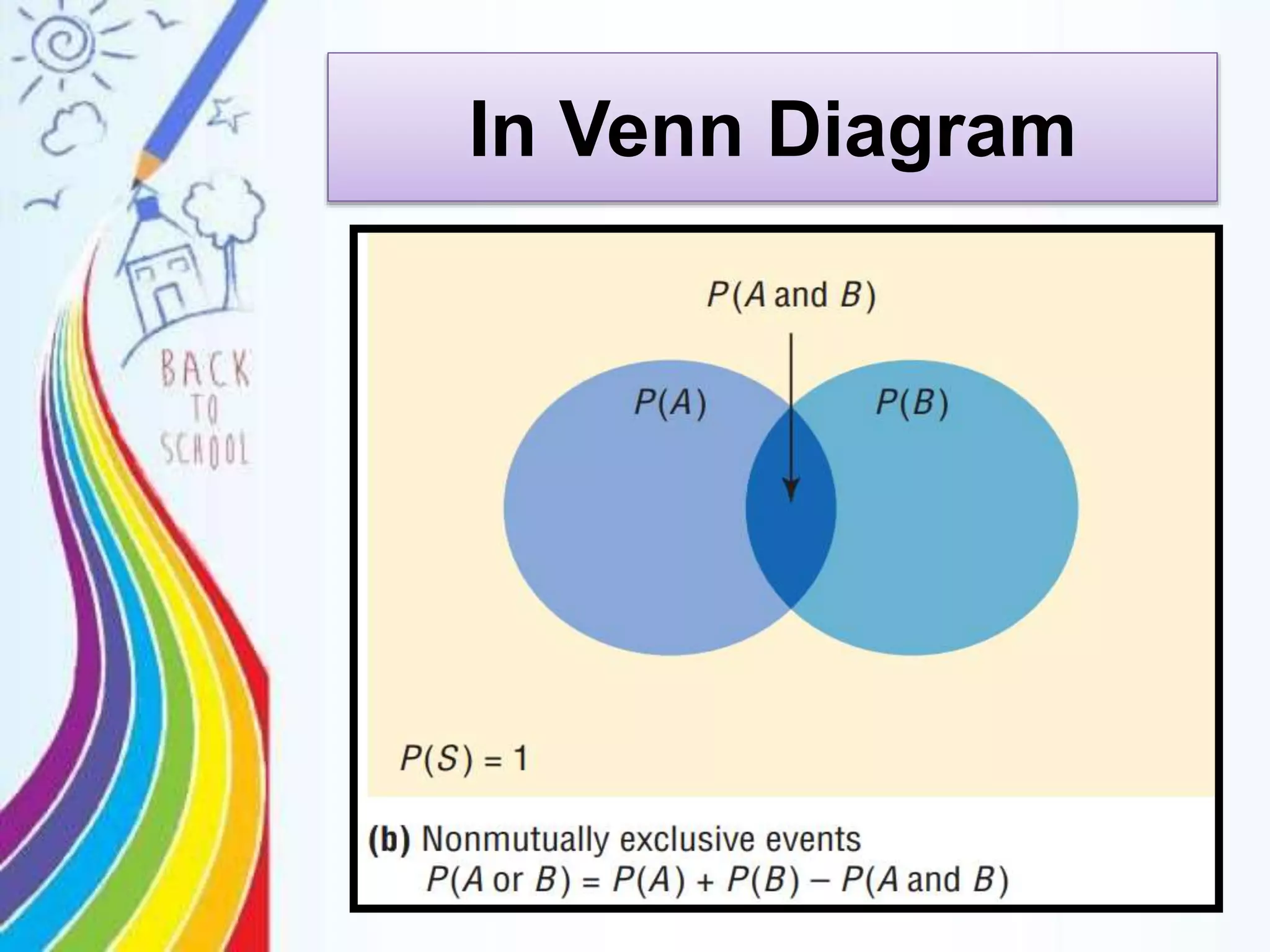
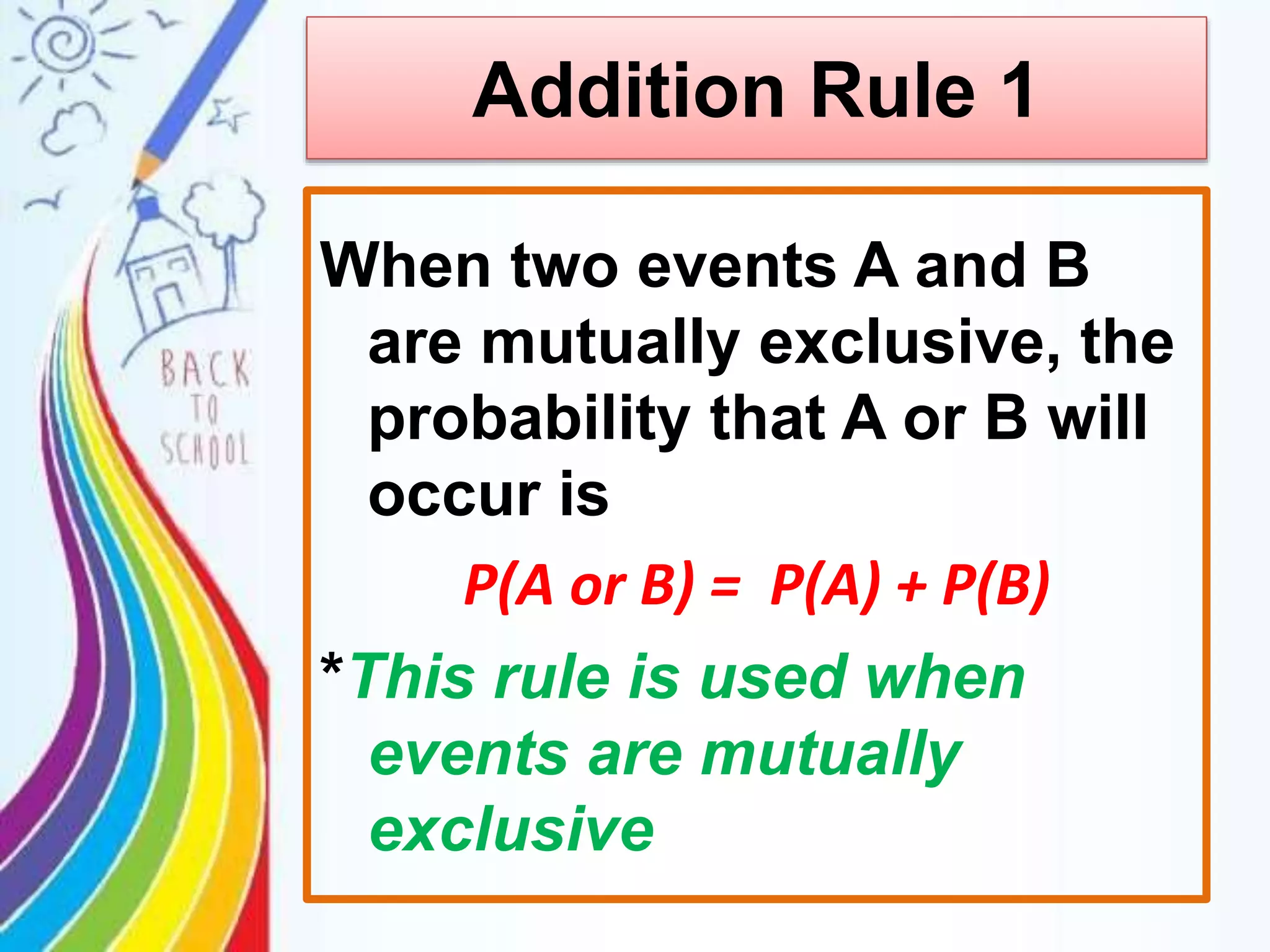
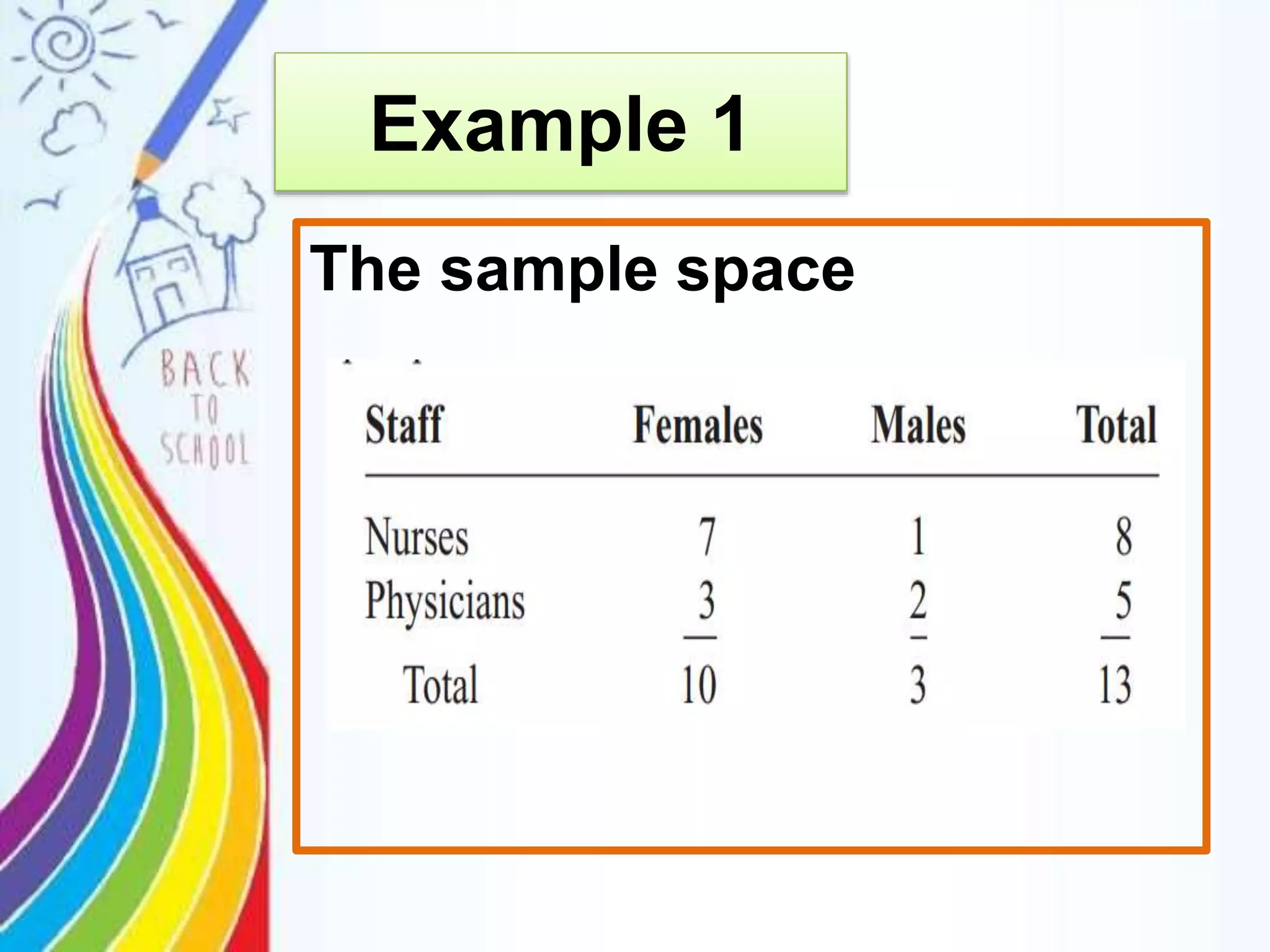
