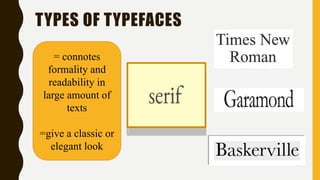
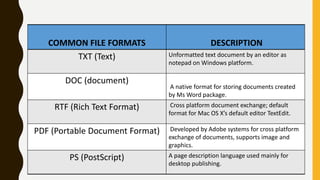
This document discusses text media and information. It provides characteristics of text, different types of text including hypertext and plaintext, common file formats, and design principles for text like emphasis, proximity and alignment. Text is a flexible way to present information in various sources, from short phrases to lengthy articles, and can be customized through options like fonts, formatting and typefaces to achieve different styles and convey different meanings or emotions.