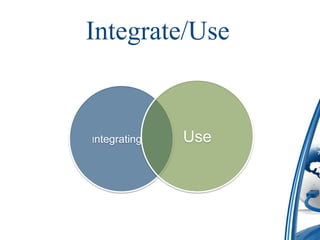
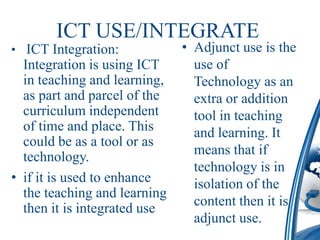
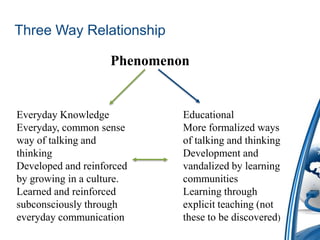
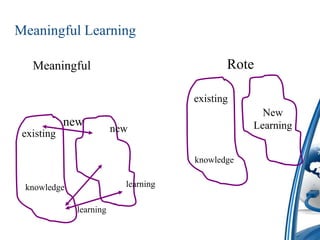
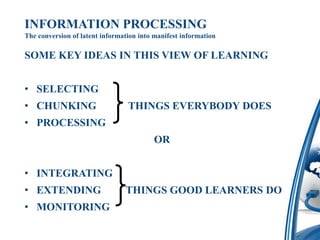
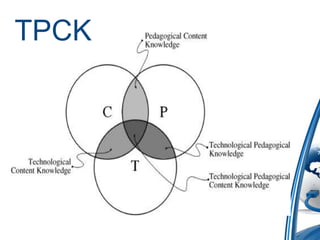
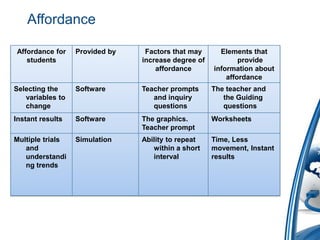
This document discusses how to integrate technology in teaching under low-resourced environments. It defines integration as using technology as an inherent part of the curriculum, and distinguishes it from merely using technology as an additional tool. The document also outlines several principles that should guide technology integration, such as enhancing learning through tools that allow retrieval, reversal of concepts, and avoiding obsolescence.