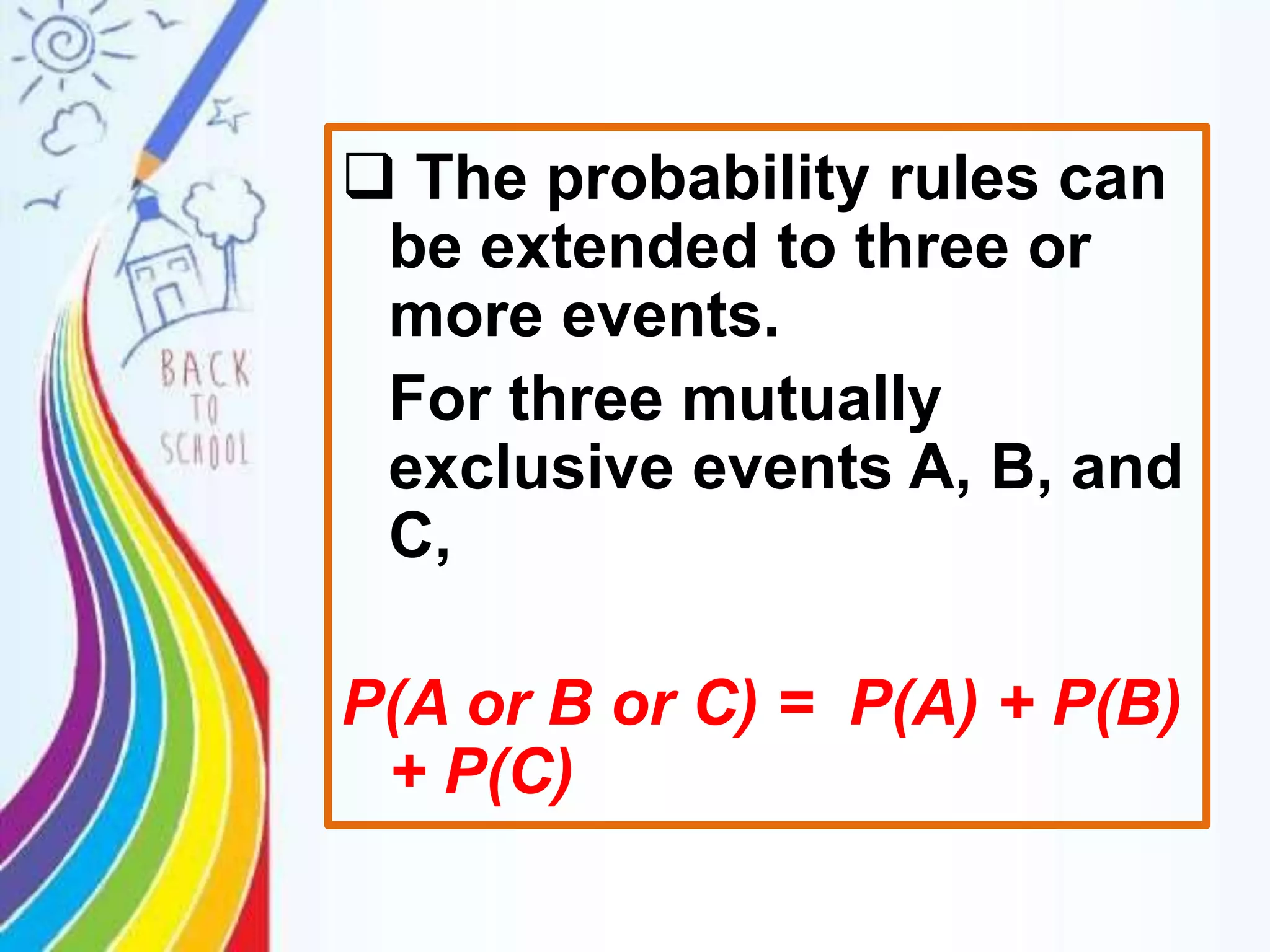
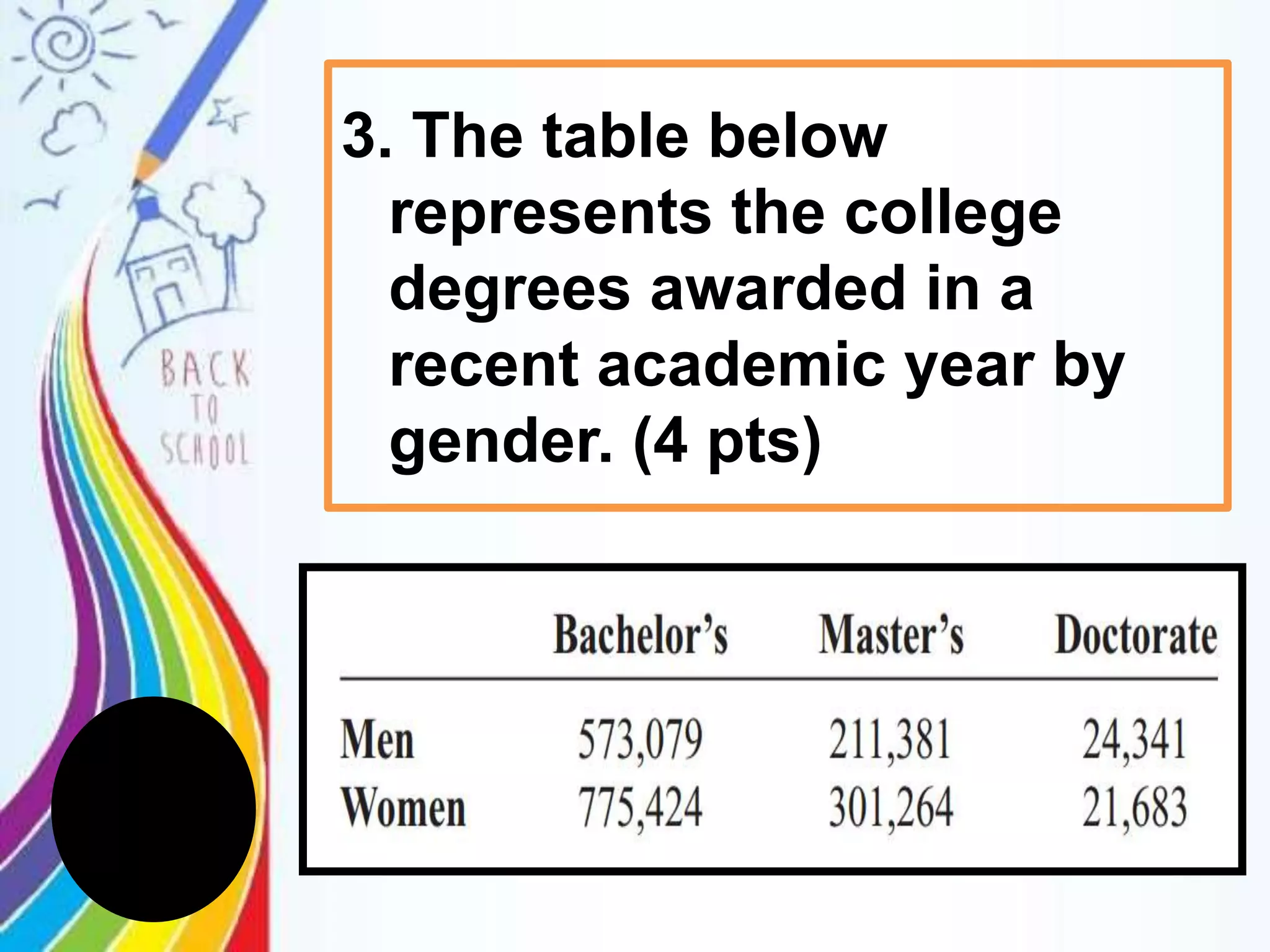
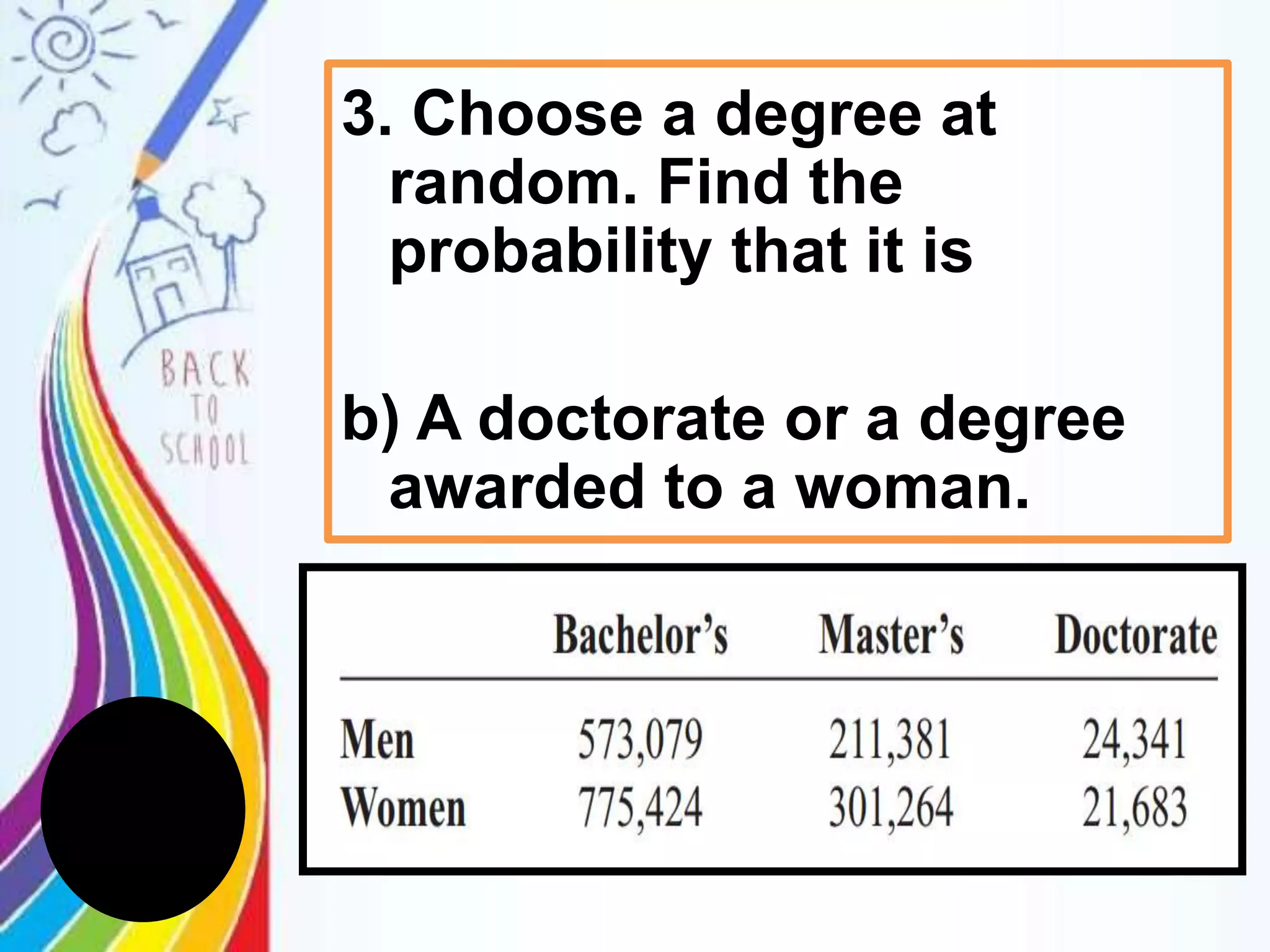
