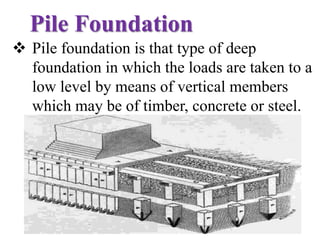
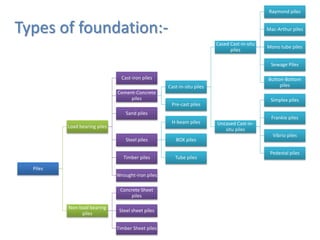
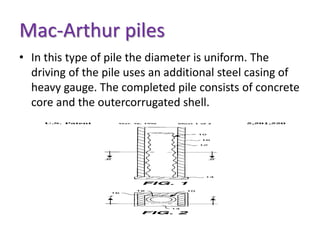
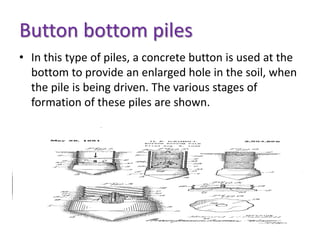
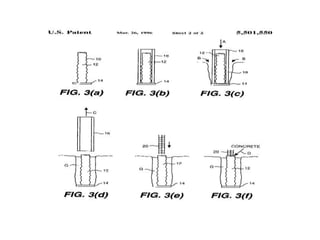
Pile foundations are used when a simple spread foundation is not possible due to deep, compressible, or waterlogged soil that cannot provide adequate bearing capacity. Piles transfer structural loads deep into the ground to stronger soil or bedrock layers. There are several types of piles that differ in material (wood, concrete, steel, etc.) and installation method (driven, cast-in-place, precast, etc.). Common pile types include H-beam steel piles, concrete-filled tube piles, precast concrete piles, and timber piles. Pile foundations allow buildings and structures to be supported in difficult soil conditions.