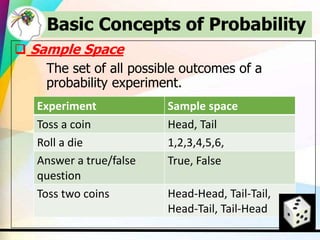
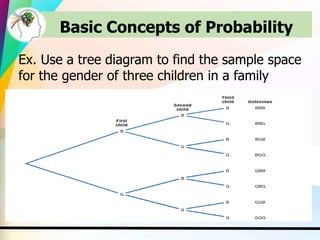
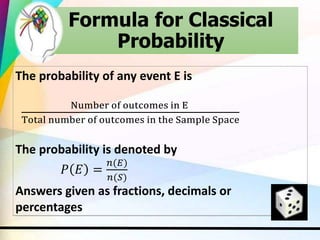
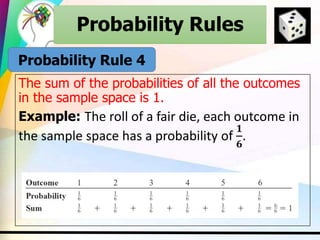
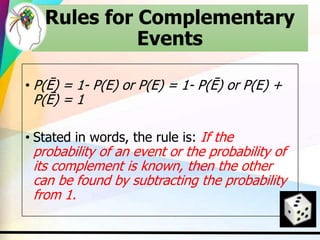
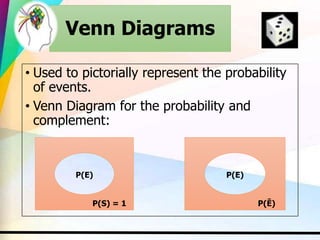
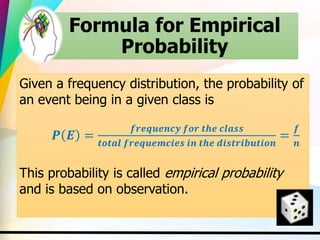
This document discusses key concepts in probability including experiments, outcomes, sample spaces, classical probability, empirical probability, subjective probability, complementary events, and the law of large numbers. Probability can be calculated classically by considering the number of outcomes in an event over the total number of outcomes, empirically by observing frequencies, or subjectively based on estimates. Understanding probability is important for properly evaluating risks and uncertainties.