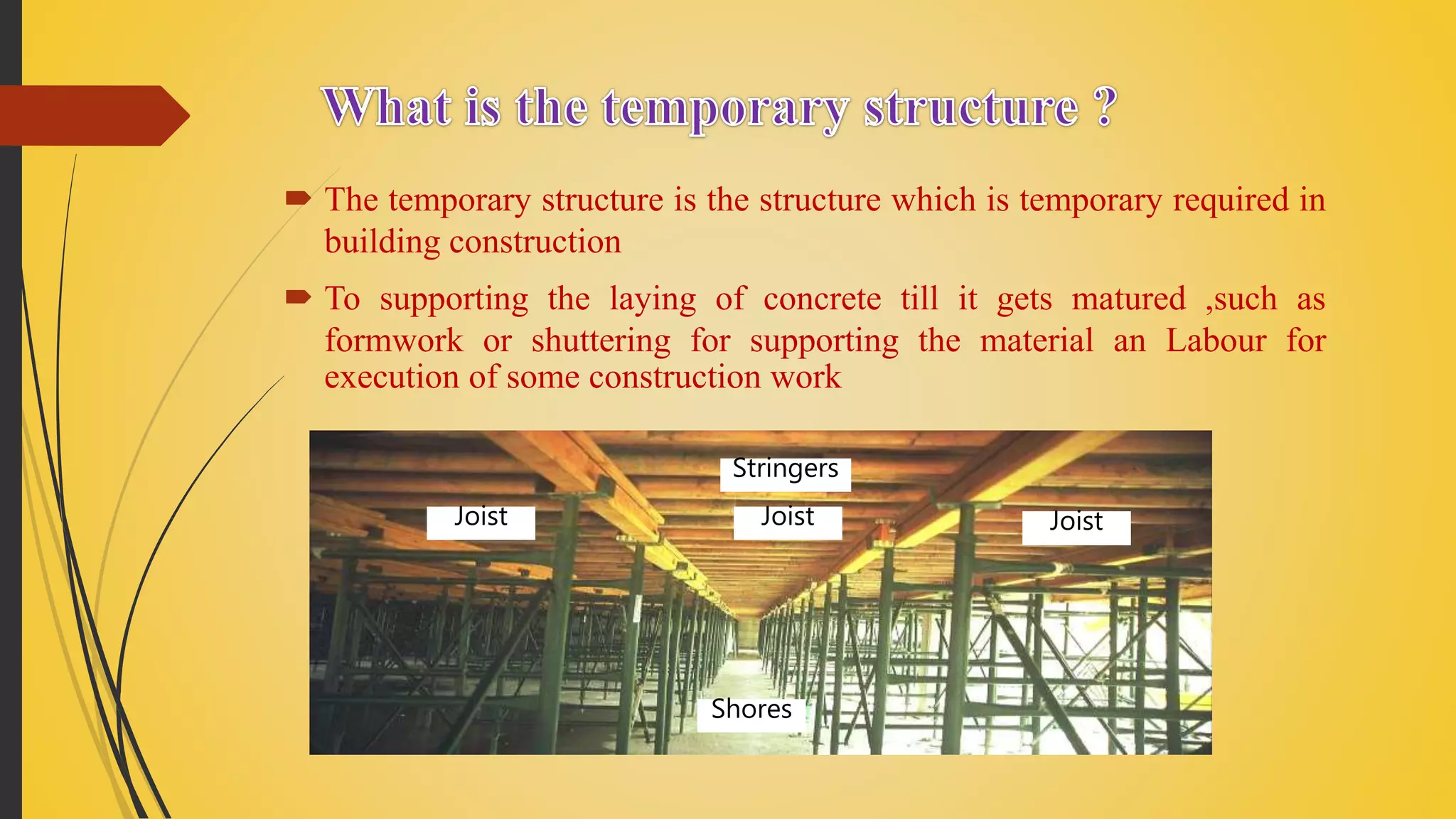
Temporary formwork is used in construction to support fresh concrete until it cures. There are different types of formwork materials including timber, steel, aluminum, fiberglass, and plywood. Factors like strength, rigidity, cost, and number of reuses vary between each type. Formwork design involves sheets, studs, ties, and other components configured for walls, beams, slabs, columns, and decks based on the structural element. Slipforming is a specialized technique where formwork is continuously lifted as concrete is placed, allowing vertical structures like chimneys to be built without side forms. This method was used to rapidly construct tall building cores and highway pavement.