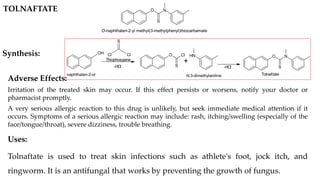
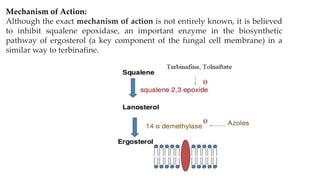
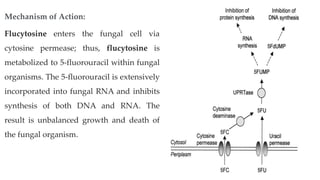
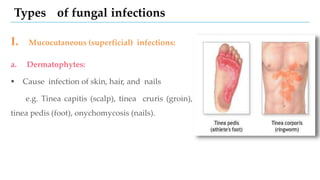
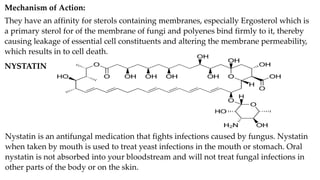
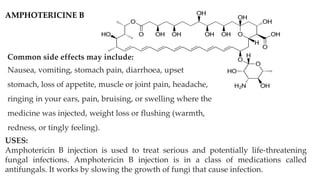
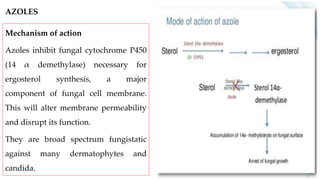
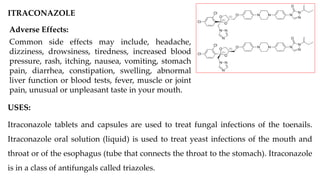
This document provides information on various antifungal agents including their mechanisms of action, uses, and common side effects. It discusses several major classes of antifungals such as azoles (imidazoles, triazoles), polyenes (nystatin, amphotericin B), allylamines (tolnaftate, terbinafine), and echinocandins (caspofungin). It also summarizes the mechanisms, structures, and structure-activity relationships of individual antifungal drugs like fluconazole, itraconazole, clotrimazole, and flucytosine.






![GRISEOFULVIN
(2S,6'R)-7-chloro-2',4,6-trimethoxy-6'-methyl-
3H-spiro[1-benzofuran-2,1'-cyclohexan]-2'-
ene-3,4'-dione.
Adverse Effects:
The more common side effects of griseofulvin can include: Rash, numbness or
tingling in your hands or feet, yeast infections in your mouth, stomach pain, diarrhea,
heartburn, nausea, vomiting.
USES:
Griseofulvin is an antifungal medicine that is used to treat infections such as
ringworm, athlete's foot, jock itch, and fungal infections of the scalp, fingernails, or
toenails. Griseofulvin may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication
guide.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-220410052728/85/Antifungal-agents-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![N
N
Cl
1-[(2-chlorophenyl)(diphenyl)methyl]-1H-imidazole
Cl
Cl
+ N
H
N
-HCl
N
N
Cl
Clotrmazole
1-chloro-2-[chloro(diphenyl)methyl]benzene
1H-imidazole
CLOTRMAZOLE
Synthesis:
USES:
Clotrimazole is used to treat skin infections such as athlete's foot, jock itch, ringworm,
and other fungal skin infections (candidiasis).
Adverse Effects:
Some side effects can be serious. If
you experience any of the following
symptoms, stop
using clotrimazole and call your
doctor immediately:
•rash.
•hives.
•stomach pain.
•fever.
•chills.
•nausea.
•vomiting.
•foul-smelling vaginal discharge.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-220410052728/85/Antifungal-agents-pptx-16-320.jpg)
![KETOCONAZOLE
O
O
N
N
Cl
Cl O
N N
O
ketoconazole should be used only when you cannot use other antifungal
medications. Ketoconazole can cause serious harm to your liver that may result in
liver transplant or cause death.
1-[4-(4-{[2-(2,4-Dichlorophényl)-2-(1H-imidazol-
1-ylméthyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl] méthoxy} phényl)
-1-pipérazinyl] éthanone
Adverse Effects:
Common side effects of Nizoral include: nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, itching or
skin rash, headache, dizziness, breast swelling.
USES:
Ketoconazole is used to treat skin infections such as athlete's foot, jock itch,
ringworm, and certain kinds of dandruff. This medication is also used to treat a skin
condition known as pityriasis (tinea versicolor), a fungal infection that causes a
lightening or darkening of the skin of the neck, chest, arms, or legs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-220410052728/85/Antifungal-agents-pptx-17-320.jpg)
![MICONAZOLE
O
N
N
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
1-{2-[(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)oxy]-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl}-1H-imidazole
USES:
Vaginal miconazole is used to treat vaginal yeast infections in adults and children 12
years of age and older. Miconazole is in a class of antifungal medications called
imidazoles. It works by stopping the growth of fungi that cause infection.
Adverse effects:
Burning, stinging, swelling, irritation,
redness, pimple-like bumps, tenderness, or
flaking of the treated skin may occur. If any
of these effects persist or worsen, notify
your doctor or pharmacist promptly.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-220410052728/85/Antifungal-agents-pptx-18-320.jpg)
![FLUCONAZOLE
Adverse Effects:
Headache, diarrhea, nausea or upset stomach, dizziness, stomach pain, vomiting,
changes in the way food tastes, severe rash in people with lowered immunity.
USES:
Fluconazole is used to treat serious fungal or yeast infections, such as vaginal
candidiasis, oropharyngeal candidiasis (thrush, oral thrush), esophageal candidiasis
(candida esophagitis), other candida infections (including urinary tract infections,
peritonitis [inflammation of the lining of abdomen or stomach].
2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl) propan-2-
ol.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-220410052728/85/Antifungal-agents-pptx-20-320.jpg)