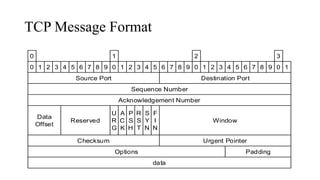
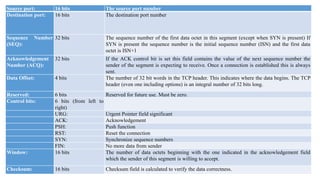
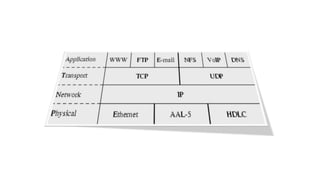
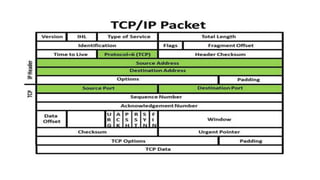
- TCP and IP are core protocols of the Internet Protocol Suite, with TCP operating at the transport layer and providing reliable data transmission, and IP operating at the internet layer and routing packets between hosts.
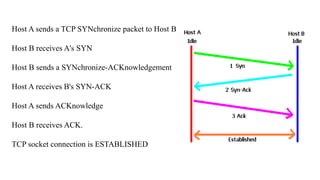
- TCP establishes a virtual connection between hosts to send data reliably and in order using mechanisms like flow control, error checking, and acknowledgments.
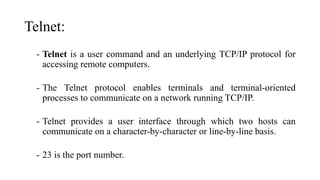
- Common applications of TCP/IP include Telnet (port 23) for remote access, FTP (ports 20/21) for file transfer, and TFTP (port 69) for simple file transfer without authentication.