This document provides an overview of probability concepts including:
- Probability is the chance of an event occurring and is calculated using the classical or empirical formulas
- Events can be simple, compound, mutually exclusive or complementary
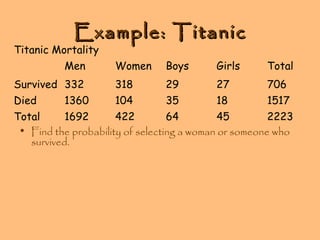
- The addition rule states that for mutually exclusive events the probability of event A or B is P(A) + P(B), and for non-mutually exclusive events it is P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B)
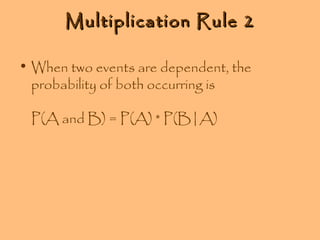
- The multiplication rule states that if events are independent, the probability of both occurring is P(A) × P(B)
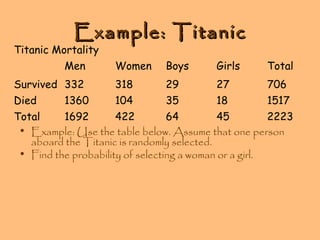
- Conditional probability is the probability of one event occurring given that another event has occurred
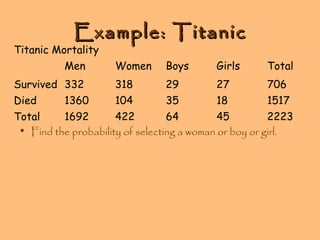
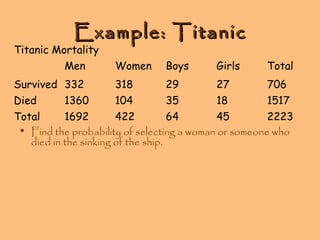
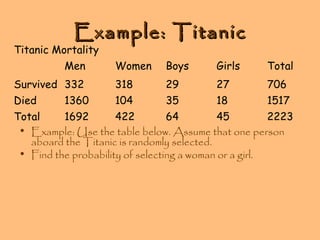
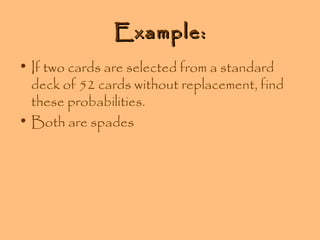
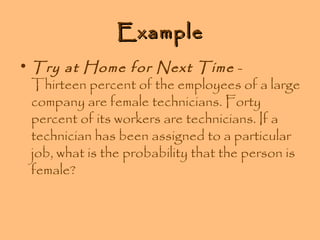
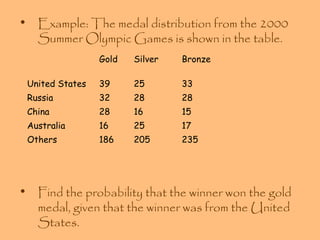
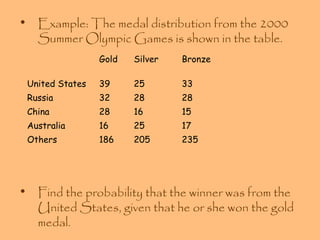
- Examples are provided to