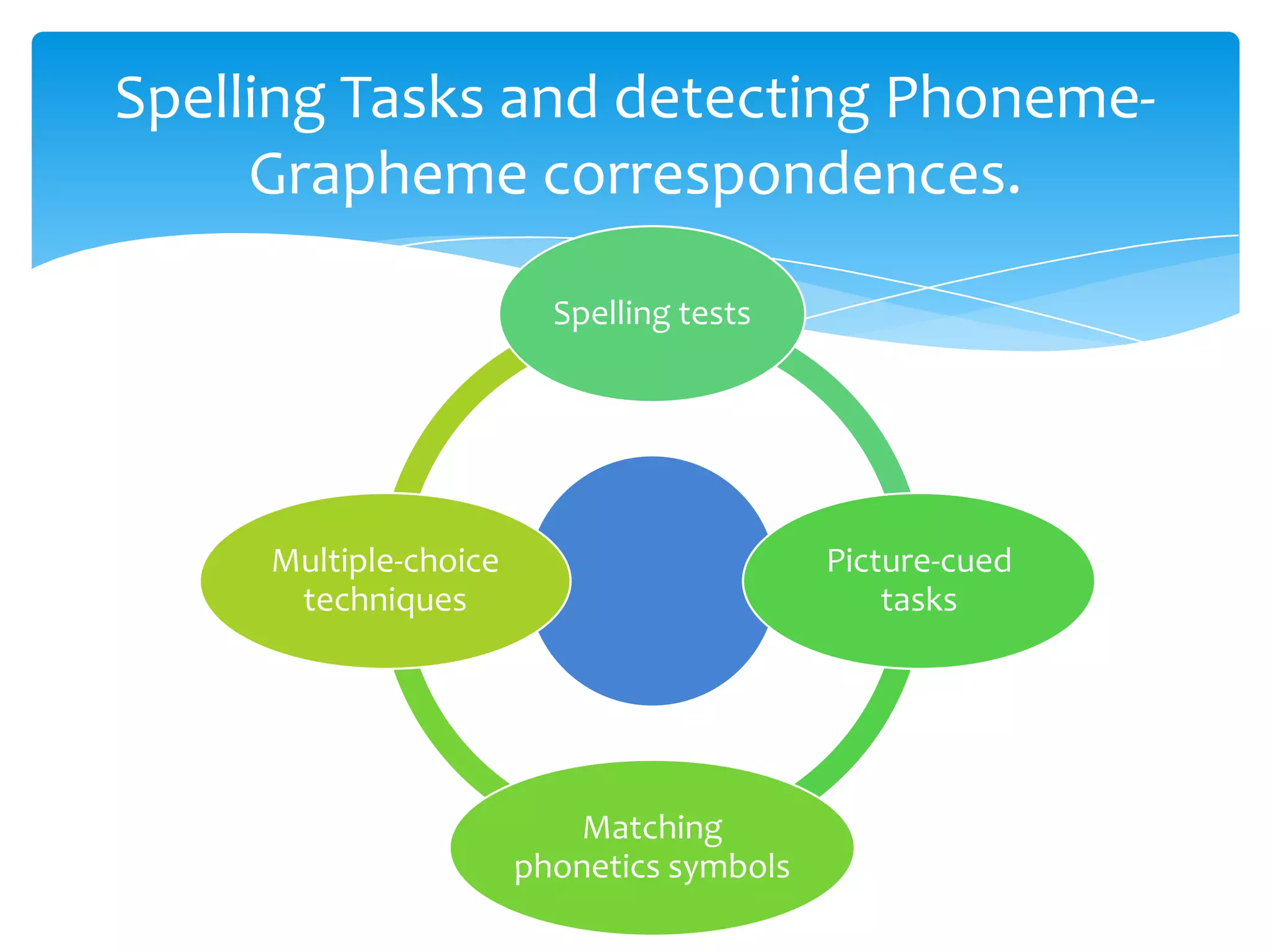
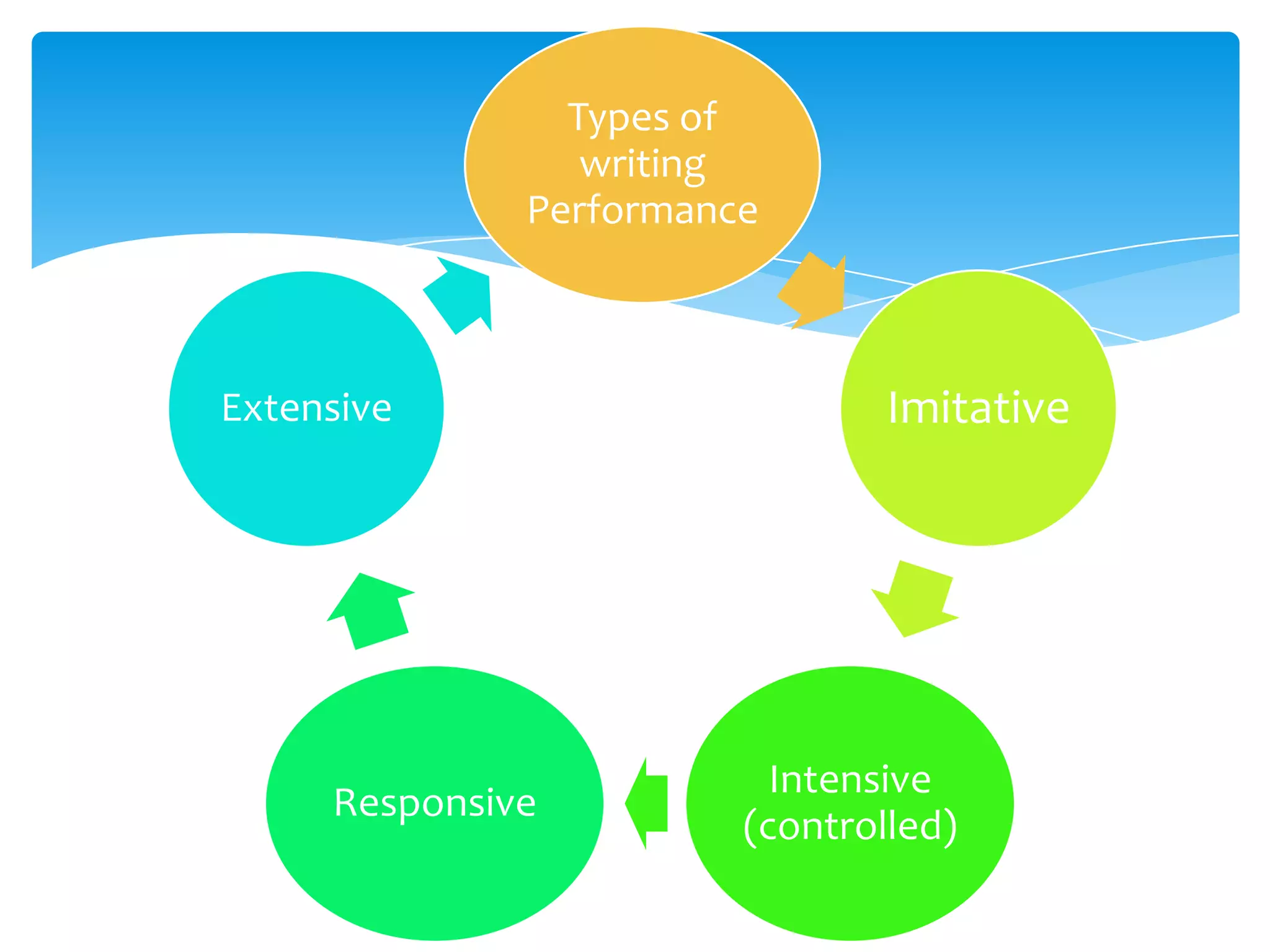
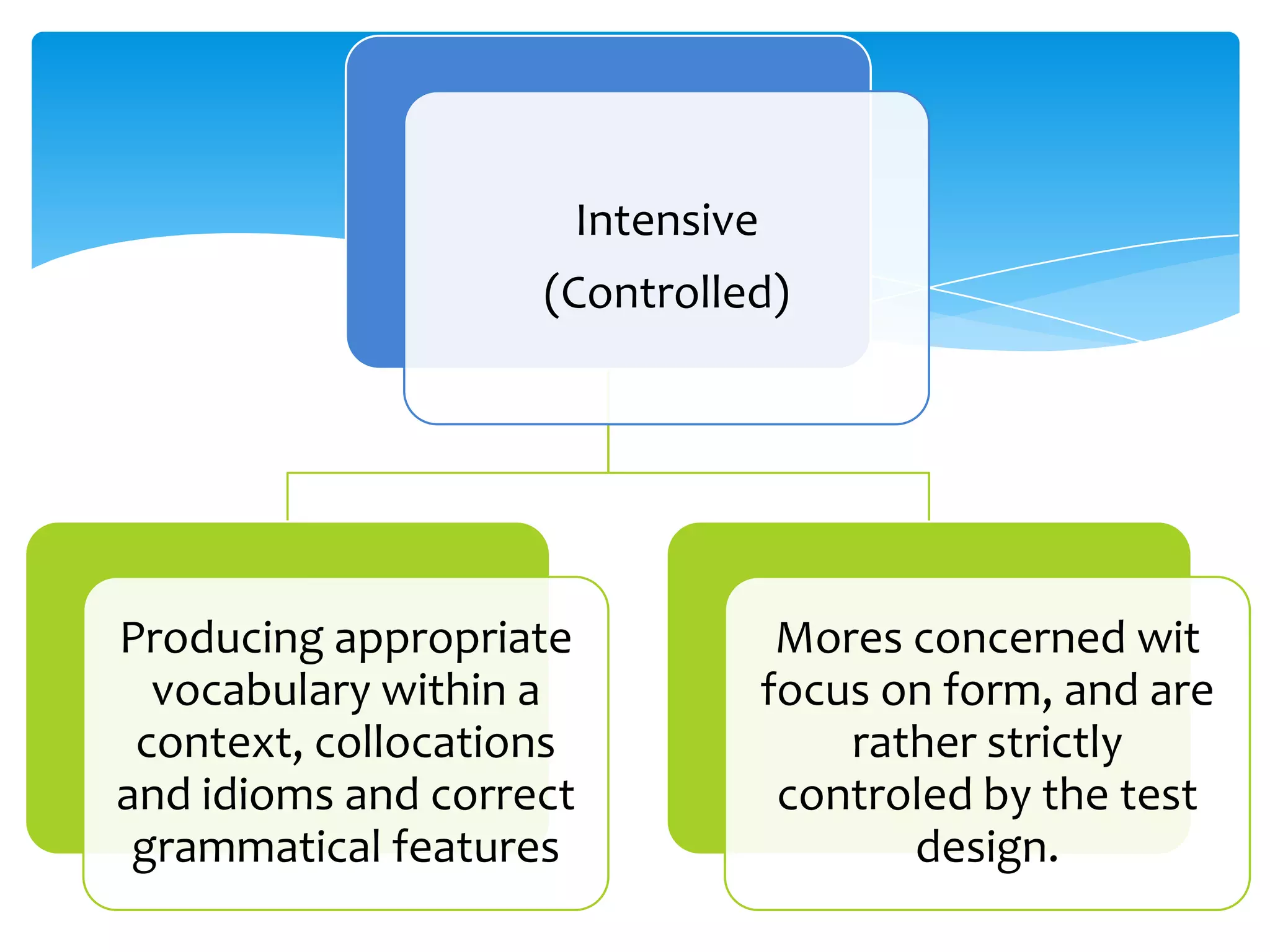
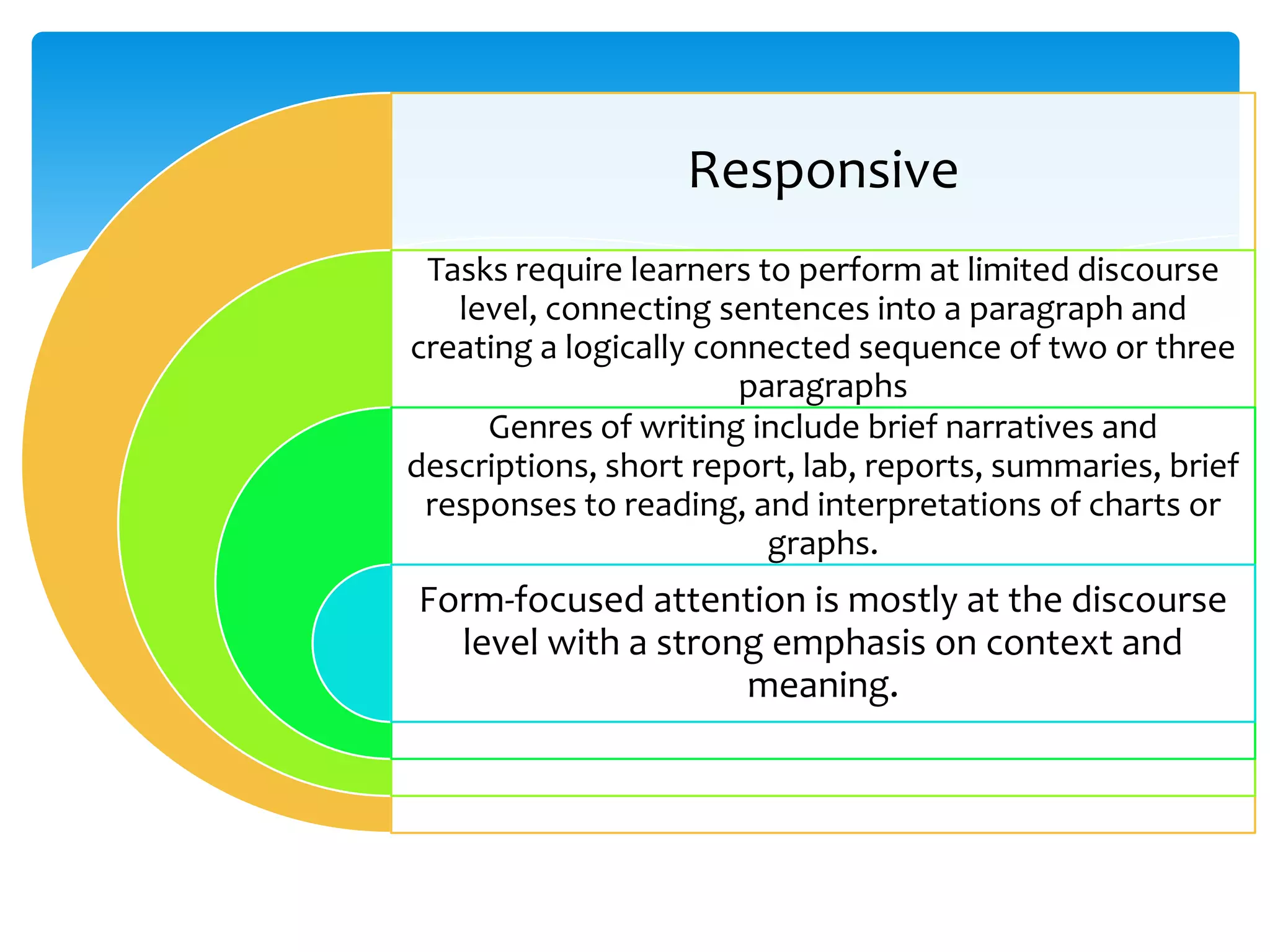
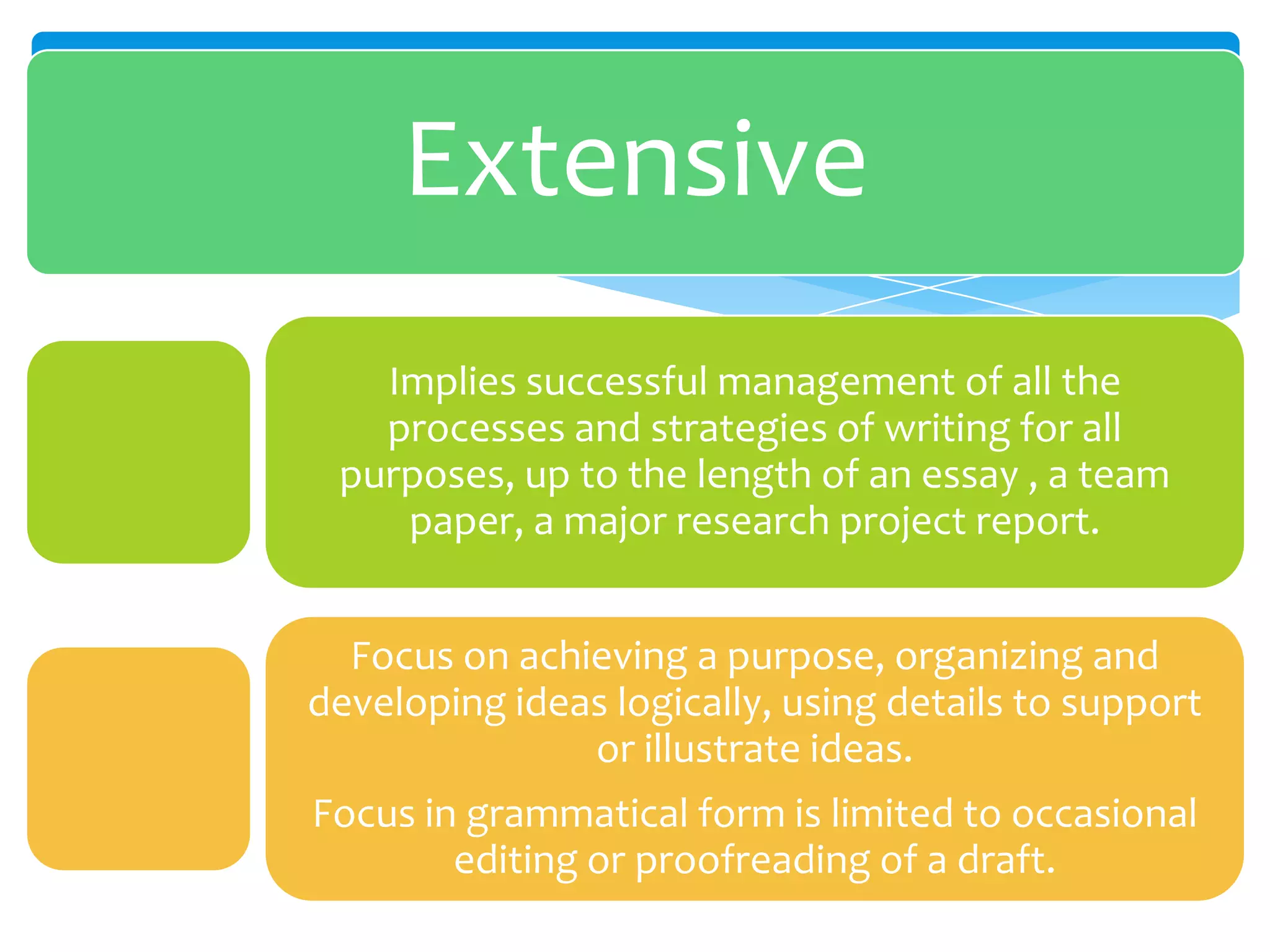
This document discusses approaches to assessing writing ability. It identifies 5 types of writing: imitative, intensive (controlled), responsive, extensive, and job-related. For imitative writing, tasks focus on handwriting, copying, and spelling. Intensive writing focuses on using correct vocabulary, grammar, and form within a context. Responsive writing connects sentences and paragraphs around a topic. Extensive writing involves longer essays and research projects. Micro-skills include spelling, handwriting, and grammar, while macro-skills involve organization, purpose, and conveying meaning. The document provides examples of assessment tasks for different writing types and skills.






![Designing assessment tasks:
Imitative writing
Tasks in [hand] writing
letters, words, and
Punctuation
• 2.- Listening cloze
1.- Copying selection tasks
• 3.-Picture-cued tasks.
• 5.- Converting
4.-Form completion numbers and
task abbreviations to
words.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assessingwriting-130411233155-phpapp01/75/Assessing-writing-12-2048.jpg)