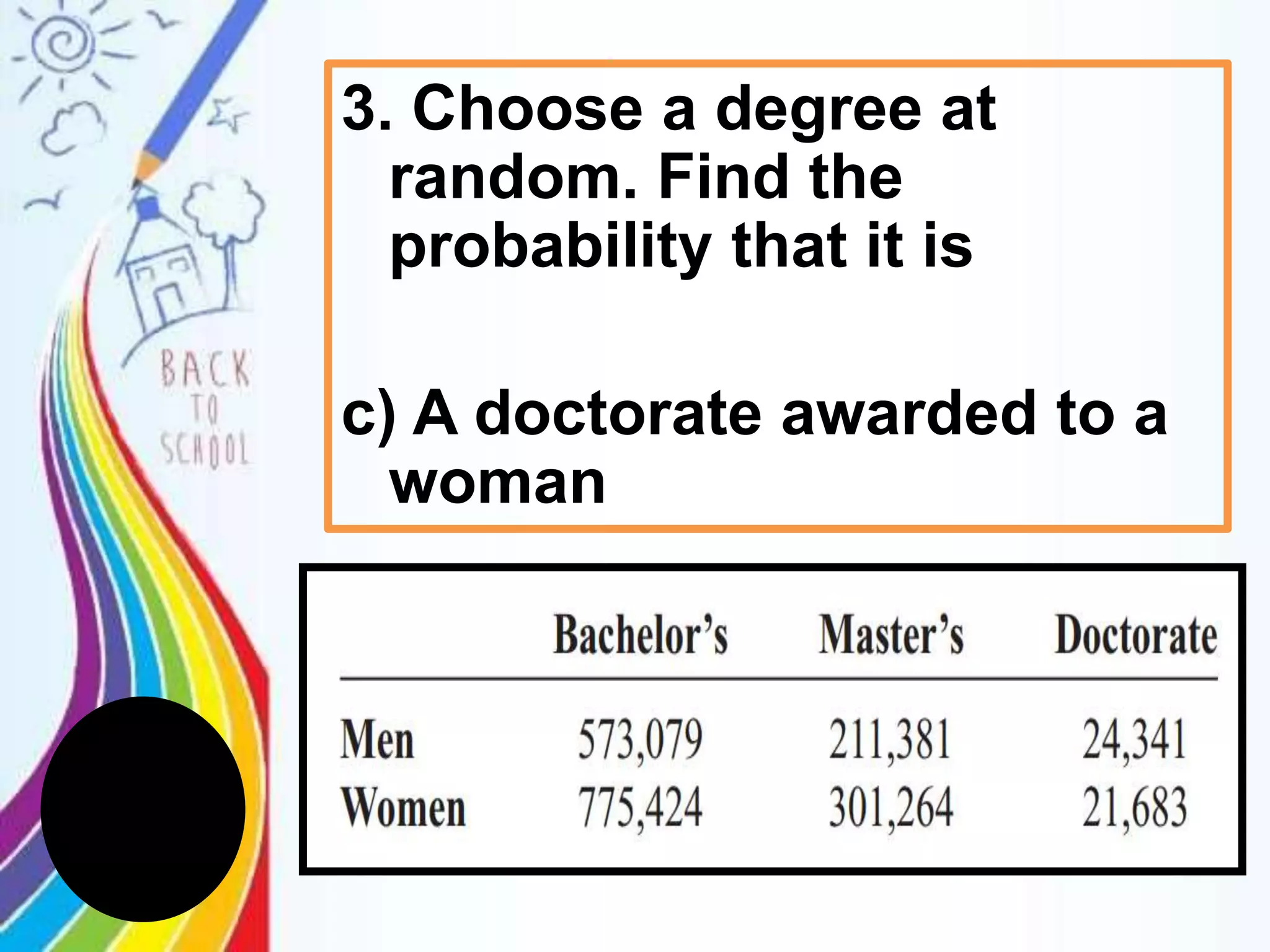
This document discusses probability rules for addition when events are mutually exclusive or not mutually exclusive. It provides examples of applying the addition rules to calculate probabilities. For mutually exclusive events A and B, the probability of A or B is P(A) + P(B). For non-mutually exclusive events, the probability is P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B). The document also discusses examples of mutually exclusive and non-mutually exclusive events using dice rolls, card draws, and real world scenarios. It provides a quiz with probability calculation problems applying the addition rules.