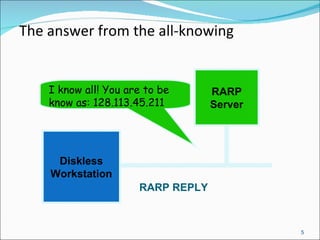
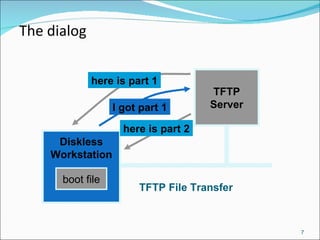
TFTP is designed for transferring files between processes with minimal overhead. It uses UDP and is easy to implement, making it suitable for inclusion in firmware or for booting diskless workstations and network devices. The TFTP protocol uses five message types - Read request, Write request, Data, ACK, and Error. It supports two transfer modes, netascii for text files and octet for binary files.