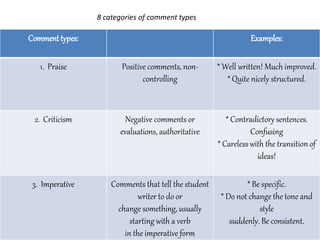
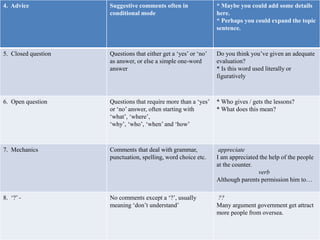
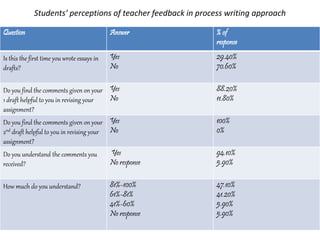
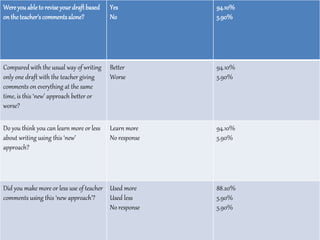
This document summarizes a study on analyzing different types of feedback provided by teachers on student essays. It identifies 8 categories of feedback:
1. Praise
2. Criticism
3. Imperatives
4. Advice
5. Closed questions
6. Open questions
7. Comments on mechanics
8. Comments marked with a '?'
The study found that marginal requests for information, requests in any grammatical form, and summary comments on grammar led students to make the most substantive revisions that improved their papers. A second study surveyed students and found that most understood the feedback and found the process of receiving comments on multiple drafts helpful for revising and learning.